Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A1u2 Parent Letter Algebra1
Uploaded by
api-328200095Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A1u2 Parent Letter Algebra1
Uploaded by
api-328200095Copyright:
Available Formats
Algebra I Unit 2
Reasoning with Linear
Equations & Inequalities
Volume 1 Issue 2
References Dear Parents
HMH Georgia
Coordinate Algebra
Text:
Unit 1: Modules 1; Unit
2 Modules 3-5, 9-10,
12-13; Unit 3 Modules
8-9
Check with you
teacher for online
access: my.hrw.com
Web Resources
http://www.regentsprep
.org/Regents/math/AL
GEBRA/AE3/indexAE3.
htm
http://www.regentsprep
.org/Regents/math/AL
GEBRA/AE85/indexAE8
5.htm
http://www.regentsprep
.org/Regents/math/AL
GEBRA/AE9/indexAE9.
htm
http://regentsprep.org/
Regents/math/algtrig/
ATP2/ArithSeq.htm
http://www.regentsprep
.org/Regents/math/AL
GEBRA/AP3/LFunction.
htm
http://www.regentsprep
.org/Regents/math/AL
GEBRA/AC1/Rate.htm
http://www.regentsprep
.org/Regents/math/AL
GEBRA/AC1/EqLines2.
htm
http://www.mathplay.com/slopeintercept-game.html
http://www.webmath.co
m/equline1.html
http://www.mathplanet.
com/education/algebr
a-1/systems-of-linearequations-andinequalities/systems-
Below you will find a list of concepts that your child will use and understand
while completing Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations & Inequalities.
Also included are references, vocabulary and examples that will help you
assist your child at home.
Concepts Students will Use and Understand
Create Equations that Describe Numbers or Relationships
Solve Equations & Inequalities
Build a Function that Models a Relationship Between Two Quantities
Understand the Concept of Function & Use Function Notation
Interpret Functions that Arise in Applications in Terms of Context
Analyze Functions using Different Representations
Vocabulary
Arithmetic Sequence. A sequence of numbers in which the
difference between any two consecutive terms is the same.
Average Rate of Change. The change in the value of a quantity by
the elapsed time. For a function, this is the change in the y-value
divided by the change in the x-value for two distinct points on the
graph.
Constant Rate of Change. With respect to the variable x of a linear
function y = f(x), the constant rate of change is the slope of its graph.
Continuous. Describes a connected set of numbers, such as an
interval.
Discrete. A set with elements that are disconnected.
Domain. The set of x-coordinates of the set of points on a graph; the
set of x-coordinates of a given set of ordered pairs. The value that is
the input in a function or relation.
End Behaviors. The appearance of a graph as it is followed farther
and farther in either direction.
Explicit Formula. A formula that allows direct computation of any
term for a sequence a1, a2, a3, .. . , an, . .
Factor. For any number x, the numbers that can be evenly divided
into x are called factors of x. For example, the number 20 has the
factors 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, and 20.
Interval Notation. A notation representing an interval as a pair of
numbers. The numbers are the endpoints of the interval. Parentheses
and/or brackets are used to show whether the endpoints are excluded
or included.
Linear Function. A function with a constant rate of change and a
straight line graph.
Linear Model. A linear function representing real-world phenomena.
The model also represents patterns found in graphs and/or data.
Parameter. The independent variable or variables in a system of
of-linear-inequalities
https://www.quia.com/r
r/79715.html?
AP_rand=1474276100
http://www.purplemath.
com/modules/fcnops.h
tm
equations with more than one dependent variable.
Range. The set of all possible outputs of a function.
Recursive Formula. A formula that requires the computation of all
previous terms to find the value of an.
Slope. The ratio of the vertical and horizontal changes between two
points on a surface or a line.
X-intercept. The point where a line meets or crosses the x-axis
Y-intercept. The point where a line meets or crosses the y-axis
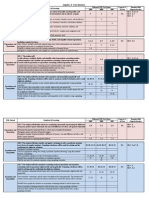
Algebra 1 Unit 2 Practice Problems
Formulas
Slope-Intercept:
y = mx + b
Arithmetic Sequence:
An=a1 + (n-1)d
Example 1
The sum of two consecutive integers is less than 83. Find the pair of integers
with the greatest sum.
Example 2
Pablo and his family are driving to California for vacation. The trip is 1,505
miles and they drive at an average speed of 59 mph. Which equation would
give the number of miles remaining until they reach their destination, M, in
terms of h, the number of hours they have driven?
