Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Pain
Uploaded by
Yeana AlonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Pain
Uploaded by
Yeana AlonCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
Name: JM Student Nurse: Yeana S. Alon
Age: 44 y.o Year and Section: BN3B
Sex: Female
Date of Admission: Feb. 03, 2010
Chief Complaints: abdominal enlargement
Medical Diagnoses: Ovarian New Growth
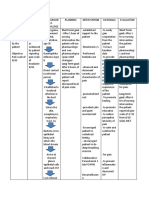
Assessment Nursing Dx Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification Evaluation
Actual/Abnormal Cues: Acute pain r/t tissue Predisposing Factor: Age After 8 hours of nurse- After 8 rourse of nurse-
Client stated, “gasakit trauma s/t post (44 y.o) client interaction, my client interaction, my
siya kun mag-ubo kag abdominal surgery AEB client will be able to: Independent: client:
magkadlaw ko”. reported pain with a scale
Client stated, “kis-a indi of 8, sleep disturbance & Increased luteinizing 1. Verbalize minimized Monitor v/s and check Alterations from 1. Goal Met. Stated that,
ko masyado katulog di”. guarded behavior on hormone or controlled feeling of dressing of affected normal may be signs “Kun mag ubo kag
Guarded behavior affected area. pain. surgical site. of infection. Moistened kun gatawa ko dira
Pain Scale= 8 dressings are man lng siya gasakit,
(10 as highest) Definition: Hyperstimulated ovaries favorable site for pero gadula dula man
BP=130/90mmHg Unpleasant Sensory and microorganisms. siya ah. Ok naman
emotional experience Assess for signs of To aid in evaluating ko.”
Risk/Related Factors: arising from actual or Hormonal imbalance pain, location, and need for proper
potential tissue damage intensity and use of pain intervention. 2. Goal Met.
Coughing causes pain
or describe in terms such scale (0-10) and Continued pain may Distinguished ways on
at surgical site.
damage; sudden or slow Formation of Ovarian evaluate characteristics indicate developing how to relieve pain.
Sudden body
onset of any intensity New Growth of pain. complication. Client stated, “Gainom
movement causes pain
from mild to severe with Inform client to avoid Prevent from nalng ko tubi para indi
at the surgical site
an anticipated or weight bearing until complications on the magkatol akon
predictable end and a TAHBSO lymphnode allowed. incision site. tutunlan kag indi na
Strengths/Wellness:
duration of less than 6 evaluation ko mag-ubo.”
Strong Family support months. 2. Verbalize methods
Compliance to medicine Encourage diversional Allow the muscle to
that provide relief. activities and use of relax and serve as 3. Goal Met. Verbalized
Strong faith with God Source: Tissue trauma her way of relaxation.
relaxation exercises diversion from pain.
Douges, M.E. et.al., such as focused Client stated, “Gailis
(2002). Nurse’s pocket breathing. ilis lang ko sang
guide: diagnosis, Disruption of cell Encourage adequate Promote healing by posisyon ko di sa
interventions & membrane rest and sleep. reducing basal katre kag gaginhawa
rationales. (8th Edition). metabolic rate and man ko kis.a dalum
Philadelphia: F.A. Davis allowing oxygen &
Company. Start of inflammatory nutrients to be utilized
process for tissue regeneration
3. Demonstrate use of
Provide comfort Provide non-
Release of relaxation skills &
measures such as back pharmacologic pain
prostaglandin/bradykinin diversional activities
rub & change of management.
as indicated for her
position.
situation.
Acute pain on surgical Assist client in Reduce swelling &
site with pain scale of 8 performing deep prevent stiffnes.
breathing exercise and Decreased lung
dorsiflexing of foot and capacity & decreased
Sleep disturbance, arms cough efficiency are
guarded behavior on predisposing factors of
surgical site. respiratory infection.
Collaborative:
Administration of NSAID activity
analgesics (Mefenamic includes modulation of
Source: Acid) T-cell function,
Smeltzer, S.C. & Bare, inhibition of
B.G. (2004).Textbook of inflammatory cell
medical-surgical chemotaxis,
nursing(10th Edition, decreased release of
Volume 2). Philadelphia: superoxide radicals or
Lippincott Williams and increased scavenging
Wilkins. of these compounds at
inflammatory site.
Administration of Antibiotics are used to
antibiotics (Amoxicillin) treat & prevent
infections caused by
susceptible pathogens
in skin structure.
Source:
Douges, M.E. et.al.,
(2002). Nurse’s pocket
guide: diagnosis,
interventions &
rationales. (8th Edition).
Philadelphia: F.A. Davis
Company.
