Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Plan For Year 5 Science
Uploaded by
Helyza HayesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Plan For Year 5 Science
Uploaded by
Helyza HayesCopyright:
Available Formats
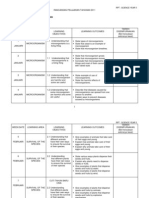
YEARLY PLAN SCIENCE
YEAR 5 (2010)
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
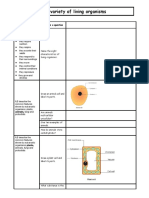
INVESTIGATING LIVING THINGS
1 1. Microorgani 1.1Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(4-8 JANUARY) sm microorganism is a 1.1.1 State types of microorganisms.
living thing. 1.1.2 State that yeast is an example of microorganism.
2 PROGRAM MAJU DIRI
(11-15 (AFTER RECESS)
JANUARY)
2 1.1.3 State that microorganism breathes.
(11-15JANUARY)
3 1.1.4 State that microorganism grows.
(18-22 1.1.5 State that microorganism moves.
JANUARY) 1.1.6 Conclude that microorganisms are living things and
most of them cannot be seen with naked eyes.
4 1.1State examples of use At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(25-29 of microorganisms. 1 State examples of use of microorganisms.
JANUARY) 1.2.2 State the harmful effects of microorganisms.
1.2.3 Describe that diseases caused by
microorganisms can spread
from one person to another.
1.2.4 Explain ways to prevent diseases caused by
microorganisms.
5 1. Survival of 1.1Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(1-5 FEBRUARY) the species different animals have 1.1.1 Give examples of animals that take care of their
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
their own ways to eggs and young.
ensure the survival of 2.1.2 Explain how animals take care of their eggs and
their species. young.
1.1.2 Explain why animals take care of their eggs and
young.
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
6 1.2Understanding that 1.2.1 State various ways plants disperse their seeds and
(8-11 different plants have fruits.
their own ways to 1.2.2 Explain why plants need to disperse seeds or fruits.
FEBRUARY)
ensure the 1.2.3 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and
survival of their fruits by water.
species. 1.2.4 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and
fruits by wind.
1.2.5 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and
fruits by animals.
1.2.6 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds by
explosive mechanism.
1.2.7 Relate characteristics of seeds and fruits to the
ways they are dispersed.
1.3 Realising the 1.3.1 predict what will happen if some species of animals
importance of survival or plants do not survive.
of the species.
7 3 Food chain 3.1Understanding food 3.1.1 Identify animals and the food they eat.
(15-19 and food chains. 3.1.2 Classify animals into herbivore, carnivore and
FEBRUARY) webs. omnivore.
3.1.3 Construct food chain.
3.1.4 Identify producer.
3.1.5 Identify consumer.
15 & 16 FEBRUARY
CHINESE NEW YEAR
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
8 3.2Synthesizing food 3.2.1 Construct a food web.
(22-26 chains to construct 3.2.2 Construct food webs of different habitats.
FEBRUARY) food web. 3.2.3 Predict what will happen if there is a change in
population of a certain species in a food web.
3.2.4 Explain what will happen to certain species of
animals if they eat only one type of food.
24 FEBRUARY
CROSS COUNTRY
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
9 1. Microorgani Answering technique for At the end of this lesson pupils should be able to:
(1-5 MARCH) sm section B Answering Science Process Skills questions:
2. Survival Of
i. Observing
The Species
ii. Making inferences
3. Food Chain
iii. Controlling variables
and Food
iv. Making hypothesis
Webs
v. Interpreting data
10
(8-12 MARCH) UJIAN PENGESANAN PERTAMA
11
(15-19 MARCH) MID TERM 1 HOLIDAYS
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGY
12 1. Energy 1.1Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(22-26 MARCH) uses of energy. 1.1.1 Explain why energy is needed.
1.1.2 Give examples where and when energy is used.
1.1.3 State various sources of energy.
13 1.2Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(29 MARCH – energy can be 1.2.1 State the various forms of energy.
2 APRIL) transformed from one 1.2.2 State that energy can be transformed.
form to another. 1.2.3 Give examples of appliances that make use of
energy transformation.
14 1.3Understanding At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(5-9 APRIL) renewable and non- 1.3.1 State what renewable energy is.
renewable energy. 1.3.2 State what non-renewable energy is.
