Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internet of Things Security: Yassine Chahid, Mohamed Benabdellah, Abdelmalek Azizi
Uploaded by
Christopher HerringOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internet of Things Security: Yassine Chahid, Mohamed Benabdellah, Abdelmalek Azizi
Uploaded by
Christopher HerringCopyright:
Available Formats
Internet of Things Security
Yassine Chahid*, Mohamed Benabdellah, Abdelmalek Azizi
ACSA Laboratory, Faculty of Sciences,
Mohammed First University, Oujda, Morocco
chahid1yassine@gmail.com, {med_benabdellah, abdelmalekazizi}@yahoo.fr
AbstractThe consequences of security problems In Section III, we discuss the problems of each layer,
are increasingly serious. These problems can now lead analyzing their protocols, sensors and how used in
to personal injury, prolonged downtime and attacks aimed at its weak points. In section IV, we
irreparable damage to capital goods. To achieve this, describe attacks that affect the tags, reader and
systems require end-to-end security solutions that network protocol. We also provide possible ways to
cover the layers of connectivity, furthermore, counter these attacks. In the last section, we cite some
guarantee the privatization and protection of data solutions proposed by the various companies and
circulated via networks. In this paper, we will give a
organizations in the field of IoT security. Finally,
definition to the Internet of things, try to dissect its
Section V concludes the paper which was just a
architecture (protocols, layers, entities ...), thus giving
reflection on this complicated subject, and gives
a state of the art of security in the field of internet of
possible future directions.
things (Faults detected in each layer ...), finally,
mention the solutions proposed until now to help
researchers start their researches on internet of things
security subject.
KeywordsSecurity, Internet of Things, Layers,
Protocols, Privacy, Network.
I. INTRODUCTION
T
he beginning of the web is marked by the
appearance of the web 0.1 still called
traditional web which is primarily a static
web, centered on the distribution of
information. It is characterized by product-oriented
sites, which require little intervention from users [1].
The appearance of social networks (Facebook,
Twitter, LinkedIn ...), blogs, and forums has
revolutionized the web, it's the web 0.2. Currently,
they privilege the amount of sharing (texts, videos,
Fig. 1. Internet of Things domain
images...) [1]. They sees the emergence of social
networks, smartphones and blogs. This is where we All this seems interesting for the first sight, but what
want to go, even if the web 0.3 is not completely does this revolution bring us?
defined, it would be the semantic web, which aims to
organize the mass of information available according II. INTERNET OF THINGS SECURITY
to the context and the needs of each user, taking into
A. Internet of Things security, a black past
consideration its location, preferences [1], it is the
internet of things (IoT). The security of IoT is a riddle, it gets its value
The Internet of Things represents a vision in which when it fails, it rests on 3 pillars [2] called "CIA", here
the Internet extends into the real world including are the 3 things that can be done to personal and
everyday objects. Physical elements are no longer confidential user data:
disconnected from the virtual world, but can be - Theft them (confidentiality),
controlled remotely and serve as physical access - Modify them (Integrity),
points to Internet services. - You prevent to get them (Access).
This paper is organized as follows: In the paragraphs below, we will cite some
In section II, we first approach the black past of examples of the black past in the IoT field security.
IoT, citing some outstanding examples in the world. In 2000, an Australian was imprisoned two years
Afterwards, we also dehull each IoT layer. Finally we after hacking a remote sewage treatment plant, causing
explain the security of the IoT architecture (protocols, the discharge of raw sewage into public places [22].
services, support technologies ...)
978-1-5090-6681-0/17/$31.00 2017 IEEE
In 2005, the industry area was touched, US form in all domains in order to earn money from the
automotive manufacturing plants were infected for service provided and it runs in a loop for a more
several hours, because the Microsoft Windows system meaningful final service than the existing one [5] [23].
presented a flaw exploited by this infection, which
stopped the production of vehicles and thousands of C. The internet of things security architecture
workers were forced to leave their posts during the
breakdown.
In 2010, the global digital attacks were used as a
weapon, in fact, the Iranian installations were
infiltrated by a virus called "Stuxnet", which destroyed
the military equipment [19] [20].
In June 2016, Sucuri security experts reported
discovering a botnet of more than 25,000 closed-
circuit television devices used to launch distributed
Denial of Service attacks. "Sucuri" found that the
malicious botnet was using IP addresses in more than
105 countries around the world [21].
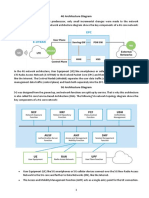
B. Internet of things layers
Fig. 3. Internet of Things security architecture.
Security structure in IoT can be divided into three
layers, which are the perception layer, the network
layer, and the application layer. Some systems use
network support technology (such as network
processing, computer technology, middleware
technology, etc.) as a processing layer. [6] Shows the
structure of the IoT system divided by the three layers.
