Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Appendicitis - Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy
Uploaded by
Yehuda Agus SantosoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendicitis - Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy
Uploaded by
Yehuda Agus SantosoCopyright:
Available Formats
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
Appendicitis
Author:SandyCraig,MDChiefEditor:BarryEBrenner,MD,PhD,FACEPmore...
Updated:Dec27,2015
PracticeEssentials
Appendicitisisdefinedasaninflammationoftheinnerliningofthevermiform
appendixthatspreadstoitsotherparts.Despitediagnosticandtherapeutic
advancementinmedicine,appendicitisremainsaclinicalemergencyandisoneof
themorecommoncausesofacuteabdominalpain.Seetheimagebelow.
Transversegradedcompressiontransabdominalsonogramofanacutelyinflamedappendix.
Notethetargetlikeappearanceduetothickenedwallandsurroundingloculatedfluidcollection.
SeeAppendicitis:AvoidingPitfallsinDiagnosis,aCriticalImagesslideshow,to
helpmakeanaccuratediagnosis.
Also,seetheCan'tMissGastrointestinalDiagnosesslideshowtohelpdiagnosethe
potentiallylifethreateningconditionsthatpresentwithgastrointestinalsymptoms.
Essentialupdate:Newscreeningalgorithmforpediatricappendicitis
mayreduceCTuse
Anewalgorithmforscreeningpediatricpatients(18y)withsuspectedappendicitis
appearstoreducetheuseofcomputedtomography(CT)scanningwithoutaffecting
diagnosticaccuracy. [1,2]Thistoolalsohasimplicationsforreducingthelevelsof
radiationexposureandthecostofusingthisimagingmodality.Thealgorithm
includespediatricsurgeryconsultationwithoutimagingstudiesinpatientswithan
unequivocalhistoryforthosewithanequivocalhistory,physicalexamination,and
ultrasonographicfindings,thealgorithmincludesconsultationandphysical
examinationbeforeobtainingCTstudies. [2]
Investigatorsanalyzeddatafrom331pediatricpatientswithsuspectedappendicitis
2yearsbefore(41%n=136)and3yearsafter(59%n=195)implementationof
thenewalgorithmandfoundasignificantdecreaseintheuseofCTscanningfrom
39%to18%,respectively. [1,2]Moreover,althoughthenegativeappendectomyrate
rosefrom9%preimplementationofthealgorithmto11%postimplementation,this
increasewasnotsignificantandtherewasnoassociationbetweennegative
appendectomyandCTscanutilization. [1,2]
Signsandsymptoms
Theclinicalpresentationofappendicitisisnotoriouslyinconsistent.Theclassic
historyofanorexiaandperiumbilicalpainfollowedbynausea,rightlowerquadrant
(RLQ)pain,andvomitingoccursinonly50%ofcases.Featuresincludethe
following:
Abdominalpain:Mostcommonsymptom
Nausea:6192%ofpatients
Anorexia:7478%ofpatients
Vomiting:Nearlyalwaysfollowstheonsetofpainvomitingthatprecedes
painsuggestsintestinalobstruction
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
1/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
Diarrheaorconstipation:Asmanyas18%ofpatients
Featuresoftheabdominalpainareasfollows:
Typicallybeginsasperiumbilicalorepigastricpain,thenmigratestotheRLQ
[3]
Patientsusuallyliedown,flextheirhips,anddrawtheirkneesuptoreduce
movementsandtoavoidworseningtheirpain
Thedurationofsymptomsislessthan48hoursinapproximately80%of
adultsbuttendstobelongerinelderlypersonsandinthosewithperforation.
Physicalexaminationfindingsincludethefollowing:
Reboundtenderness,painonpercussion,rigidity,andguarding:Most
specificfinding
RLQtenderness:Presentin96%ofpatients,butnonspecific
Leftlowerquadrant(LLQ)tenderness:Maybethemajormanifestationin
patientswithsitusinversusorinpatientswithalengthyappendixthat
extendsintotheLLQ
Maleinfantsandchildrenoccasionallypresentwithaninflamedhemiscrotum
Inpregnantwomen,RLQpainandtendernessdominateinthefirst
trimester,butinthelatterhalfofpregnancy,rightupperquadrant(RUQ)or
rightflankpainmayoccur
Thefollowingaccessorysignsmaybepresentinaminorityofpatients:
Rovsingsign(RLQpainwithpalpationoftheLLQ):Suggestsperitoneal
irritation
Obturatorsign(RLQpainwithinternalandexternalrotationoftheflexed
righthip):Suggeststheinflamedappendixislocateddeepintheright
hemipelvis
Psoassign(RLQpainwithextensionoftherighthiporwithflexionofthe
righthipagainstresistance):Suggeststhataninflamedappendixislocated
alongthecourseoftherightpsoasmuscle
Dunphysign(sharppainintheRLQelicitedbyavoluntarycough):Suggests
localizedperitonitis
RLQpaininresponsetopercussionofaremotequadrantoftheabdomenor
tofirmpercussionofthepatient'sheel:Suggestsperitonealinflammation
Marklesign(painelicitedinacertainareaoftheabdomenwhenthe
standingpatientdropsfromstandingontoestotheheelswithajarring
landing):Hasasensitivityof74% [4]
SeeClinicalPresentationformoredetail.
Diagnosis
Thefollowinglaboratorytestsdonothavefindingsspecificforappendicitis,butthey
maybehelpfultoconfirmdiagnosisinpatientswithanatypicalpresentation:
CBC
Creactiveprotein(CRP)
Liverandpancreaticfunctiontests
Urinalysis(fordifferentiatingappendicitisfromurinarytractconditions)
UrinarybetahCG(fordifferentiatingappendicitisfromearlyectopic
pregnancyinwomenofchildbearingage)
Urinary5hydroxyindoleaceticacid(5HIAA)
CBC
WBC>10,500cells/L:8085%ofadultswithappendicitis
Neutrophilia>7578%ofpatients
Lessthan4%ofpatientswithappendicitishaveaWBCcountlessthan
10,500cells/Landneutrophilialessthan75%
Ininfantsandelderlypatients,aWBCcountisespeciallyunreliablebecausethese
patientsmaynotmountanormalresponsetoinfection.Inpregnantwomen,the
physiologicleukocytosisrenderstheCBCcountuselessforthediagnosisof
appendicitis.