1.3.3 List renewable energy resources.
1.3.4 List non-renewable energy resources.
15 At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(12-16 APRIL) 1.3.5 Explain why we need to use energy wisely.
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
1.3.6 Explain why renewable energy is better than non-
renewable energy.
1.3.7 Give examples on how to save energy.
1.3.8 Practise saving energy.
16 2. Electricity 2.1Knowing the sources of At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
(19-23 APRIL) electricity. 2.1.1 State the sources of electricity.
2.2Understanding a series At the end of this lesson pupils should be able to:
circuit and parallel 2.2.1 Identify the symbols of various components in a
circuit. simple electric circuit.
2.2.2 Draw circuit diagrams.
2.2.3 Identify the difference in the arrangement of bulbs
in series and
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
Parallel circuits.
17 At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(26-30 APRIL) 2.2.4 Build a series circuit.
2.2.5 Build a parallel circuit.
2.2.6 Compare the brightness of the bulbs in a series and
a parallel circuit.
2.2.7 Compare the effect on the bulbs when various
switches in a series circuit and a parallel circuit are
off.
18 2.3Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(3-7 MAY) safety precautions to 2.3.1 Describe the danger of mishandling electrical
be taken when appliances.
handling electrical 2.3.2 Explain the safety precautions to be taken when
appliances. using electrical appliances.
3. Light 3.1Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
light travels in a 3.1.1 State that light travels in a straight line.
straight line. 3.1.2 Give examples to verify that light travels in a
straight line.
19 At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(10-14 MAY) 3.1.3 Describe how shadow is formed.
3.1.4 Design a fair test to find out what cause the size of
a shadow to change by deciding what to keep the
same, what to change and what to observe.
3.1.5 Design a fair test to find out what factors cause the
shape of a shadow to change by deciding what to
keep the same, what to change and what to
observe.
20 3.2 Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(17-21 MAY) light can be reflected. 3.2.1 State that light can be reflected.
3.2.2 Draw ray diagrams to show reflection of light.
3.2.3 Give examples of uses of reflection of light in
everyday life.
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
21 REVISION FOR MID YEAR EXAM
(24-28 MAY) 28 MAY : WESAK DAY
22
(31 MAY – 4 MID YEAR EXAMINATION
JUNE)
23 & 24
MID YEAR HOLIDAYS
(5 -20 JUNE)
25 3 Heat 3.1Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(21-25 JUNE) temperature is 3.1.1 State that when a substance gains heat it will
indicator of degree of become warmer.
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
hotness. 3.1.2 State that when a substance loses heat it will
become cooler.
3.1.3 Measure temperature using the correct technique
state the metric unit for temperature.
3.1.4 State the metric unit for temperature.
26 At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(28 JUNE – 2 3.1.5 State that temperature of an object or material
JULY) increases as it gains heat.
3.1.6 State that temperature of an object or material
decreases as it loses heat.
3.1.7 Conclude that the temperature is an indicator to
measure hotness.
27 3.2Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(5-9 JULY) effects of heat on 3.2.1 State that matter expands when heated.
matter. 3.2.2 State that matter contracts when cooled.
3.2.3 Give examples of the application of the principle of
expansion and contraction in everyday life.
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
INVESTIGATING MATERIALS
28 1. States of 1.1 Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(12-16 JULY) Matter. matter exist in the 1.1.1 Classify objects and materials into three states of
form of solid, liquid matter.
and gas. 1.1.2 State the properties of solid.
At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
1.1.3 State the properties of liquid.
1.1.4 State that some liquids flow faster than others.
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
1.1.5 State the properties of gas.
29 1.2Understanding that At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(19-23 JULY) matter can change 1.2.1 State that water can change its state.
from one state to 1.2.2 Conclude that water can exist in any of the three
another. states of matter.
1.2.3 Identify the processes involved when a matter
changes from one state to another.
1.2.4 Identify factors that affect the rate of evaporation of
water.
30 REVISION FOR UJIAN PENGESANAN KEDUA
(26-30 JULY)
31
UJIAN PENGESANAN KEDUA
(2-6 AUGUST)
32 1.3Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(9-13 AUGUST) water cycle. 1.3.1 Describe how clouds are formed.
1.3.2 Describe how rain is formed.
1.3.3 Explain how water is circulated in the environment.
1.3.4 Explain the importance of water cycle.
1.4Appreciating the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
importance of water 1.4.1 Give reasons why we need to keep our water
resources. resources clean.
