Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
Uploaded by
Gaurav PandeyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
Uploaded by
Gaurav PandeyCopyright:
Available Formats
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
LTE is the first technology designed explicitly for Next Generation Networking (NGN) and is set
to become the de-facto NGN mobile access network standard. It takes advantage of NGN
capabilities to provide an always-on mobile data experience comparable to wired networks.
LTE supports peak data rates of more than 100 Mbps on the downlink when using 20
MHz channel bandwidth, two transmit antennas at the base station and two receive
antennas at the User Equipment (UE). LTE also supports peak data rates of more than
50 Mbps on the uplink when using a 20 MHz channel bandwidth; and single transmit
antennas at the UE and base station.
LTE generates ten to twelve times the throughput on the downlink and eight to ten times
the throughput on the uplink relative to 3GPP Release 6.
LTE improves spectrum efficiency as defined relative to Release 6. The uplink and
downlink capabilities are two to four times the spectral efficiency of High-Speed Packet
Access (HSPA).
LTE has flexible duplex methods. Both Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time
Division Duplex (TDD) are valid spectrum allocations and allow LTE to accommodate
various channel bandwidths in the available spectrum.
LTE interoperates with W-CDMA, GSM, and CDMA2000 systems. Multimode UEs will
support handover to and from these other systems.
Legacy technologies such as HSPA+ and Enhanced EDGE will continue to operate
within the new network architecture.
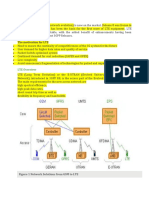
Downlink Key Features
Uplink Key Features
OFDM based, 15 kHz sub-carrier spacing
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM modulation
Variable RF bandwidth, 1.4 - 20 MHz
MIMO in the form of transmit diversity or
spatial multiplexing
Scheduling, link adaptation, HARQ and
measurements similar to 3.5G
Single Carrier FDMA, 15 kHz sub-carrier
spacing
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM modulation
Variable RF bandwidth, 1.4 - 20 MHz
Scheduling, link adaptation, HARQ and
measurements similar to 3.5G
Random access procedures
TDD/FDD Access - LTE standards support the use of both TDD (Time Domain Duplex) and FDD
(Frequency Domain Duplex) from the same set of standards, and with the same air interface
characteristics.
Multiple Input Multiple Out (MIMO) - MIMO is an antenna technology that, together with signal
processing, can either increase capacity (spatial multiplexing) or signal-to-noise ratio (transmit
diversity) in a radio link.
In LTE using 2x2 MIMO with spatial multiplexing, the user data is separated into two data sets each
fed to two transmit antennas and received by two receive antennas. Because of multi-path, each
data set travels a distinct RF path with different propagation characteristics. The algorithm used to
split and recombine the data allows the system to make use of the independence of these two paths
in order to improve throughput. The two data streams occupy the same RF channel at the same
time. This doubles the data rate possible on the air interface link.
You might also like
- How To Open Locks Without Keys or PicksDocument33 pagesHow To Open Locks Without Keys or PicksJamie Thompson100% (5)
- DLP ProjectorsDocument62 pagesDLP ProjectorsVenkatesh Subramanya100% (1)
- LTE-Advanced: A Practical Systems Approach to Understanding 3GPP LTE Releases 10 and 11 Radio Access TechnologiesFrom EverandLTE-Advanced: A Practical Systems Approach to Understanding 3GPP LTE Releases 10 and 11 Radio Access TechnologiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- BurpSuite PDFDocument24 pagesBurpSuite PDFbabuNo ratings yet
- Examining Data Runs of A Fragmented File in NTFSDocument15 pagesExamining Data Runs of A Fragmented File in NTFSCarlos CajigasNo ratings yet
- Audition Cheat Sheet.Document8 pagesAudition Cheat Sheet.Criesna Adi FadlikaNo ratings yet
- The Mobile Broadband Standard: LTE OverviewDocument4 pagesThe Mobile Broadband Standard: LTE OverviewradioNo ratings yet
- ONLINE-AUCTION-GUIDEDocument29 pagesONLINE-AUCTION-GUIDEmayanknuty86% (7)
- Auto HFM Flyer 2017Document8 pagesAuto HFM Flyer 2017Nikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Rutter VDR-100 G2 User ManualDocument62 pagesRutter VDR-100 G2 User ManualkaporaluNo ratings yet
- How To Commision FSMFDocument9 pagesHow To Commision FSMFGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- LTE PlanningDocument112 pagesLTE PlanningIva Atyna100% (1)
- Noontec V9Document57 pagesNoontec V9clpiauNo ratings yet
- LTE ArchitectureDocument80 pagesLTE ArchitecturesotodolNo ratings yet
- Communication Based Train Control SystemDocument25 pagesCommunication Based Train Control SystemArthiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE) and its Evolution to LTE-AdvancedDocument40 pagesIntroduction to 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE) and its Evolution to LTE-AdvancedMarco SignoriniNo ratings yet
- Antrenamentul Abilitatilor de Comunicare Stefan Prutianu PDFDocument4 pagesAntrenamentul Abilitatilor de Comunicare Stefan Prutianu PDFSacal's Carlos0% (2)
- LTE Air Interface PDFDocument26 pagesLTE Air Interface PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is LTE?: 3G WCDMA (R99) 3.5G HSPA LTEDocument20 pagesWhat Is LTE?: 3G WCDMA (R99) 3.5G HSPA LTEWaad AlteeNo ratings yet
- FILE003Document52 pagesFILE003Vikas NigamNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Overview and Channel Structure of LTEDocument34 pagesModule-3 Overview and Channel Structure of LTENithesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- LTE Networks Are Based On OFDMADocument8 pagesLTE Networks Are Based On OFDMAVicenteMarioHernándezGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Long Term EvolutionDocument11 pagesLong Term EvolutionRuby EshNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio Interface Overview - ARIMASDocument2 pagesLTE Radio Interface Overview - ARIMASchooty80No ratings yet
- 3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution)Document36 pages3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution)Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- LTE Mobile Report SummaryDocument13 pagesLTE Mobile Report SummaryDebashis DalaiNo ratings yet
- LTE TutorialDocument13 pagesLTE TutorialsedjaliNo ratings yet
- RMCS - Lecture 7 v12 - 1 - Annotated PDFDocument8 pagesRMCS - Lecture 7 v12 - 1 - Annotated PDFDhanuka AbeysekeraNo ratings yet
- An Introduction of 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE)Document38 pagesAn Introduction of 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE)Pankaj DebnathNo ratings yet
- Plan General: 1.1.1 I 5 1.1.2 D ' 6 1.1.3 E N B 6 1.2.1 L'EPC (E P C) 8 1.2.2 L'EPS (E P S) 8Document24 pagesPlan General: 1.1.1 I 5 1.1.2 D ' 6 1.1.3 E N B 6 1.2.1 L'EPC (E P C) 8 1.2.2 L'EPS (E P S) 8nnydenNo ratings yet
- How Advanced Is LTE Advanced PDFDocument7 pagesHow Advanced Is LTE Advanced PDFJasminder SahniNo ratings yet
- Lte - Lte-ADocument10 pagesLte - Lte-Awcdma123No ratings yet
- LTE (Long Term Evolution)Document8 pagesLTE (Long Term Evolution)MuhammadKhalidRehanChNo ratings yet
- WCE2014 pp150-155 PDFDocument6 pagesWCE2014 pp150-155 PDFvpsampathNo ratings yet
- 4GDocument10 pages4Gjiteshsunny20063421No ratings yet
- The 3g Long-Term Evolution Radi Interface PDFDocument5 pagesThe 3g Long-Term Evolution Radi Interface PDFSehat SitorusNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio Access Fundamentals ExplainedDocument2 pagesLTE Radio Access Fundamentals ExplainedAshwani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- LTE Single Carrier FDMA ModulationDocument9 pagesLTE Single Carrier FDMA ModulationQuoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- LTE & LTE AdvDocument10 pagesLTE & LTE AdvVIKAS NIGAMNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report: Department of Electronics & CommunicationsDocument7 pagesA Seminar Report: Department of Electronics & CommunicationsVipul PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lte and Its Unique TechnologiesDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Lte and Its Unique TechnologiesMohamed HussienNo ratings yet
- LTE Part IIDocument3 pagesLTE Part IIThanh Nguyen VpNo ratings yet
- Itu-R Cellular System: - Branded Samsung LTE ModemDocument9 pagesItu-R Cellular System: - Branded Samsung LTE ModemVivek NayeeNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of MIMO Over MIMO-LTE For MQAM Considering Rayleigh Fading DistributionDocument9 pagesPerformance Analysis of MIMO Over MIMO-LTE For MQAM Considering Rayleigh Fading DistributionAli Najim Al-AskariNo ratings yet
- 3GPP Long Term EvolutionDocument3 pages3GPP Long Term EvolutionAnonymous pTtEWaaNo ratings yet
- Lte Quick Guide Lte OverviewDocument18 pagesLte Quick Guide Lte OverviewDevanshu RastogiNo ratings yet
- Lte Quick Guide Lte OverviewDocument18 pagesLte Quick Guide Lte OverviewAbdul Rahim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 4G Refers To The Fourth Generation ofDocument12 pages4G Refers To The Fourth Generation ofsahithsindhuNo ratings yet
- LTE Understanding the Evolution to LTEDocument45 pagesLTE Understanding the Evolution to LTEsonuvikas775No ratings yet
- 3gpp r8 Lte OverviewDocument134 pages3gpp r8 Lte Overview박지홍No ratings yet
- 4G Refers To The Fourth Generation of Cellular Wireless Standards. It Is A Successor To 3G and 2G Families ofDocument6 pages4G Refers To The Fourth Generation of Cellular Wireless Standards. It Is A Successor To 3G and 2G Families ofvitchu_123No ratings yet
- High Speed 1.6 Tbps Hybrid TWDM-OfDDocument29 pagesHigh Speed 1.6 Tbps Hybrid TWDM-OfDSinghshNo ratings yet
- High Speed SSSWZCDocument30 pagesHigh Speed SSSWZCSinghshNo ratings yet
- WC <E 4G - 17EC81 - Module - 1 - Key Enablers For LTE FeatureDocument18 pagesWC <E 4G - 17EC81 - Module - 1 - Key Enablers For LTE FeatureJyothi MelinamaniNo ratings yet
- Long Term EvolutionDocument19 pagesLong Term EvolutionAbhishek JainNo ratings yet
- 3Gpp-Lte: The Motivation For LTEDocument5 pages3Gpp-Lte: The Motivation For LTEVaishnavi PunaginNo ratings yet
- Long Term Evolution (LTE) MAR2023Document17 pagesLong Term Evolution (LTE) MAR2023Janet MuendiNo ratings yet
- LTE-Advanced-Evolution of LTE - Radio Transmission ExperimentsDocument15 pagesLTE-Advanced-Evolution of LTE - Radio Transmission ExperimentskyfeeeNo ratings yet
- LTE Module 3 Notes 1Document35 pagesLTE Module 3 Notes 1Shreemahathma HdNo ratings yet
- 3 Ratna Singh ThakurDocument5 pages3 Ratna Singh ThakurDivine Grace BurmalNo ratings yet
- 4G LTE TutorialDocument35 pages4G LTE TutorialErdal AliNo ratings yet
