Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer Biochem For Nucleotides
Uploaded by
Nino D. AtilanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer Biochem For Nucleotides
Uploaded by
Nino D. AtilanoCopyright:
Available Formats
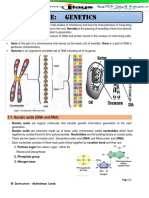
NUCLEOTIDES High Heat= Denaturation
A=T When temperature is slowly lowed then it will
G=C renature its self, by restacking the base pairs and
hydrogen bond between complimentary strand.
Each Nucleotide of DNA includes a The ability of short single-stranded nucleic acids
nitrogen-containing base. (Either DNA or RNA) to hybridize with longer poly
Base Adenine and Guanine are called nucleotide chains is the bases for a number for a
Purines Genes encode Proteins
Base Cytosine and Thymine are called The complimentarity of the two strands of DNA is
Pyrimidines essential for its function as the storehouse of genetic
However information, since this information must be
Ribonucleic acid containeds REPLICATED, for each generation.
Uracil instead of Thymine
*DNA Contains Bases ACGT while RNA Containes A portion of the DNA is transcribed to produce a
Bases ACGU complementary strand of RNA, then the RNA is
Atom N9 of Purine and atom Translated into protein
N1 of Pyrimidine is linked to a
five-carbon sugar to form a An organisms complete set of genetic information is
Nucleoside called its genome.
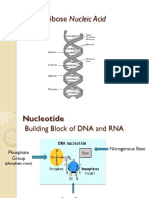
A nucleoside + a phosphate group linked to 5 =
Nucleotide Template strand- Non-coding strand 3 5
Vitamin= compound that must be obtained from a
diet The strand that is paired by the RNA Coding
strand5 3
DNA is a double helix
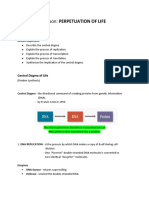
Linkage between two bonds = Transcribed RNA is known as Messenger RNA
Phosphodiester bond (mRNA), since it carries the same genetic message
End of Polymer bearing a phosphate as the gene.
group at C5 is 5end
End of Polymer bearing a free OH group mRNA is translated in the Ribosome, a cellular
at C3 is the 3end particle consisting of protein and ribosomal RNA
Base sequence of a polynucleotide is (rRNA).
read from the 5 end (left) to the 3 end
(right). 5->3 Left to Right
DNA contains two polynucleotide strands
whose bases pair through hydrogen At the ribosome, small molecules called
bonding. transferRNA (tRNA) which carry amino acids,
Two hydrogen bonds link adenine and recognize sequential sets of three bases (known as
thymine, 3 hydrogen bonds link guanine CODONS).. in the mRNA, through complementary
and cytosine. base pairing.
Watson and Crick Model The ribosome covalently links the amino acids carried
Two Polynucleotide strands are by successivee tRNAs to form a protein.
AntiParallel The proteins amino acid sequence therefore
One strand 53 while other strand ultimately depends on the nucleotide sequence of
35 the DNA
Dna The correspondence between amino acids and mRna
DNA segment is expressed in units of codons is known as the Genetic code.
base pairs (BP) Total of 64 Codons: 3 of these are stop signals
Short single stranded polymer of that terminate translation. The other 61 represent
nucleotides are called Oligonucleotides the standard amino acids found in proteins.
Nucleotides are polymerized by the In CF patients, the gene is missing three nucleotides.
action of enzymes known as This results in the deletion of a single phenylalanine
POLYMERASES residue.
Phosphodiester bonds linking nucleotide
residues can be broken by the action of GENE number is roughly correlated with organismal
Nucleases. complexity.
Exonuclease- removes a residue from
the end of a polynucleotide chain
Endonuclease- cleaves at some other Simple orgaisms= Simple genes
point the chain. Humans and many other organisms are
Polymerases and Nucleases are Diploid (having two sets of genetic
usually specific for either DNA or RNA. In information, one from each parent.
the absence of these enzymes, the One set of genetic instructions/information =
structures of nucleic acids are remarkably Haploid)
stable. Higher noncoding DNA as complexity of the
organism increases.
Over 98% of the human genome is noncoding
DNA
RNA But 80% of the human genome may actually be
Rna is SINGLE STRANDED transcribed to RNA.
Rna strand can fold back on itself so that base pairs Short segments of DNA that are copied many
form between complementary segments of the same times and inserted randomly into the
strand. chromosomes are Transposable Elements.
RNA molecules tend to assume 3-d shapes Highly repetitive sequences account for
Resides of RNA are also capable of base-pairing with another 3% of the human genome. (DNA
a complementary single strand of DNA to produce an Fingerprint)
RNA-DNA hybrid double helix. About 45% of the human DNA consists of
moderately repetitive sequences.