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
1.4.2 Describe ways to keep our water resources clean.
33 1 Acid and 1.1 Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(16-20 AUGUST) Alkali. properties of acidic, 1.1.1 Identify acidic, alkaline and neutral substances
alkaline and neutral using litmus paper.
substances. 1.1.2 Identify the taste of acidic and alkaline food.
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
1.1.3 Conclude the properties of acidic alkaline and
neutral substances.
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
INVESTIGATING THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE
34 1 Constellatio 1.1 Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(23-27 n. constellation. 1.1.1 State what constellation is.
AUGUST) 1.1.2 Identify constellations.
1.1.3 State the importance of constellations.
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
27 AUGUST
NUZUL AL-QURAN
35 1 The Earth, 1.1Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(30 AUGUST – The Moon movements of the 1.1.1 State that the Earth rotates on its axis.
3 SEPTEMBER) and The Earth, the Moon and 1.1.2 State that the Earth rotates and at the same time
Sun. the Sun. moves round the Sun.
1.1.3 State that the Moon rotates on its axis.
1.1.4 State that the Moon rotates and at the same time
moves round the Earth.
1.1.5 State that the Moon and the Earth move round the
Sun at the same time.
31 AUGUST
NATIONAL DAY
36 MID TERM 2 HOLIDAYS
(4-12
(10 & 11 SEPTEMBER : HARI RAYA AIDILFITRI)
SEPTEMBER)
37 At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(13-17 1.1.6 Describe the changes in length and position of the
SEPTEMBER) shadow throughout the day.
1.1.7 Conclude the Earth rotates on its axis from west to
east.
16 SEPTEMBER
MALAYSIA DAY
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
38 1.2 Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(20-24 occurrence of day and 1.2.1 State that it is day time for the part of the Earth
SEPTEMBER) night. facing the Sun.
1.2.2 State it is night time or the part of the Earth facing
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
away from the Sun.
1.2.3 Explain that day and night occur due to the rotation
of the earth on its axis.
39 1.3Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(27 SEPTEMBER phases of the Moon. 1.3.1 State that the Moon does not emit light.
– 1.3.2 Explain that the Moon appears bright when it
1 OCTOBER) reflects sunlight.
1.3.3 Describe the phases of the Moon.
WEEK LEARNING LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
AREA
INVESTIGATING TECHNOLOGY
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
40 1. Strength 1.1Knowing the shapes of At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
(4-8 OCTOBER) and objects in structures. 1.1.1 State the shapes of objects.
Stability. 1.1.2 Identify shapes in structure.
1.2Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
strength and stability 1.2.1 Identify shapes of objects that are stable.
of a structure. 1.2.2 Identify the factors that affect stability of objects.
1.2.3 Explain how base area affects stability.
1.2.4 Explain how height affects stability.
1.2.5 Identify the factors that affect the strength of a
structure.
41
(11-15 REVISION FOR FINAL YEAR EXAM
OKTOBER)
42 & 43
FINAL YEAR EXAMINATION
(18-29
OKTOBER)
1. Strength 1.1 Understanding the At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to :
44 and strength and stability 1.2.6 Design a model that is strong and stable.
(2-5 Stability. of a structure.
NOVEMBER) 3 NOVEMBER
DEEPAVALI
45
(8-12 CLASS MANAGEMENT
NOVEMBER)
46 CLASS MANAGEMENT
(15-19 17 NOVEMBER
NOVEMBER) HARI RAYA AIDILADHA
FINAL YEAR HOLIDAYS
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
SEKOLAH KEBANGSAAN SUNGAI BUAYA,
48010, RAWANG, SELANGOR DARUL EHSAN.
