Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cornellnotesbiologyunit 4
Uploaded by
api-330069738Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cornellnotesbiologyunit 4
Uploaded by
api-330069738Copyright:
Available Formats
Cornell Notes
Topic/Objective:
Name: meredith
Class/Period:6th hour biology
Date:
Essential Question:
Questions:
2phases of photosynthesis
1 light dependent
-uses energy from the sun to produce ATP
-energy from light breaks water in the thylakoid membrane to power ATP the
left over oxygen from water is released as 02.
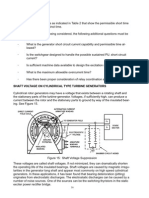
LIGHT DEPENDENT PHASE
-ATP and NADPH forced by light dependent phase.
reaction contains energy, need ti be stored in stable compound like glucose
for later use.
light dependent reaction occurs in the thyloikds inside the cholorplast
steps to photosynthesis:
step 1:light enters the system II.
step 2:these high energy electrons are passed onto the electron transport
chain.
Step 3:enzymes are going to break water molecules into 3.
-hydrogen ions
-oxygen ions
-energized electrons
step 4: oxygen is released
step 5: NADP + picks ups the electrons and along with the hydrogen plus
from broken down water molecules, NADPH is produced
step 6: ATP Synthase allows hydrogen plus ions to pass through and form
ATP by rotating and binding with ADP and a phosphate group
CALVIN CYCLE:
-the calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH from th light dependent reactions to
produce high energy sugars
FORMULA: CO2+H2O====C6H1206 + 02
Summary:
Questions:
Notes:
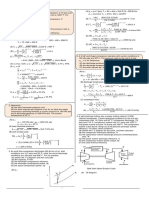
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
cellular respiration has 3 stages
-Glycolysis
-kreb cycle
-electron transport chain
GLYCOLYSIS:
STEP 1: glucose is broken into 2 carbon molecules by investing 2 atp and
releasing ADP.
step 2 : 2 NADP+ are added and 2 NADP and 4 adp are converted into 2 atp
and are sent to the electron transport chain.
Step3 :pyruvic acid is created and sent to stage fermentation if there is no
oxygen. If Oxygen is present then the acids go straight to the Kreb cycle
inside the mitochondria.
there are 2 types of fermentations lactic and alcoholic.
KREB CYCLE:
step 1:pyruvic acid is changed into a 2 carbon molecules by acetyl 1 coA
taken a carbon.
step 2: the taken carbon is exhaled.
step 3: citric acid enters into 6 molecules converted into 2 pieces
step 4: nad+ is used then creating NADH that sent to the etc. (electron
transport chain.)
step 5; NADH ADP is created to ATP
step 6: theres a H caron molecule that duplicates itself
step 7: oxalic acid back to carbon molecule
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN:
step 1 hydrogen is separated by NAPH and taken into the mitochondrial
membrane.
step2 :electrons transport hydrogen to intermembrane space
step3: hydrogen is collected and taken into ATP synthase and collected to
create ATP.