It summarizes threats and requirements analysis on the
IoT security architecture. [7] Puts forward a typical
model of the IoT architecture in the future (U2IoT). It
Fig. 2. Internet of things layers embodies the concept of human central nervous
system and social structure. This article will treat the
The first layer is the perception layer, the lowest of three layer structures.
the Internet of things architecture. It consists in
perceiving the data of the environment. Moreover,
III. FAULTS DETECTED IN EACH LAYER
some operations are being done at this layer, which
manages the collection of data with a portion reserved We learn that these problems are complex and
for detection through sensors, bar code labels, RFID difficult. Therefore, we must understand all sorts of
tags, GPS... Its main objective is to identify the object security issues of different layers, and potential
and collect the data [3] [23] [24]. attacks. Considering the system as a whole, security
The second layer called the "network layer" issues need to be addressed early in the design
receives the information and data from the perception process. Therefore, [8] raises the application for the
layer, like the network and transport layer of the OSI IoT safety assessment based on the gray correlation
model, collecting data from the lower layer and links it algorithm, which has put several common attacks as a
with the Internet From the network. The network layer safety factor, to perform a quantitative evaluation of
cannot include a gateway from one interface to the The network on environment and status. It also
another that is to say sensor to other related to the lists the specific steps that apply this algorithm to
internet. It may include an information center [23] perform the security status assessment. In the
[25]. paragraph below, we will discuss security issues in
The fourth layer called "application layer", it each layer.
receives information from the previous layer
(middleware) and gives a more general management A. Perceptual layer security problems
of the application presenting this information, and it The main equipment in the perception layer
depends on the type of device and their purpose of the includes RFID, ZigBee, and all kinds of sensors.
layer of perception [4]. Then the middleware layer When the data is collected, the mode of transmission
according to the needs of the user and finally the layer of the information is essentially the transmission of the
of the application which presents the data in desired
wireless network. The signals are displayed in the basis of the individual's point of view and does
public place. If effective protective measures are not necessarily relate to communication between
lacking, the signals will be monitored, intercepted and the machines. The use of existing security
disturbed easily. Most detection devices are deployed mechanisms divides the logical relationship
at unsupervised monitoring sites. Attackers can easily between IoT machines. Access networks have
access, control or physically damage equipment. For multi-access methods. Heterogeneity makes
example, DPA (Differential Power Analysis) is a very security, interoperability and coordination worst.
effective attack [26]. Several types of common It easily has security vulnerabilities [10].
attacks are as follows [9]: - Cluster security issues: Including network
congestion, DoS attack, authentication problem,
- The gateway node: The gateway node is a etc. IoT has a large number of devices. If it uses
sensitive element, it is easily controlled by the the existing authentication mode authenticated
attackers. It can leak all information, including device, a large amount of data traffic will likely
the group communication key, the corresponding block the network. Existing IP technology does
key, radio key etc., and threatens the security of not apply to a large number of node IDs. Mutual
the entire network. authentication between a large numbers of
- False node and malicious data: Attackers add a devices causes serious waste of key resources
node to the system, and enter the wrong code or [10].
data. They stop transmitting real data. The sleep - Privacy Statement: With the development of
of the limited node of energy is refused. They information retrieval technology and social
consume valuable node energy, and potentially engineering, hackers can easily gather a lot of
control or destroy the entire network. information about the privacy of the particular
- DoS: DoS attack is the most well-known attack in user [10].
WSN and Internet. It causes loss of network
resources and renders the service unavailable C. Application layer security problems
[27].
- Sync: The attackers analyze the execution time of In the application layer, for different industries or
the encryption algorithm in order to obtain more environment, its security problems are also different.
information about the hacking method to be used At present, there are no universal standards for the
[28]. construction of the IoT application layer. But some
- Routing: The user can create routing loops, cause companies perform M2M (Machine to Machine) the
or resist transmission of the network, extend or mode of the IdO, as intelligent community, smart
shorten the source path, form error messages, home, medical, etc. [11] highlights an intelligent
increase the number of end-to-end delay, etc [30]. household security system design system. [12] Gives
- Replay: To obtain the confidence of the system to some solutions based on the 6LoWPAN architecture
attack, the attacker launches a packet received by (IPv6 on low power WPAN) [29]. They are used to
the destination host. It is mainly used in the support the medical detection system. Although
processing of authentication, destruction and application layer security is more complex and costly,
certification validation. it can still summarize some common security issues:
- SCA: Time consuming, energy consumption or - Authentication: Different applications have
electromagnetic radiation are the key information different users; each application will have a large
used by an attacker to tag encryption devices, and number of users. In order to prevent illegal user
they are also called data leaks. intervention, should take effective authentication
technology. Spam and the identification and
B. Network Layer security problems processing of malicious information should also
be considered.