YEARLY PLAN SCIENCE
YEAR 5
2010
TEACHER’S : PN. HELYZA BT. HAYES
NAME
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
CLASS : 5 (NILAM & ZAMRUD)
HELYZA HAYES (SK. SUNGAI BUAYA)
You might also like
- RPT SC Yr5 2011Document6 pagesRPT SC Yr5 2011gurlzmiuraNo ratings yet
- RPT: Science Year 5Document10 pagesRPT: Science Year 5vzaidiNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Document5 pagesYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000No ratings yet
- RPT Science Year 5Document4 pagesRPT Science Year 5skppasirNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Document4 pagesYearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Mohd ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- SK Kota Masai Science FiveDocument10 pagesSK Kota Masai Science FiveNor Rasidah Binti AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work For Science Year 5Document9 pagesYearly Scheme of Work For Science Year 5Anonymous LrLmtf100% (1)
- Year 6 Science Curriculum SpecificationsDocument7 pagesYear 6 Science Curriculum SpecificationsFeFe VictorNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Noe Ballesteros - Chapter 5 Study GuDocument4 pagesKami Export - Noe Ballesteros - Chapter 5 Study GuNoe BallesterosNo ratings yet
- SK Year 5 Science Plan Covers Microorganisms, Survival, Food ChainsDocument6 pagesSK Year 5 Science Plan Covers Microorganisms, Survival, Food ChainsSally Salha SiladjanNo ratings yet
- Jsu Pks1 2010 THN 5Document2 pagesJsu Pks1 2010 THN 5serojajinggaNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument39 pagesThe Big Picture: Characteristics of Living OrganismsSoumiya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- (Environmental Science) Charlene May BSA 1-1Document3 pages(Environmental Science) Charlene May BSA 1-1Caseñas Charlene MayNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 0 7 First SemesterDocument9 pagesScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 0 7 First SemesterzakitamsirNo ratings yet
- Bio Science - Zoology STD - ViiiDocument3 pagesBio Science - Zoology STD - ViiiSabsNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Unit 1 Organisms and Life Processes - Self-Assessment SheetDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Unit 1 Organisms and Life Processes - Self-Assessment SheetBeanserNo ratings yet
- Gcse Biology Edexcel B1 The Variety of Living Organism Target SheetDocument5 pagesGcse Biology Edexcel B1 The Variety of Living Organism Target SheetSuki ChanNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapterwise Old Questions (Ism)Document16 pagesBiology Chapterwise Old Questions (Ism)Deepak MalgeNo ratings yet
- TMK Yr2Document73 pagesTMK Yr2Rosnita Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- LFSC-March-QP & Memo-2020-Gr11Document13 pagesLFSC-March-QP & Memo-2020-Gr11dhdkwosohdhdhdNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Unit 1 Organisms and Life Processes - Self-Assessment SheetDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Unit 1 Organisms and Life Processes - Self-Assessment SheetBeanserNo ratings yet
- SC - Ed. 449 Animal Science IVDocument7 pagesSC - Ed. 449 Animal Science IVRadio GorkhaNo ratings yet
- SC Yearly 5 PlanDocument9 pagesSC Yearly 5 PlanHani OsmanNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Study GuideDocument4 pagesCH 5 Study Guideapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Grade 5, Science CurriculumDocument3 pagesGrade 5, Science CurriculumJoel C. Yuvienco67% (3)
- Blooms Taxonomy Level of LearningDocument11 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Level of LearningJi AnaNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Concept and Uses of Classification SystemsDocument51 pagesThe Big Picture: Concept and Uses of Classification SystemsSoumiya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyiteachclassroom100% (2)
- JAC 11th Biology Syllabus 2023-24Document8 pagesJAC 11th Biology Syllabus 2023-24Akanksha KumariNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Year Five: SE M. WEE K Themes Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes SPSDocument8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Year Five: SE M. WEE K Themes Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes SPSdialexanneNo ratings yet
- Abraham Hernandez - Copy of PT 7Document7 pagesAbraham Hernandez - Copy of PT 7api-653578039No ratings yet
- DLL ScienceDocument4 pagesDLL ScienceMark Adrian ArenasNo ratings yet
- Bio PyqsDocument14 pagesBio Pyqsmrbalikai1941No ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument115 pagesEcosystemSourabh BhatiNo ratings yet
- 12th BotanyDocument2 pages12th Botanyejg0453No ratings yet