- LTE Advanced: The 4G Mobile Broadband Technology: Jolly Parikh Anuradha BasuDocument5 pagesLTE Advanced: The 4G Mobile Broadband Technology: Jolly Parikh Anuradha BasuFrensel PetronaNo ratings yet
- LTE (Long Term Evolution) PHY OverviewDocument4 pagesLTE (Long Term Evolution) PHY OverviewibrahimNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document26 pagesModule 1Varshini NNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio InterfaceDocument10 pagesLTE Radio InterfaceMehmet Can KahramanNo ratings yet
- 3G LTE Tutorial - 3GPP Long Term EvolutionDocument35 pages3G LTE Tutorial - 3GPP Long Term EvolutionShah ArafatNo ratings yet
- All CommandsDocument4 pagesAll CommandsGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Alu Mux ViewDocument8 pagesAlu Mux ViewGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- SCTP DallasDocument19 pagesSCTP DallasChristie YsidroNo ratings yet
- Monsoon Safety Monsoon Safety: Delivery, India RegionDocument6 pagesMonsoon Safety Monsoon Safety: Delivery, India RegionGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- BSC Over IP: Gujarat SummaryDocument9 pagesBSC Over IP: Gujarat SummaryGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- GSMCallFlow (New)Document44 pagesGSMCallFlow (New)Adeyemi_o_olugbileNo ratings yet
- PacketAbis Over TDM - BTS - Commissioning StepsDocument8 pagesPacketAbis Over TDM - BTS - Commissioning StepsGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Axis Hitz Proxy MethodsDocument5 pagesAxis Hitz Proxy MethodsAdi Guf100% (1)
- Opennebula Instal StepsDocument23 pagesOpennebula Instal StepsKarthikeyan PurusothamanNo ratings yet
- Clarion Dxz615 ManualDocument30 pagesClarion Dxz615 ManualmilosgtaNo ratings yet
- Diff. Data and InformationDocument12 pagesDiff. Data and InformationDenisho DeeNo ratings yet
- Content Manager Backup Recovery and High Availability Strategies Options and Procedures IBM Redbooks PDFDocument280 pagesContent Manager Backup Recovery and High Availability Strategies Options and Procedures IBM Redbooks PDFBruno Rafael Santos LopesNo ratings yet
- Ranap Release CauseDocument397 pagesRanap Release CauseKamana Khare0% (1)
- Wireless Internet Handbook Technologies - Standards - and ApplicationsDocument626 pagesWireless Internet Handbook Technologies - Standards - and ApplicationsAustin Efe DavidsNo ratings yet
- SANGFOR IAM - v11.9 User Manual - 20170223 PDFDocument689 pagesSANGFOR IAM - v11.9 User Manual - 20170223 PDFroot beerNo ratings yet
- English VSAT PresentationDocument54 pagesEnglish VSAT PresentationcheiksoNo ratings yet
- Bsc6900 Umts LMT User Guide (v900r017c10 - 02) (PDF) - enDocument327 pagesBsc6900 Umts LMT User Guide (v900r017c10 - 02) (PDF) - enmike0147230No ratings yet
- SAP LSMW Data Migration Tool Transfers Legacy Data with No CodingDocument4 pagesSAP LSMW Data Migration Tool Transfers Legacy Data with No CodingSrinivasa Rao MullapudiNo ratings yet
- 9A05602 Unix InternalsDocument4 pages9A05602 Unix InternalssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Offline Examination SystemDocument4 pagesOffline Examination Systemஅருண் ராமச்சந்திரன்50% (2)
- Hierarchy in PDMS - World, Site, ZoneDocument5 pagesHierarchy in PDMS - World, Site, ZoneMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Sending SMS in VBDocument7 pagesSending SMS in VBbrianlucheNo ratings yet
- S25FL512SDocument143 pagesS25FL512Scooolmilin1No ratings yet
- GoToMeeting Organizer QuickRef GuideDocument5 pagesGoToMeeting Organizer QuickRef GuideWin Der LomeNo ratings yet
- Brksec 3771 PDFDocument138 pagesBrksec 3771 PDFDaniel VieceliNo ratings yet
- FreebsdDocument47 pagesFreebsdMohammad Bilal MirzaNo ratings yet
- GSM Gprs Based Automatic Rain Station Kws 033 2 Pcatalog1 128Document2 pagesGSM Gprs Based Automatic Rain Station Kws 033 2 Pcatalog1 128AP1979123No ratings yet
- 2015may FE PM QuestionDocument39 pages2015may FE PM Questionjive_gumelaNo ratings yet