- Traditional security issues: The general security - Data Protection and Recovery: Communication
problems of the communications network will data involves the confidentiality of users. Data
threaten the confidentiality and integrity of the protection mechanism and data processing
data. Although the existing communication algorithm are not perfect, and it can result in data
network is relatively comprehensive of the loss and even catastrophic damage. The
security protection measures, there are still some management of mass nodes is also one of the
common threats, including illegal access reasons.
networks, listening information, privacy damage,
- The ability to process mass data: Due to a large
damage Integrity, attack DoS, man-in-themiddle
number of nodes, an enormous amount of data
attack, virus invasion, exploit attacks, and so on
transmission, and complex environment, once the
[10].
data processing capacity and adaptability cannot
- Compatibility problems: The security architecture
of the existing Internet network is designed on the
meet the requirements, it will lead to interruption RFID tags and readers this type of attacks can be
And loss of data. performed in both directions: tag to reader and
reader to tag. Since readers transmit information
IV. THE INTERNET OF THINGS SAFETY at much higher power then tags, the former are
MEASURES susceptible to this type of attacks at much greater
distances and consequently to greater degree. The
As a multi-network fusion network, IoT security information collected can be used to perform
involves different layers in IoT. Many security advanced attacks later. The feasibility of this
technologies have been applied in these independent attack depends on many factors, such as the
networks. In particular, the mobile communication distance of the attacker from the legitimate RFID
network and research on the security of the Internet devices.
have a long history. For sensor networks in IoT, the
diversity of resources and the heterogeneity of the 3) Network Protocol Attacks:
network make security research much more difficult.
This section presenting the security measures for each RFID systems are often connected with back-end
layer will focus on the security technology involved in databases and networking devices on the enterprise
the perception layer. backbone. Nevertheless, these devices are susceptible
to the sane vulnerability of general purpose
A. Security measures of the perception layer networking devices. Malicious users can use flaws in
the operating system and network protocols in order to
Because RFID and WSN are an important part of launch attacks and com-promise the back-end
the IoT perception layer, their security measures will infrastructure.
be introduced, respectively [13]. Through appropriate data collection it is possible
1) Attacks on the Tags: to detect cloned RFID tags. Alternatively, cloning
attacks can be reduced via challenge response
authentication protocols. These should also support
- Cloning: Even the most important and robust anti-brute force mechanisms. Nevertheless, the
characteristic feature of RFID systems, their inherent resource constraints that RFID tags present
unique identifier, is susceptible to attacks. lead to weak authentication protocols that are
Although in theory you cannot ask an RFID inefficient against determined attackers. Juels [16] has
manufacturer to create a clone of an RFID tag demonstrated some techniques for strengthening the
[14], in practice it has proven that the task of resistance of RPC tags against cloning attacks, using
PIN based access to achieve challenge response
replicating RFID tags does not requite a lot of
authentication. Public awareness of the security
money or expertise considering the wide implication related to cloning attacks should be the
availability of writable and reprogrammable tags. key policy to defend against. However, this is not
An ominous ex-ample is the demonstration by a always the case. For instance, none of the countries
German researcher of vulnerability of German that issue e-passports have anti-cloning mechanisms
passports [15] to cloning. [14] as suggested by the ICAO 9303 standard [15]. In
- Spoofing: Spoofing is effectively a variant of order to defend against passive eavesdropping attacks
encryption mechanisms could be used to encrypt the
cloning that does not physically replicate an
RFID communication. Spoofing and impersonation
RFID tag. In this type of attacks an adversary could be combated by using authentication protocol or
impersonates a valid RFID tag to gain its a second form of authentication such as one-time
privileges. This impersonation requires full access passwords, PINs or biometrics.
to the same communication channels as the
original tag. This includes knowledge of the B. Network layer security measures
protocols and secrets used in any authentication
In the current IoT structure, the network layer
that is going to a take place [31].
exists on the internet or on the existing communication
2) Reader Attacks: network. Some factors endanger the security of
information on the Internet, and are also IoT damage
- Impersonation: Considering the fact that in many information service. But the old network
cases RFID communication is unauthenticated, communication technology is not completely adapted
adversaries may easily counterfeit the to IoT. Traditional network routing is simple, and their
identification of a legitimate reader in order to main focus is not security. Because of the random,
elicit sensitive information or modality data on autonomous, unreliable IoT node arrangement of
RFID tags. energy limitation and communication, it leads to that
- Eavesdropping: The wireless nature of RFID IoT do not have dynamic infrastructure and topology.
makes eavesdropping one of the most serious and The attacker can easily cause attacks [10]. For
widely deployed threats. In eavesdropping an different network architecture, we need to configure
unauthorized individual uses an antenna in order the specific authentication mechanism, end-to-end
to record communications between legitimate authentication and key tuning mechanism, PKI (Public
Key Infrastructure), WPKI for wireless, security ARM core processors, Provencore runs in the
routing, intrusion detection, etc. Due to the enormous TrustZone on Cortex a core chipsets, but also works
amount of data, network availability should be on Cortex M-based architectures used in connected
considered. In addition, it should also enhance cross- object microcontrollers. This seems to be an
domain authentication and cross-network alternative to the Sansa solution, acquired by ARM.
authentication in the network layer. [17] Gives the One does not risk in any case to see appearing this
development trend of information security products kind of technology in its toothbrush connected!