- Curriculum Mapping Science 6 Prepared By: Kenneth Feliciano: Grade 6 - Matter First Quarter/First Grading PeriodDocument4 pagesCurriculum Mapping Science 6 Prepared By: Kenneth Feliciano: Grade 6 - Matter First Quarter/First Grading PeriodlouisNo ratings yet
- Grade 11document (1)Document99 pagesGrade 11document (1)ndlovumbali370No ratings yet
- LIVING ENVIRONMENT REGENTS EXAMDocument32 pagesLIVING ENVIRONMENT REGENTS EXAMHSDLAS MrKNo ratings yet
- Raniya Lee - Copy of PT 7Document8 pagesRaniya Lee - Copy of PT 7api-651645139No ratings yet
- Science Year 4 2010Document13 pagesScience Year 4 2010Meganathan BalavesivanNo ratings yet
- CLASS 8 AND 9 YEAR PLANS FOR BIO SCIENCE SUBJECTDocument4 pagesCLASS 8 AND 9 YEAR PLANS FOR BIO SCIENCE SUBJECTShyam ReddyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Course PlanDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Course PlaneeappleNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Module Week 5Document6 pagesScience 7 Module Week 5Jeannie Taino0% (1)
- Sains Bab 1 - Form 2Document7 pagesSains Bab 1 - Form 2THANABALAN A/L MUNUSWAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- 1703 VCScience Yr 7 Ecosystemsassignmentindividualsmnt 002636263737451386405Document5 pages1703 VCScience Yr 7 Ecosystemsassignmentindividualsmnt 002636263737451386405the.efroNo ratings yet
- Lenv v202 ExamDocument32 pagesLenv v202 ExamHenry LanguisanNo ratings yet
- 4 - Principles of EcologyDocument27 pages4 - Principles of EcologyshanujssNo ratings yet
- Ranc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 JsuDocument8 pagesRanc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 Jsunanac_2No ratings yet
- Grade 7Document40 pagesGrade 7Phineas sehoanaNo ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You May Be Assessed On) Significant IdeasDocument19 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You May Be Assessed On) Significant IdeasDunya Vink G11No ratings yet
- Yr5 Science Specification 2012Document17 pagesYr5 Science Specification 2012Norazura ZuraNo ratings yet
- DLL FoodchainDocument4 pagesDLL FoodchainKen Mitchell Morales100% (3)
- Curriculum Map Grade 9 ScienceDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 9 ScienceSherwinNo ratings yet
- TG FormatDocument5 pagesTG FormatEncluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet
- Biology Preparatory Test: Class - IXDocument4 pagesBiology Preparatory Test: Class - IXROG NotesNo ratings yet
- Science 3 2nd GradingDocument7 pagesScience 3 2nd GradingClaudine FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Seed Development, Dormancy and GerminationFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Seed Development, Dormancy and GerminationNo ratings yet
- Percubaan UPSR 2011 Kelantan (BHG A & B) - NewDocument23 pagesPercubaan UPSR 2011 Kelantan (BHG A & B) - NewAini DanNo ratings yet
- Sains Upsr 2008Document35 pagesSains Upsr 2008Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Trial Upsr 2011 SC Answer KLDocument2 pagesTrial Upsr 2011 SC Answer KLSamsul IrwanNo ratings yet
- Hots SainsDocument51 pagesHots SainsRiduan SeliminNo ratings yet
- Assgmt 2 EnglishDocument13 pagesAssgmt 2 EnglishHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Sewing Two Pieces TogetherDocument13 pagesSewing Two Pieces TogetherHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan PKBS2 - 2011Document3 pagesSkema Jawapan PKBS2 - 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- JSU PKBS 2 Tahun 5 - 2011Document2 pagesJSU PKBS 2 Tahun 5 - 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Ujian Pengesanan 1 (Year 6)Document2 pagesUjian Pengesanan 1 (Year 6)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Interview ReportDocument28 pagesInterview ReportHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- English 1 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Document9 pagesEnglish 1 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- English 2 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Document9 pagesEnglish 2 Year 1 (Pkbs 2) 2011Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan Year Two 2010 Theme: Learning AboutDocument11 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year Two 2010 Theme: Learning AboutHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping Year 5 Modul CemerlangDocument45 pagesMind Mapping Year 5 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (2)
- Mind Mapping Yaer 6 Modul CemerlangDocument21 pagesMind Mapping Yaer 6 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (3)
- Mind Mapping Year 4 Modul CemerlangDocument26 pagesMind Mapping Year 4 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (1)
