Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Two Component Water System
Uploaded by
slchemCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTwo Component Water System
Uploaded by
slchemPHASE RULE
TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM
THEORY
Two Component System ( Lead Silver
System )
This system has two component & four phases these are i)
Solid Silver, ii) Solid lead, iii) Solution of molten silver & lead & iv)
Vapour.
But the B.P. of Ag & Pb is completely high the vapour phase is
completely absent.
Since the press has nearly no effect on equilibrium. so the system
can be convinently represented by temp conc diagram.
Such solid liquid system with the gas phase is absent is called
condensed system
The experimental measurements of temp & conc in condensed
system are usually carried at under atm press.
Since the degree of freedom is such system is reduced by one,
therefore, it can be also termed as reduced phase rule &
represented by the equation.
1
PHASE RULE
TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM
THEORY
F=CP+1
It is more convenient to apply to solid liquid two components
condensed system. e.g. Pb Sb, Ag Pb, Zn Cd.
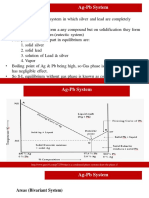
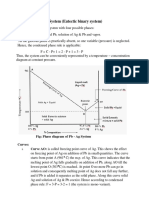
The complete phase diagram of system Silver Lead.
Diagram
961 A
F= 2P+ 1
= 3 2
= 1
Univaliant
Fr
ee
zi n
g
F= 2P+ 1
= 3 2
= 1
Liquid
cu
rv
e
Solid Ag
+ Liquid
Freezing
curve of Pb
Univariant
of
Ag
Soln get
saturated
Wr + Pb
B 327
Solid Pb +
n
Sol (Pb + Ag)
TempC
303
0
Solid electric mixture
+ Solid Ag
100% Pb
0% Ag
97.4% Pb
2.6% Ag
% Composition
% Composition
2
Solid
electric
mixture
+ Solid Pb
100% Pb
0% Ag
F= 2P+ 1
= 3 3
= 0
PHASE RULE
TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM
THEORY
From fig following silent features are observed:
i)
The Curve OA (Freezing Curve of Ag)
ii)
The Curve BO ( Freezing Curve of Pb)
iii)
The eutectic Point O
(i)
a)
Curve OA Freezing Curve of Ag
It shows the effect on freezing point of Ag on addition of
Pb in small quantities.
b)
The curve starts from A (961oC) the M.P. of Ag, where
pure Ag coexist as solid & liquid
(Vapour being
neglected).
c)
This curve indicates that the melting point of Ag fall
gradually on adding Pb, along AO, till the lowest point O
(303oC) is reached where solution gets saturated with
respect to lead. At O more Pb can go in solution &
consequently, the M.P. does not fall any further & if any
Pb is added it separates as the solid phase.
Along this curve, solid Ag & Solution (Vapour being negligible)
Coexist & hence, according to reduced phase rule equation
3
PHASE RULE
TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM
THEORY
E= 2 P + 1 i.e. F = 3 P = 3 2 = 1
i.e. system is univariant. The point O (303oC) Corresponds to a
fixed composition of 2.6% Ag & 91.4% Pb & is known as eutectic
composition.
On cooling the whole mass crystallizes out as such.
ii) Curve BO Freeing curve of Pb
i)
It represents the effect on freezing point of Pb on
gradual addition of small amount of Ag to it. Point B is
the M.P. of pure Pb-32.
ii)
Along BO, the M.P. Gradually falls on the addition of Ag
till lowest point O is reached.
iii)
At this point solution gets saturated with respect to Ag &
M.P. of Pb does not fall any more.
iv)
On cooling whole mass crystallizes out.
The system is univariant like AO.
PHASE RULE
TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM
THEORY
iii) Point O Eutectic Point
The two curve AO + BO meet at O. Where three phases
solid Ag, Solid- Pb & their solution Coexist & according to
condensed phase rule. The pt
of O represents a fixed
composition of Ag 2.6%, Pb- 97.4% is called eutectic
composition.
At eutectic comp. temp. remains constant until the whole of the
melt solidifies in block to become solid of eutectic composition.
However, further cooling results in the simultaneous crystallization
of a mixture of Ag & Pb in relative amounts corresponding to
eutectic point O.
Below temp line there are two regions
eutectic solid + solid Ag in crystalline - stable
eutectic + solid Pb in crystalline stable.
It represent solution of Pb Ag sample of Pb containing less than
2.6% Ag is taken, at an arbitrary pt on curve. On following mass
cool temp gradually falls without any charge in composition till this
point reached to curve BO (point may be P)
5
PHASE RULE
TWO COMPONENT SYSTEM
THEORY
On lowering the temp lead begins to separates out & the
composition varies along pb till point O is reached.
On cooling whole mass solidifies in block.
Applications
i)
Used in pattinsons process of desilverization of Pb.
ii)
If Pb is less than 2.6 Pb will separate out from Solution.
iii)
If Pb is more than 2.6 Ag will separate out from solution.