A. M = 59 + 1,505h
B. M = 1,505 - 59h
C. M = 1,505 + 59h
D. M = 59 - 1,505h
Example 3
Britany is leaving for an 800 mile road trip. Her plan is not to make any stops
until she has 590 miles, or less, left of the drive. She is averaging 70 miles
per hour. If x represents the number of hours driving, which of the following
inequalities symbolizes this situation?
A. 590 - 70x > 800
B. 800 - 70x < 590
C. 590 - 70x < 800
D. 800 - 70x > 590
Example 4
What is the next term in this sequence? 4, 10, 16,
Example 5
Generate ordered pairs for the function y = x + 3 for x = -2, -1, 0, 1, and
state the domain and range.
Answer Key
Example 1
Define a Variable: x = the first consecutive number, so x +1 = the second
consecutive number
Equation: x + x + 1 < 83
2x < 82
x < 41
COMPANY NAME
ADDRESS
The numbers are STREET
40 and 41
Check: 40 + 41 <CITY,
83 STATE
8100000
< 83
Example 2
D. M = 59 - 1,505h
Example 3
B. 800 - 70x < 590
Example 4
22
Example 5
(-2,1), (-1,2), (0,3), (1,4), (2,5) Domain: {-2,-1,0,1,2} Range: {1,2,3,4,5)
You might also like
- A1u2 Parent LetterDocument2 pagesA1u2 Parent Letterapi-297405956No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksLindaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2api-302577842No ratings yet
- Describe The Structure of Mathematical Model in Your Own WordsDocument10 pagesDescribe The Structure of Mathematical Model in Your Own Wordskaranpuri6No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Equations & FunctionsDocument6 pagesAlgebra 2 Equations & FunctionsHarish MulevaNo ratings yet
- Individual Development Profile Report: Muhammad, TalibahDocument5 pagesIndividual Development Profile Report: Muhammad, TalibahGlamrockFreddy TLCNo ratings yet
- CCGPS Math 8 Unit 4 Functional Relationships: References Dear ParentsDocument2 pagesCCGPS Math 8 Unit 4 Functional Relationships: References Dear ParentsmrslsarnoldNo ratings yet
- M7u2 ParentletterDocument2 pagesM7u2 Parentletterapi-292742040No ratings yet
- Factorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodFrom EverandFactorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodNo ratings yet
- Overland TrailDocument8 pagesOverland Trailapi-245623862No ratings yet
- Computational MethodDocument18 pagesComputational MethodMelkamu KfgNo ratings yet
- Statistical Modeling With R - Fall 2016 Homework 3: Wells in BangladeshDocument10 pagesStatistical Modeling With R - Fall 2016 Homework 3: Wells in BangladeshSahil BhagatNo ratings yet
- Module (Calculus)Document18 pagesModule (Calculus)Richard GomezNo ratings yet
- List of Formulas Useful For Solving Aptitude QuestionsDocument5 pagesList of Formulas Useful For Solving Aptitude Questionssrokar1234No ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering: 1. ExpressionsDocument54 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering: 1. ExpressionsVINE TUBENo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument53 pagesAlgebraJoey Calda Jr.100% (1)
- PLD Algebra IIDocument18 pagesPLD Algebra IIapi-310256368No ratings yet
- UNIt-3 TYDocument67 pagesUNIt-3 TYPrathmesh Mane DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming Week 4: OperatorsDocument36 pagesComputer Programming Week 4: Operatorstt_kobraNo ratings yet
- Annotated SPSS Output Factor AnalysisDocument20 pagesAnnotated SPSS Output Factor AnalysisrobbierajanNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document7 pagesAlgebra 2api-262893996No ratings yet
- Mfcs Hand BookDocument41 pagesMfcs Hand BookAnonymous vopE9EmDFNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Common Errors GuideDocument5 pagesMATLAB Common Errors GuideNilanaNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade CcssDocument1 page8th Grade Ccssapi-237059911No ratings yet
- Standards-K-12 8th GradeDocument3 pagesStandards-K-12 8th Gradeapi-296039056No ratings yet
- Gen Math Mod 2Document8 pagesGen Math Mod 2Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Using Linear Equations in Daily TasksDocument3 pagesUsing Linear Equations in Daily TasksSundaraneedi Naveen Kumar100% (1)
- Common Core Exponential FunctionsDocument8 pagesCommon Core Exponential Functionsapi-297804475No ratings yet
