Professional Documents
Culture Documents
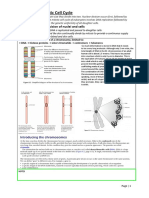
Topic 1.6 Cell Division: Instructions
Uploaded by
edeceOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 1.6 Cell Division: Instructions
Uploaded by
edeceCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 1.
6 Cell Division
Instructions:
READ FOR UNDERSTANDING: Read Pages 51 to 58 in your textbook.
Define all the vocabulary words.
Address all the understandings by provide examples/ diagrams/ explanations for
each bullet point
Address the nature of science and essential ideas using your new
understandings.
Address the Skills by answering the Data-Based Questions page 54, 59
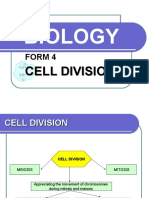
Define the vocabulary words below:
Interphase Protein synthesis tissue repair
G1 spindle embryonic
S microtubules development
G2 Mitotic spindle primary tumours
Mitosis DNA replication secondary tumors
Cytokinesis Mitochondria organ
Prophase Chloropasts tissue
Metaphase chromosomes cancer
Anaphase nuclear membrane supercoiling
Telophase centromeres mutagens
Nuclei chromatid oncogenes
Metabolic reaction asexual cyclins
reproduction mitotic index
Essential idea:
Cell division is essential but must be controlled.
Nature of science:
Serendipity and scientific discoveriesthe discovery of cyclins was accidental. (1.4)
Understandings:
Mitosis is division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei.
Chromosomes condense by supercoiling during mitosis.
Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis and is different in plant and animal cells.
Interphase is a very active phase of the cell cycle with many processes occurring in the
nucleus and cytoplasm.
Cyclins are involved in the control of the cell cycle.
Mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis are involved in the development of primary and
secondary tumours.
Applications and skills:
Evidence from Pasteurs experiments that spontaneous generation of cells and
organisms does not now occur
Application: The correlation between smoking and incidence of cancers.
Skill: Identification of phases of mitosis in cells viewed with a microscope or in a
micrograph.
Skill: Determination of a mitotic index from a micrograph.
You might also like
- CH 3 Cell DivisionDocument20 pagesCH 3 Cell DivisionDith JarillaNo ratings yet
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadJamie Hayes100% (26)
- Cytogenetics Course Module at AMYA Polytechnic CollegeDocument29 pagesCytogenetics Course Module at AMYA Polytechnic Collegeanonymous squashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document4 pagesLesson 6Thea MillanesNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Cell Division: Stages and RoleDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Cell Division: Stages and RoleKaylaNo ratings yet
- L1 Mitosis NEWDocument39 pagesL1 Mitosis NEWloaiNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 25 Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 25 Cell DivisionJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- BIO 1012 Cell Cycle OverviewDocument43 pagesBIO 1012 Cell Cycle OverviewKavindu MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6. Cell CycleDocument64 pagesLesson 6. Cell CycleSharon Nicole MasamocNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Lecture 1Document35 pagesCell Division Lecture 1api-323374257No ratings yet
- LS 6-Cell-Cycle MitosisDocument20 pagesLS 6-Cell-Cycle MitosisseanNo ratings yet
- IB Biology - Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesIB Biology - Cell DivisionPriyani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Knowing The Foundation of LifeDocument47 pagesKnowing The Foundation of LifeAlkhair SangcopanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Division Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesCell Cycle Division Lecture NotesZachary HamidNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- BIO Mod2 Cell Growth and ReproductionDocument10 pagesBIO Mod2 Cell Growth and Reproductiongeorge linNo ratings yet