Creactiveprotein
CRPlevels>1mg/dLarecommoninpatientswithappendicitis
VeryhighlevelsofCRPinpatientswithappendicitisindicategangrenous
evolutionofthedisease,especiallyifitisassociatedwithleukocytosisand
neutrophilia
Inadultswhohavehadsymptomsforlongerthan24hours,anormalCRP
levelhasanegativepredictivevalueof97100%forappendicitis [5,6,7]
Urinary5HIAA
HIAAlevelsincreasesignificantlyinacuteappendicitisanddecreasewhenthe
inflammationshiftstonecrosisoftheappendix. [8]Therefore,suchdecreasecould
beanearlywarningsignofperforationoftheappendix.
CTscanning
CTscanningwithoralcontrastmediumorrectalGastrografinenemahas
becomethemostimportantimagingstudyintheevaluationofpatientswith
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
2/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
atypicalpresentationsofappendicitis
LowdoseabdominalCTmaybepreferablefordiagnosingchildrenand
youngadultsinwhomexposuretoCTradiationisofparticularconcern [9]
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonographymayofferasaferalternativeasaprimarydiagnostictoolfor
appendicitis,withCTscanningusedinthosecasesinwhichultrasonograms
arenegativeorinconclusive
Inpediatricpatients,AmericanCollegeofEmergencyPhysicians(ACEP)
clinicalpolicyrecommendsultrasonographyforconfirmation,butnot
exclusion,ofacuteappendicitistodefinitivelyexcludeacuteappendicitis,
theACEPrecommendsCT [10,11]
Ahealthyappendixusuallycannotbeviewedwithultrasonographywhen
appendicitisoccurs,theultrasonogramtypicallydemonstratesa
noncompressibletubularstructureof79mmindiameter
Vaginalultrasonographyaloneorincombinationwithtransabdominalscan
maybeusefultodeterminethediagnosisinwomenofchildbearingage [12]
Otherimagingstudies
Kidneysuretersbladderradiographs:Insensitive,nonspecific,andnotcost
effective
Bariumenemastudy:Hasessentiallynoroleinthediagnosisofacute
appendicitis
Radionuclidescanning:LocalizeduptakeoftracerintheRLQsuggests
appendicealinflammation
MRI:Usefulinpregnantpatientsifgradedcompressionultrasonographyis
nondiagnostic
SeeWorkupformoredetail.
Management
Emergencydepartmentcareisasfollows:
EstablishIVaccessandadministeraggressivecrystalloidtherapytopatients
withclinicalsignsofdehydrationorsepticemia
KeeppatientswithsuspectedappendicitisNPO
Administerparenteralanalgesicandantiemeticasneededforpatient
comfortnostudyhasshownthatanalgesicsadverselyaffecttheaccuracyof
physicalexamination [13]
Appendectomyremainstheonlycurativetreatmentofappendicitis,but
managementofpatientswithanappendicealmasscanusuallybedividedintothe
following3treatmentcategories:
Phlegmonorasmallabscess:AfterIVantibiotictherapy,aninterval
appendectomycanbeperformed46weekslater
Largerwelldefinedabscess:AfterpercutaneousdrainagewithIVantibiotics
isperformed,thepatientcanbedischargedwiththecatheterinplace
intervalappendectomycanbeperformedafterthefistulaisclosed
Multicompartmentalabscess:Thesepatientsrequireearlysurgicaldrainage
Antibiotics
Antibioticprophylaxisshouldbeadministeredbeforeeveryappendectomy
Preoperativeantibioticsshouldbeadministeredinconjunctionwiththe
surgicalconsultant
Broadspectrumgramnegativeandanaerobiccoverageisindicated
Cefotetanandcefoxitinseemtobethebestchoicesofantibiotics
Inpenicillinallergicpatients,carbapenemsareagoodoption
PregnantpatientsshouldreceivepregnancycategoryAorBantibiotics
Antibiotictreatmentmaybestoppedwhenthepatientbecomesafebrileand
theWBCcountnormalizes
SeeTreatmentandMedicationformoredetail.
Background
Appendicitisisdefinedasaninflammationoftheinnerliningofthevermiform
appendixthatspreadstoitsotherparts.Thisconditionisacommonandurgent
surgicalillnesswithproteanmanifestations,generousoverlapwithotherclinical
syndromes,andsignificantmorbidity,whichincreaseswithdiagnosticdelay(see
ClinicalPresentation).Infact,despitediagnosticandtherapeuticadvancementin
medicine,appendicitisremainsaclinicalemergencyandisoneofthemore
commoncausesofacuteabdominalpain.
Nosinglesign,symptom,ordiagnostictestaccuratelyconfirmsthediagnosisof
appendicealinflammationinallcases,andtheclassichistoryofanorexiaand
periumbilicalpainfollowedbynausea,rightlowerquadrant(RLQ)pain,and
vomitingoccursinonly50%ofcases(seeClinicalPresentation).
