Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Road Constr
Uploaded by
Vikas KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Road Constr
Uploaded by
Vikas KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Raw materials for road construction
1- Aggregate
2-Bitumen (Tar)
3-Waste Plastics
AGGREGATE
Aggregate is a collective term for the mineral materials such as sand, gravel,
and crushed stone that are used with a binding medium (such as water,
bitumen, Portland cement, lime, etc.) to form compound materials (such as
bituminous concrete and Portland cement concrete). By volume, aggregate
generally accounts for 92 to 96 percent of Bituminous concrete and about 70
to 80 percent of Portland cement concrete. Aggregate is also used for base
and sub-base courses for both flexible and rigid pavements. Aggregates can
either be natural or manufactured. Natural aggregates are generally extracted
from larger rock formations through an open excavation (quarry). Extracted
rock is typically reduced to usable sizes by mechanical crushing.
Manufactured aggregate is often a bye product of other manufacturing
industries.
GENERAL PROCESS FOR FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT
CONSTRUCTION:-
FIRST STEP :-Plastics waste (bags ,cups , bottles ) made out of PE,PP and PS
cut into a size between 2.36mm and 4.75mm using shredding machine.
SECOND STEP:-The aggregate mix is heated to 165c (as per the HRS
specification) and transferred to mixing chamber. Amount of plastic to be
added is @8% of bitumen.
THIRD STEP:-Similarly the bitumen is to be heated up to a maximum of
160c (HRS Specification) to have good binding and to prevent weak
bonding. (Monitoring the temperature is very important).
FOURTH STEP:-At the mixing chamber, the shredded plastics waste is to be
added. It get coated uniformly over the aggregate within 30 to 60 seconds,
giving an oily look.
FIFTH STEP:-The plastics waste coated aggregate is mixed with got bitumen
and the resulted mix is used for road construction. The roller used is 8-ton
capacity.
LAST STEP:-The road laying temperature is between 110c to 120 c. And
the rollers are used have capacity 8-ton generally.
Calculation of base course thickness (tb)
Similar to the above procedure, from the CBR value of base course and
wheel load read the value of thickness of pavement which is above the base
course d(ts). From this we can find out the value of tb. tb = Tsb ts
Therefore all the values of pavement are known and cross section of
pavement is as follows.
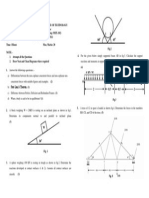
CBR method recommended by IRC (Indian road congress
In this method, the chart contains several curves (A, B, C, D, E, F, and G)
which represents the different levels of traffic intensities. Based on this we
will find out the layers thicknesses.
Data required for design:
a. CBR value of soil subgrade
b. CBR value of sub base course
c. CBR value of base course
d. Traffic intensity
Calculation of total thickness (T)
In this step, firstly for the given value of traffic intensity select appropriate
curve from classification table which is shown in the below chart. Now, from
the given CBR value of subgrade soil read the total thickness (T) with respect
to selected curve.
Calculation of sub base course thickness (tsb)
By using the above chart, for give CBR value of sub base course material and
for traffic intensity value read the thickness of pavement which is above the
soil sub base. It is denoted as (Tsb). Which is highlighted by circle in the
below fig. but here we have to find tsb.
Therefore, thickness of sub base course tsb =T Tsb
Calculation of base course thickness (tb)
Repeat the above procedure again, from the CBR value of base course and
from traffic intensity value read the value of thickness of pavement which is
above the base course (ts). From this we can find out the value of tb. tb = Tsb
ts
Therefore all the values of pavement are known and cross section of
pavement is as follows.
You might also like
- Environment Lab CuHDocument4 pagesEnvironment Lab CuHVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Environment Lab CuHDocument4 pagesEnvironment Lab CuHVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Environment Lab CuHDocument4 pagesEnvironment Lab CuHVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Role of GeosyntheticDocument7 pagesRole of GeosyntheticVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ro Recycle and Waste MaterialDocument1 pageIntroduction Ro Recycle and Waste MaterialVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Environment Lab CuHDocument4 pagesEnvironment Lab CuHVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- AvalambanDocument2 pagesAvalambanVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Toilet System in IndiaDocument2 pagesToilet System in IndiaVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- B.tech CONV - 1Document1 pageB.tech CONV - 1Vikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Toilet System in IndiaDocument2 pagesToilet System in IndiaVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ro Recycle and Waste MaterialDocument1 pageIntroduction Ro Recycle and Waste MaterialVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ro Recycle and Waste MaterialDocument1 pageIntroduction Ro Recycle and Waste MaterialVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Ground ImprovementDocument1 pageGround ImprovementVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- GeneralDocument14 pagesGeneralVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Soil StabilizationDocument4 pagesSoil StabilizationVikas Kumar100% (1)
