Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8th Grade Unit Map 2 - Sheet1
Uploaded by
api-326115943Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8th Grade Unit Map 2 - Sheet1
Uploaded by
api-326115943Copyright:
Available Formats
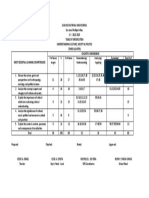
8th Grade Unit Map 2
RL4
Figurative Language, Metaphor, Simile, Personification, Idiom, Hyperbole,
Imagery, Diction, Alliteration, Onomatopoeia, Rhythm, Rhyme Scheme,
Meter, Analogy, Symbolism, Literal, Concrete, Allusion, Connotative,
Denotative, Analyze, Nuance
Effect of sound in poetry and in narrative, Identify and understand fig. lang., Identify and
understand sound devices, Poetic structure (ballad, sonnet, ode, free-verse), Difference
between analogy/allusion
RL5
Organizational Structure (Logical Order, Chronological Order, Cause/Effect,
Compare/Contrast, Problem/Solution), Foreshadowing, Pose/Answer, Frame
narrative, Epistolary novel, Graphic organizer, Dialogue, Flashback, In
Medias Res, Parallelism
Analyze & evaluate organizational structures, understand and apply voice/point of view,
author's purpose, genre expectations, audience, length and format, Recognize and
understand the practical and literary mertis of traditional structures, Plot structure devices
(frame narrative, epistolary novel, in medias res, flashback, and foreshadowing, Impact of
narrative voice on the structure (1st person vs. dialogue-heavy text)
RL6
Suspense, Point of View, Comedy, Audience, Irony, Humor, Situational Irony, Review & apply knowledge of dramatic irony (suspense & comedy), awareness and finding
Context, Dramatic Irony, Verbal Irony
examples of dramatic irony, apply DI to own writing
RI4
Domain-Specific, Analogy, Connotation, Denotation, Idiom, Allusion,
Diction, Tone, Root, Figurative, Concrete, Literal, Nuance, Etymology,
Discipline
Language aids comprehension, Author's use of words creates tone, mood, or focus, Diction
changes for audiences and purposes, Parts of Speech, Etymologies of words, Context,
Roots, Suffixes, Reference Materials
RI5
Topic Sentence, Evidence, Support, Transition, Phrase, Clause, Subordinate
Clause, Independent Clause, Modifier, Fluency, Quote, In-text Citation,
Develop, Role, Text Structure, Bibliography, Anecdote, Introduction,
Conclusion, Body Paragraph, Fluency, Quote
Textual features, Organizational structures aid in purpose of text, Placement of topic
sentence in informational documents, Varying sentence structures, Differences in structure
for paragraphs that present evidence, provide a quote, share an anecdote, or other types
Informative, Expository, Explanatory, Topic, Relevant, Pre-write,
Connotation, Denotation, Graphics, Multimedia, Multimodal, Transition,
Relationship, Domain-specific, Formal Style (APA/MLA), Cohesion,
Extraneous, Format, Literal, Concrete
Use transitions for clarity and coherence, Organizational structures w/ focus on audience &
purpose, Cite appropriately and avoid plagiarism, Use technology for graphs, maps, & other
aids, Call to action (closure strategy), Powerful introduction (anecdotal, avoid listing
points), Explore counterclaims and audience bias in argument
W7
Research, Inquiry, Focused question, Source, Citation, Annotation, Archive,
Access, Platform, Thesis, Navigate, Website, Manuscript Style (APA/MLA),
Hypothesis
Know which venues and resources most appropriate for a given search, use background
knowledge to evaluate sources, cite appropriately, avoid plagiarism, how to generate an
arguable thesis or scientific hypothesis (self-generated topics of study), appropraite
parameters of focus in inquiries, make connections among ideas
W8
Print Source, Digital Source, Summarize, Paraphrase, Citation, Annotation,
Platform, Website, Portal, Navigation, Inegration, Synthesis, Plagiarism,
Chicago Style, Turbian Style, Credible, Gather, Relevant, Accurate
Accurately summaraize without bias, annotate formally and informally, use of latest digital
trends, keyboarding skills, Know which venues and resources most appropriate for a given
search, use background knowledge to evaluate sources, cite appropriately, avoid plagiarism
W9
Literary, Rhetorical, Summary, Paraphrase, Analysis, Delineate, Evaluate,
Incorporate warrented commentary on how and why LE, RS, & Org. has desired effects,
Claim, Precis, Diction, Syntax, Tone, Imagery, Figurative Language, Rhetoric appropriate organizational structure, sets a context, focus on audience and purpose
W2 (2a, 2b, 2c,
2d, 2e, 2f)
Verbal, Gerund, Participle, Infinitive, Active Voice, Passive Voice, Indicative,
L1c: Verb Mood
Imperative, Interrogative, Conditional, Subjective, Standard English,
d: Shifts in V & M Grammar, Conventions
Review & reinforce active and passive voice, Avoid lengthy constructions in passive voice