Appendicitismayoccurforseveralreasons,suchasaninfectionoftheappendix,
butthemostimportantfactoristheobstructionoftheappendiceallumen(see
PathogenesisandEtiology).Leftuntreated,appendicitishasthepotentialforsevere
complications,includingperforationorsepsis,andmayevencausedeath(see
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
3/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
PrognosisandComplications).However,thedifferentialdiagnosisofappendicitisis
oftenaclinicalchallengebecauseappendicitiscanmimicseveralabdominal
conditions(seeDiagnosticConsiderationsandDifferentials). [14]
Appendectomyremainstheonlycurativetreatmentofappendicitis(seeTreatment
andManagement).Thesurgeon'sgoalsaretoevaluatearelativelysmallpopulation
ofpatientsreferredforsuspectedappendicitisandtominimizethenegative
appendectomyratewithoutincreasingtheincidenceofperforation.Theemergency
department(ED)clinicianmustevaluatethelargergroupofpatientswhopresentto
theEDwithabdominalpainofalletiologieswiththegoalofapproaching100%
sensitivityforthediagnosisinatime,cost,andconsultationefficientmanner.
GotoPediatricAppendicitisformoreinformationonthistopic.
Anatomy
Theappendixisawormlikeextensionofthececumand,forthisreason,hasbeen
calledthevermiformappendix.Theaveragelengthoftheappendixis810cm
(rangingfrom220cm).Theappendixappearsduringthefifthmonthofgestation,
andseverallymphoidfolliclesarescatteredinitsmucosa.Suchfolliclesincreasein
numberwhenindividualsareaged820years.Anormalappendixisseenbelow.
Normalappendixbariumenemaradiographicexamination.Acompletecontrastfilledappendix
isobserved(arrows),whicheffectivelyexcludesthediagnosisofappendicitis.
Theappendixiscontainedwithinthevisceralperitoneumthatformstheserosa,and
itsexteriorlayerislongitudinalandderivedfromthetaeniacolithedeeper,interior
musclelayeriscircular.Beneaththeselayersliesthesubmucosallayer,which
containslymphoepithelialtissue.Themucosaconsistsofcolumnarepitheliumwith
fewglandularelementsandneuroendocrineargentaffincells.
Taeniacoliconvergeontheposteromedialareaofthececum,whichisthesiteof
theappendicealbase.Theappendixrunsintoaserosalsheetoftheperitoneum
calledthemesoappendix,withinwhichcoursestheappendicularartery,whichis
derivedfromtheileocolicartery.Sometimes,anaccessoryappendicularartery
(derivingfromtheposteriorcecalartery)maybefound.
Appendicealvasculature
Thevasculatureoftheappendixmustbeaddressedtoavoidintraoperative
hemorrhages.Theappendiculararteryiscontainedwithinthemesentericfoldthat
arisesfromaperitonealextensionfromtheterminalileumtothemedialaspectof
thececumandappendixitisaterminalbranchoftheileocolicarteryandruns
adjacenttotheappendicularwall.Venousdrainageisviatheileocolicveinsandthe
rightcolicveinintotheportalveinlymphaticdrainageoccursviatheileocolicnodes
alongthecourseofthesuperiormesentericarterytotheceliacnodesandcisterna
chyli.
Appendiceallocation
Theappendixhasnofixedposition.Itoriginates1.72.5cmbelowtheterminal
ileum,eitherinadorsomediallocation(mostcommon)fromthececalfundus,
directlybesidetheilealorifice,orasafunnelshapedopening(23%ofpatients).
Theappendixhasaretroperitoneallocationin65%ofpatientsandmaydescend
intotheiliacfossain31%.Infact,manyindividualsmayhaveanappendixlocated
intheretroperitonealspaceinthepelvisorbehindtheterminalileum,cecum,
ascendingcolon,orliver.Thus,thecourseoftheappendix,thepositionofitstip,
andthedifferenceinappendicealpositionconsiderablychangesclinicalfindings,
accountingforthenonspecificsignsandsymptomsofappendicitis.
Congenitalappendicealdisorders
Appendicealcongenitaldisordersareextremelyrarebutoccasionallyreported(eg,
agenesis,duplication,triplication).
Pathophysiology
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
4/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
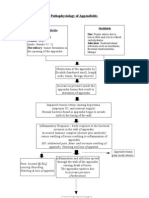
Reportedly,appendicitisiscausedbyobstructionoftheappendiceallumenfroma
varietyofcauses(seeEtiology).Independentoftheetiology,obstructionisbelieved
tocauseanincreaseinpressurewithinthelumen.Suchanincreaseisrelatedto
continuoussecretionoffluidsandmucusfromthemucosaandthestagnationof
thismaterial.Atthesametime,intestinalbacteriawithintheappendixmultiply,
leadingtotherecruitmentofwhitebloodcells(seetheimagebelow)andthe
formationofpusandsubsequenthigherintraluminalpressure.
Technetium99mradionuclidescanoftheabdomenshowsfocaluptakeoflabeledWBCsinthe
rightlowerquadrantconsistentwithacuteappendicitis.
Ifappendicealobstructionpersists,intraluminalpressurerisesultimatelyabovethat
oftheappendicealveins,leadingtovenousoutflowobstruction.Asaconsequence,
appendicealwallischemiabegins,resultinginalossofepithelialintegrityand
allowingbacterialinvasionoftheappendicealwall.
Withinafewhours,thislocalizedconditionmayworsenbecauseofthrombosisof
theappendiculararteryandveins,leadingtoperforationandgangreneofthe
appendix.Asthisprocesscontinues,aperiappendicularabscessorperitonitismay
occur.
Etiology
Appendicitisiscausedbyobstructionoftheappendiceallumen.Themostcommon
causesofluminalobstructionincludelymphoidhyperplasiasecondaryto
inflammatoryboweldisease(IBD)orinfections(morecommonduringchildhoodand
inyoungadults),fecalstasisandfecaliths(morecommoninelderlypatients),
parasites(especiallyinEasterncountries),or,morerarely,foreignbodiesand
neoplasms.
Fecalithsformwhencalciumsaltsandfecaldebrisbecomelayeredaroundanidus
ofinspissatedfecalmateriallocatedwithintheappendix.Lymphoidhyperplasiais
associatedwithvariousinflammatoryandinfectiousdisordersincludingCrohn
disease,gastroenteritis,amebiasis,respiratoryinfections,measles,and
mononucleosis.