You might also like
- Concept Map - Surgical GroupDocument25 pagesConcept Map - Surgical GroupIan ChristianNo ratings yet
- Availability: Classifications: Antihistamine Antipruritic Pregnancy Category: CDocument4 pagesAvailability: Classifications: Antihistamine Antipruritic Pregnancy Category: CCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ko BabyDocument3 pagesNCP Ko BabyDaniel ApostolNo ratings yet
- NCP New DiarheaDocument1 pageNCP New DiarheaCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument6 pagesGoutNhoydaleen SandovalNo ratings yet
- Grand Case NP 5 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument5 pagesGrand Case NP 5 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyFarida Paula R. SevillaNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNCP Proper CholecystectomyGail Lian SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DMDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan DMnikaaraaaNo ratings yet
- Pregnant Aerobics Instructor Case StudyDocument25 pagesPregnant Aerobics Instructor Case StudyGerly LagutingNo ratings yet
- Ordonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleDocument4 pagesOrdonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleKyla OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDeanne Carla DalilisNo ratings yet
- PREOP3Document1 pagePREOP3Void LessNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyLiwayway Bayoca LozanoNo ratings yet
- Buerger's DiseaseDocument4 pagesBuerger's DiseasesweetyjonasNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP PaindwightciderNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain Case: AppendicitisDocument70 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain Case: AppendicitisVenny VeronicaNo ratings yet
- OtosclerosisDocument36 pagesOtosclerosisShamsheer ShaikNo ratings yet
- Short Term Goal: After 1 Hour of Short Term Goal: After 1Document2 pagesShort Term Goal: After 1 Hour of Short Term Goal: After 1Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument7 pagesUlcerative ColitisShaira Anne Fuentes BaroniaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Environmental Sanitation Revised Dec 18Document76 pagesModule 6 - Environmental Sanitation Revised Dec 18mgllacuna0% (2)
- Malnutrition in Older AdultsDocument44 pagesMalnutrition in Older Adultsjohnjoe subaynoNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan Group12Document5 pagesDischarge Plan Group12rraksNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper TahbsoDocument3 pagesNCP Proper TahbsoMiriam EstradaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 51Document21 pagesCase Study 51henryrchouinard100% (2)
- Exploratory LaparotomyDocument24 pagesExploratory Laparotomyyynu_sia48475No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeRammiel Saylo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument2 pagesPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonNo ratings yet
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDocument1 pageSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaTyrel LozanoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Purpose of Cystoclysis: 1. Closed Bladder Irrigation SystemDocument6 pages1.2 Purpose of Cystoclysis: 1. Closed Bladder Irrigation SystemKatleen Calang AlagNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain - Mastectomy - Breast CADocument2 pagesAcute Pain - Mastectomy - Breast CAAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Case 052: Biliary ColicDocument4 pagesCase 052: Biliary ColicZauzaNo ratings yet
- Meniere's Disease - Case StudyDocument3 pagesMeniere's Disease - Case StudyZORANASNNo ratings yet
- Dehydration Symptoms and Treatment PlansDocument2 pagesDehydration Symptoms and Treatment PlansJennyu YuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Copd FinalDocument3 pagesDrug Study Copd FinalMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlankingpinNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Care DeficitKharma LigoresNo ratings yet
- 10 1056@NEJMcpc1913468 PDFDocument10 pages10 1056@NEJMcpc1913468 PDFAbdelkader HociniNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument6 pagesHyponatremiaJaymart Saclolo CostillasNo ratings yet
- Hyper Nat Remi ADocument6 pagesHyper Nat Remi Ayeof_kang08No ratings yet
- Rle Worksheet Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesRle Worksheet Nursing ProcessMARVIE JOY BALUMA CABIOCNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis Case StudyDocument12 pagesAmoebiasis Case StudyGrace NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Medical and Nursing Management Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesMedical and Nursing Management Nursing Care PlanPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Choking: by Jawad AhmedDocument25 pagesChoking: by Jawad Ahmedjawad_ahmedNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument12 pagesScriptWaleed Nadeem50% (2)
- NCP of Difficulty of BreathingDocument2 pagesNCP of Difficulty of BreathingMan GatuankoNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument12 pagesCase AnalysisFroilan TaracatacNo ratings yet
- 11 Digestion and Bowel Elimination 2019 (Nursing) Geriatric NursingDocument44 pages11 Digestion and Bowel Elimination 2019 (Nursing) Geriatric NursingDarla SaulerNo ratings yet
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument17 pagesAcute TonsillopharyngitisRachel Haide NaravalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ashraf Sayeed: Department of OphthalmologyDocument49 pagesDr. Ashraf Sayeed: Department of Ophthalmologysaiful haque100% (1)