- A Review On The Rice Husk AshDocument1 pageA Review On The Rice Husk AshVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- GeneralDocument14 pagesGeneralVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Enchanching The Soft Soil by Installation of Vertical Stone Column Fileed With Crushed Concrete DebrisDocument2 pagesEnchanching The Soft Soil by Installation of Vertical Stone Column Fileed With Crushed Concrete DebrisVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Rice Husk AshDocument1 pageA Review On The Rice Husk AshVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Enchanching The Soft Soil by Installation of Vertical Stone Column Fileed With Crushed Concrete DebrisDocument2 pagesEnchanching The Soft Soil by Installation of Vertical Stone Column Fileed With Crushed Concrete DebrisVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Impact of Surkhi On GSB Layer As Replacement To The Stone DustDocument1 pageImpact of Surkhi On GSB Layer As Replacement To The Stone DustVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Enchanching The Soft Soil by Installation of Vertical Stone Column Fileed With Crushed Concrete DebrisDocument2 pagesEnchanching The Soft Soil by Installation of Vertical Stone Column Fileed With Crushed Concrete DebrisVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Impact of Surkhi On GSB Layer As Replacement To The Stone DustDocument10 pagesImpact of Surkhi On GSB Layer As Replacement To The Stone DustVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Compaction and Swelling CharaceristicsDocument1 pageCompaction and Swelling CharaceristicsVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Reinforcement in PavementDocument1 pageBamboo Reinforcement in PavementVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 M 0.5 M 0.5 M 2 MDocument1 page2 M 0.5 M 0.5 M 2 MVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Rice Husk AshDocument1 pageA Review On The Rice Husk AshVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Rice Husk AshDocument1 pageA Review On The Rice Husk AshVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- EIA Chakdara ShamozaiDocument165 pagesEIA Chakdara ShamozaiFariaNo ratings yet
- Indoor Air Quality AnalysisDocument21 pagesIndoor Air Quality AnalysisAshmit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Mastering JMP Definitive Screening DesignsDocument39 pagesMastering JMP Definitive Screening DesignsBosco RajuNo ratings yet
- CMFRI Report On Pollution in Kayalpatnam Due To DCWDocument4 pagesCMFRI Report On Pollution in Kayalpatnam Due To DCWkayalonthewebNo ratings yet
- Elec & I&C Cable Construction Progress (As of 21 June, 2018)Document7 pagesElec & I&C Cable Construction Progress (As of 21 June, 2018)Kharisma Pangeran LanangNo ratings yet
- Dhakras Bhairavi SDocument137 pagesDhakras Bhairavi SReshma PawarNo ratings yet
- ISEA 33410 Green House GasDocument42 pagesISEA 33410 Green House GasManggala Patria WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Light Pollution in Dhaka CityDocument3 pagesLIGHT Light Pollution in Dhaka CityPrapya BarmanNo ratings yet
- Ged Written Essay - DaonDocument7 pagesGed Written Essay - DaonKeny100% (1)
- Task 2 - Writing Assignment ProductionDocument6 pagesTask 2 - Writing Assignment ProductionJeniffer MartinezNo ratings yet
- Small-scale Rural Biogas Programmes HandbookDocument5 pagesSmall-scale Rural Biogas Programmes HandbookproponeNo ratings yet
- Godrej AmbernathDocument10 pagesGodrej AmbernathVishvajit PatilNo ratings yet
- Adsorption and Its Applications in Industry and Environmental Protection Vol II Applications in Environmental ProtectionDocument1,050 pagesAdsorption and Its Applications in Industry and Environmental Protection Vol II Applications in Environmental ProtectionMuhammad Arsalan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cato Ridge LAP & Precinct Plans To ChamberDocument26 pagesCato Ridge LAP & Precinct Plans To ChamberDurban Chamber of Commerce and IndustryNo ratings yet
- Mgo (Dma) - enDocument37 pagesMgo (Dma) - enscribd_alphaNo ratings yet
- SS - PRO02 - Respiratory ProtectionDocument9 pagesSS - PRO02 - Respiratory ProtectionmadhulikaNo ratings yet
- BOD TestDocument9 pagesBOD TestFauzi ArifinNo ratings yet
- So2b4 11 13Document2 pagesSo2b4 11 13Omar SaaedNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIALPOLLUTIONCONTROLDocument17 pagesINDUSTRIALPOLLUTIONCONTROLRaijo PhilipNo ratings yet
- Membrane Filter Method For Fecal Streptococcus PDFDocument13 pagesMembrane Filter Method For Fecal Streptococcus PDFJey-r VenturaNo ratings yet
- Fast Wax MsdsDocument5 pagesFast Wax MsdsAnaditiNo ratings yet
- Cumene Process, Prod - CBIDocument2 pagesCumene Process, Prod - CBIChris LindseyNo ratings yet
- How water treatment system design and operation impact boiler feedwater purity and failuresDocument9 pagesHow water treatment system design and operation impact boiler feedwater purity and failuresJayanath Nuwan SameeraNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Examples: Air Quality and MeteorologyDocument6 pagesAir Pollution Examples: Air Quality and MeteorologyHannah PascuaNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Below Ground Waterproofing BrochureDocument8 pagesFosroc Below Ground Waterproofing Brochure15_01_1977_anandNo ratings yet
- Job Description Occupational Health and Safety SpecialistsDocument3 pagesJob Description Occupational Health and Safety SpecialistsMala MinnieNo ratings yet
- MSDS Isophorone DiisocyanateDocument6 pagesMSDS Isophorone DiisocyanateIzzuddin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 8749 Salient FeaturesDocument34 pagesRepublic Act 8749 Salient Featuresdenr02legal88% (8)
- Exp.7 Alkalinity TestDocument12 pagesExp.7 Alkalinity Testhero100% (1)
- Green MarketingDocument25 pagesGreen MarketinggeetukumariNo ratings yet