Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acids and Bases PhET
Uploaded by
Chris GayleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acids and Bases PhET
Uploaded by
Chris GayleCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:_______________________________
Period:______
Introduction to Strong and Weak Acids and Bases PhET Lab
Introduction:
What does it mean to call an Acid Strong or Weak?
In aqueous solutions, compounds can exist as molecules (undissociated) or ions
(dissociated).
When an acid or a base exists in solution as completely dissociated ions, we
refer to that acid or base as strong.
A weak acid or base will donate ions to the solution, but will remain primarily undissociated.
Notation:
ACIDS are abbreviated HA, with the H representing the proton (H+) the acid
donates to the solution. The A is referred to as the acidic anion (A-) that is left in
solution as the proton is donated.
o HA H A
STRONG BASES are abbreviated MOH, with the OH representing the
hydroxide ion (OH-) the base donates to the solution. The M is cation (M+) that
is left in solution as the hydroxide is donated.
o
MOH M OH .
AUTONIONIZATION:
Even without any acid or base added, a very small number of water molecules will form
protons and Hydroxide Ions (OH-). The protons will then form the acid ions Hydronium
(H3O+).
Acids and Bases PhET Lab:
Go to the following website, http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/acid-base-solutions
Then click
to begin the simulation.
Procedure: Select the INTRODUCTION tab
o Begin with a strong acid and lower the pH probe into the beaker. What is the pH of this solution?
o Test this strong acid with both pH paper and the conductivity probe. What color does the pH
indicator become? Is this strong acid an electrolyte? Does current travel through this solution?
o Repeat the above tests with the weak acid, the strong base, and the weak base, and water.
Collect your observations in the table below:
Strong Acid
pH meter read
(value)
pH paper
(color)
Conductivity
(bright/dim/none)
Exists as ______
(ions/molecules)
Weak Acid
Strong Base
Weak Base
Water
Procedure: select the CUSTOM SOLUTION tab
o
o
o
Complete the table below for some strong acids and bases and weak acids and bases by adjusting the
concentration settings.
o Adjust your settings to match those from the first two columns
o Remember Protons (H+) in solution are represented by the Hydronium Ions (H3O+)
Check off Molecules in the VIEWS box, to visualize concentrations of the different molecules
Make sure Equilibrium Concentration is checked off, in the VIEWS box, to obtain the information for
the table.
Strong Acids
Strength
Initial Acid Concentration (mol/L)
[HA] (mol/L)
[A-] (mol/L)
[H+] (mol/L)
pH
[HA] (mol/L)
[A-] (mol/L)
[H+] (mol/L)
pH
[MOH] (mol/L)
[M+] (mol/L)
[OH-] (mol/L)
pH
[B] (mol/L)
[BH+] (mol/L)
[OH-] (mol/L)
pH
.010 M
.050 M
.100 M
1.00 M
Weak Acids
Strength (approximately)
Initial Acid Concentration (mol/L)
.015 M
.150 M
.015 M
.150 M
Strong Bases
Strength
Initial Acid Concentration (mol/L)
.010 M
.050 M
.100 M
1.00 M
Weak Bases
Strength (approximately)
Initial Acid Concentration (mol/L)
.015 M
.150 M
.015 M
.150 M
Name: _______________________________________
Period: _______
Acids and Bases Exit Ticket
Use your completed PhET assignment to complete the following exit ticket. Circle the best word or concept that
makes the statements about Acids and Bases true.
1. A strong acid is very concentrated / exists primarily as ions.
2. A weak base is a nonelectrolyte / weak electrolyte / strong electrolyte.
3. A strong base is a nonelectrolyte / weak electrolyte / strong electrolyte.
4. At the same concentration (Molarity) a strong acid will have a higher / lower / the same pH as a weak acid.
5. As concentration of a weak acid increases, the pH increases / decreases / remains constant.
6. As concentration of a weak base increases, the pH increases / decreases / remains constant.
7. As the concentration of a weak acid increases, the number of ions increases / decreases / remains constant.
8. As the concentration of a weak acid increases, conductivity increases / decreases / remains constant.
9. As the strength of a weak acid increases, the concentration of ions increases / decreases, while the
concentration of molecules increases / decreases
10. As the strength of a weak acid increases, the conductivity increases / decreases / remains constant.
Name: _______________________________________
Period: _______
Acids and Bases Exit Ticket
Use your completed PhET assignment to complete the following exit ticket. Circle the best word or concept that
makes the statements about Acids and Bases true.