DNA can be DENATURED and RENATURED 1.5% of genome is for coding proteins.
Pairing of polynucleotide strands in a double-
stranded nucleic acid is possible because each strand
forms hydrogen bonds with complementary bases in How are genes identified?
the other strand.
Stability depends mostly on STACKING
Interactions, which are a form of Van der Waals Open reading fram (ORF), a computer
interaction, between adjacent pairs. Stacking can scan a DNA sequence for a stretch of
interactions are weak but additive along the length of nucleotides that can potentially be
a DNA molecule. transcribed or translated.
Stacking interactions between neighboring G:C pairs
are stronger than those of A:T.
Genes that appear to lack counterparts in 1) Pneomococcus Wild= Causes pneumonia and death to mice.
other species are known as Orphan Has enzyme needed to synthesize polysaccharide capsule
genes. causing virulence.
Genome maps, indicate the placement
and orientation of genes on a
Pneomococcus Mutant = Does not have enzymes needed to
chromosome.
synthesize polysaccharide. Does not cause death
When a gene is transferred between
species rather than from parent to
offspring of the same species. Ex. Viruses Pneomococcus Heat treated= Heat Destroys the polysaccharide
which can pick up extra DNA as they capsule. Does not cause Death.
insert and excise themselves from the
hosts chromoromes. Horizontal
Transfer Answer ) Mix of Pneomococcus Mutant and Heat = Heat destroys
polysaccharide capsule but DNA lives, when DNA mixes with
Pneomococcus mutant then it supplies the genes encoding the
enzymes needed for the capsule synthetic pathways the enzyme
lacks. Causes death.
5) Difference between Uracil and Thymine
Transcriptomics and Proteomics
Thymine contains a methyl group attached to C5 of
the pyrimidine ring of uracil. Thymine= Uracil + methyl group.
Identifying and quantifying all the mRNA
Methylation protects DNA.
transcripts from a single cell type yields a
profile of active genes. A population of
mRNA molecules that represent the 9) Why is it important for DNA to contain equal AG at CT
genes that are turned on, or transcribed residues? And what about RNA?
at one time. Trancriptomics
The collection of DNA sequences is called
a Microarray or DNA chip Answer) They must be equal because each base pair in the
Examination of a cells complete set of double stranded DNA molecule consists of a purine and a
proteins that are synthesized by the cell pyrimidine. Whereas in RNA, it is only single stranded.
at a particular point in its life cycle.
Proteomics.
Genetic variations have been linked to diseases 13) Since G-C is 3 H bonds and A-T is 2 H bonds, then G-C is
harder to Melt?
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), these
are the instances where the DNA sequence differs Answer) False- because the greater stability of GC is due to the
among individuals to use as genetic markers for stronger stacking interactions involving G:C base pairs and does
various diseases. On average, the DNA of any two not depend on the number of hydrogen bonds in the base pairs.
humans differs in about one base per thousand.
15) DNA from organisms that thrive in hot environments contain
DNA sequencing uses DNA polymerase to make a more G and C than from those in a temperate environment.
complementary strand Higher GC= increase stability of DNA at high temperatures.
The most widely used technique for determining the 21) TRUE OR FALSE
sequence of nucleotides in a segment of DNA is the
Sanger sequencing technique or the Dideoxy
DNA sequencing because it usese dideoxy a) A gene is the information that determines an inherited
nucleotides that is nucleotides lacking both 2 and 3 characteristic such as flower color
hydroxyl groups.
A procedure in which the molecules move through a
gel-like matrix under the influence of an electric field. b) A gene is a segment of DNA the encodes a protein
Electrophoresis
Dna polymerase cannot begin a new nucleotide c) A gene is a segment of DNA that is transcribed in all cells.
strand but can only extend a preexisting chain, a
short single-stranded primer that base pairs with the
template strand is added to the mixture. A) FALSE an inherited characteristic can be determined by more
than one gene
Polymerase chain reaction amplifies DNA
B) False Some sequences of DNA encode RNA molecules that
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences are not translated to proteins. Ex. rRNA and tRNA
Bactera produce DNA-cleaving enzymes known as C) FALSE Some genes are not transcribed during a cells
Restriction endonucleases or restriction lifetime. This can occur of the gene is expressed only under
enzymes that catalyze the breakage of certain environmental conditions or in certain specialized cells
phosphodiester bonds at or near specific nucleotide ina multicellular organism
sequences. These enzymes can destroy foreign DNA
that enters the cell by restricting the growth of the
foreign harmful DNA. 23) ACACCATGGTGCATCTGACT
Dna fragments are joined to produce recombinant DNA Write the sequence of the Complementary strand that DNA
polymerase would make
DNA ligase (an enzyme that forms new
Write the sequence of the mRNA that RNA polymerase would
phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotide
make from the gene segment
residues) Connects the nick
a) TGTGGTACCACGTAGACTGA
b) ACACCAUGGUGCAUCUGACU
QUESTION AND ANSWER
25) Is it possible for the same segment of DNA to encode two
proteins?
