Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HIRARC
Uploaded by
faizOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HIRARC
Uploaded by
faizCopyright:
Available Formats
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
1.0
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 1 of 13
Purpose
The purpose of this SOP is to provide a systematic and objective approach to assessing hazards and
their associated risks that will provide an objective measure of an identified hazard as well as provide
a method to control the risk. It is one of the general duties as prescribed under the Occupational
Safety and Health Act 1994 (Act 514) for the employer to provide a safe workplaces to their
employees and other related person.
2.0
Scope
This SOP outlines requirements associated with OSH workplace inspections, including training,
inspection checklists to be used and HIRARC report.
3.0
Definitions
Hazard means a source or a situation with a potential for harm in terms of human injury or ill health,
damage to property, damage to the environment or a combination of these.
Hazard identification means the identification of undesired events/conditions that lead to the
materialization of the hazard mechanism by which those undesired events could occur.
Inspection team / HIRARC Team means two or more people responsible for conducting the
workplace inspection
Risk means a combination of (i) the likelihood of an occurrence of a hazardous event with specified
period or in specified circumstances and (ii) the severity of injury or damage to the health of people,
property, environment or any combination of these caused by the event.
Risk assessment means the process of evaluating the risk to safety and health arising from hazards
at work.
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 2 of 13
Risk control means the process of implementing measures to control the risk associated with a
hazard.
Risk management means the total procedure associated with identifying a hazard, assessing the
risk, putting in place control measures, and reviewing the outcomes.
4.0
Responsibilities
4.1
Faculties/Divisional Management
Management in Faculties and Divisions/Departments, may, if requested, to assist the OSH
Committee to carry out workplace inspections and subsequent rectification of hazardous
conditions. Management and staff also have the responsibility to inform OSH Committee on
any potential hazards identified and/or the effectiveness of existing controls.
4.2
HIRARC Inspection Team
The inspection team is required to record workplace inspections findings as set out in this SOP
and to ensure hazards are controlled.
5.0
Workplace Safety Inspections
5.1
Inspection Frequency
The Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) 1994 require the inspection of workplace to
be done at least once in every three months.
However, inspection frequency is determined by the level of risk associated with the workplace
(faculty, division, department, laboratory). A risk assessment should be conducted by the
Faculty/Division/Department/Laboratory controlling the area to determine the risk and the
frequency of inspections required.
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 3 of 13
After receiving risk assessment reports, an inspection schedule, appropriate for the level of
risk, should be developed by the HIRARC team, to program inspection throughout the year.
This schedule should be communicated back to the respective faculty, division, department
and laboratory.
5.2
HIRARC Inspection Team
It is recommended that those conducting workplace inspections attend HIRARC training and
have knowledge and/or experience of the workplace and hazards that may be present.
The inspection team should be comprised of at least an OSH Committee member, a
Department of Estates and Facilities (DEF) representative. Inspections team may also include
a person external to the area. The in charge personnel of the area should be present during
the inspection if required by the inspection team.
HIRARC Team should prepare the inspection schedule and discuss the areas to be inspected
and time allocated for inspection. Each inspection must be fully documented. The HIRARC
form (Appendix B) must be completed by the inspection team and signed by the in charge
personnel of the location and an agreement amongst team members involved in the
inspections on counter measures and recommendations, prior to submitting the report to the
OSH committee.
5.3
Staff Involvement
Staff (science/engineering/computer laboratory/workshop etc.) have valuable on-the-job
experience and can have skills in identifying the hazards associated with particular tasks. This
information is valuable during inspections and it is recommended that staff is involved in the
inspection process or given the opportunity to provide information to the inspection team by
being present during inspections. All staff are encouraged to provide information or/and report
any potential hazards to the OSH Secretariat.
5.4
Inspection Checklists
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 4 of 13
During inspection, checklists are used to assist in the identification of hazards. Any additional
hazard should be noted at the end of the checklist. An example of a checklist can be found in
Appendix D.