Obstructionoftheappendiceallumenhaslesscommonlybeenassociatedwith
bacteria(Yersiniaspecies,adenovirus,cytomegalovirus,actinomycosis,
Mycobacteriaspecies,Histoplasmaspecies),parasites(eg,Schistosomesspecies,
pinworms,Strongyloidesstercoralis),foreignmaterial(eg,shotgunpellet,
intrauterinedevice,tonguestud,activatedcharcoal),tuberculosis,andtumors.
Epidemiology
Appendicitisisoneofthemorecommonsurgicalemergencies,anditisoneofthe
mostcommoncausesofabdominalpain.IntheUnitedStates,250,000casesof
appendicitisarereportedannually,representing1millionpatientdaysofadmission.
Theincidenceofacuteappendicitishasbeendecliningsteadilysincethelate
1940s,andthecurrentannualincidenceis10casesper100,000population.
Appendicitisoccursin7%oftheUSpopulation,withanincidenceof1.1casesper
1000peopleperyear.Somefamilialpredispositionexists.
InAsianandAfricancountries,theincidenceofacuteappendicitisisprobablylower
becauseofthedietaryhabitsoftheinhabitantsofthesegeographicareas.The
incidenceofappendicitisislowerincultureswithahigherintakeofdietaryfiber.
Dietaryfiberisthoughttodecreasetheviscosityoffeces,decreaseboweltransit
time,anddiscourageformationoffecaliths,whichpredisposeindividualsto
obstructionsoftheappendiceallumen.
Inthelastfewyears,adecreaseinfrequencyofappendicitisinWesterncountries
hasbeenreported,whichmayberelatedtochangesindietaryfiberintake.Infact,
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
5/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
thehigherincidenceofappendicitisisbelievedtoberelatedtopoorfiberintakein
suchcountries.
Thereisaslightmalepreponderanceof3:2inteenagersandyoungadultsin
adults,theincidenceofappendicitisisapproximately1.4timesgreaterinmenthan
inwomen.Theincidenceofprimaryappendectomyisapproximatelyequalinboth
sexes.
Theincidenceofappendicitisgraduallyrisesfrombirth,peaksinthelateteenyears,
andgraduallydeclinesinthegeriatricyears.Themeanagewhenappendicitis
occursinthepediatricpopulationis610years.Lymphoidhyperplasiaisobserved
moreoftenamonginfantsandadultsandisresponsiblefortheincreasedincidence
ofappendicitisintheseagegroups.Youngerchildrenhaveahigherrateof
perforation,withreportedratesof5085%.Themedianageatappendectomyis22
years.Althoughrare,neonatalandevenprenatalappendicitishavebeenreported.
Cliniciansmustmaintainahighindexofsuspicioninallagegroups.
GotoPediatricAppendicitisformoreinformationonthistopic.
Prognosis
Acuteappendicitisisthemostcommonreasonforemergencyabdominalsurgery.
Appendectomycarriesacomplicationrateof415%,aswellasassociatedcosts
andthediscomfortofhospitalizationandsurgery.Therefore,thegoalofthe
surgeonistomakeanaccuratediagnosisasearlyaspossible.Delayeddiagnosis
andtreatmentaccountformuchofthemortalityandmorbidityassociatedwith
appendicitis.
Theoverallmortalityrateof0.20.8%isattributabletocomplicationsofthedisease
ratherthantosurgicalintervention.Themortalityrateinchildrenrangesfrom0.1%
to1%inpatientsolderthan70years,theraterisesabove20%,primarilybecause
ofdiagnosticandtherapeuticdelay.
Appendicealperforationisassociatedwithincreasedmorbidityandmortality
comparedwithnonperforatingappendicitis.Themortalityriskofacutebutnot
gangrenousappendicitisislessthan0.1%,buttheriskrisesto0.6%ingangrenous
appendicitis.Therateofperforationvariesfrom16%to40%,withahigher
frequencyoccurringinyoungeragegroups(4057%)andinpatientsolderthan50
years(5570%),inwhommisdiagnosisanddelayeddiagnosisarecommon.
Complicationsoccurin15%ofpatientswithappendicitis,andpostoperativewound
infectionsaccountforalmostonethirdoftheassociatedmorbidity.
PatientEducation
Forpatienteducationinformation,seetheEsophagus,Stomach,andIntestine
Center,aswellasAppendicitisandAbdominalPaininAdults.
ClinicalPresentation
ContributorInformationandDisclosures
Author
SandyCraig,MDResidencyProgramDirector,CarolinasMedicalCenterAssociateProfessor,DepartmentofEmergencyMedicine,UniversityofNorthCarolinaatChapel
HillSchoolofMedicine
SandyCraig,MDisamemberofthefollowingmedicalsocieties:AlphaOmegaAlpha,SocietyforAcademicEmergencyMedicine
Disclosure:Nothingtodisclose.
ChiefEditor
BarryEBrenner,MD,PhD,FACEPProfessorofEmergencyMedicine,ProfessorofInternalMedicine,ProgramDirectorforEmergencyMedicine,CaseMedicalCenter,
UniversityHospitals,CaseWesternReserveUniversitySchoolofMedicine
BarryEBrenner,MD,PhD,FACEPisamemberofthefollowingmedicalsocieties:AlphaOmegaAlpha,AmericanHeartAssociation,AmericanThoracicSociety,
ArkansasMedicalSociety,NewYorkAcademyofMedicine,NewYorkAcademyofSciences,SocietyforAcademicEmergencyMedicine,AmericanAcademyofEmergency
Medicine,AmericanCollegeofChestPhysicians,AmericanCollegeofEmergencyPhysicians,AmericanCollegeofPhysicians
Disclosure:Nothingtodisclose.