- 6 Cell Division Cell Cycle 1633188130443Document25 pages6 Cell Division Cell Cycle 1633188130443Utkarsh AnandNo ratings yet
- Bio Review Ooray!!Document1 pageBio Review Ooray!!Zara Zalaal [Student]No ratings yet
- 1.6 Binary Fission and MitosisDocument16 pages1.6 Binary Fission and Mitosisedensatire21No ratings yet
- Lecture On Mitosis and MeosisDocument105 pagesLecture On Mitosis and MeosisKaye Selene Raphaelle Sy100% (1)
- Extracted Pages From Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Students Book 2nd Edition (C. J. Clegg, Geoff Goodwin) (Z-Lib - Org) 1Document5 pagesExtracted Pages From Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Students Book 2nd Edition (C. J. Clegg, Geoff Goodwin) (Z-Lib - Org) 1BonnyNo ratings yet
- Cell Modifications Cell CycleDocument76 pagesCell Modifications Cell CycleGuen GanubNo ratings yet
- at NeoplasmDocument50 pagesat NeoplasmNazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructures of CellsDocument2 pages1.2 Ultrastructures of CellsedeceNo ratings yet
- Replication and Reproduction of DNADocument9 pagesReplication and Reproduction of DNASamay katariaNo ratings yet
- To Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksDocument34 pagesTo Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksPawpaw Chan0% (1)
- M2L1 ActivateDocument2 pagesM2L1 ActivateVenice De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle ExpDocument24 pagesCell Cycle ExpIvan GalletoNo ratings yet
- Fish Genetics and Breeding ExplainedDocument27 pagesFish Genetics and Breeding ExplainedHanna Beth Butiong TandayagNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument17 pagesMitosisr2591220No ratings yet
- Q1 GenBio1 SLKWeek4 EditDocument9 pagesQ1 GenBio1 SLKWeek4 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle All ChapterDocument16 pagesCell Cycle All ChapterPASSORN SAE JEWNo ratings yet
- Biology Is The Only Subject in Which Is The Same Thing As : Multiplication DivisionDocument23 pagesBiology Is The Only Subject in Which Is The Same Thing As : Multiplication DivisionKate Ashly Mae AteradoNo ratings yet
- Lecture at University of IndonesiaDocument58 pagesLecture at University of IndonesiaFikriNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Topic 5 The Mitotic Cell Cycle Supernotes 2022Document20 pagesKami Export - Topic 5 The Mitotic Cell Cycle Supernotes 2022Yulbin LeeNo ratings yet
- 3-259-Ch.3 C - Cell Division and GeneticsDocument74 pages3-259-Ch.3 C - Cell Division and Geneticslouise navorNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Cell ReproductionDocument105 pagesCH 8 Cell ReproductionArshe OmaguingNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Division ExplainedDocument37 pagesCell Cycle and Division ExplainedLinda Yurani Carvajal AngaritaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell Division: - Biology - Form 4 - 2021Document46 pagesChapter 6 Cell Division: - Biology - Form 4 - 2021Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Izat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmDocument18 pagesIzat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmSuhailina Mohd IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Dna Replication Mitososis MeiosisiDocument54 pagesGenetic Dna Replication Mitososis Meiosisiptm2409tempNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lec - Quiz 1 HandoutsDocument7 pagesGenetics Lec - Quiz 1 Handoutsvada_soNo ratings yet
- St. Hubert - JIaoRicci - Activity On Table Completion Lets ApplyDocument4 pagesSt. Hubert - JIaoRicci - Activity On Table Completion Lets ApplyHanelore Takotsa MixsignalsNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisiongbuDocument7 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisiongbuadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument16 pagesCell DivisionmiqdadxpNo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Chapter5celldivision 170616144458Document47 pagesChapter5celldivision 170616144458Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Cell DivisionDocument52 pagesCell Cycle Cell DivisionBelleNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020Document20 pagesTOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020reeNo ratings yet