Faculty/Division/Department/Laboratory can include additional hazards in the checklist for their
units as long as OSH Secretariat is informed.
Inspection checklist is used to produce HIRARC report.
5.4
Preventive / Corrective Action
Once potential hazards or hazards are identified, measures should be taken to ensure the
hazards are controlled. Once an inspection is completed those items that require preventive /
corrective actions should be addressed.
The HIRARC report should be sent to OSH
Secretariat within ten working days after the inspection is done. The Secretariat would ensure
that the reports are sent to an appropriate department/person for action. The Secretariat
should follow-up to verify that action has been taken or is completed and review the risk to
ensure that it has been eliminated or minimized.
Where a hazard presents an immediate risk to safety and health, the HIRARC team / Safety
and Health Officer should attempt to make the area safe and notify the area in charge
personnel for further action.
5.5
Inspection Reports / Documentation
Inspection report should consist of checklists and an HIRARC Form (inspection/hazard
summary).
OSH Secretariat should disseminate the HIRARC report to the relevant
Dean/Director/HOD/Laboratory Officer.
A HIRARC Report should detail, but not limited to, the following:
Area inspected
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
6.0
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 5 of 13
Area supervisor
Inspection team
Area supervisor / Person in-charge
Hazard identification
Risk assessment
Risk control (Recommendations, action to be taken by, due date/status)
Appendices
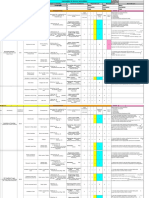
Appendix A: Flowchart of HIRARC Process
Appendix B: HIRARC Form
Appendix C: HIRARC Form (Example)
Appendix D: Checklist (General Area)
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Appendix A
Flowchart of HIRARC Process
HIRARC Team to complete/assess:
a) scheduled building inspections after risk assessment is done,
b) identified potential hazards or hazards,
c) any work activities.
Consultation with staff for specify work
activities e.g. machine operation, chemicals
handling.
Identify Hazards from the information
gathered.
Assessing the risk (high/medium/low) after
hazard identification.
Review
Develop control measures/action plan
Implement the control measures/action plan
and follow up
Page No: 6 of 13
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 7 of 13
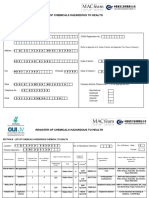
Appendix B
HIRARC FORM
Faculty/Location/Block
Conducted by:
Campus
PK / K-V
Name:
Name:
Name:
Designation/Dept:
Designation/Dept:
Designation/Dept:
Date:
(from to)
Time:
Next Review Date:
Ref. No. for Follow Up Action:
Risk
Hazard Identification (HI)
Assessment
Risk Control (RC)
(RA)
Risk
No
Hazard / Defect Identified and which can cause / effect
(High/Medium/
Low)
Recommended Control Measures
Action By &
Due Date/Status
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 8 of 13
Appendix C (i)
HIRARC FORM (Example)
Faculty/Location/Block
Conducted by:
PE (CFS-PJ)
Campus
PK / K-V
Name: Benedict Tong
Name: Chu Ling Onn
Name: David Chan
Designation/Dept: SHO/DSS
Designation/Dept: Lecturer
Designation/Dept: Manager/DEF
Date:
(from to)
2 Nov 2009
Time:
10 am to 2 pm
Next Review Date:
31 Nov 2009
Ref. No. for Follow Up Action:
th
PE/4 Q 2009/1 (2, 3 and so on)
Hazard Identification (HI)
Risk
Assessment
(RA)#
Risk
(High/Medium
/Low)
No
Hazard / Defect Identified and which can cause / effect
No alarm, sprinkles, detectors, hydrants observed / no warnings during
emergencies e.g. fire may cause fatality
No emergency numbers displayed. First aiders
contact nos. not available / delay in getting assistance during emergency e.g. first aid,
ambulance, BOMBA services.