- Aravind Rangamreddy 500195259 cs3Document8 pagesAravind Rangamreddy 500195259 cs3Aravind Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomics Calculus Module: RD THDocument5 pagesIntermediate Microeconomics Calculus Module: RD THCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomics Calculus Module: RD THDocument5 pagesIntermediate Microeconomics Calculus Module: RD THCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Efficient Derivative Codes Through Automatic Differentiation and Interface Contraction: Application in BiostatisticsDocument13 pagesEfficient Derivative Codes Through Automatic Differentiation and Interface Contraction: Application in Biostatisticsgorot1No ratings yet
- I.S.F.D y T. #103: Profesorado de Técnicos Prof: Martín MellerDocument11 pagesI.S.F.D y T. #103: Profesorado de Técnicos Prof: Martín MellerAriel LeucipoNo ratings yet
- Midpoint & Distance Formulas GuideDocument1 pageMidpoint & Distance Formulas GuidenavaeliNo ratings yet
- Applications of Rational FunctionsDocument8 pagesApplications of Rational FunctionsLara Hulbert100% (1)
- 03 OperatorsDocument8 pages03 OperatorsramiNo ratings yet
- L No 15-ADocument25 pagesL No 15-AThiyagu VasuNo ratings yet
- AMME3500 2013 Assignment 2Document5 pagesAMME3500 2013 Assignment 2JinDownloaderFree92No ratings yet
- C OperatorsDocument10 pagesC OperatorsDipanshu HandooNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Investigation3 OverviewDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Investigation3 OverviewKimmy jNo ratings yet
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementFrom EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics (FUNCTIONS)Document36 pagesGeneral Mathematics (FUNCTIONS)Kevan jaymes KatipunanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods 1Document7 pagesNumerical Methods 1oscarcbz0288No ratings yet
- MATH98Document7 pagesMATH98ChristineNo ratings yet
- MEA 20 Manoj PokharelDocument9 pagesMEA 20 Manoj PokharelManoj PokharelNo ratings yet
- Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Faculty of Automation and Computer Science Department of Computer Science 2nd Semester 20!1-20Document12 pagesTechnical University of Cluj-Napoca Faculty of Automation and Computer Science Department of Computer Science 2nd Semester 20!1-20Serban PetrescuNo ratings yet
- ErrorDocument5 pagesErrordidiek noorNo ratings yet
- Package Amelia': February 19, 2015Document23 pagesPackage Amelia': February 19, 2015Marco Alberto Benjumeda BarquitaNo ratings yet
- Control StatementsDocument7 pagesControl StatementsMahamad AliNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic OperatorsDocument8 pagesArithmetic OperatorsGhanshyam Dass GuptaNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Error in Product FormulasDocument15 pagesPropagation of Error in Product FormulasVitu Verctor ViyuyiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physics: 1.5 Analysing Scientific InvestigationDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Physics: 1.5 Analysing Scientific Investigationajwad_hashim5No ratings yet
- Power Engineering Systems Learning Unit 5Document30 pagesPower Engineering Systems Learning Unit 5John CorneliusNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Crns 12-13 4th Nine WeeksDocument19 pagesAlgebra 2 Crns 12-13 4th Nine Weeksapi-201428071No ratings yet
- Principal Components Analysis and Redundancy AnalysisDocument18 pagesPrincipal Components Analysis and Redundancy AnalysisJosé António PereiraNo ratings yet
- Solving Inequalities Compound 1Document1 pageSolving Inequalities Compound 1api-328200095No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study Guide1 EhmsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Study Guide1 Ehmsapi-328200095No ratings yet
- Math Trains 1 2 - Square and Cubic Numbers - StudentDocument1 pageMath Trains 1 2 - Square and Cubic Numbers - Studentapi-328200095No ratings yet
- M8u2 Parent LetterDocument2 pagesM8u2 Parent Letterapi-328200095No ratings yet
- Aiu1 Study GuideDocument2 pagesAiu1 Study Guideapi-328200095No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study Guide1 EhmsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Study Guide1 Ehmsapi-328200095No ratings yet
- M8u2 Parent LetterDocument2 pagesM8u2 Parent Letterapi-328200095No ratings yet
