Professional Documents
Culture Documents
April 14
Uploaded by
Raj Vishwakarma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesQuestion Paper
Original Title
APRIL 14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentQuestion Paper
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesApril 14
Uploaded by
Raj VishwakarmaQuestion Paper
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
{Central Technological Institute, Maharashtra State}
Matunga, Mumbai-400 019
SEMESTER EXAMINATION: DATE OF EXAM: 2 §-04- 2c}4
SEMESTER & PROGRAM: —VI_D.EIn.E TIME: J 30am. to 12-207 wy
TIME ALLOWED: 3 HRS. MARK: 100
COURSE (Course Code): Digital Communication (09 ~ EE - 644)
Instructions Al Questions are COMPULSORY
B)
Q2
Q3
‘Answer fo two sections must be written in separate Answer Books.
Figures to the right indicate full marks.
‘Assume suitable data if necessary
Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary
SECTION -1
Answer any five in one sentence.
‘a) Calculate amount of information if binary digits occur with equal (2)
likelihood in binary PCM
b) What is cause of aliasing?
c) Define dynamic range.
4) What is quantization error?
¢) Define Information Capacity
£) What is the purpose of clock recovery circuit?
g) If the message being transmitted is known to receiver then what is
amount of information carried?
Answer any two 10
a) What is Entropy? What are the properties of Entropy? 6)
b) Calculate entropy when Py=0, Py=0.5 & Py=l. 6)
©) State advantages and disadvantages of Digital Communication Systems. (5)
Solve any Three, (15)
a) Explain how PAM is generated with Sample and Hold circuit. ©)
b) What is role of quantizer in PCM? How to reduce quantization error &
©) What is basic difference between PCM & DM? Explain delta modulation (5)
technique with neat block diagram.
d) Explain working of DPCM with neat block diagram. (sy
is)
8) Draw FSK waveforms, Explain detailed working of FSK demodulator. (5)
OR
a) Write working of DBPSK transmitter and receiver.
b) Draw and explain BPSK transmitter with detailed working of Balanced (10)
ring modulator.
OR
b) With neat block diagram explain working of QPSK receiver.
I |
Qa
3]
Q6
SECTION - IT
(0)
Answer any five in one sentence.
a) What is source coding? @)
b) What is syndrome? @)
c) What is need for multiplexing? @)
d) What is FDM? Q)
e) What is TDMA? Q)
1) What is the basic use of PN sequence? @
12) What is basic difference between Direct sequence Spread Spestram and (2)
Frequency Hop Spread Spectrum?
Answer any Two (20)
a) Explain polar RZ, NRZ and Split Phase Manchester coding formal 6)
b) Explain odd parity check, even party check. How vertical and horizontal (5)
parity check is advantageous over odd & even parity check?
©) Consider (6, 3) Linear code whose generator matrix is (6)
1001070
G=|o 1 1 (|
o o1o011
(i) List all the code vectors.
(ii) Draw Encoder circuit
Answer any Three (15)
a) Which multiplexing technique is used for continuous transmission of 6)
data? Explain working of transmitter for the same.
b) Write short note on FDMA. (3)
¢) Draw & explain TDM receiver.
@) What are the advantages of TDMA over FDMA?
(3)
a) Find the PN sequence for (4, 1) tapping. 6)
OR
a) Explain the concept of Direet sequence Spread Spectrum in detail.
b) Explain the principle and working of FHSS in detail. Differentiate (10)
between slow frequency hopping and fast frequency hopping.
OR
by For FH-MFSK system (Fast frequency hopping), show the frequency
illustration of output with respect to input binary data symbols-
Input binary data: 10 11 11 10.01 00 10
PN Sequence: 001 110 011 001 001
You might also like
- Self Declarationbyne1212Document1 pageSelf Declarationbyne1212Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument7 pagesLicenseManni MantasticNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Template: Strictly ConfidentialDocument2 pagesWorking Capital Template: Strictly ConfidentialRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- New Format Kiosk BankingDocument2 pagesNew Format Kiosk BankingRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Declaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by Link Branch)Document1 pageDeclaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by Link Branch)Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Precalc 08Document76 pagesPrecalc 08Asim RazaNo ratings yet
- Declaration by CSP ApplicantDocument1 pageDeclaration by CSP ApplicantRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Print TicketDocument2 pagesPrint TicketSean MINo ratings yet
- Family MembersDocument1 pageFamily MembersRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Btech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Document98 pagesBtech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Raj Vishwakarma0% (1)
- Experiment No. 4 AIM: To Study RE Cascaded Transistor Amplifier ApparatusDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 4 AIM: To Study RE Cascaded Transistor Amplifier ApparatusRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Customer Request PDFDocument2 pagesCustomer Request PDFRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Veermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionDocument8 pagesVeermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Btech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDFDocument144 pagesBtech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDFRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Veermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionDocument8 pagesVeermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Direct Second Year Admission FeesDocument2 pagesDirect Second Year Admission FeesswapnilNo ratings yet
- PLD NotesDocument10 pagesPLD NotesRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IndiaDocument13 pagesHuman Rights in IndiaRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Ies Ee New SyllabusDocument2 pagesIes Ee New SyllabusHimanshu Kumar SagarNo ratings yet
- Btech Semi Erotx 6 To 8Document144 pagesBtech Semi Erotx 6 To 8Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- New WordDocument8 pagesNew WordRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Btech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Document98 pagesBtech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Raj Vishwakarma0% (1)
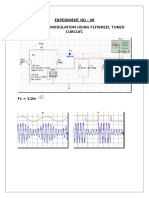
- Experiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitDocument1 pageExperiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Manual Arduino UnoDocument8 pagesManual Arduino UnoNuwando IbrahimaNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitDocument1 pageExperiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)