Spoiled chairs to be removed. (1st Floor) / obstruct escape
during emergency.
High
Medium
Low
Risk Control (RC)
Recommended Control Measures
Request the owner on
providing these facilities.
Emergency numbers should be displayed
at strategy locations. First aiders
numbers should be displayed nearby or inside
the first aid kit
To remove the chairs as soon as possible
Action By &
Due Date/Status
DEF/
31 Dec 2009
DSS
31 Nov 2009
DEF/
9 Nov 2009
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 9 of 13
# Risk Assessment (High/Medium/Low) is derived from the table below:
Appendix C (ii)
Severity (S)
Likelihood (L)
10
15
20
25
12
16
20
12
15
10
High
15-25
Medium
5-12
Low
1-4
A HIGH risk requires immediate action to control the hazard as detailed in the hierarchy of control. Actions taken
must be documented on the risk assessment form including date for completion.
A MEDIUM risk requires a planned approach to controlling the hazard and applies temporary measure if required.
Actions taken must be documented on the risk assessment form including date for completion.
A risk identified as LOW may be considered as acceptable and further reduction may not necessary. However, if the
risk can be resolved quickly and efficiently, control measures should be implemented and recorded.
Hence, risk can be calculated using the following formula:
L x S = Risk
L = Likelihood
S = Severity
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 10 of 13
Appendix C (iii)
Below is one of the examples of Likelihood:
Likelihood is an event likely to occur within the specific period or in specified circumstances.
Likelihood (L)
Example
Rating
Most likely
The most likely result of the hazard / event being realized
Possible
Has a good chance of occurring and is not unusual
Conceivable
Might be occur at sometime in future
Remote
Has not been known to occur after many years
Inconceivable
Is practically impossible and has never occurred
Severity is outcome from an event such as severity of injury or health of people, or damage to property, or insult to environment, or any
combination of those caused by the event.
Severity (S)
Example
Rating
Catastrophic
Numerous fatalities, irrecoverable property damage and productivity.
Fatal
Approximately one single fatality, major property damage if hazard is realized
Serious
Non-fatal injury, permanent disability
Minor
Disabling but not permanent injury
Negligible
Minor abrasions, bruises, cuts, first aid type injury
Source: Guidelines for Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control, 2008, DOSH, Ministry of Human Resources
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 11 of 13
Appendix D
GENERAL AREA INSPECTION CHECKLIST
Inspection Carried
Out By :
Location :
Inspection Date/
Time :
* Boxes to be ticked as items are satisfactory () or required action (X), or otherwise NA
indicates the item is not applicable to this area.
No.
Criteria
Floors, Aisles, Walls,
Ceilings, Stairs and
Landings
Do floors have even surfaces
(no cracks or holes)?
Are the floors and aisles clear
of rubbish, materials and
equipment?
Are walkways clear of
obstructions and trip hazards
(e.g. electrical cords)?
Are walls in good condition
(no cracks or holes)?
Are ceilings in good condition
(no crack, sagging and water
stain/water leaking)?
Are stairs in good condition
(no worn or broken treads)?
Are handrails in good
condition?
Are non-skid strips in good
condition?
Are landings clear of
obstructions?
Emergency Procedures
Are emergency numbers
clearly displayed?
a
b
d
e
f
g
h
i
2
a
/X
or
NA
Result of Inspection
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
k
l
m
n
o
p
q
3
a
Are fire extinguishers located
in an easy to see location?
Have fire extinguishers been
serviced/tagged/expired?
Are fire extinguishers free
from obstruction (clearing at
least 1 meter)?
Are accesses to Hose Reel free
from obstruction?
Have the smoke detectors
functioning/been tested?
Have the fire alarm
functioning/been tested?
Are overhead
sprinkler/detectors clear of
obstructions, stores etc?
Are emergency evacuation
map easy to understand, up to
date and clearly displayed?
