Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WiMAX White Paper - V1 - Approved
Uploaded by
dtizikaraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WiMAX White Paper - V1 - Approved
Uploaded by
dtizikaraCopyright:
Available Formats
White Paper
WiMAX Planning
The AIRCOM Perspective
Author:
Date:
Nishita Hathi
12 September 2005
Ref:
Version:
Status:
Sec. Class:
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
1
Approved
Customer Confidential
Copyright 2005 AIRCOM International - All rights reserved. No part of this work, which is protected by copyright, may be reproduced in
any form or by any means - graphic, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping or storage in an information
retrieval system without the written permission of the copyright owner.
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Contents
1
2
Introduction......................................................................................................................... 3
WiMAX Overview................................................................................................................ 3
2.1.1
WIMAX Standard ................................................................................................. 3
2.1.2
Application and Deployment ................................................................................ 3
2.1.3
WiMAX Network Parameters ............................................................................... 4
2.1.4
WiMAX Technologies........................................................................................... 4
3 Planning a WiMAX Network with the Enterprise Suite ....................................................... 5
3.1 Microwave Backhaul Planning...................................................................................... 5
3.1.1
Equipment............................................................................................................ 6
3.1.2
Point-to-point link Creation................................................................................... 7
3.1.3
Height Profiler ...................................................................................................... 8
3.1.4
Interference Analysis ........................................................................................... 9
3.2 Access Network Planning............................................................................................. 9
3.2.1
Propagation Models ............................................................................................. 9
3.2.2
Equipment.......................................................................................................... 11
3.2.3
WiMAX Base Stations........................................................................................ 11
3.2.4
Signal Strength Calculation ............................................................................... 12
3.2.5
Interference Analysis ......................................................................................... 13
3.3 WiMAX Network Optimisation .................................................................................... 15
3.3.1
Site Selection ..................................................................................................... 15
3.3.2
Antenna and Power Optimisation ...................................................................... 16
4 Summary .......................................................................................................................... 17
5 Glossary ........................................................................................................................... 17
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 2 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Introduction
WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a fixed wireless
access technology which can support high throughput broadband connections
over long distances for portable, nomadic and eventually mobile users. It operates
in several licensed and un-licensed bands and supports multiple channel
bandwidths in the range of 1.75 MHz 20 MHz.
The WiMAX standard is developed by the WiMAX forum, an industry group set up
by equipment manufacturers and component vendors to create a single
interoperable standard. The common standard is expected to result in lower
equipment costs and wider deployment.
WiMAX supports a number of different applications. These include microwave
backhaul for hotspots and other commercial services, fixed wireless access for
broadband services and mobile access for broadband services.
This document provides an overview of WiMAX technology and describes the
WiMAX planning capabilities of AIRCOMs ENTERPRISE suite.
2
2.1.1
WiMAX Overview
WIMAX Standard
The WiMAX standard is being developed by the WiMAX forum. All equipment
which complies with the WiMAX standard and meets the interoperability
requirements will be certified as WiMAX by the WiMAX forum.
The WiMAX standard is based on IEEE802.16 MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
standards and ETSI HIPERMAN standards.
The IEEE802.16 family of standard consists of three key profiles: IEEE802.16a,
IEEE802.16d and IEEE802.16e. Initial WiMAX networks are based on 802.16a
and 802.16d. The 802.16e is a mobile extension of 802.16d and will be introduced
after 2005.
The WiMAX forum has chosen a workable subset of the IEE802.16 and the
HIPERMAN standard for the sub 11GHz range. The standard supports NLOS
communication using OFDM modulation and will be able to support mobility in the
near future.