- W9 Mitosis Chapter11Document26 pagesW9 Mitosis Chapter11Ibrahim AlibrahimNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations NotesDocument22 pagesCellular Aberrations NotesH50% (2)
- Cellular Aberrations NotesDocument23 pagesCellular Aberrations NotesPamela Ria HensonNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Chap 6Document53 pagesBio F4 Chap 6Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument27 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisNicolette BingtanNo ratings yet
- Aula 6 FBMCCR 2324Document28 pagesAula 6 FBMCCR 2324VanessaMarquesNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of the Immune SystemDocument16 pagesCells and Organs of the Immune SystemSatyadeep BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyDocument28 pagesCharacteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyRoxie SolisNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology: The CellDocument41 pagesCape Biology: The CellMatt BarhamNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A.P. Biology Summer WorksheetDocument10 pagesA.P. Biology Summer WorksheetedeceNo ratings yet
- ZAP! Erasing Memories: by R. Douglas FieldsDocument2 pagesZAP! Erasing Memories: by R. Douglas FieldsedeceNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (AP MC)Document2 pagesThermodynamics (AP MC)edeceNo ratings yet
- 94 MultchDocument16 pages94 MultchedeceNo ratings yet
- 2 Page Monthly PlannerDocument3 pages2 Page Monthly PlanneredeceNo ratings yet
- 8 3+Patterns+in+NatureDocument24 pages8 3+Patterns+in+NatureSonny Hothi100% (1)
- Cation Analysis 2Document22 pagesCation Analysis 2QuinNo ratings yet
- 1404 SolProduct PDFDocument30 pages1404 SolProduct PDFedeceNo ratings yet
- 1496 End PaperDocument1 page1496 End PaperedeceNo ratings yet
- 52Ex2X13 PDFDocument9 pages52Ex2X13 PDFedeceNo ratings yet
- 1 BF 11 Ex 2 PPDocument5 pages1 BF 11 Ex 2 PPedeceNo ratings yet
- January 2015: Mon, Jan 5 - Sun, Jan 11Document10 pagesJanuary 2015: Mon, Jan 5 - Sun, Jan 11Masoom FarishtahNo ratings yet
- 12U Chem Final Jan 07Document11 pages12U Chem Final Jan 07edeceNo ratings yet
- 2 1ClozeOutlineDocument2 pages2 1ClozeOutlineedeceNo ratings yet
- Plant Species Adapted To Life On LandDocument3 pagesPlant Species Adapted To Life On LandedeceNo ratings yet
- 5s ChecklistDocument4 pages5s ChecklistedeceNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules CrosswordDocument2 pagesBio Molecules Crosswordedece100% (1)
- Check List Template: # Descriptions 1 Topic 1 Check Items StatusDocument1 pageCheck List Template: # Descriptions 1 Topic 1 Check Items StatusedeceNo ratings yet
- Isotopes ChemthinkDocument25 pagesIsotopes ChemthinkedeceNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument6 pagesParticulate Nature of MatteredeceNo ratings yet
- AP Ch5 Thermochemistry (I)Document22 pagesAP Ch5 Thermochemistry (I)edeceNo ratings yet
- 5S Checklist for OfficesDocument1 page5S Checklist for OfficesManuel Dos Santos100% (3)
- Excretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17Document8 pagesExcretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17edeceNo ratings yet
- A.P. Biology Summer WorksheetDocument10 pagesA.P. Biology Summer WorksheetedeceNo ratings yet
- Wk5 ResourcesDocument13 pagesWk5 ResourcesedeceNo ratings yet
- wk3 PptrxnsansDocument1 pagewk3 PptrxnsansedeceNo ratings yet
- Excretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17Document8 pagesExcretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17edeceNo ratings yet
- Wk1 GradingDocument14 pagesWk1 GradingedeceNo ratings yet
- Stuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListDocument2 pagesStuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListedeceNo ratings yet
- wk3 PoemDocument1 pagewk3 PoemedeceNo ratings yet
- Gen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseDocument26 pagesGen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseAhmed Khodja KarimNo ratings yet