Acknowledgements
EugeneHardin,MD,FAAEM,FACEPFormerChairandAssociateProfessor,DepartmentofEmergencyMedicine,CharlesDrewUniversityofMedicineandScience
FormerChair,DepartmentofEmergencyMedicine,MartinLutherKingJr/DrewMedicalCenter
Disclosure:Nothingtodisclose.
WilliamLober,MD,MSAssociateProfessor,HealthInformaticsandGlobalHealth,SchoolsofMedicine,Nursing,andPublicHealth,UniversityofWashington
Disclosure:Nothingtodisclose.
FranciscoTalavera,PharmD,PhDAdjunctAssistantProfessor,UniversityofNebraskaMedicalCenterCollegeofPharmacyEditorinChief,MedscapeDrugReference
Disclosure:MedscapeSalaryEmployment
References
1.PolitesSF,MohamedMI,HabermannEB,etal.Asimplealgorithmreducescomputedtomographyuseinthediagnosisofappendicitisinchildren.Surgery.2014
Jun19.[Medline].
2.DouglasD.AlgorithmcutspediatricCTuseinsuspectedappendicitis.ReutersHealthInformation.July10,2014.[FullText].
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
6/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
3.YehB.Evidencebasedemergencymedicine/rationalclinicalexaminationabstract.Doesthisadultpatienthaveappendicitis?.AnnEmergMed.2008Sep.52(3):301
3.[Medline].
4.MarkleGB4th.Heeldropjarringtestforappendicitis.ArchSurg.1985Feb.120(2):243.[Medline].
5.ThimsenDA,TongGK,GruenbergJC.ProspectiveevaluationofCreactiveproteininpatientssuspectedtohaveacuteappendicitis.AmSurg.1989Jul.55(7):4668.
[Medline].
6.deCarvalhoBR,DiogoFilhoA,FernandesC,BarraCB.[Leukocytecount,Creactiveprotein,alpha1acidglycoproteinanderythrocytesedimentationrateinacute
appendicitis].ArqGastroenterol.2003JanMar.40(1):2530.[Medline].
7.AlbuE,MillerBM,ChoiY,etal.DiagnosticvalueofCreactiveproteininacuteappendicitis.DisColonRectum.1994Jan.37(1):4951.[Medline].
8.BolandparvazS,VaseiM,OwjiAA,AtaEeN,AminA,DaneshbodY,etal.Urinary5hydroxyindoleaceticacidasatestforearlydiagnosisofacuteappendicitis.
ClinBiochem.2004Nov.37(11):9859.[Medline].
9.KimK,KimYH,KimSY,KimS,LeeYJ,KimKP,etal.LowdoseabdominalCTforevaluatingsuspectedappendicitis.NEnglJMed.2012Apr26.366(17):1596
605.[Medline].
10.HowellJM,EddyOL,LukensTW,ThiessenME,WeingartSD,DeckerWW.Clinicalpolicy:Criticalissuesintheevaluationandmanagementofemergency
departmentpatientswithsuspectedappendicitis.AnnEmergMed.2010Jan.55(1):71116.[Medline].
11.[Guideline]NationalGuidelineClearinghouse(NGC).Guidelinesummary:Clinicalpolicy:criticalissuesintheevaluationandmanagementofemergencydepartment
patientswithsuspectedappendicitis.NationalGuidelineClearinghouse(NGC),Rockville(MD).Availableathttp://guideline.gov/content.aspx?id=15598.Accessed:
November18,2013.
12.BarloonTJ,BrownBP,AbuYousefMM,WarnockN,BerbaumKS.Sonographyofacuteappendicitisinpregnancy.AbdomImaging.1995MarApr.20(2):14951.
[Medline].
13.ManterolaC,VialM,MoragaJ,AstudilloP.Analgesiainpatientswithacuteabdominalpain.CochraneDatabaseSystRev.2011Jan19.1:CD005660.[Medline].
14.KaramanakosSN,SdralisE,PanagiotopoulosS,KehagiasI.Laparoscopyintheemergencysetting:aretrospectivereviewof540patientswithacuteabdominal
pain.SurgLaparoscEndoscPercutanTech.2010Apr.20(2):11924.[Medline].
15.NiwaH,HiramatsuT.Ararepresentationofappendicealdiverticulitisassociatedwithpelvicpseudocyst.WorldJGastroenterol.2008Feb28.14(8):12935.
[Medline].[FullText].
16.PlaceRC.Acuteurinaryretentionina9yearoldchild:anatypicalpresentationofacuteappendicitis.JEmergMed.2006Aug.31(2):1735.[Medline].
17.OtoA,ErnstRD,MileskiWJ,NishinoTK,LeO,WolfeGC,etal.LocalizationofappendixwithMDCTandinfluenceoffindingsonchoiceofappendectomyincision.
AJRAmJRoentgenol.2006Oct.187(4):98790.[Medline].
18.SedlakM,WagnerOJ,WildB,PapagrigoriadesS,ExadaktylosAK.Istherestillaroleforrectalexaminationinsuspectedappendicitisinadults?.AmJEmergMed.
2008Mar.26(3):35960.[Medline].
19.AlvaradoA.Apracticalscorefortheearlydiagnosisofacuteappendicitis.AnnEmergMed.1986May.15(5):55764.[Medline].
20.SchneiderC,KharbandaA,BachurR.Evaluatingappendicitisscoringsystemsusingaprospectivepediatriccohort.AnnEmergMed.2007Jun.49(6):77884,
784.e1.[Medline].
21.SchneiderC,KharbandaA,BachurR.Evaluatingappendicitisscoringsystemsusingaprospectivepediatriccohort.AnnEmergMed.2007Jun.49(6):77884,
784.e1.[Medline].
22.MigraineS,AtriM,BretPM,LoughJO,HincheyJE.Spontaneouslyresolvingacuteappendicitis:clinicalandsonographicdocumentation.Radiology.1997Oct.
