Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Chemistry Notes Ch09 Coordination Compounds
Uploaded by
Dinesh KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Chemistry Notes Ch09 Coordination Compounds
Uploaded by
Dinesh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE
Class 12 Chemistry
Quick Revision Notes
Chapter 9
Co-ordination Compounds
Co-ordination compounds:
1. A coordination compound contains a central metal atom or ion surrounded by number of
oppositely charged ions or neutral molecules. These ions or molecules re bonded to the
metal atom or ion by a coordinate bond.
2. Example:
3. They do not dissociate into simple ions when dissolved in water.
Double salt
1. When two salts in stoichiometric ratio are crystallised together from their saturated
solution they are called double salts
2. Example: (Mohrs salt)
3. They dissociate into simple ions when dissolved in water.
Coordination entity:
1. A coordination entity constitutes a central metal atom or ion bonded to a fixed number of
ions or molecules.
2. Example: In - represents coordination entity.
Central atom or ion:
1. In a coordination entity, the atom/ion to which a fixed number of ions/groups are bound
in a definite geometrical arrangement around it, is called the central atom or ion.
2. Example: In , is the central metal ion.
Ligands:
1. A molecule, ion or group that is bonded to the metal atom or ion in a complex or
coordination compound by a coordinate bond is called ligand.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 8
2. It may be neutral, positively or negatively charged.
3. Examples: etc.
Donor atom:
1. An atom of the ligand attached directly to the metal is called the donor atom.
2. Example: In the complex ,CN is a donor atom.
Coordination number:
1. The coordination number (CN) of a metal ion in a complex can be defined as the number
of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded.
2. Example: In the complex , the coordination number of Fe is 6.
Coordination sphere:
1. The central atom/ion and the ligands attached to it are enclosed in square bracket and are
collectively termed as the coordination sphere.
2. Example: In the complex is the coordination sphere.
Counter ions:
1. The ions present outside the coordination sphere are called counter ions.
2. Example: In the complex , K+ is the counter ion.
Coordination polyhedron:
1. The spatial arrangement of the ligand atoms which are directly attached to the central
atom/ ion defines a coordination polyhedron about the central atom.
2. The most common coordination polyhedra are octahedral, square planar and
tetrahedral.
3. Examples: is square planar, is tetrahedral while [Cu(NH3)6]3+ is
octahedral.
Charge on the complex ion: The charge on the complex ion is equal to the algebraic
sum of the charges on all the ligands coordinated to the central metal ion.
Denticity: The number of ligating (linking) atoms present in ligand is called denticity.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 8
Unidentate ligands:
1. The ligands whose only one donor atom is bonded to metal atom are called unidentate
ligands.
2. Examples:
Didentate ligands:
1. The ligands which contain two donor atoms or ions through which they are bonded to the
metal ion.
2. Examples: Ethylene diamine ( ) has two nitrogen atoms, oxalate ion
has two oxygen atoms which can bind with the metal atom.
Polydentate ligand:
1. When several donor atoms are present in a single ligand, the ligand is called polydentate
ligand.
2. Examples: In , the ligand is said to be polydentate and
Ethylenediaminetetraacetate ion is an important hexadentate ligand. It
can bind through two nitrogen and four oxygen atoms to a central metal ion.
Chelate:
1. An inorganic metal complex in which there is a close ring of atoms caused by attachment
of a ligand to a metal atom at two points.
2. An example is the complex ion formed between ethylene diamine and cupric ion,
.
Ambidentate ligand:
1. Ligands which can ligate (link) through two different atoms present in it are called
ambidentate ligand.
2. Example: and . Here, can link through N as well as O while
can link through S as well as N atom.
Werners coordination theory:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 8
1. Werner was able to explain the nature of bonding in complexes.
2. The postulates of Werners theory are:
a). Metal shows two different kinds of valencies: primary valence and secondary valence.
b). The ions/ groups bound by secondary linkages to the metal have characteristic spatial
arrangements corresponding to different coordination numbers.
c). The most common geometrical shapes in coordination compounds are octahedral, square
planar and tetrahedral.
Primary valence
1. This valence is normally ionisable.
2. It is equal to positive charge on central metal atom.
3. These valencies are satisfied by negatively charged ions.
4. Example: In , the primary valency is three. It is equal to oxidation state of central
metal ion.
Secondary valence
1. This valence is non ionisable.
2. The secondary valency equals the number of ligand atoms coordinated to the metal. It is
also called coordination number of the metal.
3. It is commonly satisfied by neutral and negatively charged, sometimes by positively
charged ligands.
Oxidation number of central atom: The oxidation number of the central atom in a
complex is defined as the charge it would carry if all the ligands are removed along
with the electron pairs that are shared with the central atom.