based on IPv6. IPv6 Network. Ercom society presented to the MWC of Barcelona
its solution Cryptosmart of security by encryption of
V. INTERNET OF THINGS SOLUTIONS the storage and communications of the smartphones
and tablets Samsung, is labeled France Cybersecurity,
Reducing the exposure area of connected objects
a member of the BxaTrust Association. CryptoSmart
to attacks is a complex task. It requires architectural
relies on an EAL5 + certified smart card and an EAL4
knowledge of the value chain that connects objects to
+ certified applet. It is enough to compose its code to
the cloud. You need to look at the objects themselves,
activate the security by local encryption of the
their sensors and processors, local and remote
terminal. Ercom also offers Mobipass, a cloud solution
networks, protocols at all levels, then servers, their
for simulation and testing of mobile networks. It
software and data processing. The needs have been
simulates the operation of thousands of terminals. In
well known for years (see "Security needs in
October 2015, Ercom and Samsung announced the
embedded systems" published in 2008). Many
integration of Ercom encryption solution into the new
companies offer tools to secure this or that part of the
Korean smartphones [18].
value chain, but they have positioned themselves for a
Famoco offers the FX100 +, a secure terminal
short time in connected objects [18].
running on Android and supporting the NFC, which
In the value chain of connected objects, you must
can serve as a payment terminal. The company was
start with the objects themselves. They often include a
exhibiting at both the 2016 Las Vegas CES and the
chipset or a microcontroller based on ARM kernels.
MWC. This is a way of isolating functions that require
The most common ARM kernels are those of the A
a high level of security in a specific terminal. It is
series found in smartphone and tablet chipsets that can
targeted at professional applications. One cannot
be worth more than $ 10 and those of the M series
reasonably expect that consumers use this kind of
found in object microcontrollers Connected devices
terminal in addition to their smartphone [33].
that are worth around $ 1. Until now, ARM proposed
The universe of telecom operators is not left
to secure chipsets using serial a kernels with its
behind. At the beginning of 2016, the GSMA
TrustZone, a secure zone for performing protected
published guidelines for securing IoT architectures, in
processes, such as conditional access control systems
partnership with telecom operators from several
in set-top boxes [32]. Pay TV. ARM announced at the
continents: AT & T, Verizon, China Telecom, Etisalat,
end of 2015 that this technology should also be
KDDI, NTT Docomo, Orange, Telefonica, Telenon
integrable in Cortex-M core microcontrollers. In July
and Gemalto. OEMs are also aiming to complete their
2015, ARM acquired the Sansa startup, which will
offerings to secure end-to-end networks, in addition to
enable them to complete the TrustZone with an
their substantial investment in preparing for future
additional software and hardware security architecture.
deployments of the 5G.
All this will happen in the ARM roadmap in 2016 and
Ericsson presented to MWC 2015 its security
thus probably in commercial secure chipsets in 2017
solutions focused on data storage in the cloud. For its
that will be integrated into mainstream connected
part, Nokia has just acquired the Nakina systems, to
objects in 2018. The process will take a little time!
secure 5G networks and the Internet of things. They
However, the value chain for the design and
target like the other mainstream IoT, connected cars,
production of embedded chipsets is fragile. It is based
e-health and big data. Huawei also wants to have a say
on the integration of functional blocks of various
in securing connected objects. It promotes a
origins ("IP blocks"), with various integration software
collaborative approach and standardization with the
and manufacturing in factories in China or elsewhere
rest of the industry [33].
that are not necessarily well secured. Hence the
emergence of technological solutions that allow to VI. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
create ultra-secure chipsets, especially adapted due to
their cost to professional applications. In the present Existing IOT security solutions were used
case, the threats are not from hackers but rather from primarily by designers of mission-critical embedded
states and large companies involved in industrial systems related to aerospace, security and defense. As
espionage. In order to secure the chipsets of connected personal perspectives, we will study security
objects for demanding applications, the French architecture and specific operating modes in the
company Prove & Run offers proven core, a secure context of the Internet of things. Next, it will be asked
and formally proven micro-kernel. It runs on hardware to propose innovative approaches to ensure the
architectures based on ARM cores and Intel x86. In availability, integrity and confidentiality of such
architecture. Finally, work will be carried out on the [20] J. Grayson, "Stuxnet and Iran's Nuclear Program," Physics
evaluation of the proposed approaches in relation to 241, 7 Mar 11
[21] Krebs, Brian (September 21, 2016). "KrebsOnSecurity Hit
the more conventional vision of the Internet of things.
with Record DDoS". Brian Krebs. 17 November 2016.
[22] Tony Smith, 2001, "Hacker jailed for revenge sewage
REFERENCES attacks" "The register" Journal
[23] Qi Jing Athanasios V. Vasilakos Jiafu Wan Jingwei Lu
[1] Sareh Aghaei, Mohammad Ali Nematbakhsh, Hadi
Dechao Qiu - Security of the Internet of Things:
Khosravi Farsani, Evolution of the World Wide Web:
perspectives and challenges - DOI 10.1007/s11276-014-
from web 1.0 to web 4.0, pp 1-5 (IJWesT) No.1, January
0761-7 Springer
2012
[24] Ying Zhang, Technology Framework of the Internet of
[2] DnielPetr, GyrgyVesztergombi, Security and trust
Things and Its Application, in Electrical and Control
challenges in the area of the Internet of Things, European
Engineering (ICECE), pp. 4109-4112
Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007/2013)
[25] Xue Yang, Zhihua Li, Zhenmin Geng, Haitao Zhang, A
agreement number (258360).