- Parallel Lines in The CityDocument3 pagesParallel Lines in The Cityapi-328200095No ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Math SyllabusDocument7 pagesAlgebra 1 Math Syllabusapi-328200095100% (1)
- HW Angles and Parallel Lines Day 1Document1 pageHW Angles and Parallel Lines Day 1api-328200095No ratings yet
- Hwids - 2012 05 22 - 19 04 00Document9 pagesHwids - 2012 05 22 - 19 04 00RONAL DAMIANO PAREJANo ratings yet
- "Smart Attendance Using F Ttendance Management Using Face Recognition" Anagement SystemDocument13 pages"Smart Attendance Using F Ttendance Management Using Face Recognition" Anagement Systemamer HNo ratings yet
- How To Review A Book in Up To 5,000 Words: First StepsDocument3 pagesHow To Review A Book in Up To 5,000 Words: First StepsAnnaNo ratings yet
- Modern Machine Shop 262180-MAR 2014Document228 pagesModern Machine Shop 262180-MAR 20141mmahoneyNo ratings yet
- Understand Shell and Rib Feature - Creo Elements ProDocument8 pagesUnderstand Shell and Rib Feature - Creo Elements ProWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- OhmDocument15 pagesOhmRhonnel Manatad Alburo88% (17)
- RDSCM HowTo GuideDocument17 pagesRDSCM HowTo GuideEric LandryNo ratings yet
- English Test 03Document6 pagesEnglish Test 03smkyapkesbi bjbNo ratings yet
- Curtis E50 Pump Parts ListDocument8 pagesCurtis E50 Pump Parts ListrobertNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyDocument2 pagesWorksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyFernando CastilloNo ratings yet
- Design Stress and FatigueDocument30 pagesDesign Stress and FatigueAshok DargarNo ratings yet
- 3D Technical Data Package Configuration Management, Modeling and Drawing ProcedureDocument175 pages3D Technical Data Package Configuration Management, Modeling and Drawing Procedurejesse_w_petersNo ratings yet
- Middle Range TheoriesDocument134 pagesMiddle Range TheoriesMary Joyce MejiaNo ratings yet
- 1SM6 2015Document63 pages1SM6 2015chikoo499No ratings yet
- Branding & Advertising (T NG H P) PDFDocument44 pagesBranding & Advertising (T NG H P) PDFNguyễn Ngọc Quỳnh Anh100% (1)
- Practical Project Planning and Tracking Using Microsoft Project v2.7Document47 pagesPractical Project Planning and Tracking Using Microsoft Project v2.7Nelson Aguirre BravoNo ratings yet
- Law As A Command of SovereignDocument12 pagesLaw As A Command of SovereignAdv BL Dewasi100% (2)
- Duplichecker Plagiarism Report 3Document3 pagesDuplichecker Plagiarism Report 3Mushfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- BrainSpace - January 2024 CADocument46 pagesBrainSpace - January 2024 CARafal ZawadkaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Climatic Tower/Eco-Tower: Bachelor of ArchitectureDocument12 pagesBio-Climatic Tower/Eco-Tower: Bachelor of ArchitectureZorawar Singh Basur67% (3)
- The Housekeeping Department: Learning Activity #1Document4 pagesThe Housekeeping Department: Learning Activity #1Limar Geoff G. RosalesNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma MotorolaDocument3 pagesSix Sigma MotorolarafaNo ratings yet
- Functional Molecular Engineering Hierarchical Pore-Interface Based On TD-Kinetic Synergy Strategy For Efficient CO2 Capture and SeparationDocument10 pagesFunctional Molecular Engineering Hierarchical Pore-Interface Based On TD-Kinetic Synergy Strategy For Efficient CO2 Capture and SeparationAnanthakishnanNo ratings yet
- Standard OFR NATIONAL L13A BDREF Ed1.1 - 24 - JanvierDocument640 pagesStandard OFR NATIONAL L13A BDREF Ed1.1 - 24 - JanvierosmannaNo ratings yet
- HypnosisDocument2 pagesHypnosisEsteban MendozaNo ratings yet
- Purchase OrderDocument2 pagesPurchase OrderNicole LomasangNo ratings yet
- METRO Otherscape PlaytestDocument101 pagesMETRO Otherscape PlaytestthomasNo ratings yet
- Collection of Books To Read Preparing For ACM ICPCDocument1 pageCollection of Books To Read Preparing For ACM ICPCJia Hong100% (2)
- Dav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkDocument3 pagesDav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkOmNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - LAS 2 LEARNING CAPSULEDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - LAS 2 LEARNING CAPSULEMark RazNo ratings yet