2.1.2
Application and Deployment
There are three key applications for WiMAX: Microwave Backhaul, Fixed
Broadband Access and Mobile Access. The first phase of WiMAX deployment will
provide fixed wireless connections via outdoor antennas which can be used for
cellular network backhaul, hotspots and other commercial services. The second
phase will support outdoor and indoor installations which can be used for fixed
BWA networks. The third and final phase will support roaming and mobility.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 3 of 17
AIRCOM International
2.1.3
Customer Confidential
WiMAX Network Parameters
The table below shows the key parameters for the various standards:
802.16
802.16a
802.16d
802.16e
HIPERMAN
Allocation
Spectrum
(GHz)
10-66
<11
Unlicensed:
2.4 and 5
Licensed: 2.3,
2.5 and 3.5
<11
Unlicensed:
2.4 and 5
Licensed: 2.3,
2.5 and 3.5
<6
<11
Unlicensed: 2.4
and 5
Licensed: 2.3, 2.5
and 3.5
Channel
Conditions
LOS
NLOS
NLOS
NLOS/Mobile
NLOS
Throughput/
Bit Rate
(Mbps)
32-134
<=75
<=75
<=15
<=75
Modulation
QPSK,
16QAM,
64QAM
20, 25
and 28
QPSK,
16QAM,
64QAM
Selectable
between 1.75
to 20
QPSK,
16QAM,
64QAM
Selectable
between 1.75
to 20
QPSK,
16QAM,
64QAM
Selectable
between 1.25
to 20
QPSK, 16QAM,
64QAM
Bandwidth
(MHz)
2.1.4
Selectable
WiMAX Technologies
The WiMAX standard does not introduce any new technologies, it is based on
technologies that are well known in the industry, and are used by existing vendor
proprietary radio systems, which include:
OFDM modulation
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing provides an efficient means of
overcoming the challenges of NLOS propagation as it can support large delay
spread of NLOS communication. As the OFDM waveform is composed of multiple
narrowband orthogonal carriers, selective fading is localised to a subset of the
carriers.
Directional antennas
Directional antennas at the CPE increase the fade margin by adding more gain.
The delay spread is also reduced as the antenna pattern suppresses a number of
the reflected signals that arrive at the CPE.
Adaptive modulation
Adaptive modulation allows the system to choose a modulation scheme based on
the SNR of the link. This allows the system to overcome time selective fading and
also extends the range that a higher modulation scheme can be supported over.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 4 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Error Correction techniques
Reed Solomon coding, Convolution coding and interleaving are used to detect and
correct errors and thus improve throughput.
Power Control
Power control is implemented at the base station. The base station sends power
control information to each of the CPEs so that the power received by the base
station is at a predetermined level. Power control reduces the overall power
consumption at the CPE and the potential interference with other co-located base
stations.
The WiMAX standard also supports some optional technologies, including:
Sub-channelisation
Sub-channelisation allows the link budget to be balanced such that the system
gain is balanced on the uplink and the downlink. Sub-channelisation concentrates
the transmit power into fewer OFDM carriers.
Transmit and receive diversity
Transmit and receive diversity increases system availability. Transmit diversity
uses space time coding to reduce the fade margin requirement. Receive diversity
uses various combining techniques to improve the availability of the system
Adaptive antenna systems
Adaptive antenna systems have beamforming properties that can steer their focus
in a particular direction. They also suppress co-channel interference from other
locations.
Planning a WiMAX Network with the Enterprise Suite
AIIRCOMs Enterprise suite of tools can be used to plan and analyse the various
different WiMAX profiles.
3.1 Microwave Backhaul Planning
Point-to-point networks for backbone can be modelled and analysed using
AIRCOMs microwave link planning tool, CONNECT.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 5 of 17
AIRCOM International
3.1.1
Customer Confidential
Equipment
The equipment used for the WiMAX backbone can be set up from within the tool or
imported into the tool in a number of different formats.
Figure 1 : Backhaul Equipment Parameter Specification
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 6 of 17
AIRCOM International
3.1.2
Customer Confidential
Point-to-point link Creation
Link templates can be defined to be used as basis for the point to point link
creation.
Figure 2: Point to Point link template
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 7 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
LOS Analysis
The LOS between a location and other locations can be determined using the LOS
wizard. The wizard allows users to determine the LOS links for a single property or
for a number of properties.
Figure 3; LOS Analysis for Property 36
3.1.3
Height Profiler
The height profiler shows the two dimensional cross section of the terrain between
two points or the cross section of an existing link. It can also be used to determine
the optimum height of the antennas, check clearance over terrains and objects
and analyse the effects of terrain reflection.
Figure 4; Height profile for link 11 and link 2 displaying building heights, LOS and
clearance of 1st and 2nd Fresnel Zones
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 8 of 17
AIRCOM International
3.1.4
Customer Confidential
Interference Analysis
Interference calculations can be performed for each individual link or for a
collection of links in the network.
Interference can be calculated for both sides of the link.
Figure 5; Results of the interference analysis for link 11 from property 29 and
property 30
3.2 Access Network Planning
Fixed wireless broadband access networks at WiMAX frequencies can be
modelled and analysed using AIRCOMs network planning tool, ASSET3G
Wide range and close range analysis can be performed by choosing the most
appropriate propagation model and cartographic data.