Are emergency evacuation
instructions easy to understand
and clearly displayed?
Have emergency lighting units
functioning/been tested?
Are emergency exit stairs
adequately lit?
Are fire doors closed but not
locked?
Are exit signs in place and
illuminated?
Are exit doors marked and
clearly visible?
Can exit doors be opened from
inside (no pad-locks)?
Are exit corridors clear of
obstructions (including outside
of the building)?
Are all fire hydrants visible
and readily accessible
(clearing at least 3 meter)?
Have the fire hydrants
functioning/been tested?
First Aid
Are first aid kit and contents
clean and orderly and properly
stocked (check expiry date)?
Do First Aid Kit signs
indicate locations of kits and
contact numbers of first
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 12 of 13
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Manual Title : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL (HIRARC)
Procedure Number : QP-DSS-005
4
a
b
5
a
b
aiders? Are the signs clearly
displayed?
Electrical
Are electrical items tested and
tagged and in date?
Are all power outlets and
switches in good condition
(not broken)?
Are all electric panels locked
and surrounding 3 ft of space
clear?
Are extension leads / power
boards used as designed
(temporary or makeshift
leads/power boards,
double adaptors, overloading)?
Lighting / Other
Is there adequate lighting for
the work being carried out?
Is the drinking water from
water dispenser clean and safe
to drink?
Are waste bins routinely
emptied?
Other Comments:
Rev No: 0
Effective Date: 07/04/2010
Page No: 13 of 13
You might also like
- Hazards and Effects Management ProcessDocument12 pagesHazards and Effects Management ProcessrwerwerwNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis (SOP)Document2 pagesUV-Vis (SOP)tyasamerta100% (1)
- Mechanical Workshop RisksDocument7 pagesMechanical Workshop RisksZarimi AcNo ratings yet
- REPORT SAFETY (Dec)Document12 pagesREPORT SAFETY (Dec)Dylan100% (1)
- Topic 2 Job Safety Analysis & HirarcDocument65 pagesTopic 2 Job Safety Analysis & HirarcrieNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures For Instruments 2012Document135 pagesStandard Operating Procedures For Instruments 2012Muhamad Bima MuriaNo ratings yet
- Gulf Tunneling Company HSEMS Forms ListDocument1 pageGulf Tunneling Company HSEMS Forms ListEiuol OinraNo ratings yet
- HIRARCDocument34 pagesHIRARCLeal Safety100% (3)
- Unsafe Act & Unsafe ConditionDocument9 pagesUnsafe Act & Unsafe ConditionGoldie Mae Abad100% (1)
- Hazard Risk Assessment FormDocument12 pagesHazard Risk Assessment FormSalman Alfarisi100% (3)
- Chemical Register Chec MacfeamDocument2 pagesChemical Register Chec MacfeamBekmengNo ratings yet
- Consignment NoteDocument20 pagesConsignment NoteRamizah MieyukiNo ratings yet
- Unisteel Technology HIRAC ProcedureDocument9 pagesUnisteel Technology HIRAC Procedurenarenmaniam100% (2)
- 3 SPS Sop RCC FullDocument14 pages3 SPS Sop RCC FullDwitikrushna RoutNo ratings yet
- PR 15 Hira Procedure Bim& Tim r1Document17 pagesPR 15 Hira Procedure Bim& Tim r1Purna Chandra BaruaNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure TemplateDocument4 pagesStandard Operating Procedure TemplatefaizNo ratings yet
- The Sampoong Department Store CollapseDocument27 pagesThe Sampoong Department Store CollapseelleNo ratings yet
