Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014
Uploaded by
Rajesh AggarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014
Uploaded by
Rajesh AggarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
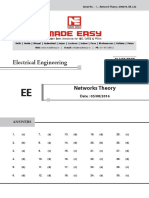
Serial No:.
ECDRH_071114_Network Theory
CL ASS TEST - 2014
Electronics Engineering
Network Theory
EC
Date : 07/11/2014
ANSWERS
1. (d)
7. (d)
13. (a)
19. (b)
25. (a)
2. (d)
8. (c)
14. (b)
20. (b)
26. (c)
3. (d)
9. (d)
15. (c)
21. (c)
27. (a)
4. (b)
10. (a)
16. (d)
22. (a)
28. (b)
5. (a)
11. (b)
17. (b)
23. (b)
29. (d)
6. (d)
12. (a)
18. (c)
24. (c)
30. (b)
CTEC14
Delhi | Noida | Bhopal | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Indore | Bhubaneswar
1. (d)
2
I2rms
1 9
= t .dt
30 3
3 3
1
t
= 9
3 0
3
=
Power =
=
=
27 A2
I2 R
27 10
270 W
2. (d)
Since the reactance are cancelling each
other, the circuit is purely resistive and the
current is in phase with the applied voltage.
The voltage across the inductor leads the
current through it by 90.
100 0
Since, I =
{10 + j(20 20)}
= 10 0
VL = jL I
= 20 10 90
= 200 90
4. (b)
Leq = L1 + L2 + 2M = 6H
1
At resonance, Leq =
C
or
f=
1
Leq . C
1
12
1
4 3
Hz
NETWORK THEORY
C o p y r i g h t : S u b j e c t m a t t e r t o M A D E E A S Y, N e w D e l h i . N o p a r t o f t h i s b o o k m a y b e re p ro d u c e d o r u t i l i s e d i n a n y f o r m w i t h o u t t h e w r i t t e n p e r m i s s i o n .
EXPLANATIONS
5. (a)
By applying KVL in loop 1.
I
(I + 1)
+
1V
1A
1=I+1
I=0A
6. (d)
Total impedance of circuit
10
j 100
10 V
j 100
ZT = 10 +(j100) + j100
= 10
Current I =
10
= 1A
10
Hence voltage across capacitor
Vc = 1 j 100 = j 100 V
7. (d)
It can be verified by checking the value of
the current at t = 0 and at t = which should
be zero and 10/1 = 10 A respectively.
8. (c)
For finding time const, we neglect current
source as a open ckt
ckt becomes
www.madeeasy.in |
Copyright :
Delhi | Noida | Bhopal | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Indore | Bhubaneswar
1F
1F
1F
2F
Ceq 2/3F
11. (b)
3
6 = Req
Time constant = Req Ceq
= 6 2/3 = 4 sec
9. (d)
z(s) =
Y(s) =
0.2 s
s + 0.1s + 2
2
s2 + 0.1s + 2
0.2 s
s
1
2
+ +
0.2 2 0.2 s
= 5s + 0.5 +
10
s
Comparing with Y(s) = Cs +
1
1
+
R
Ls
1
1
C = 5F, R =
= 2 , L =
= 0.1 H
0.5
10
10. (a)
When 5 0 is acting alone, i1(t) = 5 0
(as 10 60 is kept open)
When 10 60 is acting alone.
i1(t) = 10 60 (as 5 0 is kept open)
i1(t) = 10 60 5 0
= 5 + 8.66j 5
= 8.66j
= 5 3 90
=
10
3 90
2
NETWORK THEORY
C o p y r i g h t : S u b j e c t m a t t e r t o M A D E E A S Y, N e w D e l h i . N o p a r t o f t h i s b o o k m a y b e re p ro d u c e d o r u t i l i s e d i n a n y f o r m w i t h o u t t h e w r i t t e n p e r m i s s i o n .
1F
CTEC14
Current through the 4-ohm resistor = i
i
4
3i
.
4
Therefore, the voltage drop across it
3 i
= 4
4
= 3 i, which must be equal to V.
Thus, effective resistance faced by the
voltage source is 3 .
12. (a)
L
240 V, 50 Hz
V2
= 300
R
or
and
or
R=
1002
100
=
300
3
IR = V = 100 V
I=
100
= 3 amp.
