Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Material Selection Guide for Oil & Gas Pipelines
Uploaded by
yulianus_srOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Selection Guide for Oil & Gas Pipelines
Uploaded by
yulianus_srCopyright:
Available Formats
A Presentation on Pipelines Material
Selection in Oil & Gas Industry
Types of Pipeline in Oil & Gas Industry:
Injection lines: Pipelines injecting water / steam / polymer / gas into the wells to
improve the lift.
Flow lines: Pipelines from the well head to the nearest processing facility.
Trunk lines / Inter field lines: Pipelines between two processing facilities or from
pig trap to pig trap or from block valve station to block valve station.
Export lines / Loading lines: From the processing facility to the loading or export
point.
Transfer lines / Spur lines: Branch line exiting into trunk line or export line.
Gathering lines: One or more segment of pipelines forming network and
connected from the wells to processing facilities.
Disposal lines: Pipe line which disposes normally produced water into disposal
wells (shallow / deep).
Subsea pipelines: Pipe lines connecting the offshore production platforms to on
shore processing facilities.
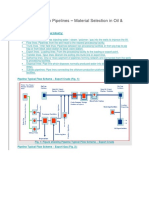
Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme Export Crude (Fig. 1):
Fig. 1: Figure showing Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme Export Crude
Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme Export Gas (Fig. 2):
Fig. 2: Figure showing Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme Export Gas
Pipeline Typical flow scheme Offshore (Fig. 3):
Fig. 3: Figure showing Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme Offshore
Codes used in Oil & Gas Industries:
Design and Construction:
ASME B31.4 Pipeline transportation Systems for liquid hydrocarbons and other
liquids
ASME B31.8 Gas Transmission and distribution piping systems
ISO 13623 Petroleum and Natural gas industries Pipeline transportation
systems
DNV F-101 Offshore Standard for submarine pipeline systems
Sour Applications:
NACE MR-01-75 Sulphide stress cracking resistant materials for oilfield
equipment
ISO 15156 Materials for use in H2S containing environments in oil and gas
production
Materials:
API 5L Specification for line pipe
API 5LC Specification for CRA line pipe
API 5LD Specification for CRA clad or Lined pipe
API 5LE Specification for Polyethylene line pipe
ISO 3183 Petroleum & Natural gas industries Steel Pipe
ISO 14692 Petroleum and Natural gas industries Glass Reinforced plastic
piping
AWWA M 45 Fibre glass pipe design
Pipeline Fittings:
ISO 15590 1 Pipeline Induction bends
ISO 15590 2 Pipeline Fittings
ISO 15590 3 Pipeline Flanges
MSS SP 75 Specification for High test Wrought Butt welding fittings
MSS SP 44 Steel Pipeline Flanges
ASTM A 694 Steel forgings for high pressure transmission service
Valves:
API 6D Pipeline valves
API 594 Check valves
API 608 Metal Ball Valves
API 609 Butterfly valves
ISO 14313 Petroleum & Natural gas industries Pipeline valves
Other Pipeline Components:
Pig launcher / Pig receivers
Barred Tees
Isolation Joints
Pig signallers
Corrosion monitoring fittings
Shrink sleeves / External coatings / Cathodic protection for buried lines
Corrosion Threats in Oil & Gas:
CO2 Corrosion (Sweet Corrosion) General metal loss due to the presence of
CO2 in the process fluid.
H2S Corrosion (Sour Corrosion) Localized metal cracking and corrosion due to
presence of H2S in the process fluid.
Chlorides and Bicarbonates Cracking in the metal due to the presence of stress
and chlorides in the process fluid.
Corrosion due to Oxygen Oxidation and metal loss due to the contact of metal
with oxygen in the process fluid.
Microbiologically induced corrosion Bacteria that induces corrosion particularly
within H2S
Erosion (Abrasion) corrosion Corrosion due to the fluid flow and velocity
within the pipe environments.
Corrosion (External) Threats in the facilities External atmospheric corrosion on
above ground lines and corrosion due to soil for buried lines.
Corrosion Under Insulation External corrosion due to water ingress under the
insulating materials.
