Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Summary (Math)
Uploaded by
jeay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pagelesson plan
Original Title
Chapter Summary(Math)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlesson plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageChapter Summary (Math)
Uploaded by
jeaylesson plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Chapter Summary
A polynomial expression in one variable x is an expression which can
be written in the form A n X+ An X + . . . + AX + Aa where An 0
and each coefficient is a real number and n is a nonnegative integer.
A polynomial function of degree n is a function which is defined by the
equation
P(x)= AnX+An1X+An2X+ . . . + AX+A
Where An, An, . . . , A are real constants, An 0, and nonnegative integer.
Synthetic division is a short method of dividing a polynomial in x by x -
r.
To solve a polynomial equation is to find the roots of the equation.
The leading coefficient of a polynomial is the coefficient of the first
term of a polynomial arranged in descending powers of the variable.
The division algorithm is the algebraic expression process of the form
Dividend= divisor (quotient) + remainder
The remainder theorem states that if a polynomial function P(x) is
divided by the binomial x c, then the constant remainder is equal to
P(c).
A prime polynomial is a polynomial that can no longer be factored.
The factor theorem states that if P(x) is a polynomial function, then the
binomial x c is a factor of P(x) if, and only if, P(c) =0.
If the factor x r occurs n times in the complete factorization of the
polynomial P(x), then r is a root of the equation P(x) =0 with
multiplicity n.
For a polynomial function P, if r is a number such that P(r) = 0, then r is
called a zero of the polynomial function, r may be a real or no real
number.
The number of variations of sign is the number of sign changes in a
polynomial as you go from left to right in an equation.
Following are the rules that can help you in solving polynomial
equations:
1. For every polynomial equation P(x) =0 of degree n, the number of
zeros is not more than n.
2. Use Descartes rule of sign to find the number of positive and
negative roots.
If P (x) = 0 is a polynomial equation with real coefficients, then
the number of positive roots of the equation is either equal to the
number of variations of the sign of P(x) or less than that by an even
number. The number of negative roots of the equation is either
equal to the number of variations in the sign of P(x) or less than
that by an even number.
3. The rational roots test
Let P(x) = AnX+AnX+An+ . . . +AX+ A
Where, An 0 and A 0, and each coefficient is an integer.
If P/q (in lowest terms) is a rational root of P(x) = 0, then p is an
integer factor A and q is an integer factor of A
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Solution Guide, Differential EquationDocument53 pagesSolution Guide, Differential EquationhmbxNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- 1000 Extension 2 Revision Questions Inc CH 1-3-2020!01!25Document77 pages1000 Extension 2 Revision Questions Inc CH 1-3-2020!01!25BelNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- MBUNGELE HW2 assignment solutionsDocument2 pagesMBUNGELE HW2 assignment solutionsDazzle Njabs MbungeleNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Absolute convergence ratio root testsDocument12 pagesAbsolute convergence ratio root testsdzikrydsNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Use LU Decomposition To Determine The Matrix Inverse For The - QuizletDocument5 pagesUse LU Decomposition To Determine The Matrix Inverse For The - QuizlettestingitNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Joint Probability FunctionsDocument7 pagesJoint Probability FunctionsBran RelieveNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- An-Intro To-Vibration MATLAB 1998a LinkedDocument22 pagesAn-Intro To-Vibration MATLAB 1998a LinkedEbrahim ZolfagharyNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Objectives To Find Compositions of Isometries, Including Glide ReflectionsDocument7 pagesObjectives To Find Compositions of Isometries, Including Glide ReflectionsAbood SafadiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- JEE Mains Free Mock Test 2015Document65 pagesJEE Mains Free Mock Test 2015smrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- College of Foundation and General Studies Putrajaya Campus Final Exam TRIMESTER 1 2012 / 2013Document4 pagesCollege of Foundation and General Studies Putrajaya Campus Final Exam TRIMESTER 1 2012 / 2013Bernard GohNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Sturm-Liouville Eigenvalue ProblemsDocument34 pagesSturm-Liouville Eigenvalue ProblemsPrasad Uday BandodkarNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document13 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Kalyan MarutiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Application of Matrices in Real LifeDocument2 pagesApplication of Matrices in Real LifeCh Ameer Hamza100% (7)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Master Theorem-: Merge SortDocument12 pagesMaster Theorem-: Merge SortChris GonsalvesNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Advanced Algebra Solution SheetDocument18 pagesAdvanced Algebra Solution Sheetmadelene gatuteoNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Algebra 2019Document1 pageAlgebra 2019anhduc phaptrinhNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elementary Numerical Analysis Prof. Rekha P. Kulkarni Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 40 Q R MethodDocument35 pagesElementary Numerical Analysis Prof. Rekha P. Kulkarni Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 40 Q R MethodAsse TenNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Exponents and Root Values Notes SheetDocument3 pagesExponents and Root Values Notes SheetKenneth NewsomeNo ratings yet
- CST 304 - Computer Graphics: 2D TransformationsDocument34 pagesCST 304 - Computer Graphics: 2D TransformationsMalu VavuNo ratings yet
- 1.7 - Diagonal, Triangular and Symmetric Matrix - 6Document10 pages1.7 - Diagonal, Triangular and Symmetric Matrix - 6ABU MASROOR AHMEDNo ratings yet
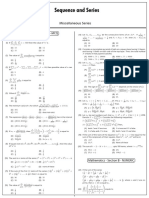
- Miscellaneous Series 1694012216Document3 pagesMiscellaneous Series 1694012216Aarush KaletwadNo ratings yet
- #Introductory Mathematics - Applications and Methods - Gordon S. Marshall - Springer (1998) .1Document233 pages#Introductory Mathematics - Applications and Methods - Gordon S. Marshall - Springer (1998) .1E6330 HAL100% (1)
- Geometry - Chapter 12 TestDocument15 pagesGeometry - Chapter 12 TestCorneliaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Discrete Math Lecture 10Document32 pagesDiscrete Math Lecture 10Tazeen zahraNo ratings yet
- An Interesting Number Theoretic Problem: 1 Introduction and MotivationDocument2 pagesAn Interesting Number Theoretic Problem: 1 Introduction and MotivationKonstantinos MichailidisNo ratings yet
- EAA111-Chapter 5Document63 pagesEAA111-Chapter 5vincentch96No ratings yet
- Mathematical Association of AmericaDocument5 pagesMathematical Association of AmericaCarlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Mid Test (OPEN BOOK) : Swiss German UniversityDocument5 pagesMid Test (OPEN BOOK) : Swiss German Universityaan nug rohoNo ratings yet
- 3 13 17weekly Homework Sheet Week 25 - 5th Grade - CcssDocument2 pages3 13 17weekly Homework Sheet Week 25 - 5th Grade - Ccssapi-328344919No ratings yet
- The Beltrami EquationDocument309 pagesThe Beltrami EquationGregório Silva NetoNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)