100
For the p.f. to be equal to unity,
1
I(L) = I
= VL
C
1
orI
=
C
or
C=
2402 1002 = 218.17 Volt
3
2 50 218.17
= 43.7 106
= 43.7 F
www.madeeasy.in |
Copyright :
Delhi | Noida | Bhopal | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Indore | Bhubaneswar
16. (d)
V+ =
4.14
V0 = V 1 +
10
=
=
or
sin t
= V
1+ j
2 V
sin t
1+ j
V0 = sin t
14. (b)
For unit step source,
I(t) =
At t = 0,
1
1
R
R
t
e L
I(t) = 0
For ramp,
At t = 0,
R
t
1
tu(t) 1 e L
I(t) =
I(t) = 0
R
For impulse input, I(t) =
Then at t = 0,I(t)=
1 Lt
e
R
1
Maximum
R
15. (c)
Since, VL = VC, then circuit is in resonance
and current,
I=
5
5
=
=1A
R
5
Now voltage, VL = 2 VR = 10
or
L = 10
L=
10
10
=
2F
10
= 31.8 mH
2 50
10 NETWORK THEORY
C o p y r i g h t : S u b j e c t m a t t e r t o M A D E E A S Y, N e w D e l h i . N o p a r t o f t h i s b o o k m a y b e re p ro d u c e d o r u t i l i s e d i n a n y f o r m w i t h o u t t h e w r i t t e n p e r m i s s i o n .
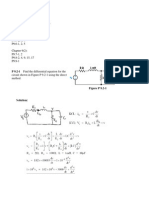
13. (a)
and
CTEC14
V = 100 Volt
and
10 =
1
v
vdt +
R
L
Differentiating, 0 =
or
v
dv 1
+
,
L
dt R
dv
R
= v .
= 200 v/s
dt
L
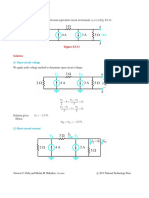
17. (b)
By star-delta transformation
Lb
L2
L3
La
Lc
L1
Lb =
L1 L 2
L1
10 20 + 20 40 + 40 10
40
= 5 mH
Lb =
18. (c)
For
u(t) = 1, t > 0
v1(t) = (1 e3t)
1
3
1
or v1(s) =
=
s s + 3
s(s + 3)
and, T(s) =
V1(s)
3
=
U(s)
s+3
3
Now, forR(s) = + 1
s
Response, H(s) = R(s) . T(s)
3
3 + s
=
s . s + 3
=
or
3
s
h(t) = 3 u(t)
www.madeeasy.in |
Copyright :
CTEC14
Delhi | Noida | Bhopal | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Indore | Bhubaneswar
C = 4 F
R = 5k
V1 (t)
V0 (t)
In the Laplace domain,
V(s) RC(s)
Vi (s)
R= i
1
RCs + 1
R+
Cs
Vi(t) = 100 tu(t)
V0(s) =
and Vi(s) =
100
s2
Hence,V0(s) =
=
100 5 103 4 10 6 s
s2 5 103 4 10 6 s + 1
2
s(2 10 2 s + 1)
2
s
V0(t) = 2 u(t)
Maximum voltage = 2 volts
21. (c)
Current I =
10 V
7
2 + RL
RL
3V
Power transferred to load
2
7
7
RL + 3
=
2 + RL
2 + RL
11 NETWORK THEORY
C o p y r i g h t : S u b j e c t m a t t e r t o M A D E E A S Y, N e w D e l h i . N o p a r t o f t h i s b o o k m a y b e re p ro d u c e d o r u t i l i s e d i n a n y f o r m w i t h o u t t h e w r i t t e n p e r m i s s i o n .
20. (b)
=
49RL
(2 + RL )
21
(2 + RL )
49RL + 21RL + 42
70RL + 42
14(5RL + 3)
(2 + RL )2
(2 + RL )2
(2 + RL )2
For maximum power transfer
dP
=0
dRL
(RL + 2)2 5 (5 RL + 3) 2(RL + 2) = 0
5R2L + 20RL + 20 2(5R2L+13RL+6) = 0
5R2L 6RL + 8 = 0
5R2L + 6RL 8 = 0
RL = 0.8 & 2
Hence,
RL = 0.8
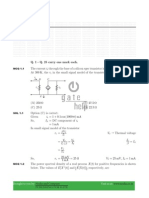
22. (a)
As the steady-state is reached at t = 0.