Homoleptic complexes: Those complexes in which metal or ion is coordinate bonded
to only one kind of donor atoms. For example:
Heteroleptic complexes: Those complexes in which metal or ion is coordinate
bonded to more than one kind of donor atoms. For example:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 8
Isomers: Two or more compounds which have same chemical formula but different
arrangement of atoms are called isomers.
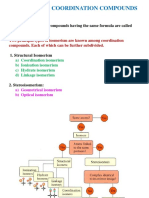
Types of isomerism:
a). Linkage isomerism
b). Solvate isomerism or hydrate isomerism
c). Ionisation isomerism
d). Coordination isomerism
1. Structural isomerism
2. Stereoisomerism
a). Geometrical isomerism
b). Optical isomerism
Structural isomerism:
1. It arises due to the difference in structures of coordination compounds.
2. Structural isomerism, or constitutional isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which
molecules with the same molecular formula have atoms bonded together in different
orders.
Ionisation isomerism:
1. It arises when the counter ion in a complex salt is itself a potential ligand and can
displace a ligand which can then become the counter ion.
2. Example:
Solvate isomerism:
1. It is isomerism in which solvent is involved as ligand.
2. If solvent is water it is called hydrate isomerism, e.g., and
.
Linkage isomerism:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 8
1. It arises in a coordination compound containing ambidentate ligand.
2. In the isomerism, a ligand can form linkage with metal through different atoms.
3. Example: and .
Coordination isomerism:
1. This type of isomerism arises from the interchange of ligands between cationic and
anionic entities of different metal ions present in a complex.
2. Example: and .
Stereoisomerism: This type of isomerism arises because of different spatial
arrangement.
Geometrical isomerism: It arises in heteroleptic complexes due to different possible
geometrical arrangements of ligands.
Optical isomerism: Optical isomers are those isomers which are non-superimposable
mirror images.
Valence bond theory:
1. According to this theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its
(n-1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridisation to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of
definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar.
2. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate
electron pairs for bonding.
Coordination
Type of hybridisation Shape of hybrid
Number
4 Tetrahedral
4 Square planar
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 8
5 Trigonalbipyramidal
(nd orbitals are involved outer orbital
6 Octahedral
complex or high spin or spin free complex)
d orbitals are involved inner orbital
6 Octahedral
or low spin or spin paired complex)
Magnetic properties of coordination compounds:
A coordination compound is paramagnetic in nature if it has unpaired electrons and
diamagnetic if all the electrons in the coordination compound are paired.
Magnetic moment where n is number of unpaired electrons.
Crystal Field Theory:
1. It assumes the ligands to be point charges and there is electrostatic force of attraction
between ligands and metal atom or ion.
2. It is theoretical assumption.
Crystal field splitting in octahedral coordination complexes:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 7 / 8
Crystal field splitting in tetrahedral coordination complexes:
For the same metal, the same ligands and metal-ligand distances, the difference in
energy between eg and t2g level is
Metal carbonyls:
1. Metal carbonyls are homoleptic complexes in which carbon monoxide (CO) acts as the
ligand.
2. Example:
3. The metal-carbon bond in metal carbonyls possess both s and p character.
4. The MC bond is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons from the carbonyl
carbon into a vacant orbital of the metal.
5. The MC bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from a filled d orbital of
metal into the vacant antibonding orbital of carbon monoxide.
6. The metal to ligand bonding creates a synergic effect which strengthens the bond
between CO and the metal.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 8 / 8
You might also like
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Co-Ordination CompoundsAbid waniNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 9.coordination CompoundsDocument46 pages9.coordination CompoundsSeenu MNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Coordination Compounds Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Coordination Compounds Chapter NotesAbhik Joydhar100% (1)
- Coordination Compounds 9 PDFDocument7 pagesCoordination Compounds 9 PDFkrishna kumar100% (1)
- Coordination CompoundsDocument48 pagesCoordination CompoundsK_S_Krishna0001No ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument118 pagesCoordination Compoundsnoorafia46No ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula Chapter9 Coordination CompoundsDocument15 pagesChemistry Formula Chapter9 Coordination CompoundsJeshanth JsNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds ExplainedDocument88 pagesCoordination Compounds ExplainedSARUNKUMAR BALATHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument14 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsAman KumarNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument19 pagesCoordination CompounddeepjoypalNo ratings yet
- Coordinaton Compounds Short NotesDocument7 pagesCoordinaton Compounds Short NotesAlokNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument14 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsHarry RoyNo ratings yet
- SSD Krishina Vatika Senior Secondary School BathindaDocument18 pagesSSD Krishina Vatika Senior Secondary School BathindaAyush JindalNo ratings yet
