Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11
Uploaded by
susana_montero_50 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pages11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document11
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pages11
Uploaded by
susana_montero_511
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Table of Contents
Preface....................................................................................................................... xi
Introduction ............................................................................................................ xiii
List of Main Symbols..............................................................................................xxiii
Chapter 1. A One-Dimensional Beam Metamodel................................................ 1
1.1. Models and metamodel .............................................................................. 2
1.2. Internally unconstrained beams.................................................................. 3
1.2.1. Kinematics.......................................................................................... 3
1.2.2. Dynamics............................................................................................ 5
1.2.3. The hyperelastic law........................................................................... 9
1.2.4. The Fundamental Problem .............................................................. 11
1.3. Internally constrained beams.................................................................... 12
1.3.1. The mixed formulation for the internally constrained beam . . . .
kinematics and constraints................................................................. 13
1.3.2. The displacement method for the internally constrained beam . . 18
1.4. Internally unconstrained prestressed beams.............................................. 24
1.4.1. The nonlinear theory........................................................................ 25
1.4.2. The linearized theory ....................................................................... 26
1.5. Internally constrained prestressed beams.................................................. 29
1.5.1. The nonlinear mixed formulation..................................................... 29
1.5.2. The linearized mixed formulation.................................................... 30
1.5.3. The nonlinear displacement formulation.......................................... 31
Table of Contents
1.6. The linearized displacement formulation...... 32The variational formulation
33
1.6.1. The total potential energy principle............................................. 34
1.6.2. Unconstrained beams........................................................................ 36
1.6.3. Constrained beams............................................................................ 37
1.6.4. Unconstrained prestressed beams..................................................... 39
1.6.5. Constrained prestressed beams......................................................... 41
1.7. Example: the linear Timoshenko beam................................................ 44
1.8. Summary................................................................................................... 47
Chapter 2. Straight Beams....................................................................................... 55
2.1. Kinematics................................................................................................ 55
2.1.1. The displacement and rotation fields........................................... 55
2.1.2. Tackling the rotation tensor.............................................................. 60
2.1.3. The geometric boundary conditions................................................. 63
2.1.4. The strain vector............................................................................... 64
2.1.5. The curvature vector......................................................................... 68
2.1.6. The strain-displacement relationships.............................................. 73
2.1.7. The velocity and spin fields............................................................. 74
2.1.8. The velocity gradients and strain-rates ............................................ 78
2.2. Dynamics.................................................................................................. 82
2.2.1. The bedance of virtual powers..................................................... 83
2.2.2. The inertial contributions................................................................. 88
2.2.3. The bidance of momentum............................................................... 91
2.2.4. The scalar forms of the balance equations...................................
and boundary conditions.................................................................... 97
2.2.5. The Lagrangian balance equations................................................... 99
2.3. Constitutive law...................................................................................... 102
2.3.1. The hyperelastic law ...................................................................... 102
2.3.2. Identification of the elastic law from a 3D-model....................... 104
2.3.3. Homogenization of beam-like structures....................................... 110
2.3.4. Linear viscoelastic laws.................................................................. 112
2.4. The Fundamental Problem ...................................................................... 114
2.4.1. Exact equations............................................................................... 115
2.4.2. The linearized theory for elastic prestressed beams........................ 118
2.5. The planar beam....................................................................................... 122