Multi- layer Security Model for Internet of Things, in
[3] Dieter Uckelamann, Mark Harrison, and Floria
Communications in Computer and Information Science,
Michahelles, Architecting the Internet of Things,
2012, Volume 312, pp 388-393
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2011.
[26] Mr. Ravi Uttarkar and Prof. Raj Kulkarni, Internet of
[4] Rafiullah Khan, Sarmad Ullah Khan, Rifaqat Zaheer, and
Things: Architecture and Security, in International Journal
Shahid Khan, Future Internet: The Internet of
of Computer Application, Volume 3, Issue 4, 2014
Things Architecture,Possible Applications and Key
[27] Kimberly Hengst, "DDoS through the Internet of Things",
Challenges, in the proceedings of 10th International
An analysis determining the potential power of a DDoS
Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology,
attack using IoT devices - Twente Student Conference on
Islamabad, Pakistan, 17-19 December, 2012.
IT
[5] Client Advisory DYN / DDoS ATTACK, redfivesecurity
[28] Krushang Sonar, Hardik Upadhyay, "A Survey: DDOS
888-733-5007, 2016
Attack on Internet of Things", International Journal of
[6] Zhuankun Wu. : Initial Study on IOT Security architecture.
Engineering Research and Development, Volume 10, Issue
J.Strategy and decision-making research (2010)
11 (November 2014), PP. 58-63
[7] Huansheng Ning, Hong Liu, Cyber-Physical-Social Based
[29] Raghavendra K, Sumith Nireshwalya, "Application Layer
Security Architecture for Future Internet of Things, J.
Security Issues and Its Solutions", IJCSET |June 2012| Vol
Scientific research (2):1-7 (2012).
2, Issue 6,1266-1269
[8] Hongbo Gao, Study of the application for the security
[30] Weizhe Zhang, Baosheng Qu, "Security Architecture of the
state assessment about the internet of things based on grey
Internet of Things Oriented to Perceptual Layer",
correlation algorithm, J. Manufacturing Automation.
International Journal on Computer, Consumer and Control
34(11) (2012).
(IJ3C), Vol. 2, No.2(2013)
[9] Shancang Li, Kewang Zhang, Principle and application of
[31] Qi Zhang, P.SilpaChaitanya, T. Sudhir, "Spoofing Attack
wireless sensor network, M. Beijing: China Machine
Detection Wireless Networks using Advanced KNN",
Press (2008).
International Journal of Smart Device and Appliance Vol.
[10] Kai Zhao, Lina Ge "A Survey on the Internet of Things
4, No. 1 (2016), pp.1-8
Security", 2013 Ninth International Conference on
[32] Rijswijk-Deij, Roland van and Poll, Erik (2013) Using
Computational Intelligence and Security, China.
Trusted Execution Environments in Two-factor
[11] Xueguang Yang, Fengjiao Li, Xiangyong Mu, Design of
Authentication: comparing approaches. In: Open Identity
security and defense system for home based on Internet of
Summit 2013, OID 2013, 9-11 September 2013, Kloster-
things, J. computer application. 30(12):300-318 (2010).
Banz, Germany (pp. pp. 20-31).
[12] Antonio J. Jara, Miguel A. Zamora, Antonio F.G.
[33] Mobile world congress 2015, Barcelona
Skarmeta. HWSN6 Hospital Wireless Sensor Networks
Based on 6LoWPAN Technology: Mobility and Fault
Tolerance Management, C. In: International Conference
on Computational Science and Engineering, 879-884
(2009)
[13] Nabil Kannouf, Youssef Douzi, Mohamed Benabdellah,
Abdelmalek Azizi, Security on RFID technology,
International Conference on Cloud Technologies and
Applications (CloudTech), 2-4 June 2015, Marrakesh,
Morocco, IEEE Xplore Digital Library.
[14] Laurie, A., Practical Attacks Against RFID, In: Network
Security, Vol. 2007, No9, pp. 4-7
[15] Mitrokotsa, A., Rieback, M.R. & Tanenbaum,
Classification of RFID Attacks, DOI: 10.1007/s10796-
009-9210-z 29 July 2009, Link Springer.
[16] Juels,A., Stengthening EPC Tags Against Cloning, In:
Proc. Of ACM WorkShop on Wireless Security (WiSe05).
ACM Press (2005), pp. 67-76.
