Professional Documents
Culture Documents
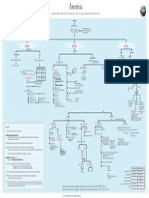
Hemolytic Anemia S
Uploaded by
dnutter012576Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemolytic Anemia S
Uploaded by
dnutter012576Copyright:
Available Formats
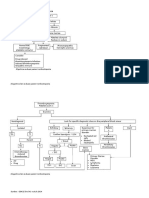
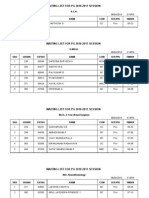
Hemolytic Anemias Testing
Click here for topics associated with this algorithm
ORDER
CBC with Platelet Count and
Automated Differential
Reticulocytes, Percent & Number
Lactate Dehydrogenase, Serum or
Plasma
Haptoglobin
Bilirubin, Total, Serum or Plasma
INDICATIONS FOR TESTING
Patient with anemia and
evidence of hemolysis
Consider environmental factors,
mechanical cardiac valve,
vasculitis, malignant hypertension
Increased D
Dimer
decreased
fibrinogen
DIC
No
Proceed based on above findings
Decreased
platelets
Consider
DIC
TTP
HELLP
HUS
ADAMTS13
activity
TTP
Consider
molecular testing
No
Yes
IgG+
No
Recluse spider
venom, clostridium
sepsis
Cold
agglutinins
disease
Suggests
microangiopathic
RBC destruction
Schistocytes
Consider
malaria,
bartonella (oroya
fever), babesia
Unusual red
cell inclusions
Consider Sickle cell disease
diverse genotypes: SS, SC,
SE, S thalassemia, S
Lepore
Sickle cells
HPLC
Yes
Acquired
Direct Coombs
(Anti-Human
Globulin)
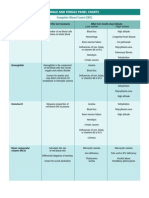
Presence of the following may provide clues to the etiology of the anemia
Increased reticulocyte count
Abnormal peripheral smear
Polychromasia, spherocytes, schistocytes, sickle cells,
stomatocytes, Heinz bodies, basophilic stippling, unusual red cell
inclusions, and agglutination
Note: lack of any of the above does not rule out hemolytic anemia
Osmotic
Fragility,
Erythrocyte
(usually
positive)
Consider
RBC membrane
disorder
(hereditary
spherocytosis,
hereditary
elliptocytosis,
autoimmune
hemolysis)
Spherocytes,
pyropoikilocytes,
elliptocytes or
acanthocytes
Basophilic
stippling
Polychromasia
only with or
without platelet
decrease
No
Congenital 5'
nucleotidase
deficiency
Yes
Consider
lead
poisoning
Acquired
Consider
PNH
Polychromasia without
other reproducible
morphologic abnormality
Autoimmune
hemolytic anemia
(consider drug
induced, hemolytic
disease of the
newborn, autoimmune
disease)
Cold
agglutinins
testing
Cold agglutinins
disease,
paroxysmal cold
hemoglobinuria
(PCH)
Confirm PCH with
Donath Landsteiner
testing
+ for
complement
2006 ARUP Laboratories. All Rights Reserved. Revised 08/20/2012
Direct Coombs
(Anti-Human
Globulin)
Consider
cold
agglutinins
disease
Heinz
bodies
Agglutination
Consider serum
lead level
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
(PNH), RBC and WBC
+C3
Yes
Consider 5'
nucleotidase testing
Consider
Pyruvate kinase
deficiency
Hexokinase deficiency
Other enzyme defects
Consider
Glucose-6-Phosphate
dehydrogenase
deficiency
Unstable hemoglobin
defects
Glutathione
metabolism defects
Hemoglobin H
disease
Consider one or
more of the
following tests
Pyruvate kinase
Hexokinase
Glucose
phosphate
isomerase
Consider one or more of
the following tests
Isopropanol heat
stability testing
Glucose-6Phosphate
Dehydrogenase
(G6PD) 2 Mutations
Enzymes of
glutathione cycle
For hemoglobin
disorders,
consider
HPLC, genetic
testing
www.arupconsult.com
You might also like
- Hematology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandHematology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hemolytic Anemia SDocument1 pageHemolytic Anemia Sdrafq2000No ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia SDocument1 pageHemolytic Anemia SvivireiNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God, Most Gracious, Most MercifulDocument22 pagesIn The Name of God, Most Gracious, Most MercifulMohammad Sadiq AzamNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blood TestDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Blood TestRueth AnnafeyeNo ratings yet
- Cytology of Body FluidDocument68 pagesCytology of Body FluidZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Document9 pagesLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- Approachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02Document63 pagesApproachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02adnansirajNo ratings yet
- ThromboDocument1 pageThromboapi-262842962No ratings yet
