Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Globalisation and Social Challengest
Uploaded by
Janardhan Juvvigunta JJCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Globalisation and Social Challengest
Uploaded by
Janardhan Juvvigunta JJCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Innovative Social Science & Humanities Research
ISSN: 2349-1876 (Print) | ISSN : 2454-1826 (Online)
Globalization and Socio-Economic challenges in India
Dr.Richa Mishra,
Assistant Professor
Lucknow Public College of Professional Studies
Lucknow
ABSTRACT
LPG (Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation) model was adopted by Indian Government during
1990-91 when Indian Economy was in a very bad shape. It was, however, adopted not as a solution to
deteriorating Indian economy but to enable itself to get further foreign exchange loans from World Bank
as its foreign exchange reserves were reduced to mere three weeks outflow. To rectify its ailing financial
health, Government simultaneously decided to amend its economic policies and go for privatization &
liberalization of its economy. In the overall view, these decisions had immediate positive effect. However,
globalization soon has proved to be a double edged weapon. It did help government temporarily meet its
emergent need of foreign exchange but it has, as a by-product, caused some permanent damage to Indian
Economic system and Indian social structure.
Keeping in view the relevance of the subject, the attempt has been made in this paper to analyse the
socio- economic chalanges of globalisation and liberalisation in the Indian Economy. The study is based on
secondary data and it is of descriptive type.
KEY WORDS: Privatization, Liberalization, current account deficits, disinvestment, western
culture.
Introduction
Globalization (or globalization) describes a process
by which regional economies, societies, and cultures
have become integrated through a global network of
communication, transportation, and trade. The term
is sometimes used to refer specifically to economic
globalization: the integration of national economies
into the international economy through trade,
foreign direct investment, capital flows, migration,
and the spread of technology. Globalization as a
spatial integration in the sphere of social relations
when he said Globalization can be defined as the
intensification of worldwide social relations which
link distant locations in such a way that local
Vol (2), Issue-2,June-2015
happenings are shaped by events occurring many
miles away and vice versa. Globalization generally
means integrating economy of our nation with the
world economy. The economic changes initiated
have had a dramatic effect on the overall growth of
the economy. It also heralded the integration of the
Indian economy into the global economy.
Globalisation can be seen as one of the most
important force impacting on the economy.
According to Brittan[4] globalisation is viewed as a
whirlwind of relentless and disruptive change which
leaves governments helpless and leaves a trail of
IJISSHR
International Journal of Innovative Social Science & Humanities Research
economic, social cultural
problems in its wake
and
environmental
Globalization was initially planned to be only a trade
relationship. But the process has, as a by- product,
integrated national & regional economies, societies
and cultures through global network of trade,
communications and migrations [1].
As per one estimate, there are about 200 million
migrants around the world today and they are
largely from underdeveloped countries to developed
countries. In addition there is large transnational
workforce. These immigrations and other human
links have changed socio-cultural face of various
countries the world over [2].
This paper would examine the economic and social
effects of ongoing globalization in India. The attempt
has been made in this paper to analyse the impact of
globalisation and liberalisation over the socioeconomic aspects of Indian Economy. The study is
based on secondary data and it is of descriptive type
India is a multilinguial, multi-religious and multicaste country and has been a dominant player in the
world system and part of the global economy since
ages. Its civilisational past has been shaped and has
evolved through a number of events, crisis, people
and communities. It has not been an isolated
country at any point of time as there has been a
continuous exchange of ideas, products and people
with other countries and civilisations. There are
evidences that it has been integrating and
assimilating ideas and people from all over the
world. However, this has not been a one side flow as
India has also influenced other regions, countries
and civilizations through its contacts and interactions
of traders, travelers, religious preachers and other
migrants. [3] India has been a part of the bigger
world system. It has kept on interacting with other
countries. It therefore becomes essential to
understand India in a global context to examine its
problems and to seek solutions. Although economic
in the core, globalization has pervasive effects on the
society (Bauman, 1998 and Castle, 1999). It has its
impact on the social structure, values, social
institutions and attitudes. India is a multilingual,
2 | Vol (2), Issue-2,June-2015
ISSN: 2349-1876 (Print) | ISSN : 2454-1826 (Online)
multiethnic and multi-cultural society. Globalization
has impacted noticeably on cultural identity and
social harmony among various social groups. The
Indian social structure is extremely categorized;
replete with a multitude of enclaves of several types
and strata. There are enclaves making rural-urban,
men-women, caste-dalits, organizedunorganized,
formal-informal, and so on.