[17] Lei Li, Jing Chen, System Security Solutions of RFID
System of Internet of Things Sensing Layer, J. Net
Security Technologies and Application, (6): 34-36 (2011)
[18] Olivier Ezratty Opinions Libres, Can we secure the
Internet of things? "Cybersecurity Conference - IOT and
Embedded Systems, Toulouse 18 February 2016
[19] B. Kesler, "The Vulnerability of Nuclear Facilities to
Cyber Attack," Strategic Insights 10, 15 (2011).
You might also like
- Security Issues & Threats in IoT InfrastructureDocument5 pagesSecurity Issues & Threats in IoT InfrastructureIjaems JournalNo ratings yet
- A Survey On IoT Security Application Areas Security Threats and Solution ArchitecturesDocument23 pagesA Survey On IoT Security Application Areas Security Threats and Solution ArchitecturesShalini RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsFrom EverandBuilding the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- R F ID: Understanding Adio Requency Entification (RFID)Document15 pagesR F ID: Understanding Adio Requency Entification (RFID)Rohan KelkarNo ratings yet
- IoT by TejaDocument16 pagesIoT by TejaEmpty MindedNo ratings yet
- Network Security Lab ManualDocument66 pagesNetwork Security Lab ManualSankalp BalannavarNo ratings yet
- IOT Networks and ProtocolsDocument27 pagesIOT Networks and Protocolsfaisul faryNo ratings yet
- Report FirewallDocument27 pagesReport FirewallAbas WaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Embedded BookDocument59 pages1 Embedded BookCHENNAISKIVE PROJECTS100% (1)
- IOT SecurityDocument28 pagesIOT Securityfaisul faryNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Techniques in Mobile NetworksDocument8 pagesIntrusion Detection Techniques in Mobile NetworksInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- SeminarDocument12 pagesSeminarNAVEEN KUMAR100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1.2 Internet of Things (Iot) : Basic ConceptDocument29 pagesChapter 1: Introduction 1.1.2 Internet of Things (Iot) : Basic ConceptJpsworldNo ratings yet
- Emerging Threats On Mobile SecurityDocument16 pagesEmerging Threats On Mobile SecuritymilleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Database ManagementDocument31 pagesChapter 10-Database ManagementUsama AkbarNo ratings yet
- IoT ConceptDocument7 pagesIoT ConceptPedro Alexis Santos HernadezNo ratings yet
- Network Monitoring Using Captive Portal in PfsenseDocument49 pagesNetwork Monitoring Using Captive Portal in PfsenseMd. Mainul Islam100% (1)
- Huawei Building A Trusted and Managed IoT World PDFDocument33 pagesHuawei Building A Trusted and Managed IoT World PDFDANIELGONFANo ratings yet
- Iot Lab Manual PDFDocument80 pagesIot Lab Manual PDFTaribahmed100% (1)
- Warid Telecom Uganda Internship Report 2010-Musanje GasterDocument65 pagesWarid Telecom Uganda Internship Report 2010-Musanje Gastermusanjegaster100% (9)
- Cloud Computing-CSA Architecture.Document13 pagesCloud Computing-CSA Architecture.Santhiya RNo ratings yet
- STUXNETDocument13 pagesSTUXNETisaacperez100% (1)
- KSK7023 Network SecurityDocument26 pagesKSK7023 Network SecurityjoezanderNo ratings yet
- Snort ProjectDocument12 pagesSnort ProjectOumaima KaoukabiNo ratings yet
- Lasya Muthyam Synthesis Paper 1Document29 pagesLasya Muthyam Synthesis Paper 1api-612624796100% (1)
- Ethical HackingDocument14 pagesEthical HackingPamNo ratings yet
- SMART CITY, Technical Seminar: PPT, by Hoysal ShettyDocument17 pagesSMART CITY, Technical Seminar: PPT, by Hoysal Shettyhoysal4s4kadmat0% (1)
- Iot Based Anti Theift Flooring SystemDocument9 pagesIot Based Anti Theift Flooring Systembabblubabblu295No ratings yet
- Network Protocols, Schemes, and Mechanisms For Internet of Things (IoT) Features, Open Challenges, and TrendsDocument25 pagesNetwork Protocols, Schemes, and Mechanisms For Internet of Things (IoT) Features, Open Challenges, and TrendsThomas LagkasNo ratings yet
- Journal of Medical Systems-Security and Privacy Issues in Wireless SensorDocument10 pagesJournal of Medical Systems-Security and Privacy Issues in Wireless Sensormarisa.yuste08No ratings yet
- (Ebook - PDF) Linux SecurityDocument152 pages(Ebook - PDF) Linux SecurityS C GaurNo ratings yet
- USB Boot Tool Manual 1.4 enDocument21 pagesUSB Boot Tool Manual 1.4 enpepe2kNo ratings yet
- Hakin9 EN 03 2014Document74 pagesHakin9 EN 03 2014xtofsetNo ratings yet
- A Forensic Analysis of Android Malware - How Is Malware Written and How It Could Be Detected?Document5 pagesA Forensic Analysis of Android Malware - How Is Malware Written and How It Could Be Detected?Tharindu RoshanaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security-MinDocument73 pagesCyber Security-MinRajendra Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Open Source IDS ToolsDocument9 pagesOpen Source IDS ToolsMadhuri DesaiNo ratings yet