3.2.1
Propagation Models
WiMAX profiles support LOS and NLOS transmission at a number of different
carrier frequencies with different channel bandwidths.
The Enterprise suite supports a number of empirical and deterministic propagation
models for the analysis of the different WiMAX network profiles.
Empirical Model
The Okumura Hata model is supported as standard for wide range analysis and
can be calibrated at WiMAX frequencies. A number of diffraction algorithms can be
considered to account for the obstacles between the base station and the CPE. In
order to further improve the accuracy of the analysis, specific loss values can be
applied to each clutter type.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 9 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Figure 6; Okumura Hata Model parameter specification
Deterministic Models
A number of deterministic models are supported within the tool. The Siradel
Volcano model has been verified at WiMAX frequencies and allows the users to
perform close range network analysis using high resolution cartographic data.
Reflection from surfaces and diffraction by edges can also be modelled.
Figure 7; Volcano Model Parameter Specification
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 10 of 17
AIRCOM International
3.2.2
Customer Confidential
Equipment
The WiMAX equipment can be defined from within the tool or can be imported into
the tool using various different formats.
Figure 8; Access network equipment parameter specification
3.2.3
WiMAX Base Stations
Each sector of the WiMAX base station can be set up independently within the tool
and is stored within a database for ease of management
Figure 9; WiMAX base station parameter specification
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 11 of 17
AIRCOM International
3.2.4
Customer Confidential
Signal Strength Calculation
In order to serve a given coverage area, WiMAX base stations can be deployed as
a single isolated base station or in a multi base station configuration. Both
deployment strategies can be evaluated in the planning tool.
Figure 10; Received signal strength plots for isolate and multi base station
configuration
Individual coverage plots can be generated for various different CPE types.
Indoor
Outdoor
Figure 11; Signal Strength for indoor and outdoor CPE
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 12 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Different minimum received signal levels can be specified for each of the
modulation and coding schemes, for the different CPE types.
Figure 12; Threshold specification for signal strength plots
The coverage can also be analysed in the form of a statistics report. The report
produces percentage statistics in terms of individual clutter categories and sector
coverage areas.
Figure 13: Coverage statistics report
3.2.5
Interference Analysis
The interference can be analysed in terms of the C/I ratio.
Carriers can be assigned to WiMAX sectors manually or using the automatic
frequency planner, ILSA.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 13 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Figure 14: Manual Assignments of carriers
Figure 15: ILSA Frequency Planer
The C/I can be calculated and displayed on the map view for the individual CPE types.
The C/I thresholds for
each of the modulation
and coding schemes
can be adjusted by the
user.
Figure 16: Results of interference calculation
In addition to viewing the interference on the map view, the user can generate a statistics
report. The report provides a breakdown of the interference per clutter type, over a specified
threshold.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 14 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Figure 17: Interference statistics report
3.3 WiMAX Network Optimisation
WiMAX networks can be optimised using AIRCOMs network optimisation tool,
ADVANTAGE. The tool allows planners to determine the most appropriate
location for the WiMAX sites based on several different criteria. It also allows
planners to optimise antenna parameters and transmit power to improve the
performance of the WiMAX network.
3.3.1
Site Selection
The number of WiMAX sites required can be optimised by choosing the best site
location from a number of predefined candidate locations.
Figure 18: Optimising site location through site selection
The selection of the optimum sites can be based on a number of different
objectives such as coverage, interference and traffic served.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 15 of 17
AIRCOM International
3.3.2
Customer Confidential
Antenna and Power Optimisation
The antenna tilt, azimuth and height can be optimised to improve the network
coverage, reduce interference or maximise the number of CPEs served in a
network.
Figure 19: Optimising Antenna parameters
The total power transmitted from a base station can also be optimised to maximise capacity
for the range of services and throughput demands.
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 16 of 17
AIRCOM International
Customer Confidential
Summary
The WiMAX standard, endorsed by the WiMAX forum will provide a unified
standard for the deployment of broadband wireless services. The broad range of
spectrum options in the licensed and un-licensed bands will provide a favourable
climate for equipment manufacturers and service providers.
This document provided an overview of the WiMAX standard and presented the
WiMAX planning capabilities of AIRCOMs Enterprise suite.
Glossary
WiMAX
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access
LOS
Line Of Sight
NLOS
Non Line OF Sight
OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
FWA
Fixed Wireless Access
BWA
Broadband Wireless Access
QPSK
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
QAM
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
CPE
Customer Premises Equipment
SNR
Signal to Noise Ratio
ILSA
IntelligenT Local Search Engine
Author: Nishita Hathi
Date: 12/08/2005
WiMAX Planning
I-PE-IN-WiMAX - WiMAX White Paper
Page 17 of 17
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Google Dorks For Credit Card DetailsDocument5 pagesGoogle Dorks For Credit Card DetailsChanning Gonzales50% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- TRN 4010 003 01 - SG Ins - Lec - ENDocument257 pagesTRN 4010 003 01 - SG Ins - Lec - ENAnonymous KMWzXegk100% (1)
- Basic Computer Organization and Design-IDocument54 pagesBasic Computer Organization and Design-IchodarNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Parking - The Life and After-Life of Paving..Document5 pagesA Brief History of Parking - The Life and After-Life of Paving..dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Smart Waste Management SystemDocument42 pagesSmart Waste Management SystemUsama NawazNo ratings yet
- Vim Ccs enDocument318 pagesVim Ccs enUmair Qamar0% (1)
- 2 Gul Per Zte FDD Ran Roadmap v1.02 2014q1Document24 pages2 Gul Per Zte FDD Ran Roadmap v1.02 2014q1dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Next Generation NetworkDocument3 pagesNext Generation NetworkmusharafNo ratings yet
- Safe Vs LessDocument4 pagesSafe Vs Lesssaikatsakura78100% (1)
- 2.2 Core Networks & Point To Point LinksDocument32 pages2.2 Core Networks & Point To Point LinksdtizikaraNo ratings yet
- 1495456856introduction To The Uganda Oil Refinery Project October 2013Document19 pages1495456856introduction To The Uganda Oil Refinery Project October 2013dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- East IA Harmansah Stoneworlds FinalDocument36 pagesEast IA Harmansah Stoneworlds FinaldtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Proposed Road Network: LegendDocument1 pageProposed Road Network: LegenddtizikaraNo ratings yet
- 597 - Semiconductor in Equilibrium&Pn Junction1Document65 pages597 - Semiconductor in Equilibrium&Pn Junction1dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument22 pagesElectronics - Britannica Online EncyclopediadtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Equipment ManualDocument8 pagesEquipment ManualdtizikaraNo ratings yet
- N 220 PDFDocument263 pagesN 220 PDFdtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Landscape Typology As The Basis For Landscape Protection and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesLandscape Typology As The Basis For Landscape Protection and DevelopmentdtizikaraNo ratings yet
- (Architecture Ebook) Architectural Design - Multiunit HousingDocument235 pages(Architecture Ebook) Architectural Design - Multiunit HousingAndy Vs AdryNo ratings yet
- Campus Landscaping For BiodiversityDocument12 pagesCampus Landscaping For BiodiversitydtizikaraNo ratings yet
- GSM9001800 BSS&PCU Network Planning Data Configuration Specification (v3.1)Document144 pagesGSM9001800 BSS&PCU Network Planning Data Configuration Specification (v3.1)dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- (Architecture Ebook) Architectural Design - Multiunit HousingDocument235 pages(Architecture Ebook) Architectural Design - Multiunit HousingAndy Vs AdryNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group IEEE 802.16 Technical Backgrounder 2002-05-24Document4 pagesIEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group IEEE 802.16 Technical Backgrounder 2002-05-24hashemlababidiNo ratings yet
- WiMAX July 2005 1Document21 pagesWiMAX July 2005 1dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- WiMAX July 2005 1Document21 pagesWiMAX July 2005 1dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Equipment For B-MAX Hands-On 05-06-01Document5 pagesEquipment For B-MAX Hands-On 05-06-01dtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Case Study UMTSDocument16 pagesCase Study UMTSAShok Kumar JoshiNo ratings yet