You might also like
- Stereochemistry MSCDocument29 pagesStereochemistry MSCBapu Thorat50% (2)
- Theories of ChromatographyDocument13 pagesTheories of ChromatographyZarish Iftikhar100% (1)
- Phase EquilibriaDocument19 pagesPhase EquilibriaAlexis PulhinNo ratings yet
- Phase EquilibriumDocument20 pagesPhase EquilibriumjacNo ratings yet
- Partition of SetsDocument6 pagesPartition of Setsslchem0% (1)
- Electrochemical Cell PotentiometryDocument46 pagesElectrochemical Cell PotentiometryMohammad Sabir HussainNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram of the Lead-Silver SystemDocument3 pagesPhase Diagram of the Lead-Silver SystemVora AyushNo ratings yet
- Two Component System (Pb-Ag) and (ZN-MG) PDFDocument12 pagesTwo Component System (Pb-Ag) and (ZN-MG) PDFManiNo ratings yet
- One Compenent Water SystemDocument7 pagesOne Compenent Water Systemslchem75% (4)
- Isoelectric Point of LeguminDocument5 pagesIsoelectric Point of Legumin门门No ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Phase Equilibria 4 PDF FreeDocument77 pagesChapter 06 Phase Equilibria 4 PDF FreeGabriel SilvaNo ratings yet
- Phase Rule Water & CO2systemsDocument9 pagesPhase Rule Water & CO2systemsAtul GautamNo ratings yet
- Unit-3: Phase EquilibriaDocument94 pagesUnit-3: Phase EquilibriaNiboli K ZhimomiNo ratings yet
- SCH 302 Axial ChiralityDocument22 pagesSCH 302 Axial ChiralityArangaNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium Diagram ExplainedDocument20 pagesPhase Equilibrium Diagram ExplainedGlesie Devara CabacangNo ratings yet
- The Sulphur SystemDocument16 pagesThe Sulphur Systemhoney2102100% (1)
- GC-AAS Analysis of ElementsDocument9 pagesGC-AAS Analysis of ElementsSubhasish DashNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Non-Ideal SolutionsDocument3 pagesIdeal and Non-Ideal SolutionsJamshaid AliNo ratings yet
- Phase Rule: 3 Component SystemsDocument5 pagesPhase Rule: 3 Component SystemsDarshan ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 NitrationDocument77 pagesLecture 2 Nitrationzeeshan100% (1)
- 2D NMRDocument10 pages2D NMRHariprasad Reddy100% (1)
- 3820 Lecture Chapter - 3 - Part1 - 2004 PDFDocument15 pages3820 Lecture Chapter - 3 - Part1 - 2004 PDFPhuongUblMyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Organic Chemistry-I (MPC 102T) Unit-I: Rearrangement ReactionDocument5 pagesAdvanced Organic Chemistry-I (MPC 102T) Unit-I: Rearrangement Reactionumme sultana LimaNo ratings yet
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)Document9 pagesDifferential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)DanielNo ratings yet
- Assay of Sodium BenzoateDocument6 pagesAssay of Sodium BenzoateMeziane BouktitNo ratings yet
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction PrinciplesDocument34 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction PrinciplescocoayisaNo ratings yet
- Smt. Kishoritai Bhoyar College of Pharmacy, New Kamptee.: BY Guided by Bhavik S.Kotak Dr. K.R.GuptaDocument33 pagesSmt. Kishoritai Bhoyar College of Pharmacy, New Kamptee.: BY Guided by Bhavik S.Kotak Dr. K.R.Guptadil_009100% (3)
- Chapter 15 Parallels Between Main Group and Organometallic ChemistryDocument46 pagesChapter 15 Parallels Between Main Group and Organometallic ChemistryTarang BhatiNo ratings yet
- SALCsDocument5 pagesSALCsOscar FilippeschiNo ratings yet
- APPROVAL SHEETDocument26 pagesAPPROVAL SHEETRafidah AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmaceutics-Ii: B. Pharm (IV Sem) Physical Pharmacy-II BP 403T Unit - III Coarse DispersionsDocument7 pagesPhysical Pharmaceutics-Ii: B. Pharm (IV Sem) Physical Pharmacy-II BP 403T Unit - III Coarse Dispersionsdipti_sriv0% (1)
- MetalloporphyrinsDocument5 pagesMetalloporphyrinsVenu KagneNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Operations and Point GroupDocument13 pagesSymmetry Operations and Point GroupRahul AroraNo ratings yet
- Solid SolutionsDocument42 pagesSolid SolutionsrkaruppasamyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Property RelationsDocument24 pagesThermodynamic Property RelationsRichard Jess ChanNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument6 pagesLab ManualArun Kumar RathoreNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of Coordination ComplexesDocument14 pagesMagnetic Properties of Coordination ComplexesbnkjayaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document5 pagesLab 2tariqwaece100% (1)
- Distribution of Acetic Acid Between Two Immiscible Solution by Simple Simple Methods PapooDocument11 pagesDistribution of Acetic Acid Between Two Immiscible Solution by Simple Simple Methods PapooHasnain SaifiNo ratings yet