- Edge Computing SeminarDocument24 pagesEdge Computing SeminarNitin RanjanNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things (IoT) : Research, Architectures and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesInternet of Things (IoT) : Research, Architectures and ApplicationsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things Security, Device Authentication and Access Control A ReviewDocument11 pagesInternet of Things Security, Device Authentication and Access Control A Reviewfalconinayat0% (1)
- 7 ITE403 Whitman Ch05 W5C2Document19 pages7 ITE403 Whitman Ch05 W5C2namo nrtNo ratings yet
- Heat Stroke Mini ProjectDocument59 pagesHeat Stroke Mini ProjectSweety ShivaniNo ratings yet
- Securing The Internet of Things IoTDocument23 pagesSecuring The Internet of Things IoTMoustafa NajmNo ratings yet
- Week11 Assignment AnswerDocument2 pagesWeek11 Assignment AnswerMohanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Device Forensics ReviewDocument27 pagesMobile Device Forensics ReviewLiam LamNo ratings yet
- Snort As Intrusion Detection and Prevention Tool - RESEARCH PAPER 1Document20 pagesSnort As Intrusion Detection and Prevention Tool - RESEARCH PAPER 1kim891No ratings yet
- INFORMATION IN CROSS-MEDIA: FROM DESKTOP TO MOBILE - The Case of Marine Traffic: Designing A Website For Mobile Phones.Document230 pagesINFORMATION IN CROSS-MEDIA: FROM DESKTOP TO MOBILE - The Case of Marine Traffic: Designing A Website For Mobile Phones.Natalía PapadopoúlouNo ratings yet
- Iot Material 2019 A4Document57 pagesIot Material 2019 A4AmarNo ratings yet
- Iot Workshop Concept ProposalDocument14 pagesIot Workshop Concept ProposalNguyễn HàNo ratings yet
- DSc Research in Digital ForensicsDocument15 pagesDSc Research in Digital ForensicsRajiv Dharaskar100% (1)
- IOT Cyber Security Framework PDFDocument99 pagesIOT Cyber Security Framework PDFbaye omar SoceNo ratings yet
- IOT ReportDocument20 pagesIOT ReportChaithu GowdruNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesSeminar ReportSahil Sethi100% (1)
- 4&5G CyberSecurityDocument23 pages4&5G CyberSecurityLEVENT TASNo ratings yet
- Java Ring Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesJava Ring Seminar ReportSugam KatariaNo ratings yet
- Defending Microsoft environments at scaleDocument31 pagesDefending Microsoft environments at scalekeepzthebeezNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things and Wearable Technology: Addressing Privacy and Security Concerns Without Derailing InnovationDocument93 pagesThe Internet of Things and Wearable Technology: Addressing Privacy and Security Concerns Without Derailing InnovationMercatus Center at George Mason UniversityNo ratings yet
- Ultraprivate SmartphonesDocument10 pagesUltraprivate SmartphonesrakeshrakeshNo ratings yet
- IOT FundamentalsDocument104 pagesIOT FundamentalsTulipNo ratings yet
- Seminar PDF of FirewallDocument12 pagesSeminar PDF of FirewallRamaraju Vegesna0% (1)
- CH 1 Introduction To DatabaseDocument50 pagesCH 1 Introduction To DatabaseChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction PDFDocument72 pages1 Introduction PDFChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Alzimer Disease 2021Document13 pagesAlzimer Disease 2021Christopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Ieee Conference Paper TemplateDocument5 pagesIeee Conference Paper TemplateChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Srivastav A 1988Document3 pagesSrivastav A 1988Christopher HerringNo ratings yet
- 00 Paper I General PDFDocument20 pages00 Paper I General PDFChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Simple SentsDocument12 pagesSimple SentsChristopher Herring100% (1)
- Teachers Form PDFDocument4 pagesTeachers Form PDFChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Admission FormDocument2 pagesAdmission FormChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- PH.D Computer Scirnce 03082017Document2 pagesPH.D Computer Scirnce 03082017Christopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BSCDocument24 pagesSyllabus BSCChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Computer Binary DigitsDocument2 pagesComputer Binary DigitsChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- An Outline of The History of KashmirDocument16 pagesAn Outline of The History of KashmirChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- NIELIT Scientist B' Recruitment 2016 - Computer Science - GeeksforGeeksDocument15 pagesNIELIT Scientist B' Recruitment 2016 - Computer Science - GeeksforGeeksChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Plete PDFDocument201 pagesPlete PDFChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Role of Knowledge Engineering in The Development of A Hybrid Knowledge Based Medical Information System For Atrial FibrillationDocument6 pagesRole of Knowledge Engineering in The Development of A Hybrid Knowledge Based Medical Information System For Atrial FibrillationloveboxNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument6 pagesMachine LearningChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Security Through Hacking: Netcat TutorialDocument10 pagesSecurity Through Hacking: Netcat TutorialJairo TorresNo ratings yet