11. A strong acid is very concentrated / exists primarily as ions.
12. A weak base is a nonelectrolyte / weak electrolyte / strong electrolyte.
13. A strong base is a nonelectrolyte / weak electrolyte / strong electrolyte.
14. At the same concentration (Molarity) a strong acid will have a higher / lower / the same pH as a weak acid.
15. As concentration of a weak acid increases, the pH increases / decreases / remains constant.
16. As concentration of a weak base increases, the pH increases / decreases / remains constant.
17. As the concentration of a weak acid increases, the number of ions increases / decreases / remains constant.
18. As the concentration of a weak acid increases, conductivity increases / decreases / remains constant.
19. As the strength of a weak acid increases, the concentration of ions increases / decreases, while the
concentration of molecules increases / decreases
20. As the strength of a weak acid increases, the conductivity increases / decreases / remains constant.
You might also like
- F W N C: Ormula Riting and Aming of OmpoundsDocument4 pagesF W N C: Ormula Riting and Aming of OmpoundsrenNo ratings yet
- Test BanksDocument21 pagesTest Banksalex_flutistNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibria and Buffer CalculationsDocument20 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria and Buffer CalculationsDi Vlad PeÑa PrietoNo ratings yet
- AP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizDocument8 pagesAP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizHussain MerchantNo ratings yet
- MoleDocument2 pagesMoleMario GonzálezNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument16 pagesProteinRosnadia RosliNo ratings yet
- Chem 2105 Topic 11 Titrations in Analytical ChemistryDocument40 pagesChem 2105 Topic 11 Titrations in Analytical ChemistryDanica Rose ZapanzaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - ReviewDocument5 pagesWorksheet - Reviewapi-270403367No ratings yet
- Limiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetDocument1 pageLimiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetFandy ArdyNo ratings yet
- GocDocument108 pagesGocAtul VermaNo ratings yet
- Naming Common Chemical CompoundsDocument7 pagesNaming Common Chemical CompoundsSnorlax Magno100% (1)
- Redox ReactionsDocument4 pagesRedox Reactionsmahika gaurNo ratings yet
- BIO 11 LAB REVIEW: MICROSCOPY, CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSDocument6 pagesBIO 11 LAB REVIEW: MICROSCOPY, CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSJewelle Anne Estanilla LimenNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Buffer: Experiment No: 1 DateDocument5 pagesPreparation of Buffer: Experiment No: 1 DatePraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument4 pagesExperiment 3: Le Chatelier's PrinciplespaghetticurlersNo ratings yet
- Buffer and Buffer Capacity Activity ExplainedDocument2 pagesBuffer and Buffer Capacity Activity ExplainedValenzuela Allene GraceNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument4 pagesStoichiometryCourtney JenningsNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Acids and BasesDocument25 pagesTopic 7 Acids and BasesadamskbdNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 2Document42 pagesChapter15 2Jonathan HuNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument50 pagesAnalytical ChemistryNguyễn Trịnh Anh MinhNo ratings yet
- Chem PDFDocument539 pagesChem PDFArmghan Saeed100% (3)
- Chap 04 - Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry 08Document11 pagesChap 04 - Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry 08Rashid KanetsaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFDocument55 pagesElectrochemistry 494 PDFHarsh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Final Report Chem - Acids, Bases, & SaltsDocument7 pagesFinal Report Chem - Acids, Bases, & SaltsCharmaine Uri0% (1)
- CH 13 Titrations in Analytical ChemistryDocument14 pagesCH 13 Titrations in Analytical ChemistryHenrique CostaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument16 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetAgot Barbero NorillaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - MCQs Test - 1Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - MCQs Test - 1Prasant Kumar100% (1)
- Test Gas LawsDocument5 pagesTest Gas LawsCenando BodanioNo ratings yet
- AP Unit9 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAP Unit9 Worksheet AnswersAAVANINo ratings yet
- 7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyDocument8 pages7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyXazerco LaxNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Nernst Equation PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Nernst Equation PDFLedd SleddNo ratings yet