step 4:when NADP released hydrogen NAD+ is taken to glycolysis or krebs
cycle
Summary:
Cornell Notes
Topic/Objective:
Name:
Class/Period:
Date:
Essential Question:
Questions:
Summary:
Questions:
Summary:
Notes:
You might also like
- Cornellnotesbiologyunit4 2Document5 pagesCornellnotesbiologyunit4 2api-330069738No ratings yet
- Cornellnotesbiologyunit4 1Document5 pagesCornellnotesbiologyunit4 1api-330069738No ratings yet
- Biology Final Smart GoalDocument3 pagesBiology Final Smart Goalapi-330069738No ratings yet
- Smart Goals Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSmart Goals Worksheet 1api-333317612No ratings yet
- Learner Profile Reflection Sheet CompletedDocument2 pagesLearner Profile Reflection Sheet Completedapi-330069738No ratings yet
- Cornellnotes 1Document3 pagesCornellnotes 1api-330069738No ratings yet
- Smart Goals Worksheet 1Document3 pagesSmart Goals Worksheet 1api-330069738100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Material Spec 1.4571Document2 pagesMaterial Spec 1.4571Vishal GoelNo ratings yet
- Engine Diesel PerfomanceDocument32 pagesEngine Diesel PerfomancerizalNo ratings yet
- Somayya Polytechnic, Wadgaon, Chandrapur Department of Mining and Mine Surveying 2 Year - Subject Notes Subject: Mine Ventilation Unit: 01 - Mine AirDocument136 pagesSomayya Polytechnic, Wadgaon, Chandrapur Department of Mining and Mine Surveying 2 Year - Subject Notes Subject: Mine Ventilation Unit: 01 - Mine AirMayur BawaneNo ratings yet
- Beam Powered PropulsionDocument19 pagesBeam Powered PropulsionSai Sushma100% (1)
- DEY's IED Sustainable DevelopmentDocument236 pagesDEY's IED Sustainable DevelopmentHemaline Rose100% (1)
- Portable welding load banks for testing AC/DC welding powerDocument2 pagesPortable welding load banks for testing AC/DC welding powerlauguicoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for permissible short time overload current and excitation system design questionsDocument2 pagesGuidelines for permissible short time overload current and excitation system design questionsJuan Fernando UbeiraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Physics EconomicsDocument6 pagesJournal of Physics EconomicsmauudyNo ratings yet
- Fluent Combustion AnalysisDocument31 pagesFluent Combustion AnalysisVignesh SambanNo ratings yet
- Nav MW (U-1)Document62 pagesNav MW (U-1)Navneet guptaNo ratings yet
- 21 Non Lethal Weapons PDFDocument43 pages21 Non Lethal Weapons PDFMichael100% (3)
- North Sea safety transformed by Piper Alpha disaster legacyDocument3 pagesNorth Sea safety transformed by Piper Alpha disaster legacycrackerz83No ratings yet
- FP 238Document32 pagesFP 238Mahmoud Atia100% (2)
- Electrohydraulics Basic LevelDocument202 pagesElectrohydraulics Basic LevelSavio Fernandes100% (9)
- Sedimentation PDFDocument16 pagesSedimentation PDFjamaiiicaNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Document6 pagesWelding Procedure Specification (WPS)Mohamad Marwan HamwiNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument28 pagesTransport in PlantsGautam Dayal100% (1)
- Northside-Southside TOD StudyDocument265 pagesNorthside-Southside TOD StudynextSTL.comNo ratings yet
- SRG Major Test Paper 12-12-2023Document28 pagesSRG Major Test Paper 12-12-2023pal018488No ratings yet
- SNP Tanker ReportDocument3 pagesSNP Tanker ReportfikrifadzalNo ratings yet
- Led Taxi Light TestingDocument2 pagesLed Taxi Light Testingajaydce05No ratings yet
- Ecu MappingDocument8 pagesEcu MappingVitor SegniniNo ratings yet
- 818PetroleumHistory6 PDFDocument1 page818PetroleumHistory6 PDFMazhar BadrNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical Industry in India - Determinants, ChallengesDocument5 pagesPetrochemical Industry in India - Determinants, Challengesvvk2cool100% (1)
- CSE Engineering Course DetailsDocument233 pagesCSE Engineering Course DetailsVenkatesh Kumar0% (1)
- En 609-1 PDFDocument14 pagesEn 609-1 PDFSURESHKUMARNo ratings yet
- COACHING SET 2 MergedDocument17 pagesCOACHING SET 2 Mergedjohn-john castañedaNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level Geography 9696 Core Model Answers v1Document31 pagesCaie As Level Geography 9696 Core Model Answers v1kgethilwemakgotsoNo ratings yet
- Temp Effect Final VersionDocument5 pagesTemp Effect Final VersionBranislavPetrovicNo ratings yet
- Energetics QuestionsDocument2 pagesEnergetics QuestionsBrandeice BarrettNo ratings yet