205(1):558.[Medline].
23.CobbenLP,deVanOtterlooAM,PuylaertJB.Spontaneouslyresolvingappendicitis:frequencyandnaturalhistoryin60patients.Radiology.2000May.215(2):349
52.[Medline].
24.DueholmS,BagiP,BudM.Laboratoryaidinthediagnosisofacuteappendicitis.Ablinded,prospectivetrialconcerningdiagnosticvalueofleukocytecount,
neutrophildifferentialcount,andCreactiveprotein.DisColonRectum.1989Oct.32(10):8559.[Medline].
25.GurleyikE,GurleyikG,UnalmiserS.AccuracyofserumCreactiveproteinmeasurementsindiagnosisofacuteappendicitiscomparedwithsurgeon'sclinical
impression.DisColonRectum.1995Dec.38(12):12704.[Medline].
26.ShakhatrehHS.TheaccuracyofCreactiveproteininthediagnosisofacuteappendicitiscomparedwiththatofclinicaldiagnosis.MedArh.2000.54(2):10910.
[Medline].
27.AsfarS,SafarH,KhoursheedM,DashtiH,alBaderA.WouldmeasurementofCreactiveproteinreducetherateofnegativeexplorationforacuteappendicitis?.JR
CollSurgEdinb.2000Feb.45(1):214.[Medline].
28.ErkasapS,AtesE,UstunerZ,SahinA,YilmazS,YasarB,etal.Diagnosticvalueofinterleukin6andCreactiveproteininacuteappendicitis.SwissSurg.2000.
6(4):16972.[Medline].
29.GronroosJM,GronroosP.LeucocytecountandCreactiveproteininthediagnosisofacuteappendicitis.BrJSurg.1999Apr.86(4):5014.[Medline].
30.OrtegaDeballonP,RuizdeAdanaBelbelJC,HernandezMatiasA,GarciaSeptiemJ,MorenoAzcoitaM.Usefulnessoflaboratorydatainthemanagementofright
iliacfossapaininadults.DisColonRectum.2008Jul.51(7):10939.[Medline].
31.GronroosJM.IstherearoleforleukocyteandCRPmeasurementsinthediagnosisofacuteappendicitisintheelderly?.Maturitas.1999Mar15.31(3):2558.
[Medline].
32.YangHR,WangYC,ChungPK,etal.Roleofleukocytecount,neutrophilpercentage,andCreactiveproteininthediagnosisofacuteappendicitisintheelderly.Am
Surg.2005Apr.71(4):3447.[Medline].
33.GronroosJM.DonormalleucocytecountandCreactiveproteinvalueexcludeacuteappendicitisinchildren?.ActaPaediatr.2001Jun.90(6):64951.[Medline].
34.StefanuttiG,GhirardoV,GambaP.Inflammatorymarkersforacuteappendicitisinchildren:aretheyhelpful?.JPediatrSurg.2007May.42(5):7736.[Medline].
35.MohammedAA,DaghmanNA,AboudSM,OshibiHO.ThediagnosticvalueofCreactiveprotein,whitebloodcellcountandneutrophilpercentageinchildhood
appendicitis.SaudiMedJ.2004Sep.25(9):12125.[Medline].
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
7/8
7/29/2016
Appendicitis:PracticeEssentials,Background,Anatomy
36.YangHR,WangYC,ChungPK,ChenWK,JengLB,ChenRJ.Laboratorytestsinpatientswithacuteappendicitis.ANZJSurg.2006JanFeb.76(12):714.
[Medline].
37.TundidorBermudezAM,AmadoDieguezJA,MontesdeOcaMastrapaJL.[Urologicalmanifestationsofacuteappendicitis].ArchEspUrol.2005Apr.58(3):20712.
[Medline].
38.RaoPM,RheaJT,RattnerDW,etal.IntroductionofappendicealCT:impactonnegativeappendectomyandappendicealperforationrates.AnnSurg.1999Mar.
229(3):3449.[Medline].
39.McGoryML,ZingmondDS,NanayakkaraD,MaggardMA,KoCY.Negativeappendectomyrate:influenceofCTscans.AmSurg.2005Oct.71(10):8038.[Medline].
40.HarswickC,UyenishiAA,KordickMF,ChanSB.Clinicalguidelines,computedtomographyscan,andnegativeappendectomies:acaseseries.AmJEmergMed.
2006Jan.24(1):6872.[Medline].
41.FreiSP,BondWF,BazuroRK,RichardsonDM,SierzegaGM,ReedJF.Appendicitisoutcomeswithincreasingcomputedtomographicscanning.AmJEmergMed.
2008Jan.26(1):3944.[Medline].
42.PickhardtPJ,LawrenceEM,PoolerBD,BruceRJ.Diagnosticperformanceofmultidetectorcomputedtomographyforsuspectedacuteappendicitis.AnnInternMed.
2011Jun21.154(12):78996.[Medline].
43.KepnerAM,BacasnotJV,StahlmanBA.Intravenouscontrastalonevsintravenousandoralcontrastcomputedtomographyforthediagnosisofappendicitisinadult
EDpatients.AmJEmergMed.2012May23.[Medline].
44.BrennerDJ,HallEJ.Computedtomographyanincreasingsourceofradiationexposure.NEnglJMed.2007Nov29.357(22):227784.[Medline].
45.ZilbertNR,StamellEF,EzonI,SchlagerA,GinsburgHB,NadlerEP.Managementandoutcomesforchildrenwithacuteappendicitisdifferbyhospitaltype:areas
forimprovementatpublichospitals.ClinPediatr(Phila).2009Jun.48(5):499504.[Medline].
46.DoriaAS,MoineddinR,KellenbergerCJ,EpelmanM,BeyeneJ,SchuhS,etal.USorCTforDiagnosisofAppendicitisinChildrenandAdults?AMetaAnalysis.