The capacitor will be open and inductor will
be short and current through inductor and
voltage across capacitor will not change
after switch is closed.
K
I2
t=0
1H
5V
2
+
1F
t = 0
I2(0) = 0 A
and
Vc(0) = 10 V
at
t = 0+
st
Aply KVL in I loop
at
www.madeeasy.in |
Copyright :
10 V
Delhi | Noida | Bhopal | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Indore | Bhubaneswar
then the current
I2
2
5V
V C(0 )
10 V
1F
1
+
2
5V
I2 = 0
+
10 V
10 V
5 I 2I 10 = 0
3I = 5
I=
5
A
3
23. (b)
Applying KVL in loop-II.
VL 2
5
10 + 10 = 0
3
VL =
10
dI (0+ )
=L 2
3
dt
dI2 (0+ )
10
A/s
=
dt
3
24. (c)
Let the given load is z
A
I
Isc
Zeq VAB
C o p y r i g h t : S u b j e c t m a t t e r t o M A D E E A S Y, N e w D e l h i . N o p a r t o f t h i s b o o k m a y b e re p ro d u c e d o r u t i l i s e d i n a n y f o r m w i t h o u t t h e w r i t t e n p e r m i s s i o n .
I=
Zeq
I
Z + Zeqq sc
...(i)
Given I = 70 mA
Isc = 75 mA
VAB = 0.6 V
From equation (i)
70 =
Zeq
75
Z + Zeq
75
Z
= 1+
70
Zeq
Zeq = 14 Z
and VAB = ZI
0.6 = Z 70 103
Zeq = 14
60
= 120
7
25. (a)
The Y parameter of two networks in parallel
are the sums of the corresponding Yparameters,
I1
V1
As
I2
V2
1 1
Y1 =
,
1 1
4 2
Y2 =
1 1
Y = Y1 + Y2
5 1
=
0 2
12 NETWORK THEORY
CTEC14
www.madeeasy.in |
Copyright :
Delhi | Noida | Bhopal | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Indore | Bhubaneswar
26. (c)
From the circuit,
I1 = (V1 V2) YC + V1 . YA
= V1 (YA + YC) V2 . YC
I2 = V1YC + V2(YB + YC)
YA + YC = Y11 = 8
YC = Y12 = Y21 = 6
YB + YC = Y22 = 6
then, YA = 2,
YB = 0,
YC = 6
... (i)
... (ii)
1 k
iC
10 V
+
0.01 F
t=0
VC
3 k
VC(0) =
10
3 = 7.5 V
1+ 3
After the switch closes, at t = 0
VC = 7.5 e105 t . t
iC = C
dVC
dt
= 0.01 106 7.5 105 e105 t
= 7.5 103 e105 t A
28. (b)
By applying voltage divider rule
2 k
9V
V1
1 k
13 NETWORK THEORY
10 F
20 F
V2
C o p y r i g h t : S u b j e c t m a t t e r t o M A D E E A S Y, N e w D e l h i . N o p a r t o f t h i s b o o k m a y b e re p ro d u c e d o r u t i l i s e d i n a n y f o r m w i t h o u t t h e w r i t t e n p e r m i s s i o n .
The voltage
27. (a)
1 k
CTEC14
V1 =
Z1 =
and
Z2 =
1
9 V
1+ 2
1
j 10 10 6
1
j 20 10 6
2 k
9V
V1
Z1
1 k
V2
Z2
Again by applying voltage divider rule:
V2 =
Z2
3 V
Z1 + Z2
Z2
3 V = 1 V
2Z2 + Z2
29. (d)
when S1 is closed & S2 is open
VC1 (0) = VC1 (0+) = 3 V
when S1 is open & S2 is closed
VC2 (0+) = VC1 (0+) = 3 V
30. (b)
Voltage across 2 resistor
VS
4
=
2
2
=2A
=I
= 4V
Io double the current, VS is to be doubled.