- 30 Important MCQs on Pharmaceutical Organic ChemistryDocument32 pages30 Important MCQs on Pharmaceutical Organic ChemistryVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Shapiro Reaction and BamfordDocument13 pagesShapiro Reaction and BamfordharishNo ratings yet
- Cram's RuleDocument13 pagesCram's RulePablo Romo ValdesNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry 10th Edition by WhittenDocument8 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry 10th Edition by Whittena160741701100% (2)
- B. Pharm 3rd Semester Previous Year Question PaperDocument20 pagesB. Pharm 3rd Semester Previous Year Question PaperAkanksha MadhaleNo ratings yet
- Isomerism IN Compounds: CoordinationDocument19 pagesIsomerism IN Compounds: CoordinationEmilyNo ratings yet
- XRD Particle Size PDFDocument2 pagesXRD Particle Size PDFgizachew100% (1)
- Three-Component SystemDocument18 pagesThree-Component SystemThiban KumarNo ratings yet
- Phase EquilibriaDocument11 pagesPhase EquilibriaNandhanNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument7 pagesAnalytical ChemistrySamra ButtNo ratings yet
- Electochemistry PDFDocument29 pagesElectochemistry PDFAnshu KarmacharyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 Diffusion IN SOLIDSDocument72 pagesLecture2 Diffusion IN SOLIDSidownloadbooks3133No ratings yet
- HybridizationDocument9 pagesHybridizationtan jigNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument13 pagesSample Lab ReportJellyShapes0% (1)
- PH and PH MeterDocument9 pagesPH and PH Metermanimozhi0% (1)
- Conductometric Titrations: Hasan Qayyum Chohan, Reg. No. 2009-CH-204 University of Engineering & Technology Lahore (KSK)Document9 pagesConductometric Titrations: Hasan Qayyum Chohan, Reg. No. 2009-CH-204 University of Engineering & Technology Lahore (KSK)cutetamtam101No ratings yet
- PB Ag SystemDocument2 pagesPB Ag SystemAtul Gautam100% (2)
- Lead Silver System: No. of Components: 2Document4 pagesLead Silver System: No. of Components: 2MadhavanIceNo ratings yet
- Two Component System (Ag-Pb)Document11 pagesTwo Component System (Ag-Pb)freak264530No ratings yet
- PHASE RULE: IntroductionDocument48 pagesPHASE RULE: Introductiontenguria samriddhNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Session 3Document31 pagesModule 2 - Session 3DUE DATENo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument21 pagesPhase DiagramsJnrNo ratings yet
- Solved PartitionsDocument7 pagesSolved PartitionsslchemNo ratings yet
- Operations On Sets and Properties of SetsDocument10 pagesOperations On Sets and Properties of SetsslchemNo ratings yet
- Calorific ValuesDocument3 pagesCalorific ValuesslchemNo ratings yet
- Solved Laws of Set TheoryDocument3 pagesSolved Laws of Set TheoryslchemNo ratings yet
- Compounding of PlasticsDocument3 pagesCompounding of PlasticsslchemNo ratings yet
- Solved Opearations and Properties of SetsDocument4 pagesSolved Opearations and Properties of SetsslchemNo ratings yet
- SolvedDocument4 pagesSolvedslchemNo ratings yet
- Laws of Set TheoryDocument4 pagesLaws of Set TheoryslchemNo ratings yet
- Sets and Operations On SetsDocument4 pagesSets and Operations On SetsslchemNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problems-1.2 PDFDocument1 pageUnsolved Problems-1.2 PDFslchemNo ratings yet
- Natural Rubber and VulcanisationDocument3 pagesNatural Rubber and Vulcanisationslchem100% (1)
- Polymers Theory: Polymer - Poly (Many) + Miros (Parts)Document3 pagesPolymers Theory: Polymer - Poly (Many) + Miros (Parts)slchemNo ratings yet
- SolvedDocument3 pagesSolvedslchemNo ratings yet
- Synthetic RubberDocument3 pagesSynthetic RubberslchemNo ratings yet
- Natural Rubber and VulcanisationDocument3 pagesNatural Rubber and Vulcanisationslchem100% (1)
- Moulding of PlasticsDocument4 pagesMoulding of PlasticsslchemNo ratings yet
- Classification of LubricantsDocument12 pagesClassification of Lubricantsslchem100% (5)
- Melting and Glass Transition PhenomenaDocument3 pagesMelting and Glass Transition PhenomenaslchemNo ratings yet
- Introduction and LubricationDocument9 pagesIntroduction and LubricationslchemNo ratings yet
- Additives and Selection of LubricantDocument5 pagesAdditives and Selection of LubricantslchemNo ratings yet
- Zeolite or Permutit Process - Zeolite: Na ZeDocument3 pagesZeolite or Permutit Process - Zeolite: Na ZeslchemNo ratings yet
- Comparison and ClassificationDocument4 pagesComparison and ClassificationslchemNo ratings yet
- Two Component Water SystemDocument6 pagesTwo Component Water SystemslchemNo ratings yet
- EdtaDocument6 pagesEdtaslchemNo ratings yet