Material Selection Process:
Identify corrosion threats
Define the corrosion circuits
Calculate the corrosion rate per year
Calculate the Service Life Corrosion (SLC) based on design life
Consider the materials options
Carry out the Life Cycle Costing (LCC) Capex / Opex / Install
Review the materials selection w.r.t design / operating / constructability
Finally select the choice materials
Corrosion Agents in Oil & Gas:
Carbon Dioxide CO2
Hydrogen Sulphide H2S
Oxygen O2
Chlorides ClWater H2O
Material Options
Metals:
CS with corrosion allowance
Stainless Steel
Duplex Stainless Steel
Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Metals + Lining:
CS with internally coated FBE
CS with internal PE lining
CRA clad / lined materials
Non Metals:
Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE)
Polyethylene (HDPE)
Advantages & Disadvantages of Material Options (Fig. 4):
Fig. 4: Advantages and Disadvantages of materials
Corrosion Control in Oil & Gas Pipeline Chemical Injections
Description:
Purpose of injection
Corrosion inhibitor:
Basically meant for CS pipelines, forms a
layer of film on the surface and protects the core pipe from corrosion attack.
Batch injection or continuous
Scale Inhibitor:
Prevents scale formation in the pipelines by dissolving
scale forming salts
Wax inhibitor :
Dissolves the wax within the crude
Oxygen Scavenger :
Reacts and removes oxygen in the fluid
Biocide:
Destroys the bacteria , algae and fungi in the process fluid.
Coagulant / Anti foam: Normally mixed in the separators to improve mixing and
reducing the foam
Demulsifier:
Prevents emulsion in the multiphase system
Dehydration agents:
Removes moisture in the gas normally Glycol injection
Odorant:
leakage
Added to the fluid to add smell and detect the
You might also like
- Corrosion of Steels in Sour Gas EnvironmentDocument179 pagesCorrosion of Steels in Sour Gas Environmentaathittaya100% (1)
- Data Input Flowline Properties: Pipe Pipe Pipe 3Document12 pagesData Input Flowline Properties: Pipe Pipe Pipe 3Septian FirdausNo ratings yet
- ASME B31.12 Hydrogen Piping and Pipeline Code Design Rules and Their Interaction With Pipeline Materials Concerns, Issues and ResearchDocument9 pagesASME B31.12 Hydrogen Piping and Pipeline Code Design Rules and Their Interaction With Pipeline Materials Concerns, Issues and Researchchannu rolliNo ratings yet
- Material Selection For PipingDocument16 pagesMaterial Selection For PipingYousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Eni S.p.A. Functional SpecificationDocument20 pagesEni S.p.A. Functional Specificationhalim_kaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Small Bore Piping SystemsDocument69 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Small Bore Piping SystemsbashirNo ratings yet
- Guidelines and Application Procedures For API 578 PMI FinalDocument26 pagesGuidelines and Application Procedures For API 578 PMI Finalixotee100% (1)
- 2 - NRG - Wall Thickness DesignDocument34 pages2 - NRG - Wall Thickness DesignBalan100% (1)
- Piping Study Guide ASME Codes Standards MaterialsDocument15 pagesPiping Study Guide ASME Codes Standards MaterialsnandajntuNo ratings yet
- FuturePipe Installation Manual 18-7-05 PDFDocument25 pagesFuturePipe Installation Manual 18-7-05 PDFPaul WoworNo ratings yet
- Wall Thickness CalDocument6 pagesWall Thickness CalNorazlan Shah MahadiNo ratings yet
- L&T Double Block and Bleed Plug ValvesDocument12 pagesL&T Double Block and Bleed Plug Valvesvijay10484No ratings yet
- 00300E04Document30 pages00300E04halim_kaNo ratings yet
- 02 Samss 012 PDFDocument10 pages02 Samss 012 PDFnadeem shaikhNo ratings yet
- Internal Corrosion Direct Assessment-1Document25 pagesInternal Corrosion Direct Assessment-1Mir AsifNo ratings yet
- Leakage Acceptance Rates Comparison Metal & Soft Seated Valves Api 598/api 6D/Mss Sp-61/Fci 70-2Document5 pagesLeakage Acceptance Rates Comparison Metal & Soft Seated Valves Api 598/api 6D/Mss Sp-61/Fci 70-2Ashfaq AnwerNo ratings yet
- API 5L-2007 Specification For Line PipeDocument153 pagesAPI 5L-2007 Specification For Line Pipetom787485100% (1)
- 20019.MAT - COR.PRG Selezione Maeriali Servizio Marino Rev. 0 - Aprile 2009Document45 pages20019.MAT - COR.PRG Selezione Maeriali Servizio Marino Rev. 0 - Aprile 2009MatteoNo ratings yet
- The Suitability of CRA Lined Pipes For Flowlines Susceptible To Lateral BucklingDocument13 pagesThe Suitability of CRA Lined Pipes For Flowlines Susceptible To Lateral Bucklingmaz234No ratings yet
- Monolithic Insulating JointsDocument5 pagesMonolithic Insulating JointsTran Thanh TungNo ratings yet
- Tech. Spec. For Flanges and Spectacle BlindsDocument6 pagesTech. Spec. For Flanges and Spectacle Blindssanjay421No ratings yet
- Norms Overview.: Pipeline ConstructionDocument3 pagesNorms Overview.: Pipeline ConstructionRjeb mohamedNo ratings yet
- Standards For Pipeline Coatings: CanadDocument11 pagesStandards For Pipeline Coatings: CanadMohamed DewidarNo ratings yet
- Extend Life Aging PipelinesDocument20 pagesExtend Life Aging PipelinesPar MadNo ratings yet
- A182a182m PDFDocument17 pagesA182a182m PDFIng. Adolfo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Route Selection and Deepwater Pipeline DesignDocument19 pagesRoute Selection and Deepwater Pipeline DesignSampurnanand PandeyNo ratings yet
- API STANDARD For PipingDocument28 pagesAPI STANDARD For PipingsahaNo ratings yet
- Quality Requirements For Line Pipe: JanuaryDocument14 pagesQuality Requirements For Line Pipe: JanuaryJose Anisio Silva100% (1)
- ASME Nuclear Conformity Assessment ProcessDocument23 pagesASME Nuclear Conformity Assessment ProcessAzhar Bashir KasuriNo ratings yet
- HERTEL Metal GasketsDocument40 pagesHERTEL Metal Gasketshvdb72No ratings yet
- Piping Design Requirements PDFDocument6 pagesPiping Design Requirements PDFkarunaNo ratings yet
- Some Notes About Corrosion Coupons InstallationDocument23 pagesSome Notes About Corrosion Coupons InstallationHadi VeyseNo ratings yet
- Barred TeesDocument1 pageBarred TeesAdvisNo ratings yet
- What Is Nace MR0175 Iso 15156Document1 pageWhat Is Nace MR0175 Iso 15156Quality controllerNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Paln For LSAWDocument4 pagesInspection and Test Paln For LSAWkbpatel123No ratings yet
- List Some Standards ISODocument2 pagesList Some Standards ISOAnonymous n4bJbeLAqNo ratings yet
- Description of Damage: 5.1.1.1 Amine Corrosion 5.1.1.1.1Document5 pagesDescription of Damage: 5.1.1.1 Amine Corrosion 5.1.1.1.1Ajmi HmidaNo ratings yet
- ACI, ANSI, API standards for construction, safety, petroleum measurementDocument32 pagesACI, ANSI, API standards for construction, safety, petroleum measurementDesmond Chang100% (1)
- 3 Lead Engineer For Subsea Pipeline Systems LDNDocument2 pages3 Lead Engineer For Subsea Pipeline Systems LDNVijay_DamamNo ratings yet
- AMEC Specification For Titanium 01Document9 pagesAMEC Specification For Titanium 01cenkturkerNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Transporting Hydrogen in Existing Carbon Steel PipelinesDocument9 pagesThe Feasibility of Transporting Hydrogen in Existing Carbon Steel PipelinesomiitgNo ratings yet
- ALFA ENGINEERING ISOLATION JOINTS Brochure PDFDocument11 pagesALFA ENGINEERING ISOLATION JOINTS Brochure PDFSamrandNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Transmission Pipeline Temperature Drop CalculationDocument5 pagesNatural Gas Transmission Pipeline Temperature Drop CalculationCarina QuibinitNo ratings yet
- FD534 0000 MW RT 1001 - D0 PDFDocument32 pagesFD534 0000 MW RT 1001 - D0 PDFshervinyNo ratings yet
- Piping Design Enginerring & Construction: Atul PatelDocument19 pagesPiping Design Enginerring & Construction: Atul Patelसरदार अतुल भाई पटेलNo ratings yet
- Valve MaterialTypeEquivalent PDFDocument3 pagesValve MaterialTypeEquivalent PDFInaamNo ratings yet
- Risk-Based Pipeline Integrity Management CourseDocument3 pagesRisk-Based Pipeline Integrity Management CourseMahmoud AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Wall Thickness Calculation: 3.2 Calculated Using SCH WT W/o CorrosionDocument2 pagesPipeline Wall Thickness Calculation: 3.2 Calculated Using SCH WT W/o CorrosionImmanuel SNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Pigging Philosophy for Rumaila ProjectDocument15 pagesPipeline Pigging Philosophy for Rumaila ProjectfadhilNo ratings yet
- 01-SAMSS-035 2018 API Line PipeDocument29 pages01-SAMSS-035 2018 API Line PipeWHWENNo ratings yet
- Nfa 49 215 Grade Tu 37c Tubes PDFDocument1 pageNfa 49 215 Grade Tu 37c Tubes PDFMitul MehtaNo ratings yet
- Din en Iso 16135Document26 pagesDin en Iso 16135Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- ADCO Amendments 30-99-12-3207 Rev.1 To DEP 31.38.01.31 Steel Piping 2013...Document22 pagesADCO Amendments 30-99-12-3207 Rev.1 To DEP 31.38.01.31 Steel Piping 2013...aymanNo ratings yet
- Pipelines Material Selection in The Oil Gas Industry PDFDocument7 pagesPipelines Material Selection in The Oil Gas Industry PDFMohammed KamalNo ratings yet
- On Hore and Off ShoreDocument7 pagesOn Hore and Off ShoreQayyum KhanNo ratings yet
- Piping SystemDocument33 pagesPiping SystemIrvan Yudhistira100% (1)
- Piping: Piping Sometimes Refers To Piping Design, The Detailed Specification of TheDocument5 pagesPiping: Piping Sometimes Refers To Piping Design, The Detailed Specification of ThesiswoutNo ratings yet
- ASME B31.3 Piping Design - Part ADocument46 pagesASME B31.3 Piping Design - Part AA_Uossef100% (1)
- Piping - WPK PDFDocument7 pagesPiping - WPK PDFsiswoutNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Elliptical Head Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument1 pageElliptical Head Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Program BPJS-TK JKKDocument3 pagesProgram BPJS-TK JKKyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Standard2 7 3Document22 pagesStandard2 7 3Chaker AmirNo ratings yet
- High-Level Efficiency: Demag Universal CranesDocument24 pagesHigh-Level Efficiency: Demag Universal Cranesyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Program BPJS-TK JHTDocument3 pagesProgram BPJS-TK JHTyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- B209M ASTM Aluminum StandardsDocument26 pagesB209M ASTM Aluminum StandardsDanny SeeNo ratings yet
- Grey Water Re-Use Primary Treatment TankDocument1 pageGrey Water Re-Use Primary Treatment Tankyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Detailed Border New Year FlyerDocument2 pagesDetailed Border New Year Flyeryulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope ThimblesDocument1 pageWire Rope Thimblesyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Cafco FENDOLITE® MII - Product Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesCafco FENDOLITE® MII - Product Datasheet PDFyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- 3000 Litre Transcube Fuel TankDocument1 page3000 Litre Transcube Fuel Tankyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Road CrossingDocument1 pageRoad Crossingyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Fixing Clips (Sket)Document1 pageFixing Clips (Sket)yulianus_srNo ratings yet
- HD Jack 3-11Document1 pageHD Jack 3-11yulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Cafco FENDOLITE® TGDocument4 pagesCafco FENDOLITE® TGyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- 2-1-bf6kz PDF FR 17 PDFDocument4 pages2-1-bf6kz PDF FR 17 PDFyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Uptime Brochure Tcm4-581762Document2 pagesUptime Brochure Tcm4-581762yulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Bs en Iso 15848 2pdf Ebook and ManualDocument1 pageBs en Iso 15848 2pdf Ebook and Manualyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Weld ConnectionDocument1 pageWeld Connectionyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Unequal Welding DesignDocument1 pageUnequal Welding Designyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Plate Joint PDFDocument1 pagePlate Joint PDFyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Bevel and Trim Detail PDFDocument1 pageBevel and Trim Detail PDFyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Bevel and Trim DetailDocument1 pageBevel and Trim Detailyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Barred TeeDocument1 pagePipeline Barred Teeyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Static Presssure TestDocument14 pagesStatic Presssure TestBalakumar100% (1)
- Rubber Lining SpecDocument1 pageRubber Lining Specyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy For Power GenerationDocument9 pagesGeothermal Energy For Power Generationyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Typical Road Crossing DetailDocument1 pageTypical Road Crossing Detailyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Piping Layout DrawingDocument2 pagesPiping Layout Drawingyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Piping Hook UpDocument1 pagePiping Hook Upyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Personal Dust Exposure of The Rice Mill Workers in AssamDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Personal Dust Exposure of The Rice Mill Workers in AssamIJAMTESNo ratings yet
- A Humanistic Approach To Medical PracticeDocument3 pagesA Humanistic Approach To Medical PracticeFilipos ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Louise L HAY AffirmationsDocument10 pagesLouise L HAY AffirmationsEvi Kutasi100% (2)
- Adrv9008 1Document68 pagesAdrv9008 1doubleNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ Mec201Document10 pagesSample MCQ Mec201UjjalKalitaNo ratings yet
- Save and share GZCL training spreadsheets onlineDocument263 pagesSave and share GZCL training spreadsheets onlinejohn wick100% (1)
- 310 Ta PDFDocument8 pages310 Ta PDFVincent GomuliaNo ratings yet
- Excipients As StabilizersDocument7 pagesExcipients As StabilizersxdgvsdgNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework for Measuring Job Satisfaction (SampleDocument4 pagesTheoretical Framework for Measuring Job Satisfaction (SampleJoseEdgarNolascoLucesNo ratings yet
- Pos 324 Module 2 Unit 1 ElaborateDocument2 pagesPos 324 Module 2 Unit 1 ElaborateMaricar PaduaNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 981 15 4630 3 PDFDocument170 pages10.1007@978 981 15 4630 3 PDFRohit G100% (1)
- Blaylock Face Masks Pose Serious Risks To The HealthyDocument8 pagesBlaylock Face Masks Pose Serious Risks To The HealthyDonnaveo ShermanNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument29 pagesCholinergic DrugsKiranNo ratings yet
- Asian Organized CrimeDocument17 pagesAsian Organized CrimeMagr EscaNo ratings yet
- CN LSHC The Future of Pharmacy en 031120Document8 pagesCN LSHC The Future of Pharmacy en 031120marina_netNo ratings yet
- PRC 2017 Annual Report ENDocument88 pagesPRC 2017 Annual Report ENmuhammad suryadiNo ratings yet
- Greek God and Goddess ListDocument3 pagesGreek God and Goddess Listapi-359276609No ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Generators: 15-360 kVA 15-300 KWDocument10 pagesAtlas Copco Generators: 15-360 kVA 15-300 KWAyoub SolhiNo ratings yet
- Examples: Inability To Sit Still, Pacing, Wringing of Hands, or Pulling of ClothingDocument14 pagesExamples: Inability To Sit Still, Pacing, Wringing of Hands, or Pulling of ClothingFaith Dianasas RequinaNo ratings yet
- Home & Garden 2015Document32 pagesHome & Garden 2015The Standard NewspaperNo ratings yet
- Jeremy Tan Resume and CVDocument3 pagesJeremy Tan Resume and CVapi-359540985No ratings yet
- A Text Book On Nursing Management AccordDocument790 pagesA Text Book On Nursing Management AccordMohammed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Tabata Its A HIITDocument8 pagesTabata Its A HIITbertabastionniNo ratings yet
- Rendemen Dan Skrining Fitokimia Pada Ekstrak DaunDocument6 pagesRendemen Dan Skrining Fitokimia Pada Ekstrak DaunArdya YusidhaNo ratings yet
- Global Chlor - Alkali Market Statistics Update June 16 2014Document31 pagesGlobal Chlor - Alkali Market Statistics Update June 16 2014diego_cáceres_30No ratings yet
- Sodium Chloride MSDSDocument5 pagesSodium Chloride MSDSIbaharmovic LpuNo ratings yet
- Neet Structural Organisation in Animals Important QuestionsDocument18 pagesNeet Structural Organisation in Animals Important QuestionsARKA NEET BIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- What is Intermodulation InterferenceDocument3 pagesWhat is Intermodulation InterferencedekcarcNo ratings yet
- Campus Waste Lab Proposal To Substitute Single-Use Plastic With Paper Products and Plastic Utensils For BambooDocument14 pagesCampus Waste Lab Proposal To Substitute Single-Use Plastic With Paper Products and Plastic Utensils For Bambooapi-529878933No ratings yet
- 2016 Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of The Middle Meningeal ArteryDocument5 pages2016 Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of The Middle Meningeal ArteryJulio Cesar Velasco CastroNo ratings yet