(writing), Varying sentence construction
L2 (2a, 2b, 2c)
Conventions, Standard, Non-standard, Capitalization, Punctuation, Legible,
Comma, Ellipsis, Dash, Hyphen, Omission, Grammar, Conventions,
Abbreviation, Independent Clause, Clause, Phrase, Dependent Clause,
Coordinating Conjunction, Subordinating Conjunction
Watch abbreviations, Rules of comma, ellipsis, and dash usage - use them correctly, how
sentences are built and how they work
L5 (5a, 5b, 5c)
Figurative, Literal, Connotation, Denotation, Metaphor, Simile,
Personification, Hyperbole, Idiom, Mythological, Allusion, Synonym,
Antonym, Analogy
Translate figurative expressions into concrete language
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Language (Ed. by Ernest Lepore Barry C. Smith) (2008)Document841 pagesThe Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Language (Ed. by Ernest Lepore Barry C. Smith) (2008)IsraelEscMar100% (1)
- XI Theories and Schools of Modern LinguisticsDocument62 pagesXI Theories and Schools of Modern LinguisticsAlmabnoudi SabriNo ratings yet
- Introduction to AI & ML: A Concise HistoryDocument31 pagesIntroduction to AI & ML: A Concise HistoryGAME ZONENo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Diss Defining Social ScieDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Diss Defining Social ScieCerelina MestiolaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Assignment #3Document4 pagesSimulation Assignment #3Betsegaw DemekeNo ratings yet
- Assessment of PersonalityDocument3 pagesAssessment of PersonalityRahman ButtNo ratings yet
- Adjectives: Describes A Noun or Pronoun. Usually Comes Before The Word It DescribesDocument4 pagesAdjectives: Describes A Noun or Pronoun. Usually Comes Before The Word It DescribesJohn Ian SalidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument26 pagesChapter IIRizki Amelia IsmailNo ratings yet
- Research Design and Types of ResearchDocument53 pagesResearch Design and Types of Researchjoshipooja100% (5)
- Philosophy of EducationDocument4 pagesPhilosophy of Educationapi-459081643No ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument4 pagesChapter IIIjek vinNo ratings yet
- To Study Design Effectiveness & Role of Visual Merchandising in Creating Customer AppealDocument3 pagesTo Study Design Effectiveness & Role of Visual Merchandising in Creating Customer AppealAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Introduction Qualitative MethodsDocument16 pagesPart 1 Introduction Qualitative MethodsJane MuliNo ratings yet
- Division of Biñan City: Self - Learning ModuleDocument9 pagesDivision of Biñan City: Self - Learning ModuleBayoyong NhsNo ratings yet
- The Myth of A Superhuman AI PDFDocument21 pagesThe Myth of A Superhuman AI PDFjoseramirezeNo ratings yet
- Teacher Rubric Guide for Evaluating EducatorsDocument17 pagesTeacher Rubric Guide for Evaluating EducatorsDrAmira El-amir KhaterNo ratings yet
- Lam Van Dang: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesLam Van Dang: ObjectiveDũng NguyênNo ratings yet
- Clauses & PhrasesDocument2 pagesClauses & PhrasesmrskumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Essays: A Guide to 17 Common TypesDocument6 pagesTypes of Essays: A Guide to 17 Common Typesnour edhohaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Kids Lesson Plan AlphabetDocument4 pagesTeaching Kids Lesson Plan AlphabetJesRomeroNo ratings yet
- The Metamorphosis of Filipino As National LanguageDocument15 pagesThe Metamorphosis of Filipino As National LanguageKyel LopezNo ratings yet
- Concepcion Integrated School MAPEH Lesson LogDocument3 pagesConcepcion Integrated School MAPEH Lesson Logdaniel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Rural Sociology and Educational PsychologyDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Rural Sociology and Educational PsychologyVeera PandianNo ratings yet
- HeuristicDocument6 pagesHeuristicCarlos ArenasNo ratings yet
- How Machine Learning Is Changing E-GovernmentDocument10 pagesHow Machine Learning Is Changing E-GovernmentDaniela Sepulveda MoralesNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics and Decision Making ConceptsDocument3 pagesGroup Dynamics and Decision Making Conceptserin fernandezNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Graphic Design Elements and PrinciplesDocument3 pagesGrade 6 - Graphic Design Elements and PrinciplesBea Valerie GrislerNo ratings yet
- Mastering Organizational Behavior 14th Edition Cooper Test BankDocument23 pagesMastering Organizational Behavior 14th Edition Cooper Test Bankgadsmanoutfitqcs100% (31)
- Managerial Communication - Lesson 4 Report Writing-2Document15 pagesManagerial Communication - Lesson 4 Report Writing-2Ajaya Dhungana100% (1)
- Tos - Ucsp 3rd QRTRDocument1 pageTos - Ucsp 3rd QRTRJessie IsraelNo ratings yet