Answer) The same segment of DNA can encode two different
proteins if each strand is a coding strand.
You might also like
- DNA Structure and Replication ExplainedDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and Replication ExplainedJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry SemiDocument5 pagesBiochemistry SemiTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids SummaryDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids SummaryIvan MiglioriniNo ratings yet
- Molecular-BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular-BiologyJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument45 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Gene To Protein FlashcardsDocument2 pagesGene To Protein FlashcardsTim DAVISNo ratings yet
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument11 pagesMicrobial GeneticskimeehhNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceSneha HipparkarNo ratings yet
- EXPRESSION OF BIOLOGICAL INFORMATIONDocument6 pagesEXPRESSION OF BIOLOGICAL INFORMATIONNUR FAQIHAH BINTI FARISH MoeNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pages2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic Acidsstu.suman-iftikharNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocument55 pagesNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Study Dna DnaDocument45 pagesStudy Dna DnaKrystel BeltranNo ratings yet
- DNA (Scie)Document3 pagesDNA (Scie)Michaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- GENETIC MATERIALS: DNA, GENES, CHROMOSOMES, REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATIONDocument1 pageGENETIC MATERIALS: DNA, GENES, CHROMOSOMES, REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATIONDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- self_assessment_answers_6_asal_biology_cbDocument2 pagesself_assessment_answers_6_asal_biology_cbsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Protein SynthesisJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument38 pagesChapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationCate KristineNo ratings yet
- 6 Genetics PDFDocument97 pages6 Genetics PDFasaNo ratings yet
- DNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytoDocument3 pagesDNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytozairahNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument3 pagesDNA and RNAHans PNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Unit III - Living Things and Its Environment - Heredity: Inheritance & VariationDocument4 pagesGenetics: Unit III - Living Things and Its Environment - Heredity: Inheritance & VariationKirito TobioNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument10 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologyOday MadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument38 pagesChapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationParsottambhai RathaviNo ratings yet
- DNAto ProteinDocument41 pagesDNAto ProteinJimmy gogoNo ratings yet
- Science Q3 WK5.Document14 pagesScience Q3 WK5.Hellow FriendzNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Lesson DNA RNA Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesCentral Dogma Lesson DNA RNA Protein SynthesisAngelica Pardeño100% (1)
- CH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Document3 pagesCH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dani Jo OwensNo ratings yet
- BCH 305 (Chemistry & Metabolism of Nucleic Acids)Document30 pagesBCH 305 (Chemistry & Metabolism of Nucleic Acids)ihebunnaogochukwu24No ratings yet
- Replication Transcription and TranslationDocument16 pagesReplication Transcription and TranslationBalangat Regine L.No ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyAlthea Mandal100% (1)
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument28 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologysannsannNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument29 pagesStructure and Function of DNAMatthew Justin Villanueva GozoNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMartires, Vea Janela P.100% (1)
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument6 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- DNA Overview Central DogmaDocument56 pagesDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesis NotesCarpioNo ratings yet
- DNA replication and protein synthesisDocument4 pagesDNA replication and protein synthesisKingNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Revision Tut 2 Block 1Document10 pagesRevision Tut 2 Block 1Matsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument5 pagesWhat Is DNA꧁༒૮αll ʍ૯ ૨αj༒꧂No ratings yet
- MODULE-2-HEREDITY_INHERITANCE-AND-VARIATION-CENTRAL-DOGMADocument36 pagesMODULE-2-HEREDITY_INHERITANCE-AND-VARIATION-CENTRAL-DOGMAseph20lupozNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- Genetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiDocument14 pagesGenetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids Structure and FunctionMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 35 Transcription TranslationJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Genetics Auto Saved)Document7 pagesGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notesp11925885No ratings yet
- Postpositivism Vs Constructvism Vs PragmatismDocument2 pagesPostpositivism Vs Constructvism Vs PragmatismNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Learning Check On Childhood DisordersDocument3 pagesAbnormal Psychology Learning Check On Childhood DisordersNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Learning Check On Sexual DisordersDocument3 pagesAbnormal Psychology Learning Check On Sexual DisordersNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Nucleotides TypesDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 3 Nucleotides TypesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Emotion and Motivation PowerpointDocument73 pagesEmotion and Motivation PowerpointNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ReviewerDocument6 pagesCarbohydrates ReviewerNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument5 pagesLipidsNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet