Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Magnetism
Uploaded by
rchandra24730 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageMagnetism 2017
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMagnetism 2017
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageTest Magnetism
Uploaded by
rchandra2473Magnetism 2017
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
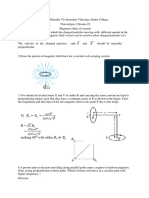
Shivalik Classes
Magnetism
1. What can be the causes of helical motion of a charged particle??
2. State Amperes circuital law. Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current
carrying wire. How are the magnetic field lines different from the electrostatic field lines?
3. State the principle of a cyclotron. Show that the time period of revolution of particles in a cyclotron
is independent of their speeds. Why is this property necessary for the operation of a cyclotron?
4. State Biot Savart law. Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a
current carrying circular loop of radius R distant x from the center. Hence, write the magnetic
field at the center of a loop.
5. (i)Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
(ii) Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
(iii) Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage
sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
6. Derive the expression for the torque on a rectangular current carrying loop suspended in a uniform
magnetic field.
7. A small compass needle of magnetic moment m is free to turn about an axis perpendicular to the
direction of uniform magnetic field B. The moment of inertia of the needle about the axis is I. The
needle is slightly disturbed from its stable position and then released. Prove that it executes simple
harmonic motion. Hence deduce the expression for its time period.
8. Two concentric circular coils X and Y of radii 16 cm and 10 cm, respectively, lie in the same vertical
plane containing the north to south direction. Coil X has 20 turns and carries a current of 16 A; coil
Y has 25 turns and carries a current of 18 A. The sense of the current in X is anticlockwise, and
clockwise in Y, for an observer looking at the coils facing west. Give the magnitude and direction of
the net magnetic field due to the coils at their centre.
9. A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 and the meter shows full scale deflection for a current
of 3 mA. How will you convert the meter into a voltmeter of range 0 to 18 V?
10. For a circular coil of radius R and N turns carrying current I, the magnitude of the magnetic field at
a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre is given by,
(a) Show that this reduces to the familiar result for field at the, centre of the coil.
(b) Consider two parallel co-axial circular coils of equal radius R, and number of turns N, carrying equal
currents in the same direction, and separated by a distance R. Show that the field on the axis around
the mid-point between the coils is uniform over a distance that is small as compared to R, and is given
by,
** Time 75 min.
You might also like
- Magnetic Fields, Special Relativity and Potential Theory: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryFrom EverandMagnetic Fields, Special Relativity and Potential Theory: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsDocument8 pagesCBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsAdhish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Document36 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Rishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Resistivity and Conductivity of MaterialsDocument3 pagesResistivity and Conductivity of MaterialsAsher MuhammedNo ratings yet
- W 1Document3 pagesW 1ypurushothamreddy006No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSDocument8 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSroyal ghostNo ratings yet
- Questions Chap 4 Moving Charges & Magnetism - 77547 - 2023 - 02 - 06 - 22 - 57Document4 pagesQuestions Chap 4 Moving Charges & Magnetism - 77547 - 2023 - 02 - 06 - 22 - 57Ranjith MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsDocument31 pagesUnit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- Test Physics CBSE Class XIIDocument1 pageTest Physics CBSE Class XIIAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- REVISION SHEETS GR 12Document13 pagesREVISION SHEETS GR 12itachirao5No ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument2 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismAslam FaruqiNo ratings yet
- Physics CHDocument3 pagesPhysics CHdhriti1996singhNo ratings yet
- TEST 9 CH 4Document3 pagesTEST 9 CH 4kumarvishwaa1No ratings yet
- 12 VBQ C4Document67 pages12 VBQ C4SWETA PUJARINo ratings yet
- XII Q Group 2Document3 pagesXII Q Group 2Sanskriti VermaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetis1m Sneh CH - 4 and CH - 5 - SnehDocument7 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current and Magnetis1m Sneh CH - 4 and CH - 5 - SnehJarjar BinksNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument3 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetismdhanish942006No ratings yet
- MovingChargesMagnetismDocument4 pagesMovingChargesMagnetismSheena RizviNo ratings yet
- Test-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)Document3 pagesTest-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)L.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Module 3Document2 pagesAssignment - Module 3Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect Full ChapterDocument17 pagesMagnetic Effect Full ChaptervasanthiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Eff of CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Eff of CurrentR K SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsRAHIM MDNo ratings yet