- EC Council CoursesDocument1 pageEC Council CoursesChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument101 pagesComputer ArchitectureSoyak_1987No ratings yet
- DR Tripathi's Analysis of Fundamental Rights & Directive PrinciplesDocument31 pagesDR Tripathi's Analysis of Fundamental Rights & Directive PrinciplesChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights and DutiesDocument21 pagesFundamental Rights and DutiesChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDFDocument45 pagesUnit 1 PDFLakshmi NarayananNo ratings yet
- Bulk Sms PresentationDocument16 pagesBulk Sms PresentationChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Fallacies of Reasoning ExplainedDocument21 pagesFallacies of Reasoning ExplainedChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Legy 201Document14 pagesLegy 201krishnendu_balNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01 - Iit - Iartificial Intelligence 2 AI PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 01 - Iit - Iartificial Intelligence 2 AI PDFVille4everNo ratings yet
- Algol 68 GDocument703 pagesAlgol 68 GChristopher HerringNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence - IIT KanpurDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence - IIT KanpurSangramNo ratings yet
- GeoDrive-1.0 SP4 QuickStartDocument40 pagesGeoDrive-1.0 SP4 QuickStartQuestionumber1No ratings yet
- Manual KlsDocument171 pagesManual KlsAliosmán GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Windows VistaDocument291 pagesWindows VistaDhanii AgustianNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Controller TCW121B en R3Document13 pagesEthernet Controller TCW121B en R3vasile_silionNo ratings yet
- Confronting Cyber Risk in Critical InfrastructureDocument36 pagesConfronting Cyber Risk in Critical InfrastructureAlexandru BurucNo ratings yet
- RSE Skills Assess - Student TRNG - ExamDocument14 pagesRSE Skills Assess - Student TRNG - Examamine mehdiNo ratings yet
- Catalog DORMA Usi Rotative KTV PDFDocument16 pagesCatalog DORMA Usi Rotative KTV PDFMaria-Cristina ArghirNo ratings yet
- Barangay Record System Streamlines Philippine Village ManagementDocument7 pagesBarangay Record System Streamlines Philippine Village ManagementGonzalo JohnNo ratings yet
- WLAN AC V200R021C00SPC100 Release NotesDocument17 pagesWLAN AC V200R021C00SPC100 Release NotesJulián PosadaNo ratings yet
- (Roll No Slip) : Competition Commission of Pakistan (CCP) (Screening Test For Trainee Officers)Document1 page(Roll No Slip) : Competition Commission of Pakistan (CCP) (Screening Test For Trainee Officers)Hafiz Saddique MalikNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Kriptografi Keamanan Komputer "Rc4Engine With Java-Netbeans"Document3 pagesAplikasi Kriptografi Keamanan Komputer "Rc4Engine With Java-Netbeans"Dmaz Krewol Pengen GenahNo ratings yet
- SQL Injection Presentation by Vivek PancholiDocument13 pagesSQL Injection Presentation by Vivek PancholiEr Vivek PancholiNo ratings yet
- AMEX CardDocument2 pagesAMEX CardnakedheadNo ratings yet
- PDF ReportDocument42 pagesPDF ReportsuyogNo ratings yet
- Appraisal Assistant User ManualDocument55 pagesAppraisal Assistant User ManualDamian Padilla100% (3)
- Martin Screw Conveyor-SecHDocument176 pagesMartin Screw Conveyor-SecHcontact@coreeslNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes on Cryptography: One-Way Functions and Trapdoor FunctionsDocument289 pagesLecture Notes on Cryptography: One-Way Functions and Trapdoor FunctionsMerry SinhaNo ratings yet
- Acp 122 Echg 1Document66 pagesAcp 122 Echg 1api-3731349No ratings yet
- Pre - Functional Checklist Documentation 7Document2 pagesPre - Functional Checklist Documentation 7renjithv_4No ratings yet
- Electronic ticket receiptDocument2 pagesElectronic ticket receipttassiahNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document11 pagesBook 1laodesyuhadarNo ratings yet
- Network Security History Importance and FutureDocument13 pagesNetwork Security History Importance and FutureBandarAlHarbiNo ratings yet
- Copilot SpecDocument20 pagesCopilot SpectroubledsoulNo ratings yet
- PGPCMDDocument88 pagesPGPCMDascchninNo ratings yet
- GAPP Privacy Framework for AccountantsDocument4 pagesGAPP Privacy Framework for AccountantshardyNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Based On IEC 62351 and IEC 62443 For IEC 61850 SystemsDocument7 pagesCybersecurity Based On IEC 62351 and IEC 62443 For IEC 61850 SystemshvananthNo ratings yet
- The Growth of Machine Learning in CybersecurityDocument17 pagesThe Growth of Machine Learning in CybersecurityZachary StandridgeNo ratings yet
- RersdexDocument41 pagesRersdexRohit PNo ratings yet
- IPControl 6.0 Install GuideDocument56 pagesIPControl 6.0 Install GuideRaja Rozali Raja HasanNo ratings yet