2.5.1. Kinematics....................................................................................... 122
2.5.2. Dynamics......................................................................................... 124
2.5.3. The Virtual Power Principle........................................................... 126
2.5.4. Constitutive laws............................................................................. 127
2.5.5. The Fundamental Problem ............................................................. 127
2.6. Summary.................................................................................................. 129
Chapter 3. Curved Beams ................................................................................... 133
3.1. The reference configuration and the initial curvature.......................... 133
4 Mathematical Models of Beams and Cables
3.2. The beam model in the 3D-space......................................................... 137
3.2.1. Kinematics...................................................................................... 137
3.2.2. Dynamics........................................................................................ 142
3.2.3. The elastic law................................................................................ 144
3.2.4. The Fundamental Problem ............................................................ 144
3.3. The planar curved beam....................................................................... 152
3.3.1. Kinematics...................................................................................... 153
3.3.2. Dynamics........................................................................................ 155
3.3.3. The Virtual Power Principle........................................................... 157
3.3.4. Constitutive law ............................................................................. 157
3.3.5. Fundamental Problem..................................................................... 158
3.4. Summary................................................................................................. 160
Chapter 4. Internally Constrained Beams............................................................ 163
4.1. Stiff beams and internal constraints .................................................... 163
4.2. The general approach .......................................................................... 166
4.3. The unshearable straight beam in 3D................................................... 168
4.3.1. The mixed formulation ............................................................... 169
4.3.2. The displacement formulation ....................................................... 172
4.4. The unshearable straight planar beam.................................................. 177
4.5. The inextensible and unshearable straight beam in 3D........................ 180
4.5.1. Hybrid formulation: Version I .................................................... 181
4.5.2. Hybrid formulation: Version II....................................................... 182
4.6. The inextensible and unshearable straight planar beam....................... 183
4.6.1. Hybrid formulation: Version I .................................................... 183
4.6.2. Hybrid formulation: Version II....................................................... 185
4.6.3. The mixed formulation .................................................................. 186
4.6.4. The direct condensation of the elastica equilibrium equations . . . 188
4.7. The inextensible, unshearable and untwistable straight beam............. 190
4.8. The foil-beam.......................................................................................... 192
4.9. The shear-shear-torsional beam.............................................................. 193
4.10. The planar unshearable and inextensible curved beam...................... 197
4.10.1. The hybrid formulation................................................................ 197
4.10.2. The mixed formulation................................................................. 200
4.11. Summary............................................................................................... 201
Chapter 5. Flexible Cables..................................................................................... 205
5.1. Flexible cables as a limit of slender beams............................................. 205
5.2. Unprestressed cables............................................................................... 207
5.2.1. Kinematics...................................................................................... 207
5.2.2. Dynamics........................................................................................ 213
5.2.3. Constitutive law ............................................................................. 217
5.2.4. The Fundamental Problem ............................................................ 218
5.3. Prestressed cables ................................................................................... 220
Table of Contents
5.3.1. Quasi-exact models ....................................................................... 220
5.3.2. The hnearized theory ..................................................................... 225
5.3.3. Taut strings..................................................................................... 227
5.4. Shallow cables........................................................................................ 230
5.4.1. An approximated nonlinear model................................................. 231
5.4.2. An approximated linearized model................................................ 234
5.5. Inextensible cables.................................................................................. 235
5.5.1. Inextensible unprestressed cables................................................... 236