Radiology.2006Oct.241(1):8394.[Medline].
47.BoggsW.Ultrasound/MRIStrategyDiagnosesAppendicitisinKidsWithoutRadiation.MedscapeMedicalNews.Availableat
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/821332.Accessed:March12,2014.
48.AspelundG,FingeretA,GrossE,KesslerD,KeungC,ThirumoorthiA,etal.Ultrasonography/MRIVersusCTforDiagnosingAppendicitis.Pediatrics.2014Mar3.
[Medline].
49.CobbenLP,GrootI,HaansL,BlickmanJG,PuylaertJ.MRIforclinicallysuspectedappendicitisduringpregnancy.AJRAmJRoentgenol.2004Sep.183(3):6715.
[Medline].
50.RepplingerMD,LevyJF,PeethumnongsinE,etal.SystematicreviewandmetaanalysisoftheaccuracyofMRItodiagnoseappendicitisinthegeneralpopulation.J
MagnResonImaging.2015Dec22.[Medline].
51.ThiemeME,LeeuwenburghMM,ValdehuezaZD,BoumanDE,deBruinIG,SchreursWH,etal.DiagnosticaccuracyandpatientacceptanceofMRIinchildrenwith
suspectedappendicitis.EurRadiol.2013Oct19.[Medline].
52.SingerDD,ThodeHCJr,SingerAJ.EffectsofpainseverityandCTimagingonanalgesiaprescriptioninacuteappendicitis.AmJEmergMed.2016Jan.34(1):36
9.[Medline].
53.ErikssonS,GranstrmL.Randomizedcontrolledtrialofappendicectomyversusantibiotictherapyforacuteappendicitis.BrJSurg.1995Feb.82(2):1669.
[Medline].
54.SalminenP,PaajanenH,RautioT,etal.AntibioticTherapyvsAppendectomyforTreatmentofUncomplicatedAcuteAppendicitis:TheAPPACRandomizedClinical
Trial.JAMA.2015Jun16.313(23):23408.[Medline].
55.BonadioW,RebillotK,UkwuomaO,SaracinoC,IskhakovA.Managementofpediatricperforatedappendicitis:comparingoutcomesusingearlyappendectomyvs
solelymedicalmanagement.PediatrInfectDisJ.2015Dec14.[Medline].
56.BickellNA,AufsesAHJr,RojasM,BodianC.Howtimeaffectstheriskofruptureinappendicitis.JAmCollSurg.2006Mar.202(3):4016.[Medline].
57.AbouNuktaF,BakhosC,ArroyoK,KooY,MartinJ,ReinholdR,etal.Effectsofdelayingappendectomyforacuteappendicitisfor12to24hours.ArchSurg.2006
May.141(5):5046discussion5067.[Medline].
58.FairBA,KubasiakJC,JanssenI,etal.Theimpactofoperativetimingonoutcomesofappendicitis:aNationalSurgicalQualityImprovementProjectanalysis.AmJ
Surg.2015Mar.209(3):498502.[Medline].
59.BoomerLA,CooperJN,AnandalwarS,etal.Delayingappendectomydoesnotleadtohigherratesofsurgicalsiteinfections:amultiinstitutionalanalysisofchildren
withappendicitis.AnnSurg.2015Dec16.[Medline].
60.[Guideline]KorndorfferJRJr,FellingerE,ReedW.SAGESguidelineforlaparoscopicappendectomy.SurgEndosc.2010Apr.24(4):75761.[Medline].[FullText].
61.WilasrusmeeC,SukratB,McEvoyM,AttiaJ,ThakkinstianA.Systematicreviewandmetaanalysisofsafetyoflaparoscopicversusopenappendicectomyfor
suspectedappendicitisinpregnancy.BrJSurg.2012Nov.99(11):14708.[Medline].
62.LiangMK,LoHG,MarksJL.Stumpappendicitis:acomprehensivereviewofliterature.AmSurg.2006Feb.72(2):1626.[Medline].
63.BarclayL.Ultrasound,CTComparabletoDetectAppendicitisinChildren.MedscapeMedicalNews.Availableathttp://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/817370.
Accessed:December9,2013.
64.LeJ,KurianJ,CohenHW,WeinbergG,ScheinfeldMH.Doclinicaloutcomessufferduringtransitiontoanultrasoundfirstparadigmfortheevaluationofacute
appendicitisinchildren?.AJRAmJRoentgenol.2013Dec.201(6):134852.[Medline].
65.HurstAL,OlsonD,SommeS,etal.Oncedailyceftriaxoneplusmetronidazoleversusertapenemand/orcefoxitinforpediatricappendicitis.JPediatricInfectDis
Soc.2015Dec24.[Medline].