- Breadth First Search (BFS) Depth First Search (DFS) A-Star Search (A ) Minimax Algorithm Alpha-Beta PruningDocument31 pagesBreadth First Search (BFS) Depth First Search (DFS) A-Star Search (A ) Minimax Algorithm Alpha-Beta Pruninglevecem778No ratings yet
- 5 Nighttime Image Enhancement Using A NewDocument7 pages5 Nighttime Image Enhancement Using A NewNithish CenaNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Observations of Teaching-Learning in Actual School EnvironmentDocument8 pagesFS 1 Observations of Teaching-Learning in Actual School EnvironmentJessie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- MicroProcessadores ZelenovskyDocument186 pagesMicroProcessadores ZelenovskyDavid SantosNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGeography Lesson Planapi-204977805100% (3)
- Angel FishDocument1 pageAngel FishWilla CrowellNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 1 18 116 PDFDocument27 pagesExhibit 1 18 116 PDFSimonNo ratings yet
- Complaint FTC V SkechersDocument60 pagesComplaint FTC V SkechersLara PearsonNo ratings yet
- Corporations Defined and FormedDocument16 pagesCorporations Defined and FormedSheryn Mae AlinNo ratings yet
- 28/08/2016 1 Advanced Research Methodology... RU, Bangalore-64Document38 pages28/08/2016 1 Advanced Research Methodology... RU, Bangalore-64Ananthesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Markard Et Al. (2012) PDFDocument13 pagesMarkard Et Al. (2012) PDFgotrektomNo ratings yet
- Procurement of Railway Infrastructure Projects - ADocument15 pagesProcurement of Railway Infrastructure Projects - ADan NanyumbaNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument4 pagesHuman Physiologyshahzain92No ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT English Q4 W3 Day 2Document17 pagesGrade 5 PPT English Q4 W3 Day 2Rommel MarianoNo ratings yet
- CeramicsDocument39 pagesCeramicsD4-dc1 Kelas100% (1)
- On Hereditary Italian WitchcraftDocument79 pagesOn Hereditary Italian WitchcraftAlbion JamesNo ratings yet
- Micro810 Allen Bradley User ManualDocument120 pagesMicro810 Allen Bradley User ManualStefano MontiNo ratings yet
- Design Proposal For North Public & Suite Areas Decorative Lighting, Solaire Quezon CityDocument42 pagesDesign Proposal For North Public & Suite Areas Decorative Lighting, Solaire Quezon CityRichard Libunao BelduaNo ratings yet
- RMAN Backup and Recovery Strategies with Oracle DatabaseDocument26 pagesRMAN Backup and Recovery Strategies with Oracle DatabaseCristiano Vasconcelos BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Martina: Available Colors For This VersionDocument2 pagesMartina: Available Colors For This VersionUmeshNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 UMTS Hardware Description (V900R017C10 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument224 pagesBSC6900 UMTS Hardware Description (V900R017C10 - 01) (PDF) - enmike014723050% (2)
- Mr. Frank Remedios Certified Career Counselor Authorised Franchise-Brain CheckerDocument24 pagesMr. Frank Remedios Certified Career Counselor Authorised Franchise-Brain Checkerrwf0606No ratings yet
- Please Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies CompanyDocument22 pagesPlease Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies Company20c552244bNo ratings yet
- Joou No Gohoubi - Tate No Yuusha No Nariagari 288869 Doujin - EdoujinDocument25 pagesJoou No Gohoubi - Tate No Yuusha No Nariagari 288869 Doujin - Edoujinaura.nazhifa10020% (1)
- The 4Ms of Operations: Prepared By: Karla Jane F. BangaysisoDocument18 pagesThe 4Ms of Operations: Prepared By: Karla Jane F. BangaysisoKarla BangFerNo ratings yet
- Java Material 1Document84 pagesJava Material 1tvktrueNo ratings yet
- Powerful Technical Computing with MathematicaDocument3 pagesPowerful Technical Computing with MathematicazoksiNo ratings yet
- Patanjali PDFDocument11 pagesPatanjali PDFSiddharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- User Interface Analysis and Design TrendsDocument38 pagesUser Interface Analysis and Design TrendsArbaz AliNo ratings yet