www.madeeasy.in |
Copyright :
You might also like
- Intro To Psychology by Charles StangorDocument861 pagesIntro To Psychology by Charles StangorAidan Alexis67% (9)
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (2)
- Static Electricity ExplainedDocument6 pagesStatic Electricity ExplainedCarter SiyNo ratings yet
- RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesRL RC CircuitDavex GwapoNo ratings yet
- ECE225Midterm2 SolDocument23 pagesECE225Midterm2 SolnonreplicaNo ratings yet
- Class Test - 2015: Electrical EngineeringDocument6 pagesClass Test - 2015: Electrical EngineeringMichael DavisNo ratings yet
- B Network 09-09-16 1494Document10 pagesB Network 09-09-16 1494arunNo ratings yet
- CL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014Document5 pagesCL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Ispitni Zadaci - ElektrotehnikaDocument14 pagesIspitni Zadaci - ElektrotehnikaAleksandar KrčuljNo ratings yet
- GATE EC 2012 MCQ Questions 1-15Document50 pagesGATE EC 2012 MCQ Questions 1-15Gautam KunalNo ratings yet
- EC 2012 With SolutionsDocument50 pagesEC 2012 With Solutionsprabhjot singh1No ratings yet
- Electric Circuit and FieldsDocument24 pagesElectric Circuit and Fieldssamg27No ratings yet
- EE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13Document43 pagesEE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13ozanistzNo ratings yet
- Ies 2013 Ece SolutionDocument16 pagesIes 2013 Ece SolutionGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument25 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsHariPonnanaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications: Elec1111Document7 pagesElectrical Engineering & Telecommunications: Elec1111uploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering 2016 2016 2016 2016 2016: Networks TheoryDocument10 pagesElectrical Engineering 2016 2016 2016 2016 2016: Networks TheoryarunNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentSumathi AmbunathanNo ratings yet
- Virtual WorkDocument3 pagesVirtual WorksepidehahmadyNo ratings yet
- Week 4: Grantham University Key ConceptsDocument9 pagesWeek 4: Grantham University Key ConceptsAbu BakarNo ratings yet
- CircuitsII SH1Document4 pagesCircuitsII SH1aymanabuzNo ratings yet
- Electrotechnics 1b Outcome B Test 1 Memo 2021Document7 pagesElectrotechnics 1b Outcome B Test 1 Memo 2021spm0826722No ratings yet
- Detailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'Document12 pagesDetailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'vijaynarayan guptaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current Theory - EDocument12 pagesAlternative Current Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- Post Task - Cristian Leonardo PiragauraDocument11 pagesPost Task - Cristian Leonardo PiragauraGERMANEDU2000No ratings yet
- Linear Systems Analysis PDFDocument8 pagesLinear Systems Analysis PDFpadmajasivaNo ratings yet
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocument5 pagesSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNo ratings yet
- Phys102 Final Exam Key ConceptsDocument15 pagesPhys102 Final Exam Key ConceptsammuNo ratings yet
- CT Saturation from DC Offset CurrentDocument20 pagesCT Saturation from DC Offset CurrentAngga Wira PramanaNo ratings yet
- Solution - Tutorial 3Document11 pagesSolution - Tutorial 3zgalionoooNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2010 With SolutionsDocument49 pagesGATE EE 2010 With SolutionsKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- RC Circuits TutorialDocument9 pagesRC Circuits TutorialPiyush DubeyNo ratings yet
- Solve Problems in RC Series CircuitsDocument6 pagesSolve Problems in RC Series CircuitsAmer ArtesanoNo ratings yet
- Solved 540 541 AIEEE Past 5 Years’ PapersDocument35 pagesSolved 540 541 AIEEE Past 5 Years’ PapersAmal Krishna TNo ratings yet
- GATE in 2013 Solutions GATE AspireDocument14 pagesGATE in 2013 Solutions GATE Aspirenickynick2007No ratings yet
- Iit Jee Screening Physics 2005 SolutionDocument7 pagesIit Jee Screening Physics 2005 Solutionsaurav guptaNo ratings yet
- EENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnDocument7 pagesEENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnFredy AlbornozNo ratings yet
- 2012 Gate EC Solved PaperDocument48 pages2012 Gate EC Solved PaperChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit Analysis Using PhasorsDocument22 pagesAC Circuit Analysis Using PhasorsvsabioniNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument58 pagesElectrical EngineeringNor Syahirah MohamadNo ratings yet