- Approach To Hemolytic AnemiaDocument63 pagesApproach To Hemolytic AnemiaSarath Menon R100% (2)
- Learning Objectives: Table 1Document25 pagesLearning Objectives: Table 1Mihu DragostinNo ratings yet
- Kuliah AnemiaaDocument44 pagesKuliah AnemiaaAhmad Umar AfNo ratings yet
- Hematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891Document8 pagesHematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891padmaNo ratings yet
- Hematology Mnemonics: Macrocytic Anemia CausesDocument8 pagesHematology Mnemonics: Macrocytic Anemia CausespadmaNo ratings yet
- Anemia (: /Ə Ni Miə/ Also Spelled Greek Red Blood Cells HemoglobinDocument13 pagesAnemia (: /Ə Ni Miə/ Also Spelled Greek Red Blood Cells HemoglobinAryana BudiawanNo ratings yet
- Hematology Trends in Emma NierDocument8 pagesHematology Trends in Emma NierTin CunetaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument17 pagesAnemiaBeeBee SethNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Thrombocytopenia Evaluation - IngDocument3 pagesAlgorithm For Thrombocytopenia Evaluation - IngNurAinaSuryaNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia 110616032010 Phpapp02Document82 pagesPolycythemia 110616032010 Phpapp02Ahmad Ripani Musyaffa AhdanLabNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument21 pagesAnemiaMarie WagasNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory Values: Reference Manual V 36 No 6 14 15Document1 pageCommon Laboratory Values: Reference Manual V 36 No 6 14 15Putri Agustin MereNo ratings yet
- Anemia AlgoritmaDocument1 pageAnemia AlgoritmaAmilia WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Hematology/Oncology Board Review: Vaibhav Sahai MD MSC Hem/Onc Fellow Northwestern UniversityDocument77 pagesHematology/Oncology Board Review: Vaibhav Sahai MD MSC Hem/Onc Fellow Northwestern UniversityMark MaNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion ReactionsDocument26 pagesBlood Transfusion ReactionsRakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- PejowebApproach To Anemia by Dr. Joel Solorzani RomeroDocument57 pagesPejowebApproach To Anemia by Dr. Joel Solorzani RomeroAshraf FaragNo ratings yet
- Anemia Extrinsic FactorsDocument4 pagesAnemia Extrinsic FactorsCiariz CharisseNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Smear Review: Diagnostic Aid for Blood DisordersTITLEDocument31 pagesPeripheral Smear Review: Diagnostic Aid for Blood DisordersTITLEDaniel McFarlandNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument4 pagesCase PresKislev Othel MoraledaNo ratings yet
- Components of Blood ChartAnemia FlowchartDocument1 pageComponents of Blood ChartAnemia Flowchartivankcurry100% (1)
- Results: Not A Definitive TestDocument2 pagesResults: Not A Definitive TestShelleyMaeSilaganMartosNo ratings yet
- HemolysisDocument22 pagesHemolysisMohamoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- Approach To Anemia and PolycythemiaDocument7 pagesApproach To Anemia and PolycythemiaambutlangnimoNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument60 pagesHemolytic AnemiaReta megersaNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE BLOOD PICTURE Ok-1 PDFDocument78 pagesCOMPLETE BLOOD PICTURE Ok-1 PDFEmanuel100% (1)
- Red Blood Cell Development and Anemia in NewbornsDocument22 pagesRed Blood Cell Development and Anemia in NewbornsJaime BarraganNo ratings yet
- 209-Hematology Review - Case StudiesDocument129 pages209-Hematology Review - Case StudiesKhalid Khalidi100% (2)
- Anemia (Pronounced: o o o o o o oDocument12 pagesAnemia (Pronounced: o o o o o o opamela100181No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument10 pagesAnemiaGulzada ShadymanovaNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Diagnostic ApproachDocument36 pagesAnemia: Diagnostic ApproachRizky LumalessilNo ratings yet
- Guide to Transfusions and CoagulopathiesDocument10 pagesGuide to Transfusions and Coagulopathieskep1313No ratings yet
- EDTA Induce ThrombocytopeniaDocument38 pagesEDTA Induce ThrombocytopeniaFabian PitkinNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About AnemiaDocument14 pagesEverything You Need to Know About AnemiaHermawan HmnNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hemolytic Anemia GuideDocument37 pagesCongenital Hemolytic Anemia GuideSomendra Mohan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory TestsDocument90 pagesBasic Laboratory Testsansjoh0217No ratings yet