- Caffeine Extraction 1 PDFDocument25 pagesCaffeine Extraction 1 PDFShanay ShahNo ratings yet
- 09 - Flinn - Stoichiometric Ratio of A ReactionDocument8 pages09 - Flinn - Stoichiometric Ratio of A ReactionDerek Hammons100% (1)
- ACID Base Equil P Test MCDocument5 pagesACID Base Equil P Test MCctyre34No ratings yet
- Calculations in Chemistry - CH. 13-14Document64 pagesCalculations in Chemistry - CH. 13-14Carlos DomaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesUnit 5 Answer Keyapi-273525891No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Chapter22Document8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Chapter22RangikaNo ratings yet
- A) Iron's Molar Mass Must Be Known To Calculate The Moles of Iron in SolutionDocument5 pagesA) Iron's Molar Mass Must Be Known To Calculate The Moles of Iron in SolutionBla NkNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsNajmusawwa Aulia RahmahNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and The Nernst EquationDocument53 pagesElectrochemistry and The Nernst EquationMaha RajNo ratings yet
- 1e Aldehyde & KetoneDocument48 pages1e Aldehyde & KetoneJonathan Wyatt100% (1)
- Worksheet For Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesWorksheet For Inorganic ChemistryVincent FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- Understanding PH and BufferDocument2 pagesUnderstanding PH and BufferRyan Carlo Conde100% (1)
- OsmosisDocument2 pagesOsmosisapi-3420108090% (1)
- Day 2 - Introduction To Stoichiometry Guided Notes AssignmentDocument15 pagesDay 2 - Introduction To Stoichiometry Guided Notes AssignmentDaveNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Concepts (Quiz With Answers)Document12 pagesAcid Base Concepts (Quiz With Answers)heylinssNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations PDFDocument4 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations PDFLeroyJonesNo ratings yet
- CHM 1045L Lab Manual Fall 2016Document61 pagesCHM 1045L Lab Manual Fall 2016Greg K0% (1)
- Lab Manual SK 2020Document60 pagesLab Manual SK 2020Nrl MysrhNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Homework - Bruno BiologyDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Homework - Bruno Biologyapi-2769442650% (1)
- 11 Chemistry Redox Reactions Test Paper 01Document1 page11 Chemistry Redox Reactions Test Paper 01mohapatramugdha99No ratings yet
- Acid Base Titration AnalysisDocument8 pagesAcid Base Titration Analysispankaj111No ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Syllabus - ICDocument15 pagesChem 26.1 Syllabus - ICDoom RefugeNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric and Spectrophotometric Determination of Phosphoric Acid Content in Some Beverages P.I. Utange, R.A. Wuana and T.V. AkpogholDocument20 pagesPotentiometric and Spectrophotometric Determination of Phosphoric Acid Content in Some Beverages P.I. Utange, R.A. Wuana and T.V. Akpogholanon_4195199No ratings yet
- Multiple choice questions on chemical equilibriumDocument14 pagesMultiple choice questions on chemical equilibriumMutasimNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument95 pagesAnalytical ChemistryHugo WNo ratings yet
- C - Done at School - To Move Home Strong and Weak Acids and Bases Phet LabDocument2 pagesC - Done at School - To Move Home Strong and Weak Acids and Bases Phet Labapi-262304087No ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document4 pagesChapter 15Ayesha MohamudNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Unit 8 - Acids and Bases Study GuideDocument6 pagesIB Chemistry Unit 8 - Acids and Bases Study GuideHamzah JoharNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Titration: Ha + H O H O + A (Acid) B O BH + Oh (Base)Document6 pagesAcid Base Titration: Ha + H O H O + A (Acid) B O BH + Oh (Base)Ben AbellaNo ratings yet
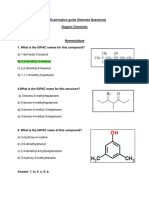
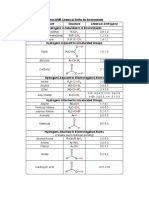
- Proton NMR Chemical Shifts by Functional GroupDocument1 pageProton NMR Chemical Shifts by Functional GroupChris GayleNo ratings yet
- 08 Early 1800s Political CartoonsDocument1 page08 Early 1800s Political CartoonsChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Proton NMR Chemical Shifts by Functional GroupDocument1 pageProton NMR Chemical Shifts by Functional GroupChris GayleNo ratings yet
- LabSafetyEssentialsDocument8 pagesLabSafetyEssentialsChris GayleNo ratings yet
- 6 Stoichiometry ProblemsDocument2 pages6 Stoichiometry ProblemsChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Han and Roman DBQDocument3 pagesHan and Roman DBQChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument1 pageAnswer KeyChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Paying For Higher Education PPT 2.3.5.G1Document38 pagesPaying For Higher Education PPT 2.3.5.G1Chris GayleNo ratings yet