MedscapeReference2011WebMD,LLC
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773895overview#showall
8/8
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- APPENDICITISDocument36 pagesAPPENDICITISsjamilmdfauzie100% (4)
- A Case Study On Acute AppendicitisDocument56 pagesA Case Study On Acute AppendicitisIvy Mae Evangelio Vios92% (13)
- Dokumen - Tips - Upaya Penanggulangan Gizi Buruk Pada Balita Melalui Penjaringan Dan Pelacakan Kasus PDFDocument7 pagesDokumen - Tips - Upaya Penanggulangan Gizi Buruk Pada Balita Melalui Penjaringan Dan Pelacakan Kasus PDFAdy Fitra SaragihNo ratings yet
- AudiometryDocument6 pagesAudiometryYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Upload A Document - ScribdDocument8 pagesUpload A Document - ScribdYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Mal UnionDocument10 pagesMal UnionYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding - ClinicalKeyDocument20 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding - ClinicalKeyYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Dysfunctions and Psychological Symptoms in Migraine Without Aura: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument8 pagesCognitive Dysfunctions and Psychological Symptoms in Migraine Without Aura: A Cross-Sectional StudyYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis A and E - ClinicalKeyDocument32 pagesViral Hepatitis A and E - ClinicalKeyYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Noncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Imaging - Overview, Radiography, Computed TomographyDocument6 pagesNoncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Imaging - Overview, Radiography, Computed TomographyYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kuliah DR MataDocument7 pagesTugas Kuliah DR MataYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- 1 C1 AtlasVertebraRealignmentHypertension6pagesDocument6 pages1 C1 AtlasVertebraRealignmentHypertension6pagesDenise MathreNo ratings yet
- Fracture Healing - The Diamond ConceptDocument4 pagesFracture Healing - The Diamond ConceptPekerja KesunyianNo ratings yet
- Mal UnionDocument10 pagesMal UnionYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- AudiometryDocument6 pagesAudiometryYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis B and D - ClinicalKeyDocument40 pagesViral Hepatitis B and D - ClinicalKeyYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- How Can Safety Culture Be ImprovedDocument3 pagesHow Can Safety Culture Be ImprovedYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- The Comprehensive Unit For LeadDocument4 pagesThe Comprehensive Unit For LeadYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- To Err Is Human 1999 Report Brief PDFDocument8 pagesTo Err Is Human 1999 Report Brief PDFAjib A. Azis100% (3)
- Prem & Sec Hiper DapusDocument1 pagePrem & Sec Hiper DapusYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Hospital FinanceDocument54 pagesHospital FinancePadmanabha Narayan100% (3)
- Hypovolemic Shock Clinical Presentation - History, Physical, CausesDocument4 pagesHypovolemic Shock Clinical Presentation - History, Physical, CausesYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Workup - Approach Considerations, CBC Count, C-Reactive ProteinDocument8 pagesAppendicitis Workup - Approach Considerations, CBC Count, C-Reactive ProteinYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock - Background, PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHypovolemic Shock - Background, PathophysiologyYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument30 pagesAcute AppendicitisYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Helmet Removal Periprocedural Care - Equipment, Patient Preparation, Monitoring & Follow-UpDocument3 pagesHelmet Removal Periprocedural Care - Equipment, Patient Preparation, Monitoring & Follow-UpYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Medication - Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides, Carbapenems, Fluoroquinolones, Anti-Infective Agents, AnalgesicsDocument5 pagesAppendicitis Medication - Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides, Carbapenems, Fluoroquinolones, Anti-Infective Agents, AnalgesicsYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- APSA Family Site - Imperforate AnusDocument4 pagesAPSA Family Site - Imperforate AnusYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Medication - Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides, Carbapenems, Fluoroquinolones, Anti-Infective Agents, AnalgesicsDocument5 pagesAppendicitis Medication - Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides, Carbapenems, Fluoroquinolones, Anti-Infective Agents, AnalgesicsYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Sample: AppendectomyDocument8 pagesSample: AppendectomyTahtawi 'Afid' Rifai RidhoNo ratings yet
- Algorithms - SVT PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithms - SVT PDFYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Sabitson - Appendiks EngDocument17 pagesSabitson - Appendiks Engzeek powerNo ratings yet
- What Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisVonn Bryan CalumiaNo ratings yet
- Zollinger Apendicitis PDFDocument8 pagesZollinger Apendicitis PDFCINDY ADILIA FLORES HERNÁNDEZNo ratings yet
- Gomes WSES 15Document6 pagesGomes WSES 15zakyNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy GuideDocument4 pagesCholecystectomy GuideKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument2 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyLeviThomasStafford100% (1)
- Appendicitis&AppendectomyDocument5 pagesAppendicitis&AppendectomyJestine Joy CustodioNo ratings yet
- PS 3103Document9 pagesPS 3103JayeshNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & PreventionDocument2 pagesAppendicitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & PreventionJr MateoNo ratings yet
- SAEP-134 - Preparation of Saudi Aramco Engineering ProceduresDocument5 pagesSAEP-134 - Preparation of Saudi Aramco Engineering ProceduresQA QCNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Method EngDocument10 pagesAppendicitis Method EngMohammad AyoubNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument51 pagesAppendectomymoqtadirNo ratings yet
- Case Study Acute AppendecitisDocument13 pagesCase Study Acute AppendecitisDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument21 pagesAppendicitis Case Studyshayne100% (13)
- Lampiran G - Guidelines Report FypDocument9 pagesLampiran G - Guidelines Report FypfieqaNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis and AppendectomyDocument5 pagesAppendicitis and AppendectomyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Made EasyDocument8 pagesAcute Appendicitis Made EasyTakpire DrMadhukarNo ratings yet
- Acute appendicitis symptoms and causesDocument20 pagesAcute appendicitis symptoms and causesAiyaz AliNo ratings yet
- Appendices Example in Research PaperDocument4 pagesAppendices Example in Research Paperfvg7vpte100% (1)
- B. Tech. Project Report Guide Lines SummaryDocument8 pagesB. Tech. Project Report Guide Lines SummaryRaju KumarNo ratings yet
- 1706509515565-Intestinal Diseases Congenital and Inflammatory LesionsDocument18 pages1706509515565-Intestinal Diseases Congenital and Inflammatory LesionsmyarjddbzNo ratings yet
- Morbidity and Mortality Review for December and JanuaryDocument68 pagesMorbidity and Mortality Review for December and Januaryndifor bonnyNo ratings yet
- Cancer Is CurableDocument111 pagesCancer Is Curablelang19No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisDivine Jane Purcia67% (3)
- Laporan Kasus AppendicitisDocument21 pagesLaporan Kasus AppendicitisjessicaNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument6 pagesAppendectomyMarie Nelle Escriba LimpocoNo ratings yet
- Appendices To The BQSM Accreditation ManualDocument51 pagesAppendices To The BQSM Accreditation Manualariff.arifinNo ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument2 pagesAPPENDICITISRay Dan Aro CelerianNo ratings yet