5.5.2. Inextensible prestressed cables....................................................... 237
5.6. Summary................................................................................................. 240
Chapter 6. Stiff Cables .......................................................................................... 243
6.1. Motivations............................................................................................. 243
6.2. Unprestressed stiff cables........................................................................ 246
6.2.1. Kinematics...................................................................................... 246
6.2.2. Dynamics........................................................................................ 249
6.2.3. The elastic law................................................................................ 251
6.2.4. The Fundamental Problem ............................................................ 251
6.3. Prestressed stiff cables............................................................................ 252
6.3.1. Nonlinear model............................................................................. 253
6.3.2. The hnearized model...................................................................... 256
6.3.3. Taut strings..................................................................................... 258
6.4. Reduced models...................................................................................... 261
6.4.1. Sagged cables................................................................................. 261
6.4.2. Shallow cables................................................................................ 263
6.5. Inextensible stiff cables........................................................................... 264
6.5.1. Unprestressed cables...................................................................... 265
6.5.2. Prestressed cables .......................................................................... 266
6.5.3. Reduced model............................................................................... 268
6.6. Summary................................................................................................. 269
Chapter 7. Locally-Deformable Thin- Walled Beams .......................................... 271
7.1. Motivations............................................................................................. 271
7.2. A one-dimensional direct model for double-symmetric TWB................ 273
7.3. A one-dimensional direct model for non-symmetric TWB.................... 277
7.4. Identification strategy from 3D-models of TWB ................................... 284
7.5. A fiber-model of TWB............................................................................ 285
7.6. Warpable, cross-undeformable TWB...................................................... 289
7.6.1. Kinematics...................................................................................... 289
6 Mathematical Models of Beams and Cables
7.6.2. Identification procedure................................................................. 293
7.6.3. The Fundamental Problem ............................................................ 299
7.7. Unwarpable, cross-deformable, planar TWB ...................................... 299
7.7.1. Kinematics...................................................................................... 300
7.7.2. Identification procedure................................................................. 303
7.7.3. The Fundamental Problem ............................................................ 307
7.8. Summary................................................................................................. 308
Chapter 8. Distortion-Constrained Thin-Walled Beams ....................................... 311
8.1. Introduction............................................................................................. 311
8.2. Internal constraints.................................................................................. 312
8.2.1. The Vlasov constraint for open TWB ......................................... 312
8.2.2. The Bredt constraint for tubular TWB........................................... 314
8.2.3......................................................................................................... The
Brazier constraint for planar TWB ......................................................... 316
8.3. The non-uniform torsion problem for bi-symmetric cross-sections ... 317
8.3.1. The unconstrained model............................................................... 317
8.3.2. The mixed formulation for the constrained model...................... 319
8.3.3. The displacement formulation for the constrained model........... 323
8.4. The general problem for warpable TWB................................................ 324
8.5. Cross-deformable planar TWB............................................................... 328
8.6. Summary................................................................................................. 332
Bibliography .......................................................................................................... 335
Index
345
You might also like
- KDocument20 pagesKsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Element Forces - Beams TableDocument225 pagesElement Forces - Beams Tablesusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Element Forces - Beams TableDocument225 pagesElement Forces - Beams Tablesusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- (Asce) 0733-9445 (1984) 110 5 (1021)Document14 pages(Asce) 0733-9445 (1984) 110 5 (1021)susana_montero_5No ratings yet