- The Cell Membrane and OrganellesDocument16 pagesThe Cell Membrane and OrganellesChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Feed The Cows Homework AP PhysicsDocument1 pageFeed The Cows Homework AP PhysicsChris GayleNo ratings yet
- DBQ Essay MuslimsDocument1 pageDBQ Essay MuslimsChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 Empirical Formula of Silver OxideDocument6 pagesLab 12 Empirical Formula of Silver OxideChris GayleNo ratings yet
- 2015 Common 11th Grade SyllabusDocument4 pages2015 Common 11th Grade SyllabusChris GayleNo ratings yet
- AP World ReviewDocument10 pagesAP World ReviewChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Cell Quiz: Eukaryotic Organelles & StructuresDocument7 pagesCell Quiz: Eukaryotic Organelles & StructuresChris GayleNo ratings yet
- ViscosityDocument2 pagesViscosityChris GayleNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Study GuideDocument5 pages5.1 Study GuideChris GayleNo ratings yet
- My Personal Wellness Plan GoalsDocument8 pagesMy Personal Wellness Plan GoalsChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Contextualization Activity Khalid ChaudhariDocument2 pagesContextualization Activity Khalid ChaudhariChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-4 ScoresDocument2 pagesLesson 1-4 ScoresChris GayleNo ratings yet
- ChemsitruDocument1 pageChemsitruChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Study GuideDocument2 pagesAlgebra 2 Study GuideChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Powerpoint - Student VersionDocument141 pagesChapter 16 Powerpoint - Student Versionroshni rNo ratings yet
- Conductivity Guide enDocument59 pagesConductivity Guide enehagar60100% (1)
- PH and Titratable Acidity: Catrin TylDocument18 pagesPH and Titratable Acidity: Catrin TyladmsNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument13 pagesAcid-Base TitrationSham WawNo ratings yet
- Eq WTDocument11 pagesEq WTjames johnNo ratings yet
- CH 018Document23 pagesCH 018phdf5s2p5gNo ratings yet
- Non Aqueous - Lecture-1-1Document51 pagesNon Aqueous - Lecture-1-1Sayed AlamNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base and RedoxDocument53 pagesAcid and Base and RedoxH M AwaisNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Jirah GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesAnalytical ChemistryChristian FloresNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFDocument118 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFSayan Dutta100% (1)
- SAT ABS Bronsted LowryDocument7 pagesSAT ABS Bronsted LowryCatherine Galano PradoNo ratings yet
- Principles of acid-base titrations and buffersDocument10 pagesPrinciples of acid-base titrations and buffersAlmira Bhel MorquianosNo ratings yet
- Teori Asam Basa (B.inggris)Document31 pagesTeori Asam Basa (B.inggris)Lukman Al AminNo ratings yet
- KIMIA REPORT 4 Mahira t6Document12 pagesKIMIA REPORT 4 Mahira t6Md IjazNo ratings yet
- Salt, Hydrolysis of SaltsDocument13 pagesSalt, Hydrolysis of Saltslianchen2511100% (1)
- Ch. 6: Chemical Equilibrium: Updated Oct. 5, 2011: Minor Fix On Slide 11, New Slides 31-42Document42 pagesCh. 6: Chemical Equilibrium: Updated Oct. 5, 2011: Minor Fix On Slide 11, New Slides 31-42Ankit RawatNo ratings yet
- PharChem Lecture 3 - ACIDS and BASES (Pharmaceutical Aids and Necessities)Document65 pagesPharChem Lecture 3 - ACIDS and BASES (Pharmaceutical Aids and Necessities)Gamotkoto PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibria Questions PDFDocument4 pagesIonic Equilibria Questions PDFdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- A. Chapter 3 Lesson 1-Unique Properties of WaterDocument13 pagesA. Chapter 3 Lesson 1-Unique Properties of WaterCHARINA SATONo ratings yet
- Ionic+Equilibrium VEDANTUDocument295 pagesIonic+Equilibrium VEDANTUKing GokulNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument28 pagesAcid BaseDwi Fitriyana PutriNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1412. Chapter 16. Acids and Bases - Homework - SDocument13 pagesCHEM 1412. Chapter 16. Acids and Bases - Homework - STrisha Anne SyNo ratings yet
- 2 Acid Base EquilibriumDocument30 pages2 Acid Base Equilibriumu3537671No ratings yet
- 9.3 - Section 3Document23 pages9.3 - Section 3Joseph WongNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report #1 - Basic Principles in BiochemistryDocument8 pagesLaboratory Report #1 - Basic Principles in BiochemistryLala HalaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document72 pagesChap 2miguel0angel0ramos-1100% (6)
- Non Aqeuous TitrationDocument7 pagesNon Aqeuous Titrationsurabhi tadeNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Indicators Spectrophotometric Ka LabDocument6 pagesAcid-Base Indicators Spectrophotometric Ka Labmuskaan0% (2)