- Hirarc Form Fork LiftDocument5 pagesHirarc Form Fork LiftSurendran NagiahNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Contoh-Hirarc PDFDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips Contoh-Hirarc PDFtenry_03No ratings yet
- SDS-Anchor Spray PaintDocument17 pagesSDS-Anchor Spray Paintamin100% (3)
- Hirarc JKKP ClosingDocument40 pagesHirarc JKKP ClosingThegym le Greene100% (1)
- Sho Exam Workshop - 17 Oct 2021Document60 pagesSho Exam Workshop - 17 Oct 2021hew ka yee100% (2)
- Hazard Identification and Risk Management DSFY 2063 Chemical Health Risk Assessment (CHRA)Document15 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Management DSFY 2063 Chemical Health Risk Assessment (CHRA)natashahkhanNo ratings yet
- Franchising: An Entrepreneur's Guide 4e: by Jonathan Comish, Scott Julian, Richard J. Judd and Robert T. JustisDocument21 pagesFranchising: An Entrepreneur's Guide 4e: by Jonathan Comish, Scott Julian, Richard J. Judd and Robert T. JustisHafsah Ahmad najibNo ratings yet
- HIRARCDocument13 pagesHIRARCbobocikoNo ratings yet
- Taguig City Ordinance No. 034-17Document12 pagesTaguig City Ordinance No. 034-17Kristine Pacariem100% (9)
- GRP-SHQ-FOR-001-08 Visitor Supplier SHE Induction Briefing FormDocument2 pagesGRP-SHQ-FOR-001-08 Visitor Supplier SHE Induction Briefing FormgrantNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Control: (Template)Document2 pagesHazard Identification Risk Assessment and Control: (Template)roland magoNo ratings yet
- GDSN Trade Item Implementation GuideDocument459 pagesGDSN Trade Item Implementation Guideqiaohongzedingtalk.comNo ratings yet
- OSH Legal Register KMSBDocument30 pagesOSH Legal Register KMSBMohammad Zairul Indra ShapriNo ratings yet
- ABC Industries Meeting Minutes Environmental ProjectsDocument1 pageABC Industries Meeting Minutes Environmental ProjectsMaint0% (1)
- PPE Issue Record - TemplateDocument1 pagePPE Issue Record - TemplatevsauNo ratings yet
- DEE EHU-03!5!1 Health and Safety Committee Meeting MinutesDocument2 pagesDEE EHU-03!5!1 Health and Safety Committee Meeting MinutesFred AlmaNo ratings yet
- Template 5 ERCMC Organization ChartDocument1 pageTemplate 5 ERCMC Organization ChartMaintNo ratings yet
- Surat Perlantikan Chaiman of SHCDocument2 pagesSurat Perlantikan Chaiman of SHCmuzica muzNo ratings yet
- Oh S Risk MG T ProcedureDocument9 pagesOh S Risk MG T Procedurekarl_poorNo ratings yet
- Hirarc SampleDocument84 pagesHirarc SampleAbdul Samad100% (1)
- Accident&Incident Reporting FlowchartDocument1 pageAccident&Incident Reporting FlowchartAtika MaulannaNo ratings yet
- ERT Formation & ResponsibilitiesDocument37 pagesERT Formation & ResponsibilitiesMalar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- A Pocket Guide To CGMP SamplingDocument36 pagesA Pocket Guide To CGMP Samplinganilpharma102275% (4)
- Hiradc ServicingDocument4 pagesHiradc ServicingAyub Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - CepswamDocument41 pagesModule 3 - CepswamShamsul Azhar Mohd100% (2)
- Guideline USECHHDocument28 pagesGuideline USECHHYo Soy MasriNo ratings yet
- Safety Induction Application FormDocument1 pageSafety Induction Application Formsyoolove100% (2)
- Delhi HT 01-12-2022Document32 pagesDelhi HT 01-12-2022Hemabh ShivpuriNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS Primax 97: Safety Data SheetDocument16 pagesPETRONAS Primax 97: Safety Data SheetJaharudin Juhan100% (1)
- Akta Kualiti Alam Sekitar (Buangan TerjadualDocument25 pagesAkta Kualiti Alam Sekitar (Buangan Terjadualshafie.buang67% (3)