- Examination Nov 2012Document16 pagesExamination Nov 2012Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Class Test - 2016: Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesClass Test - 2016: Electrical EngineeringarunNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA CIRCUIT ANALYSIS TOPICSDocument115 pagesUNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA CIRCUIT ANALYSIS TOPICSAzlin HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Scans of CircuitsDocument7 pagesScans of CircuitsTyler AbercicleNo ratings yet
- ELEG 220 (Fall 2014) Final Exam: Title: Electric Circuits Score: / 140 /35Document18 pagesELEG 220 (Fall 2014) Final Exam: Title: Electric Circuits Score: / 140 /35Saied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- IES Conv.-1Document11 pagesIES Conv.-1PawanKumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Analog Elec - 13-09-16 - 1526Document9 pagesAnalog Elec - 13-09-16 - 1526arunNo ratings yet
- Rec6 SolutionsDocument4 pagesRec6 SolutionsChen Marie DyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: MOCK GATE (2012) - 2Document12 pagesEngineering Academy: MOCK GATE (2012) - 2shrish9999No ratings yet
- Assessment Clo1 Clo2 Clo3 Clo4 Clo5 Plo1 Plo2 Plo2 Plo1Document12 pagesAssessment Clo1 Clo2 Clo3 Clo4 Clo5 Plo1 Plo2 Plo2 Plo1Ma Liu Hun VuiNo ratings yet
- ZZ - Electricity & MagnetismDocument137 pagesZZ - Electricity & Magnetismvenkyrocker777750% (4)
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisFrom EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Iasbaba Prelims Daily Quiz - Day 15Document3 pagesIasbaba Prelims Daily Quiz - Day 15saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Iasbaba Prelims Daily Quiz - Day 14Document4 pagesIasbaba Prelims Daily Quiz - Day 14saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Day 50Document11 pagesDay 50saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- MBA in Manufacturing ManagementDocument2 pagesMBA in Manufacturing Managementsaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Ies 2Document5 pagesIes 2saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Ae EtDocument3 pagesAe Etsaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Day 46Document14 pagesDay 46saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Day 7-1Document4 pagesDay 7-1saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Day 47Document11 pagesDay 47saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Day 48Document16 pagesDay 48saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- S&T Syllabus 20151130Document22 pagesS&T Syllabus 20151130nannurahNo ratings yet
- Je EtDocument3 pagesJe Etsaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Apply UPCL Online Registration 22.01.2016 to 15.02.2016Document1 pageApply UPCL Online Registration 22.01.2016 to 15.02.2016saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- AssistantengandUDC (IT)Document13 pagesAssistantengandUDC (IT)NitinNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Indian Education SystemDocument89 pages4 1 Indian Education Systemsaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Happy Maths 2Document32 pagesHappy Maths 2curlycurlNo ratings yet
- Arunachal Pradesh PSC Assistant Engineer Electrical Vacancies NotificationDocument3 pagesArunachal Pradesh PSC Assistant Engineer Electrical Vacancies Notificationsaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- 02 Awc Shilpi BanerjeeDocument8 pages02 Awc Shilpi Banerjeesaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Steps For Using EagleDocument2 pagesSteps For Using Eaglesaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- New Machin VisionDocument91 pagesNew Machin Visionsaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Basic RoboticsDocument136 pagesBasic Electronics Basic Roboticsrakesh_rodyNo ratings yet
- Isro 2012 PDFDocument19 pagesIsro 2012 PDFsharada_346460992No ratings yet
- Datasheet 20X4 LCDDocument10 pagesDatasheet 20X4 LCDKe RoboticssNo ratings yet
- ROBOTICS-A Beginners GuideDocument58 pagesROBOTICS-A Beginners Guidesaurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- CL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014Document6 pagesCL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- Kit UsesDocument1 pageKit UsesLavakesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- BSNL Jto 2006Document17 pagesBSNL Jto 2006saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- BSNL JTO Electrical 2009Document12 pagesBSNL JTO Electrical 2009saurabhdabas7No ratings yet