- Pediatics Glomerular DiseasesDocument75 pagesPediatics Glomerular DiseasesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mahmmoud Ayish Lecture on AnemiaDocument21 pagesDr. Mahmmoud Ayish Lecture on AnemiaRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Anemias: What Is Anemia, How Do You Diagnose Anemia, and How Are The Different Anemias Classified?Document78 pagesClassification of Anemias: What Is Anemia, How Do You Diagnose Anemia, and How Are The Different Anemias Classified?Kaushik BhuvaNo ratings yet
- Lab Exam Results SummaryDocument11 pagesLab Exam Results SummaryKiyla92100% (1)
- Blood Transfusions: Dr. Asoka de SilvaDocument23 pagesBlood Transfusions: Dr. Asoka de SilvaanojanNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia: Pearla LasutDocument22 pagesPolycythemia: Pearla LasutFuji YantoNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisordersDocument108 pagesHematologic DisordersEmma IntiaNo ratings yet
- PolycythemiaDocument82 pagesPolycythemiaTiffany Mae Arud100% (3)
- Post PregnantDocument27 pagesPost PregnantShreyas RavishankarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Sepsis & SIRSDocument44 pagesUnderstanding Sepsis & SIRSDaintyGarciaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis & SIRS: Wade Woelfle, MD, FAAEM UW ECC 2016 June 21,2016Document44 pagesSepsis & SIRS: Wade Woelfle, MD, FAAEM UW ECC 2016 June 21,2016Elavarasi GanesanNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation TherapyFrom EverandAnticoagulation TherapyJoe F. LauNo ratings yet
- SPARQ Info For ClubsDocument5 pagesSPARQ Info For Clubsdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Cad DR A Guidelines 2011 Teacher Assess FormDocument3 pagesCad DR A Guidelines 2011 Teacher Assess Formdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Gait and StationDocument17 pagesGait and Stationsarguss14100% (3)
- Mhsus Documentation Manual 2015Document86 pagesMhsus Documentation Manual 2015dnutter012576100% (3)
- Ocd Family TXDocument12 pagesOcd Family TXdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument1 pageMegaloblastic Anemiadnutter012576No ratings yet
- Cap 2013 0134Document7 pagesCap 2013 0134dnutter012576No ratings yet
- WISCONSIN INFORMED CONSENT FOR OPIOID ANTAGONIST MEDICATIONDocument3 pagesWISCONSIN INFORMED CONSENT FOR OPIOID ANTAGONIST MEDICATIONdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Amantadine - A Review of Use in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2013 Ccap22 - 1p0055Document6 pagesAmantadine - A Review of Use in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2013 Ccap22 - 1p0055dnutter012576No ratings yet
- Narcolepsy in African Americans SP-759-14Document31 pagesNarcolepsy in African Americans SP-759-14dnutter012576No ratings yet
- Premonitory Urge For Tics Scale (PUTS)Document2 pagesPremonitory Urge For Tics Scale (PUTS)dnutter012576No ratings yet
- BEARS Sleep Screening Tool Assesses 5 DomainsDocument2 pagesBEARS Sleep Screening Tool Assesses 5 Domainsdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Psychiatry and EM RVUs 2013Document10 pagesPsychiatry and EM RVUs 2013dnutter012576No ratings yet
- Johns Hopkins Depression Checklist for Children (HDCL-CDocument2 pagesJohns Hopkins Depression Checklist for Children (HDCL-Cdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Patient Information UpdateDocument1 pagePatient Information Updatednutter012576No ratings yet
- AIMS scale measures involuntary movementsDocument3 pagesAIMS scale measures involuntary movementssilviaindriaprianNo ratings yet
- 54 InvertDocument13 pages54 InvertwatersklNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Screening Questionnaire for ADHD Stimulant MedicationDocument1 pageCardiac Screening Questionnaire for ADHD Stimulant Medicationdnutter012576No ratings yet
- BEARS Sleep Screening Tool Assesses 5 DomainsDocument2 pagesBEARS Sleep Screening Tool Assesses 5 Domainsdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Suicidal Risk Assessment - Becks Suicide Intent ScaleDocument3 pagesSuicidal Risk Assessment - Becks Suicide Intent Scalednutter012576100% (2)
- AQ AdolescentDocument5 pagesAQ Adolescentdnutter012576No ratings yet