- Improving Scheduled Waste Management ComplianceDocument3 pagesImproving Scheduled Waste Management ComplianceMdnor RahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Scheduled WasteDocument72 pagesChapter 7-Scheduled WasteSyahmi100% (1)
- CPD Hours Guideline 2018Document16 pagesCPD Hours Guideline 2018labNo ratings yet
- Field Training ReportDocument56 pagesField Training Reportkikovioletto100% (1)
- Business Correspondence TypesDocument54 pagesBusiness Correspondence TypesTegiuNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENT Site Safety DocumentsDocument3 pagesDOCUMENT Site Safety DocumentsMinami Chieng100% (1)
- FTR (1) XDocument4 pagesFTR (1) XIzzatyNabihah ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Checklist For The Preparation of Cepswam Field Training Report1Document12 pagesChecklist For The Preparation of Cepswam Field Training Report1Mdnor Rahim100% (1)
- Chemical Register GuidelineDocument3 pagesChemical Register GuidelineMohd ZulhaidyNo ratings yet
- Schedule Waste HandlingDocument3 pagesSchedule Waste Handlingosha911No ratings yet
- Xbep4103 Final Question Sep 2013Document5 pagesXbep4103 Final Question Sep 2013Roy Seven SymptomsNo ratings yet
- Nadopod HirarcDocument27 pagesNadopod HirarcZulKhaliliNo ratings yet
- Integrated HSE Management SystemDocument82 pagesIntegrated HSE Management SystemMwansa Mwamba KennethNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health Officer Regulations 1997Document25 pagesSafety and Health Officer Regulations 1997Mohd Khairol JambliNo ratings yet
- Scheduled Waste Storage Inspection PBJVDocument2 pagesScheduled Waste Storage Inspection PBJVBekmengNo ratings yet
- Hirarc Form: 1.hazard Identification 2.risk Analysis 3.risk ControlDocument2 pagesHirarc Form: 1.hazard Identification 2.risk Analysis 3.risk ControlAiman HakimiNo ratings yet
- Daily SSS Work Report 2 July 2019 - Copy 1Document7 pagesDaily SSS Work Report 2 July 2019 - Copy 1Ahmad FaridNo ratings yet
- Assignment OSH Act Legal RegisterDocument18 pagesAssignment OSH Act Legal RegisterMOHD RASHIDI BIN AWANG JAMAN (BOMBA-WPLABUAN)No ratings yet
- Official declaration templateDocument1 pageOfficial declaration templateMdnor RahimNo ratings yet
- Development of SWPDocument8 pagesDevelopment of SWPJoniNo ratings yet
- JKKP 6 - Report For Occupational Accident / Dangerous OccurrenceDocument2 pagesJKKP 6 - Report For Occupational Accident / Dangerous OccurrenceSyarmine Aqila IsaNo ratings yet
- Sakhalin Energy Investment Company Ltd. Safety Consequence Management StandardDocument13 pagesSakhalin Energy Investment Company Ltd. Safety Consequence Management StandardAnilNo ratings yet
- Metal and organic wastes scheduleDocument6 pagesMetal and organic wastes scheduleBazlaa HasmanNo ratings yet
- SMS Process For Element 8Document5 pagesSMS Process For Element 8Syed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument13 pagesAction PlanfaizNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Ergonomics Rick Assessment at Workplace 2017 - July Edited Rev.002 PDFDocument155 pagesGuidelines On Ergonomics Rick Assessment at Workplace 2017 - July Edited Rev.002 PDFfaizNo ratings yet
- Disposal form letterhead templateDocument1 pageDisposal form letterhead templatefaizNo ratings yet
- Surat Kuasa 2Document1 pageSurat Kuasa 2faizNo ratings yet