- GM SH 123456Document426 pagesGM SH 123456susana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Element Forces - Beams TableDocument225 pagesElement Forces - Beams Tablesusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Muro HC-PredimensionamientoDocument1 pageMuro HC-Predimensionamientosusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Porcentajes de Participación de MasaDocument1 pagePorcentajes de Participación de Masasusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Structural Column ScheduleDocument2 pagesStructural Column Schedulesusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- EC2 DesignDocument62 pagesEC2 Designmihaitimofte100% (1)
- Precio PDFDocument1 pagePrecio PDFsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Wall Quantities by AssemblyDocument1 pageWall Quantities by Assemblysusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- I Love Everything About YouDocument3 pagesI Love Everything About Yoususana_montero_5No ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1susana_montero_5No ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument2 pagesExamplessusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- InstallDocument1 pageInstallsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Structural Beams & Bracing QuantitiesDocument5 pagesStructural Beams & Bracing Quantitiessusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- C3 TraduccionDocument68 pagesC3 Traduccionsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- FprintDocument8 pagesFprintsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- PPPDocument2 pagesPPPsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Impri MirDocument6 pagesImpri Mirsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Mario Paz & William Leigh - Integrated Matrix Analysis of StructuralDocument334 pagesMario Paz & William Leigh - Integrated Matrix Analysis of Structuralkevin arnoldNo ratings yet
- C3 TraduccionDocument68 pagesC3 Traduccionsusana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Indice AISC Design Examples V13 - 1Document8 pagesIndice AISC Design Examples V13 - 1susana_montero_5100% (1)
- Traducir 01Document14 pagesTraducir 01susana_montero_5No ratings yet
- Practical C Charts and Graphics - 9780979372506Document571 pagesPractical C Charts and Graphics - 9780979372506enikő_ferenc_1100% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Printable Collection of Bode Plot Web PagesDocument48 pagesPrintable Collection of Bode Plot Web PagesThan HtetNo ratings yet
- Economics and Optimization TechniquesDocument163 pagesEconomics and Optimization TechniquesKiran KuppaNo ratings yet
- FloresAlejandro Exercise1Document10 pagesFloresAlejandro Exercise1kero92No ratings yet
- 5 CATapult Courseware Module 2 - Practice Exercise SolutionsDocument124 pages5 CATapult Courseware Module 2 - Practice Exercise SolutionsLakshit ShahNo ratings yet
- BS Unit 2Document24 pagesBS Unit 2Sherona ReidNo ratings yet
- Wakissha Mock 1 2016Document3 pagesWakissha Mock 1 2016Kwomu JosephNo ratings yet
- Electomagnetictheory Maxwell Equations & Electromagnetic WavesDocument31 pagesElectomagnetictheory Maxwell Equations & Electromagnetic WavesAyush kumar joshiNo ratings yet
- Mit Micro Economics LectureDocument9 pagesMit Micro Economics LectureAnushka ShettyNo ratings yet
- Wavefunctions and Probability DensitiesDocument6 pagesWavefunctions and Probability Densities張湧浩100% (1)
- Set TheoryDocument20 pagesSet TheoryAbdulmejidAyalewNo ratings yet
- Matrix and Plot Functions TutorialDocument4 pagesMatrix and Plot Functions TutorialAjitYadavNo ratings yet
- IGCSE (9-1) Mathematics & Further Mathematics Topic BreakdownDocument4 pagesIGCSE (9-1) Mathematics & Further Mathematics Topic BreakdownabrarjayNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central Tendency PDFDocument47 pagesMeasure of Central Tendency PDFAbdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Runge KuttaDocument3 pagesRunge KuttaAllen Jerry Aries100% (1)
- h03 Essential MathDocument13 pagesh03 Essential Mathakyadav123No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme June 2007 6665 Core Mathematics C3Document8 pagesMark Scheme June 2007 6665 Core Mathematics C3AhmedNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Opeartion ResearchDocument1 pageFinal Exam Opeartion ResearchAllen CostNo ratings yet
- A Method For Solving Quadratic Programming Problems Having Linearly Factorized Objective FunctionDocument5 pagesA Method For Solving Quadratic Programming Problems Having Linearly Factorized Objective FunctionIJMERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document69 pagesChapter 10Trần Thái ThuậnNo ratings yet
- Laplace QB - DSEDocument1 pageLaplace QB - DSEmirek22938No ratings yet
- Caie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Document19 pagesCaie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Nat Gari100% (2)
- IC 2217 Nonlinear Control Systems (NCS) - Course Plan PDFDocument2 pagesIC 2217 Nonlinear Control Systems (NCS) - Course Plan PDFSaiKiranHegdeNo ratings yet
- FibonacciDocument15 pagesFibonacciMonirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - BismathDocument7 pagesCourse Outline - BismathGhazi AzhariNo ratings yet
- Dirichlet'S Theorem and Applications: Opencommons@UconnDocument73 pagesDirichlet'S Theorem and Applications: Opencommons@Uconnalok pradhanNo ratings yet
- TS JUNIOR INTER MATHS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS 2022-23Document7 pagesTS JUNIOR INTER MATHS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS 2022-23Priya BhavanaNo ratings yet
- Nucl - Phys.B v.669Document477 pagesNucl - Phys.B v.669buddy72No ratings yet
- Response SpectrukmDocument24 pagesResponse SpectrukmpreranagannaNo ratings yet
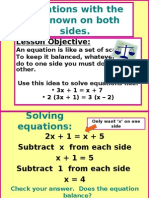
- Equations With Unknown On Both SidesDocument10 pagesEquations With Unknown On Both SidessaaimanmNo ratings yet
- Cake Design and Packaging Polynomial FunctionsDocument2 pagesCake Design and Packaging Polynomial FunctionsMaria Niña Rojas100% (1)