- Handover management in cellular networksDocument11 pagesHandover management in cellular networksPeter KatongoleNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument20 pagesGSM Architecturemehr66tNo ratings yet
- Sjzl20094800-ZXG10 IBSC (V6.20.10) Performance Counter ReferenceDocument1,657 pagesSjzl20094800-ZXG10 IBSC (V6.20.10) Performance Counter ReferencedtizikaraNo ratings yet
- ZG ShoDocument4 pagesZG ShodtizikaraNo ratings yet
- GSM TCH Congestion & SolutionsDocument29 pagesGSM TCH Congestion & Solutionszaid_asiaNo ratings yet
- Online Automated Tuning of RRM Parameters of UMTS Networks: Uplink Load Factor ThresholdDocument4 pagesOnline Automated Tuning of RRM Parameters of UMTS Networks: Uplink Load Factor ThresholddtizikaraNo ratings yet
- ZG Compressed ModeDocument7 pagesZG Compressed ModedtizikaraNo ratings yet
- 3-1 Gul Der ZXSDR Bs8700 Product Description Ur13 v1.00 20140403Document84 pages3-1 Gul Der ZXSDR Bs8700 Product Description Ur13 v1.00 20140403dtizikara100% (1)
- Sjzl20094800-ZXG10 IBSC (V6.20.10) Performance Counter ReferenceDocument1,657 pagesSjzl20094800-ZXG10 IBSC (V6.20.10) Performance Counter ReferencedtizikaraNo ratings yet
- Period Start Time PLMN Name: RTCH - Attempts RTCH Assignment Fail Rate2Document72 pagesPeriod Start Time PLMN Name: RTCH - Attempts RTCH Assignment Fail Rate2danielNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy-Logic Based Target Classification Using DroolsDocument4 pagesFuzzy-Logic Based Target Classification Using Droolseditorijsaa100% (1)
- Digital Safety Survey ProjectDocument27 pagesDigital Safety Survey Projectrajat4kokaneNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual DSDocument52 pagesLab Manual DSGourav KhobreNo ratings yet
- Midterm Solution 2008Document8 pagesMidterm Solution 2008Sofce JovanovskaNo ratings yet
- bpb13287 PDFDocument123 pagesbpb13287 PDFLeuca Bogdan-CostinNo ratings yet
- Specification of Hi-Target V90Document4 pagesSpecification of Hi-Target V90van mbjNo ratings yet
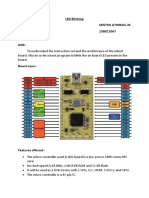
- LED Blinking ExpDocument7 pagesLED Blinking ExpSenthil AthibanNo ratings yet
- Final ThesisDocument82 pagesFinal ThesisGemma Capilitan BoocNo ratings yet
- Windows Desktop Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesWindows Desktop Interview Questions and AnswersVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Technical University, Kota Teaching & Scheme of Examination For B.Tech. (Computer Engineering)Document4 pagesRajasthan Technical University, Kota Teaching & Scheme of Examination For B.Tech. (Computer Engineering)MUKESHNo ratings yet
- AmbrogioClientManual p1-p24Document24 pagesAmbrogioClientManual p1-p24Scott CampbellNo ratings yet
- SAS Enterprise GuideDocument48 pagesSAS Enterprise GuideVidya SagarNo ratings yet
- SILABUS MATERI TRAINING Bizhub Pro 1050eDocument1 pageSILABUS MATERI TRAINING Bizhub Pro 1050einfo counterNo ratings yet
- Gonzales-2015-An E-Learning Framework-Enhancing The Student Learning StyleDocument7 pagesGonzales-2015-An E-Learning Framework-Enhancing The Student Learning StyleDENNIS GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Convertir MER 4.0 A EditableDocument11 pagesConvertir MER 4.0 A EditableHdez AhfNo ratings yet
- 009-1941-03 Savant Pro Remote X2 (REM-4000xx REM-4000xxI) Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pages009-1941-03 Savant Pro Remote X2 (REM-4000xx REM-4000xxI) Quick Reference GuideJuan PalmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Written AssessmentDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Written Assessmentselina_kollsNo ratings yet
- 2023-03-08Document24 pages2023-03-08Alberto DiazNo ratings yet
- Android Pull To Refresh Tutorial - TuteCentralDocument25 pagesAndroid Pull To Refresh Tutorial - TuteCentralAditya PabbarajuNo ratings yet
- Install Safebridge Training Client GuideDocument5 pagesInstall Safebridge Training Client GuidePrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Navigate: The Book "5 Minute Business" NOW AVAILABLE Get MyDocument11 pagesNavigate: The Book "5 Minute Business" NOW AVAILABLE Get MyMaria TwinNo ratings yet
- Bugreport RMX3231 RP1A.201005.001 2023 05 17 21 36 22 Dumpstate - Log 9681Document14 pagesBugreport RMX3231 RP1A.201005.001 2023 05 17 21 36 22 Dumpstate - Log 9681Leonardo NizamaNo ratings yet