- View Topic GAD 2-2-12Document15 pagesView Topic GAD 2-2-12dnutter012576No ratings yet
- Youth Football Speed ProgramDocument46 pagesYouth Football Speed Programdnutter01257675% (4)
- C SSRS1!14!09 BaselineDocument3 pagesC SSRS1!14!09 Baselinednutter012576No ratings yet
- Cardiac Screening Questionnaire for ADHD Stimulant MedicationDocument1 pageCardiac Screening Questionnaire for ADHD Stimulant Medicationdnutter012576No ratings yet
- Gap 50 by Bruce EienDocument33 pagesGap 50 by Bruce Eiendnutter012576No ratings yet
- 1335 1344Document10 pages1335 1344Priyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization PDFDocument3 pagesUrinary Catheterization PDFRishabh trivediNo ratings yet
- Appendix 8 PDQ39 PDFDocument3 pagesAppendix 8 PDQ39 PDFdrrselvarajNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Physical ExaminationDocument53 pagesHistory Taking and Physical ExaminationBoruuf If GammachuuNo ratings yet
- PYQDocument2 pagesPYQAisyah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Saint Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument4 pagesSaint Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingimnasNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Test Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesDigestive System Test Questions and Answersflorin100% (1)
- Waiting List For PG 2010-2011 SessionDocument7 pagesWaiting List For PG 2010-2011 SessionBrunoNo ratings yet
- Elephantiasis: Report AboutDocument8 pagesElephantiasis: Report AboutAmjadRashidNo ratings yet
- MRCS Part A 10 Jan 2017 Recalls (DR Salah Group) .Document7 pagesMRCS Part A 10 Jan 2017 Recalls (DR Salah Group) .Umair Ashfaq0% (1)
- Merged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Document15 pagesMerged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Ericsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Vas 1Document10 pagesVas 1Abdul Latiful KhabirNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in Pregnancy GuideDocument3 pagesHeart Disease in Pregnancy GuideNasehah SakeenahNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Made EasyDocument8 pagesAcute Appendicitis Made EasyTakpire DrMadhukarNo ratings yet
- Otc DrugsDocument71 pagesOtc DrugsEthan Morgan100% (2)
- Differential Diagnosis of Scalp Hair FolliculitisDocument8 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Scalp Hair FolliculitisandreinaviconNo ratings yet
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis: Clinical Prescription and TechnologyDocument8 pagesAutomated Peritoneal Dialysis: Clinical Prescription and Technologyamalia puspita dewiNo ratings yet
- DSM-IV Adult ADHD Symptom Checklist-Self Report Version # 6182Document1 pageDSM-IV Adult ADHD Symptom Checklist-Self Report Version # 6182Chris0% (1)
- ENDODONTICS Student ShareDocument48 pagesENDODONTICS Student ShareAmasi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ad70 PDFDocument7 pagesAd70 PDFDnyaneshwar Dattatraya PhadatareNo ratings yet
- Healing Through MusicDocument11 pagesHealing Through MusicMiguel MacaroNo ratings yet
- Reproduksi Dan Fertilisasi Dalam Praktik Sehari-Hari. Jakarta: Sagung SetoDocument2 pagesReproduksi Dan Fertilisasi Dalam Praktik Sehari-Hari. Jakarta: Sagung SetoDevita ImasulyNo ratings yet
- Pfin 6th Edition Billingsley Test BankDocument24 pagesPfin 6th Edition Billingsley Test BankNatalieRojasykebg100% (32)
- OmronDocument19 pagesOmrondekifps9893No ratings yet
- Using Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics as First-Line Treatment for Early-Episode SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesUsing Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics as First-Line Treatment for Early-Episode SchizophreniaFan TomasNo ratings yet
- NCMB317 Lec MidtermDocument55 pagesNCMB317 Lec Midterm2 - GUEVARRA, KYLE JOSHUA M.No ratings yet
- Immediate Loading FaizDocument85 pagesImmediate Loading FaizDrrksundar KumarNo ratings yet
- Doctors Tell All-And It's Bad - Meghan O'Rourke - The AtlanticDocument7 pagesDoctors Tell All-And It's Bad - Meghan O'Rourke - The AtlanticAlexNo ratings yet
- Immunization Case-Based Register: DHIS2 Tracker Data Model in PracticeDocument11 pagesImmunization Case-Based Register: DHIS2 Tracker Data Model in PracticeGerald ThomasNo ratings yet
- HomeopathyDocument33 pagesHomeopathyPriya Illakkiya100% (2)