- CH 4-MCM-WSDocument8 pagesCH 4-MCM-WSmmkishore067No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Moving Charges and Magnetism) UnsolvedDocument8 pagesChapter 4 (Moving Charges and Magnetism) UnsolvedDhankhar ShabNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics U3 Assignmnt1Document3 pages12 Physics U3 Assignmnt1Nikita BansalNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Revision Questions FINALDocument5 pagesMagnetism Revision Questions FINALARSHAD JAMIL100% (2)
- VELS VIDYASHRAM PHYSICS WORKSHEET ON MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISMDocument2 pagesVELS VIDYASHRAM PHYSICS WORKSHEET ON MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISMkalyani.kNo ratings yet
- W 2Document2 pagesW 2ypurushothamreddy006No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Theory Worksheet - Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - Theory Worksheet - Moving Charges and MagnetismVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Test-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)Document3 pagesTest-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)L.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Summary and Review of ElectromagentismDocument3 pagesSummary and Review of ElectromagentismterrylimNo ratings yet
- Imp. Derivation 2023Document10 pagesImp. Derivation 2023Tuhin SamantrayNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current and MagnetismDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current and MagnetismSanjay MalwiyaNo ratings yet
- REVISION ch 4Document2 pagesREVISION ch 4ssshuuushhhNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsAriyanayaka SundaramNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 07-01-2022 23.10Document6 pagesCamScanner 07-01-2022 23.10Ashit ModyNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 3Document7 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 3Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- 10th Magnetic Electric Current Test Paper-1Document6 pages10th Magnetic Electric Current Test Paper-1ashish gandreNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)Document3 pagesChapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)ghuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics WorksheetDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics WorksheetpranayNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldDocument4 pagesMagnetic FieldDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current(2022-23)Document14 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current(2022-23)joeljoseph2901No ratings yet
- CH 6Document19 pagesCH 6terasaini77No ratings yet
- Weekly Test PhysicsDocument2 pagesWeekly Test PhysicsSneha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Magnetism ?Document16 pagesPhysics 12th Magnetism ?mahatosandip1888No ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH - 04Document5 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH - 04Arunima SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment Magnetic EffectsDocument3 pagesAssignment Magnetic EffectsabcdefgNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfsdfbvshbdfNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter Wise Important QuestionsTechnical Hacks100% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesPractice Questionsp pNo ratings yet
- Class X Physics - Magnetism QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass X Physics - Magnetism Questionsavp sNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism (Autosaved)Document45 pagesElectromagnetism (Autosaved)Melai Rodriguez IbardalozaNo ratings yet
- CLASS-10 Subject: ScienceDocument62 pagesCLASS-10 Subject: ScienceZeonNo ratings yet
- 3 Magnetic Effect of Current & MagnetismDocument4 pages3 Magnetic Effect of Current & MagnetismNathanianNo ratings yet
- Compact 1115782Document4 pagesCompact 1115782J Immanuel ThomasNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii (Physics)Document8 pagesClass - Xii (Physics)Shivanshu SiyanwalNo ratings yet
- Valliammai Engineering CollegeDocument11 pagesValliammai Engineering CollegeRagunathan NarayananNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMKanak TaldaNo ratings yet
- 03 Assignment IDocument13 pages03 Assignment Irchandra24730% (1)
- Central TendencyDocument9 pagesCentral Tendencyrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Motion in Straight Line KinematicsDocument1 pageMotion in Straight Line Kinematicsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Central TendencyDocument11 pagesCentral Tendencyrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Hyper Tri Glyc Erida Emi ADocument8 pagesHyper Tri Glyc Erida Emi Archandra2473No ratings yet
- PCDocument13 pagesPCrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Central TendencyDocument11 pagesCentral Tendencyrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Quality Tools HistogramDocument15 pagesQuality Tools Histogramrchandra2473No ratings yet
- MsaDocument16 pagesMsarchandra2473No ratings yet
- Certification Course On Quality Assurance and Statistical Quality Techniques Course Level A Statistical Process Control Concepts & Control ChartsDocument28 pagesCertification Course On Quality Assurance and Statistical Quality Techniques Course Level A Statistical Process Control Concepts & Control Chartsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- RegressionDocument7 pagesRegressionrchandra2473No ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Impq Sa 1 1 Real Numbers 2Document3 pages10 Mathematics Impq Sa 1 1 Real Numbers 2Surya SriramNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight Line KinematicsDocument1 pageMotion in Straight Line Kinematicsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- SPH Bearing Draft (09.06.11)Document38 pagesSPH Bearing Draft (09.06.11)rchandra2473No ratings yet
- Resonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialDocument100 pagesResonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialSaransh Goyal80% (25)
- Report On Non Circular Pressure VesselsDocument26 pagesReport On Non Circular Pressure Vesselsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- EMI and ACDocument102 pagesEMI and ACrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Earthquake Base Shear Calculation for 3-Story Office BuildingDocument4 pagesEarthquake Base Shear Calculation for 3-Story Office Buildinggendadeyu552625100% (1)
- MagnetismDocument4 pagesMagnetismrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Solution 17012016Document8 pagesSolution 17012016rchandra2473No ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument2 pagesAlternating Currentrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave Opticsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Magnetism (2016-2010) : Shivalik ClassesDocument3 pagesMagnetism (2016-2010) : Shivalik Classesrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Rayoptics and Wave Optics Test 17012017Document2 pagesRayoptics and Wave Optics Test 17012017rchandra2473No ratings yet
- Strs ClassDocument7 pagesStrs Classrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave Opticsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Moving Charge & MagnatismDocument1 pageMoving Charge & Magnatismrchandra2473No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Value Engineering - Post-Tensioned Transfer SlabDocument19 pagesValue Engineering - Post-Tensioned Transfer SlabAmira SyazanaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0263224116306157 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0263224116306157 MainbatuhanNo ratings yet
- Chen Rayleigh Interferometer PDFDocument12 pagesChen Rayleigh Interferometer PDFkomal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter ProjectDocument30 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter ProjectArchana ArchuNo ratings yet
- CL 1000i Chemiluminescence Immunoassay SystemDocument6 pagesCL 1000i Chemiluminescence Immunoassay SystemOsama ElfadniNo ratings yet
- Catálogo SEDIVERDocument32 pagesCatálogo SEDIVEREnver Rojas DiazNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry - Practice ProblemsalphaDocument17 pagesTrigonometry - Practice Problemsalphamanu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis TechniquesDocument39 pagesFault Analysis TechniquesagarwaalaaaaNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument30 pagesPreviewpdfankitNo ratings yet
- Dekton Technical Manual ENDocument24 pagesDekton Technical Manual ENIzrada FotografijaNo ratings yet
- Comportamiento Estructural de PilasDocument8 pagesComportamiento Estructural de PilasSolis EdwinNo ratings yet
- Freemyer TWS600S IV - OR00059565 4,5 & 3.5Document38 pagesFreemyer TWS600S IV - OR00059565 4,5 & 3.5Carlos Martínez VelázquezNo ratings yet
- NYTRO® LIBRA (English) PDSDocument1 pageNYTRO® LIBRA (English) PDSFadel RajibNo ratings yet
- Analysis of High Rise Building Including Earthquake and Wind LoadsDocument52 pagesAnalysis of High Rise Building Including Earthquake and Wind Loadsclarkgagui100% (1)
- BS 7th Semester F G RecDocument30 pagesBS 7th Semester F G RecHussain RanaNo ratings yet
- Crack Initiation & Propagation: Beach Marks, StriationsDocument4 pagesCrack Initiation & Propagation: Beach Marks, StriationsJay-m DG. FaminiNo ratings yet
- Spark 2000 BS: Instruction ManualDocument63 pagesSpark 2000 BS: Instruction ManualMárcio FernandesNo ratings yet
- Kineticists of PorphyraDocument47 pagesKineticists of PorphyratonettaNo ratings yet
- QUIRINO GENERAL HIGH SCHOOL HOME LEARNING PLANDocument4 pagesQUIRINO GENERAL HIGH SCHOOL HOME LEARNING PLANPau AbuenaNo ratings yet
- TST-08 Tower-OkeDocument16 pagesTST-08 Tower-Okerostyo tioNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Patterns and SymmetriesDocument22 pagesThe Mathematics of Patterns and SymmetriesED PradoNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces TypesDocument13 pagesIntramolecular Forces Typeskiana Jessica MonroeNo ratings yet
- Viscoplastic Model LS-DynaDocument14 pagesViscoplastic Model LS-DynaJoe SatchNo ratings yet
- L04 Analysis of Statically Determinate BeamsDocument42 pagesL04 Analysis of Statically Determinate BeamsN GraceNo ratings yet
- J. Hom - Lecture Notes On Heegaard Floer HomologyDocument30 pagesJ. Hom - Lecture Notes On Heegaard Floer HomologyMladen ZekićNo ratings yet
- Rigid vs. Flexible Pile Caps - Case Study For 235 M. Delhi T.V. ToDocument6 pagesRigid vs. Flexible Pile Caps - Case Study For 235 M. Delhi T.V. ToPrashant MuleNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLC: Mr. Sagar Kishor SavaleDocument65 pagesHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLC: Mr. Sagar Kishor Savaleঠাকুর বাড়ির আঙিনায়No ratings yet
- Experiment-1: Study of Step Response of R-C NetworkDocument11 pagesExperiment-1: Study of Step Response of R-C Networkharsh bathlqNo ratings yet
- Performance of A FAKEL K10K ResistojetDocument11 pagesPerformance of A FAKEL K10K ResistojetAlien GmpNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table ProofsDocument20 pagesLaplace Table Proofskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesFrom EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (139)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (158)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)