As Boeke (1953) has put it, it is possible to
characterize a society, in the economic sense, by the
social spirit, the organizational forms and the
technique dominating it. These three aspects are
interdependent and in this connection typify a
society, in this way that a prevailing social spirit and
the prevailing forms of organization and of
technique give a society its style, its appearance, so
that in their interrelation they may be called the
social system, the social style or the social
atmosphere of that society. Less developed
economies, especially with a history of prolonged
colonial rule, often exhibit a simultaneous existence
of two (or more) enclaves of socio-economic
systems, characteristically and conspicuously
different from each other, and each dominating a
part of the society, the economy and the polity.
The Indian economy was in major crisis in
1991 when foreign currency reserves went down to
$1 billion. Globalization had its impact on various
sectors including Agricultural, Industrial, Financial,
Health sector and many others. It was only after the
LPG policy i.e. Liberalization, Privatization and
Globalization launched by the then Finance Minister
Man Mohan Singh that India saw its development in
various sectors. If to divide the entire regime into
phases :
ERAS OF GLOBALISATION
First Era of Globalization(1850-1914)
InterWar Period(1920-1939)
Cold War Era(1945-1989)
Second Era of Globalization(1989-present)
IJISSHR
International Journal of Innovative Social Science & Humanities Research
Main Form of globalization
ISSN: 2349-1876 (Print) | ISSN : 2454-1826 (Online)
Influence of globalisation
1. Public-Private partnership
1) Economic:
Under both the General Agreement on Tariffs and
Trade (GATT) and its successor the World Trade
Organization (WTO), world trade has expanded
rapidly. TNCs have been the major force in
increasing economic interdependence and several
generations of newly industrialized countries have
emerged.
2) Cultural
Mixing of cultures has occurred through - Migration Rapid spread of news, ideas and fashions through
the media, trade and travel - Growth of global
brands Nike, Coca cola, MacDonalds Western
culture has diffused to all parts of the world through
television, cinema, the internet, newspapers and
magazines. This has been reflected in media, art,
sport and leisure pursuits.
3) Political
The influence of nation states has diminished in
many areas as more and more countries organize
themselves into trade blocs. The influence of
western democracies on developing countries has
also been strong. Relationships are also political
the increasing role played by the United Nations
around the world epitomizes the developing
cooperation between nations growing importance of
cross border pressure groups Friends of the Earth,
Amnesty International global civil society. Their
actions have led to international rules on trade,
environment, human rights, war etc. Globalization
can be seen in terms of: - Urban - a hierarchy of
global cities has emerged to act as Centres for the
global economy - Demographic the growth of
international migration and the rise of multicultural
societies - Linguistic the emergence of English as
the working language of the global village Environmental the impact of activity in one
country has a clear impact in others e.g. the spread
of pollutants and the impacts of global warming
Vol (2), Issue-2,June-2015
2. Competition in public sector
3. Efficiency
4. Effectiveness
5. Transparency
6. Responsiveness
7. Accountability
8. People participation
9. Business principles
10. Specialisation
11. Use of IT
12. Increase in productivity
13. Decrease in number of employees
Impact of liberalisation
1. Flexibility in policies
2. Increase in production
3. Lessen burden of work on administration
4. Increase in creativity
5. New experiments
6. Loosen the control of administration on economic
and commercial activities
Economic challenges
The oil crisis in 1970s and various other factors had
created financial emergency in India around 1990
when foreign currency reserves were reduced to
only 3 weeks outflow. Major factors for such a
situation where stagnant economy, mounting fiscal
deficits, current account deficits in international
trade and high rate of inflation during the preceding
many years. Fiscal deficit as a percentage of GDP
( Gross domestic Product ) has been over 7 % during
previous decade and it had touched 8.4% of GDP
during 1990-91.Current account deficit was about
IJISSHR
International Journal of Innovative Social Science & Humanities Research
3.3% of GDP while rate of inflation was as high as
10%. Such a situation demanded some drastic steps
including major structural changes in Indian
Economic policies. At this point, Indian Government
had no option but to accept the precondition of
joining stream of Globalization so as to be able to
avail loan/grant facility from World Bank. It agreed
to reduce quantitative restrictions imposed through
licensing system. It also agreed to reduce custom
duties in phases to levels acceptable to WTO.
Custom tariffs were reduced in phases over the
decade 1991-2001 from weighted average of about
70% to about 30% [5]. However, realizing that
Globalization, by itself, may not help the ailing Indian
economy, the then Government of India decided to
go for privatization of its economy and to adopt
liberalized economic policies. Some steps towards
these structural changes were [5]:
Virtual abolition of Industrial licensing Raj
Free access to foreign technology
Abolition of Government control over
capital issues and creation of SEBI to
encourage equity culture in India.
Sharp reduction in industries reserved for
public sector.
Decision to go for partial disinvestment in
public sector enterprises.
Policies of Privatization and liberalization of
economy, along with the process of globalization,
had a dramatic effect on Indian Economy which
responded swiftly and positively to these measures.
Fiscal deficit immediately came down to 5.9% in
1991-92 themselves. The real GDP increased at an
annual rate of about 6%. Many new companies were
formed by Indian entrepreneurs across different
industrial segments in view of liberalized economic
policies announced by Government. A large number
of job opportunities, with good wages, became
available in India. This resulted in sharp growth in
middle Income Group which, in turn, fuelled
domestic consumption. Liberalized policies on
foreign direct investment (F.D.I) and Foreign
4 | Vol (2), Issue-2,June-2015
ISSN: 2349-1876 (Print) | ISSN : 2454-1826 (Online)
Institutional investment (F.I.I.) helped in faster
developments in telecommunication, roads, ports,
airports, Insurance and other major sectors. All
above improvements in Indian Economy were largely
due to changed Economic policies of Government of
India. Globalization had only indirect contribution, if
any, in above improvements. However, there are
some other developments- not so happy
developments- which are attributed to Globalization
process only. A few of such developments are:
A. Direct effect of Globalization is intensified
interdependence of Indian economy and world
economy. As a result, it has become very difficult for
Government of India to insulate its economy from
World Economy. Government is no more the sole
driver of Indian Economy which is influenced more
and more by international policies and international
economic conditions [5][1]. Direction and depth of
all economic activities in India is now governed
largely by global Economy.
B. Globalization has completely eroded the spirit of
Swadeshi movement run by Father of the Nation,
Mahatma Gandhi. Large scale migrations from India
and easy availability of foreign products have
increased the exposure of Indian population to high
quality and reputed foreign products/brands. Indians
now prefer global brands over Indian brands.
Globalization has adversely affected many
established companies ( like organisations
manufacturing Ambassador cars or Fiat cars etc)
which had failed to face competition from
established global players.
C. Steep and fast reductions in custom duties have
snatched large part of Indian market from Indian
Industry and passed it on to imports from
established global players. New opportunities for
exports by Indian Industry opened up by
globalization are no comparison to the loss it has
suffered on account of reduction in demand of its
products in local market of one billion people.
D. For its survival in the face of global competition,
Indian industry has transformed itself from labour
intensive processes to Capital intensive processes by
adopting global technologies and automatic
IJISSHR
International Journal of Innovative Social Science & Humanities Research
machinery. This has resulted in high rate of
unemployment in India. Unemployment is the
biggest challenge for Indian Government today.
E. We can thus observe that Globalization does not
seem to have helped Indian Industry. We may call
globalization, at best, a double edged weapon. It has
helped Indian consumers to enjoy all high Quality
global brands. It did help Government of India to
tide over its serious foreign exchange problem,
though temporarily, by enabling it to get loan from
World Bank. But, it has been at the cost of serious
erosion of control of Indian Government over its
economy and at the cost of local Industry
Social Challenges
Improved
Economic
conditions,
increased
recognition of human rights, unprecedented mobility
and interaction of people from different countries
have dented local cultures of people the world over.
Transnational workforce and large scale immigrants,
a product of globalization, are dispersing different
cultures in various countries leading to a unified
world culture that consists of a mixture of various
regional cultures [2]. Global population is getting
closer to sharing similar social values, aspirations,
attitudes and life styles. Local culture, spiritual
practices and core social - values have been getting
reframed and a new meaning is being given to
human life. It is globalization and globalization alone,
which is responsible for changing peoples outlook
and life style [6]. To highlight the fact that our
established socio culture systems have been severely
affected, we examine here below some of the
changes in various established practices: Indian
society has always been a male dominated society.
Male members have been sole bread earners and
have been the sole face of family to outside world.
Women folk have been only managing the family
within four walls of their home. Globalization has
struck a fatal blow to this established practice. Today women are working in all spheres of Indian
Economy. They have challenged male domination in
all respects. To-day men are normally not free to
take any family decision without consent of women
folk. Indian joint family system has been appreciated
Vol (2), Issue-2,June-2015
ISSN: 2349-1876 (Print) | ISSN : 2454-1826 (Online)
world over for strong relationships which provided
support to everybody to face hard times and old age
periods. Western culture has given new meaning to
life to Indian youth [7]. They want to lead an
independent life. They are getting more and more
blunt in breaking relations with elders and in
building nuclear families. Old & handicapped
persons in the families are being forced to support
themselves without any support from their children.
These nuclear families are getting further divided
due to strained relations of partners or due to
displacement of one or the other partner to a far off
place in pursuit of his/her employment.
Earlier, well defined religious practices were being
blindly followed by one and all. But globalization has
now brought in the spirit of reasoning which has
weakened established practices. Secondly, work
place integration of different cultures has intermixed the religions practices. This way old age
religious practices which differentiated people from
different religions are getting blurred [8]. Earlier life
partners were searched from local areas and from
within their caste. Now inter-caste marriages i.e.
marriages within families with totally different social
systems are quite common. Majority of such
marriages are getting fructified either in the study
institutions or at their work place. Globalization has
thus greatly affected our social fabric. The shared
experience is giving new meaning to our life and is
leading to changes in our culture, religious practices
and spirituality. Gender-based dualistic enclaves are
particularly important to mention. Globalization has
widened the gap between the two enclaves. It may
be noted that women workers are mostly employed
in the unorganized sector. They may frequently be
found in vast numbers in the mining activities and
the export industries which earn the foreign
exchange to service the countrys external debt,
stitching garments, assembling electronic circuits,
cleaning shrimp, plucking tea, working at subsistence
or below-subsistence wages. Globalization, mostly
discriminating against the unorganized sector, has
pushed them farther to the margin (Hensman
(2001), Saptari (2001), Revolutionary Publications)
IJISSHR
International Journal of Innovative Social Science & Humanities Research
ISSN: 2349-1876 (Print) | ISSN : 2454-1826 (Online)
CONCLUSION
Globalization is not only useless but dangerous too
for Indian Economy. It gave temporary relief to
Indian Government to tide over its serious foreign
exchange situation during 1990-91 by enabling it to
get loan from World Bank. But, as a byproduct, it has
caused some permanent damage to Indian Economic
system and deep rooted Indian social structure.
References:
[5] Chander Sekhran Bal krishnana - Impact of
Globalization on developing countries and India
[6]. Pieterse, Jan N ( 2003)-Globalization and culture
[1]. C Rangarajan (2002)- Globalization and its
impact.
[2]. www.global policy.org / globalization- ofculture.html.
[3] Vijay Kumar Kaul Indias Diversity
Globalisation: Unifying Forces and Innovation
[4] Brittan (1998), Impact on globalisation on
developing countries, paper delivered at the Essa
conference at somerset west.
and
[7]. Ghosa, Biswajit (2011)-Cultural changes in era of
globalization.
[8]. V. Sundram -Impact of Globalization on Indian
Culture.
Copyright 2015 Dr.Richa Mishra. This is an open access refereed article distributed under the Creative Common
Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the
original work is properly cited.
6 | Vol (2), Issue-2,June-2015
IJISSHR
You might also like
- 30 Years of Doctoral Research on French CinemaDocument37 pages30 Years of Doctoral Research on French CinemaJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- The Cinema As Therapy: Psychoanalysis in The Work of Woody AllenDocument11 pagesThe Cinema As Therapy: Psychoanalysis in The Work of Woody AllenJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Wug15 Cinema PDF FinalDocument16 pagesWug15 Cinema PDF FinalJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Rise of Theatre in IndiaDocument5 pagesRise of Theatre in IndiaJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Films From The Couch Film Theory and PsychoanalysiDocument9 pagesFilms From The Couch Film Theory and PsychoanalysiJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Middlebrow Cinema by Women Directors in The 1990sDocument16 pagesMiddlebrow Cinema by Women Directors in The 1990sJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Review of Adam Parkes A Sense of Shock TDocument4 pagesReview of Adam Parkes A Sense of Shock TJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Play Analysis Elements - TheatreDocument3 pagesPlay Analysis Elements - TheatreJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis Film PDFDocument7 pagesPsychoanalysis Film PDFJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Reading A Film - On The Rality in The CinemaDocument0 pagesReading A Film - On The Rality in The CinemaragatasuryaNo ratings yet
- EngoDocument162 pagesEngoJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Semiotics of FilmsDocument7 pagesSemiotics of FilmsJanardhan Juvvigunta JJ100% (2)
- Language Press in India: Module - 2Document12 pagesLanguage Press in India: Module - 2manali_shahNo ratings yet
- The 50 Best Plays of The Past 100 Years - New York TheaterDocument3 pagesThe 50 Best Plays of The Past 100 Years - New York TheaterJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drama: TheatricalityDocument2 pagesThe Nature of Drama: TheatricalityJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- The Story of The Indian Press PDFDocument4 pagesThe Story of The Indian Press PDFJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and Social ChallengestDocument6 pagesGlobalisation and Social ChallengestJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and Increasing Poverty in Rural South India by Dr. TDocument3 pagesGlobalisation and Increasing Poverty in Rural South India by Dr. TJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Print MediaDocument9 pagesPrint MediaJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Indian Journalism-18th To 19th CenturyuDocument2 pagesIndian Journalism-18th To 19th CenturyuJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Privacy Issues and Internet PrivacyDocument23 pagesPrivacy Issues and Internet PrivacyJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Historical Growth of Indian PressDocument10 pagesHistorical Growth of Indian PressJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- How to Optimize Your Website for Search EnginesDocument7 pagesHow to Optimize Your Website for Search EnginesJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- World Cinema Beyond The Periphery - Developing Film Cultures in BDocument330 pagesWorld Cinema Beyond The Periphery - Developing Film Cultures in BJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Changing Face of The Indian PressDocument5 pagesChanging Face of The Indian PressJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Film ThemeDocument203 pagesAnalysis of Film ThemeJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Indian Culture and GlobalisationDocument51 pagesIndian Culture and GlobalisationJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- The Idea of Arranged-Marriages in India Then and NowDocument23 pagesThe Idea of Arranged-Marriages in India Then and NowJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and Rural DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGlobalisation and Rural DevelopmentJanardhan Juvvigunta JJNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ZXA10 F822 Datasheet: Interface Function Physical PerformanceDocument1 pageZXA10 F822 Datasheet: Interface Function Physical PerformanceyodreshNo ratings yet
- V Smilnak Supervisor Rec LetterDocument1 pageV Smilnak Supervisor Rec Letterapi-639559545No ratings yet
- Curiculum Vitae - STDocument3 pagesCuriculum Vitae - STSteven ThoramNo ratings yet
- Patriarchy Article PublishedDocument3 pagesPatriarchy Article PublishedShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- Adding Fling Effects To Processed Ground-Motion Time HistoriesDocument17 pagesAdding Fling Effects To Processed Ground-Motion Time HistoriesPatrick CanceranNo ratings yet
- Airport Light Bases and Transformer HousingsDocument10 pagesAirport Light Bases and Transformer Housingsgiant360No ratings yet
- Health Service Management Lecture Note Jimma University PDFDocument10 pagesHealth Service Management Lecture Note Jimma University PDFDemeke DemlewNo ratings yet
- Items FileDocument139 pagesItems FileKzyl Joy CeloricoNo ratings yet
- ISUZU - Manual Common Rail Motor Isuzu 6DE1-1 PDFDocument35 pagesISUZU - Manual Common Rail Motor Isuzu 6DE1-1 PDFAngelNo ratings yet
- قرآن و سنت کی روشنی میں مسلم خواتین کا لباسDocument8 pagesقرآن و سنت کی روشنی میں مسلم خواتین کا لباسKhalil-Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Cause by RainDocument15 pagesDisaster Cause by RainUNCLE STATIONARYNo ratings yet
- Garden High School: Annual Examination, 2010 - 11Document4 pagesGarden High School: Annual Examination, 2010 - 11kkundu_2010No ratings yet
- Kinase InhibitorDocument85 pagesKinase InhibitorSowjanya NekuriNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: B. Sc. Computer ScienceDocument79 pagesSyllabus: B. Sc. Computer Scienceapi-545722857No ratings yet
- Ranking Metrics (2020-2024) BatchDocument3 pagesRanking Metrics (2020-2024) BatchPIYUSH GOPAL (RA2011027010124)No ratings yet
- OP 1 ReferenceDocument37 pagesOP 1 ReferenceChadwick Perry100% (2)
- MinimaxDocument10 pagesMinimaxRitesh Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- LNL Iklcqd /: Grand Total 11,109 7,230 5,621 1,379 6,893Document2 pagesLNL Iklcqd /: Grand Total 11,109 7,230 5,621 1,379 6,893Dawood KhanNo ratings yet
- VR10 Radar Installation and Functions GuideDocument24 pagesVR10 Radar Installation and Functions GuideKingsley AsanteNo ratings yet
- The York Pageant WagonDocument21 pagesThe York Pageant WagonPilar Marcos AmoNo ratings yet
- PKM - Quiz 3 - VlanDocument6 pagesPKM - Quiz 3 - VlanGodFather23No ratings yet
- Kaplan Turbine Is A Type ofDocument12 pagesKaplan Turbine Is A Type ofRaunak PrustyNo ratings yet
- Six Major Schools of Thought in PsychologyDocument2 pagesSix Major Schools of Thought in PsychologyAnonymous 4qEPpyx100% (1)
- Manual de Interlock ELEKTADocument448 pagesManual de Interlock ELEKTANicolas RonchiNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Specification and Qualification of Welding Procedures For Metallic Materials - General RulesDocument8 pagesInternational Standard: Specification and Qualification of Welding Procedures For Metallic Materials - General RulesRudi DaNo ratings yet
- What is a Bull Trap? Detecting False BreakoutsDocument2 pagesWhat is a Bull Trap? Detecting False BreakoutsAli Abdelfatah MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Aliasing PDFDocument11 pagesAliasing PDFGiannis GkouzionisNo ratings yet
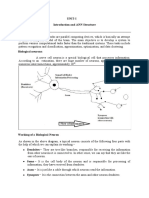
- Unit-I Introduction and ANN StructureDocument15 pagesUnit-I Introduction and ANN StructurebhavyaNo ratings yet
- First Grade Verb Worksheet Blanks2Document1 pageFirst Grade Verb Worksheet Blanks2Corina LupsaNo ratings yet
- 6241Document17 pages6241miltodiavoloNo ratings yet