- CholecystectomyDocument6 pagesCholecystectomyjhodaneNo ratings yet
- EpiglottitisDocument1 pageEpiglottitisSandra GabasNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- NCP For ChronicPain PDFDocument2 pagesNCP For ChronicPain PDFjay kusainNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSian Grace AsadaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainAshley Mae LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for SISPE PatientDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for SISPE PatientIvan A. EleginoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: EpisiorraphyDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: EpisiorraphyMaria Jessica DumdumNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Notes - Nurse's Clinical Pocket Guide (FA Davis, 2007)Document242 pagesMedSurg Notes - Nurse's Clinical Pocket Guide (FA Davis, 2007)Keron Hou97% (62)
- Postoperative Nursing CareDocument2 pagesPostoperative Nursing CareYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- NCP DengueDocument3 pagesNCP DengueYeana Alon50% (4)
- Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- Recurrent MiscarriageDocument5 pagesRecurrent MiscarriagedindaNo ratings yet
- Cupping Therapy Effect on Anterior Knee PainDocument15 pagesCupping Therapy Effect on Anterior Knee PainBee Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Biological Models of Non-Suicidal Self-InjuryDocument18 pagesBiological Models of Non-Suicidal Self-InjuryNiel DabuetNo ratings yet
- Lachesis - Homeopathic Medicine - Its Uses, Indications and DosageDocument6 pagesLachesis - Homeopathic Medicine - Its Uses, Indications and Dosagefausto omioNo ratings yet
- Boquecosa Nursing Review ReviewerDocument19 pagesBoquecosa Nursing Review ReviewerElay PedrosoNo ratings yet
- IPPS 2012 Program Book PDFDocument392 pagesIPPS 2012 Program Book PDFJanet L WarrenNo ratings yet
- Caffeine Breast Pain: Revisiting The ConnectionDocument9 pagesCaffeine Breast Pain: Revisiting The ConnectionGrace PelicioniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Chronic Pain and COPDDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: Chronic Pain and COPDneuronurse100% (1)
- Green Book, Methods For The Determination of Possible Damage, CPR 16EDocument337 pagesGreen Book, Methods For The Determination of Possible Damage, CPR 16Ejeremyg998100% (8)
- Euthanasia Position Paper - Against EuthanasiaDocument4 pagesEuthanasia Position Paper - Against EuthanasiachristiancalatcatNo ratings yet
- Sports MassageDocument18 pagesSports MassageKanak SoniNo ratings yet
- Simple Technique For Lip and Nasolabial Fold Anesthesia For Injectable FillersDocument3 pagesSimple Technique For Lip and Nasolabial Fold Anesthesia For Injectable FillersGina CastilloNo ratings yet
- Local and Regional Anaesthesia in Dogs Cats Part 1 Overview of Concepts Drugs Grubb Lobprise 2020Document9 pagesLocal and Regional Anaesthesia in Dogs Cats Part 1 Overview of Concepts Drugs Grubb Lobprise 2020Carolina Duque RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DR Yog TT Notes Rishikesh Training - Docx 2023Document21 pagesDR Yog TT Notes Rishikesh Training - Docx 2023mechevegadiazNo ratings yet
- Foot - Base of 5th Metatarsal Fracture - Final Apr22Document4 pagesFoot - Base of 5th Metatarsal Fracture - Final Apr22Simone EspositoNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Health Care 4th Edition Mitchell Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introduction To Health Care 4th Edition Mitchell Solutions Manual PDFreplantrhymevgmx08100% (14)
- Balnear and Rehabilitation Sanatorium Techirghiol - Statitical Analysis of Pathology Types of Admited PatientsDocument31 pagesBalnear and Rehabilitation Sanatorium Techirghiol - Statitical Analysis of Pathology Types of Admited PatientsThermalBathsforActivNo ratings yet
- Penurunan Intensitas Skala Nyeri Pasien Appendiks Post Appendiktomi Menggunakan Teknik Relaksasi BensonDocument10 pagesPenurunan Intensitas Skala Nyeri Pasien Appendiks Post Appendiktomi Menggunakan Teknik Relaksasi BensonReynaldi SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Oet Wrıtıng Brıtısh Academy 01 315 376 With AnswerDocument62 pagesOet Wrıtıng Brıtısh Academy 01 315 376 With Answersaramma mathewNo ratings yet
- Chestionar 2Document14 pagesChestionar 2Fărcaș Cristina OanaNo ratings yet
- NCS GlaucomaDocument47 pagesNCS GlaucomaDan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- Resume Jurnal 1 RematikDocument10 pagesResume Jurnal 1 RematikAnonymous FEy8SnNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document12 pagesNCP 1Izabela UyNo ratings yet
- Parkland formula and rule of 9Document8 pagesParkland formula and rule of 9awuahbohNo ratings yet
- Urografin Urografin 76Document8 pagesUrografin Urografin 76KartikGachinmaniNo ratings yet
- Argentum Group of MedicinesDocument23 pagesArgentum Group of MedicinesRaveendra MungaraNo ratings yet
- A Former Vatican Exorcist Son by Joshua Lokamba of Congo Part OneDocument2,105 pagesA Former Vatican Exorcist Son by Joshua Lokamba of Congo Part OneSamuelNo ratings yet
- (UPDATED) Oppura, Wennonah Alexis A. BSN3E Medical Ward Week 5 NCPDocument3 pages(UPDATED) Oppura, Wennonah Alexis A. BSN3E Medical Ward Week 5 NCPWENNONAH ALEXIS OPPURANo ratings yet
- Palliative Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesPalliative Nursing Care Planstudent_019No ratings yet
- AssessmenDocument1,083 pagesAssessmenluizamgoNo ratings yet