- Earth & Universe Year 6Document4 pagesEarth & Universe Year 6Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan Year One 2010 Theme: Learning AboutDocument11 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year One 2010 Theme: Learning AboutHelyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 2 (B)Document7 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 2 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 4 (B)Document5 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 4 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 5 (B)Document5 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 5 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Technology Year 4Document7 pagesTechnology Year 4Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Universe Year 5Document6 pagesEarth & Universe Year 5Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 3 (B)Document4 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 3 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Set 1 (B)Document7 pagesModul Cemerlang Set 1 (B)Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Technology Year 5Document9 pagesTechnology Year 5Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Technology Year 6Document7 pagesTechnology Year 6Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Universe Year 4Document7 pagesEarth & Universe Year 4Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Materials Year 6Document6 pagesMaterials Year 6Helyza HayesNo ratings yet
- Raman Effect: Fingerprinting The UniverseDocument2 pagesRaman Effect: Fingerprinting The UniverserachelNo ratings yet
- T316Document5 pagesT316ANKIT SHARMA100% (1)
- PO Pangling SalonDocument1 pagePO Pangling SalonArlin RomansyahNo ratings yet
- A510A510M-13 Standard Specification For General Requirements For Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel, and Alloy SteelDocument6 pagesA510A510M-13 Standard Specification For General Requirements For Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel, and Alloy Steeltjt4779100% (2)
- Sistema STRESSTEELDocument41 pagesSistema STRESSTEELJonathan FelixNo ratings yet
- Ae 101 GBDocument6 pagesAe 101 GBmoath1977No ratings yet
- Microbial Test KitDocument3 pagesMicrobial Test KitLutfi HidayatNo ratings yet
- تسير كهربائيDocument95 pagesتسير كهربائيaaNo ratings yet
- Cryo Regulator RegValve PDFDocument25 pagesCryo Regulator RegValve PDFdhaktodesatyajitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Stomach Acid, Its Composition and NeutralizationDocument25 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Stomach Acid, Its Composition and NeutralizationAkaar bellaneyNo ratings yet
- SM ch1 Mat Meyers 2Document37 pagesSM ch1 Mat Meyers 2infinity_azNo ratings yet
- Surface TextureDocument27 pagesSurface Texturesohkimfai6340100% (5)
- GtryeDocument66 pagesGtryePholNo ratings yet
- 9A03301 Materials Science and EngineeringDocument4 pages9A03301 Materials Science and EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument15 pagesConfined Space EntryEnginnering Section100% (1)
- Formation of Delta Ferrite in 9 WT.% CR Steel Investigated by In-Situ X-Ray Diffraction Using Synchrotron RadiationDocument9 pagesFormation of Delta Ferrite in 9 WT.% CR Steel Investigated by In-Situ X-Ray Diffraction Using Synchrotron Radiationsmallik3No ratings yet
- Power Engineering FundamentalsDocument5 pagesPower Engineering FundamentalsShriram SinghNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Factors Affecting The Rate of Reaction Between Magnesium and Hydrochloric AcidDocument4 pagesAn Investigation Into The Factors Affecting The Rate of Reaction Between Magnesium and Hydrochloric AcidDao Thi Hoang HoaNo ratings yet
- Qorpak 2018 CatalogDocument104 pagesQorpak 2018 Catalog東栄大出No ratings yet
- Diesel Fuel InjectionDocument5 pagesDiesel Fuel Injectiondamith21No ratings yet
- MOF Part 2-1-100Document100 pagesMOF Part 2-1-100Tayyaba BibiNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Berol Surfboost Ad15 Oct 2013Document2 pagesLeaflet Berol Surfboost Ad15 Oct 2013Vilas DhakappaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Vibration Control in BuildingsDocument45 pagesAn Introduction To Vibration Control in Buildingsosama alabsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Semicon) FLOYDDocument2 pagesChapter 1 (Semicon) FLOYDanon_337840562No ratings yet
- Steam Trap PerformanceDocument36 pagesSteam Trap Performancenewnse2008No ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds Chemistry GuideDocument20 pagesCarbon Compounds Chemistry Guideirisyyy27No ratings yet
- Literature Review On Carbon Dioxide Capture by AbsorptionDocument21 pagesLiterature Review On Carbon Dioxide Capture by AbsorptionTU_MTECH_ENV11No ratings yet
- Course Outline Heat, Waves & Sound LabDocument3 pagesCourse Outline Heat, Waves & Sound LabphooolNo ratings yet
- Defect SolidDocument21 pagesDefect SolidSafialMojnabin100% (1)