- GoogleDocument1 pageGooglefaizNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance On Distillation ColumnDocument4 pagesEnergy Balance On Distillation ColumnCecilia Tan67% (9)
- Job Analysis FormDocument3 pagesJob Analysis FormLisan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Resignation LetterDocument1 pageResignation LetterfaizNo ratings yet
- FMM Institute: 1 Malaysia GRIP FMM Certified Quality EngineerDocument1 pageFMM Institute: 1 Malaysia GRIP FMM Certified Quality EngineerfaizNo ratings yet
- FMM Certified Quality Engineer Course DetailsDocument3 pagesFMM Certified Quality Engineer Course DetailsfaizNo ratings yet
- 1msiagrip Cisho BrochureDocument3 pages1msiagrip Cisho BrochurefaizNo ratings yet
- SOP for Shimadzu UV-VIS in RH385Document1 pageSOP for Shimadzu UV-VIS in RH385faizNo ratings yet
- Innovation Loves CompanyDocument33 pagesInnovation Loves CompanycantuscantusNo ratings yet
- Enforce PAymentDocument1 pageEnforce PAymentJebs KwanNo ratings yet
- Value-Based Working Capital Management Determining Liquid Asset Levels in Entrepreneurial EnvironmentsDocument200 pagesValue-Based Working Capital Management Determining Liquid Asset Levels in Entrepreneurial EnvironmentsDiky WidodoNo ratings yet
- Emirates Aluminium Company, www6140,3000wDocument12 pagesEmirates Aluminium Company, www6140,3000wMuhammad IhtishamNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management (IREL) RahulDocument78 pagesWorking Capital Management (IREL) RahulunandinipatraNo ratings yet
- Annex 4 ODK ACF-E How To Author Surveys For ODKDocument40 pagesAnnex 4 ODK ACF-E How To Author Surveys For ODKAbad JoseNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal On SMEsDocument20 pagesResearch Proposal On SMEsNathan Bupe MukalulaNo ratings yet
- Teng2014 PDFDocument27 pagesTeng2014 PDFpramana putraNo ratings yet
- Payment PDFDocument1 pagePayment PDFkatiyar JitendraNo ratings yet
- Muthupettai Chennai On 18-Jun-2022Document1 pageMuthupettai Chennai On 18-Jun-2022KESHAV BALAJINo ratings yet
- Solutions for math word problemsDocument54 pagesSolutions for math word problemsAshishAmitavNo ratings yet
- U.S. FLSA Timesheet Compliance GuideDocument14 pagesU.S. FLSA Timesheet Compliance GuideAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- BMC Dam - TeegafoodieDocument1 pageBMC Dam - TeegafoodieAdam Muqrish HusniNo ratings yet
- PADS ES Suite Evaluation GuideDocument280 pagesPADS ES Suite Evaluation GuideAkhilesh AroraNo ratings yet
- 8 4企业管理咨询服务协议Document6 pages8 4企业管理咨询服务协议Chai QingqingNo ratings yet
- Zoren Electric Fuel Pump: Quality Management System IATF 16949:2016Document12 pagesZoren Electric Fuel Pump: Quality Management System IATF 16949:2016Ycnan DroidNo ratings yet
- R03 C07B01 IKP 01 RF SDW AR 10024 - CommentsDocument1 pageR03 C07B01 IKP 01 RF SDW AR 10024 - CommentsEleazar SacloloNo ratings yet
- Multinational Financial FunctionsDocument20 pagesMultinational Financial FunctionsVINITHANo ratings yet
- Open Source Software AssessmentDocument24 pagesOpen Source Software AssessmentPrashant RawatNo ratings yet
- Kyambogo University: Faculty of Arts and Social SciencesDocument13 pagesKyambogo University: Faculty of Arts and Social SciencesTumukunde JimmyNo ratings yet
- JForce Training 1Document45 pagesJForce Training 1Martin ThumbiNo ratings yet
- Compendium Vol 02 11117Document576 pagesCompendium Vol 02 11117Vaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Pasalubong RepublicDocument31 pagesPasalubong RepublicShara ValleserNo ratings yet