- Coordination COMPOUND MainDocument33 pagesCoordination COMPOUND Mainriya6370srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 An Introduction To Coordination CompoundsDocument5 pagesChapter 7 An Introduction To Coordination Compoundsbryant021593No ratings yet
- IC_Lecture1_0Document30 pagesIC_Lecture1_0DusuNo ratings yet
- Coordination Complex: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument21 pagesCoordination Complex: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHasnain Mohammad HanifNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry Theories and GeometriesDocument11 pagesCoordination Chemistry Theories and GeometriesZakiyah Rizkah Nu'manNo ratings yet
- Notes Coordination CompletedDocument24 pagesNotes Coordination CompletedRoshini VivekanandanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument64 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument11 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsYASH SONARNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds - BSC IIIDocument14 pagesCoordination Compounds - BSC IIIRojo John0% (1)
- 6 2018 11 10!08 18 38 PMDocument9 pages6 2018 11 10!08 18 38 PMAlma Tyara SNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inorganic ChemistryDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Inorganic ChemistryLeng ElmpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument14 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsRajeev Kaushik100% (1)
- Coordination Chemistry: Key Concepts of Coordination CompoundsDocument34 pagesCoordination Chemistry: Key Concepts of Coordination CompoundsShahidNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Ncert Ch09 Coordination Compounds Part 01 QuesDocument43 pages12 Chemistry Ncert Ch09 Coordination Compounds Part 01 Queshumayun khalidNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahDocument46 pagesThe Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahYouseffNo ratings yet
- Key Facts about Noble Gases and Their UsesDocument87 pagesKey Facts about Noble Gases and Their UsesNicholas ChenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Coordination Compounds: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument31 pagesChemistry of Coordination Compounds: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. Burstensanjayp25No ratings yet
- ISOMERISM AND BONDING IN COORDINATION COMPOUNDSDocument61 pagesISOMERISM AND BONDING IN COORDINATION COMPOUNDSkamoNo ratings yet
- 11 - Isomerism in TMCDocument18 pages11 - Isomerism in TMCMohit KambojNo ratings yet
- CHE1212 Coordination-LIDocument85 pagesCHE1212 Coordination-LIzahara99121No ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compounds Are The Compounds in Which The Central Metal Atom Is Linked ToDocument4 pagesCo-Ordination Compounds Are The Compounds in Which The Central Metal Atom Is Linked ToBalakrishna Arpula100% (2)
- Chemistry - Transition MetalsDocument46 pagesChemistry - Transition Metalsshan mackNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure, Chemical Formulas & NomenclatureDocument20 pagesAtomic Structure, Chemical Formulas & NomenclatureKelly PotterNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Organic Compounds: Chapter SummaryDocument390 pagesBonding in Organic Compounds: Chapter SummaryGlyzen GaleonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Coordination CompoundsDocument11 pagesChapter - 5 Coordination CompoundsSuresh Dasaraddi67% (3)
- 9 Coordinaton Compounds NewDocument11 pages9 Coordinaton Compounds NewShesha krishnaNo ratings yet
- ComplexesDocument20 pagesComplexespunt3yNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds ExplainedDocument11 pagesCoordination Compounds ExplainedShashank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 14 Lewis Structures and Molecuar Models S19Document14 pages14 Lewis Structures and Molecuar Models S19victorNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Class 12Document112 pagesCoordination Compounds Class 12nm.ananya2008No ratings yet
- Bonding and Molecular Structure ActivityDocument3 pagesBonding and Molecular Structure ActivityMarichu VelascoNo ratings yet
- Chem Project Term 1Document21 pagesChem Project Term 1Abishek ArunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document22 pagesChemistry 2Francia Mae Tanio MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Bond NoteDocument9 pagesChemical-Bond NoteDixit GautamNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 Coordination Compounds Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesJEE Main 2023 Coordination Compounds Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadaryan.aru2006No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry [PDF]Document15 pagesCoordination Compounds Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry [PDF]nishu3071singhNo ratings yet
- Internal Assignment No. 1 Paper Code: CH - 201 Paper Title: Inorganic Chemistry Q. 1. Answer All The QuestionsDocument57 pagesInternal Assignment No. 1 Paper Code: CH - 201 Paper Title: Inorganic Chemistry Q. 1. Answer All The QuestionsRahul meenaNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Document6 pagesAP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Weiyu TongNo ratings yet
- Ib Chem Bonding NotesDocument19 pagesIb Chem Bonding Notesapi-293306937100% (1)
- Coordination Compounds 11Document22 pagesCoordination Compounds 11Manan SethiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ExplainedDocument10 pagesChemical Bonding ExplainedMary Cris MovillaNo ratings yet
- Chem Chap 5 Coordination CompoundsDocument71 pagesChem Chap 5 Coordination Compoundsissacpaul382No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 11Document15 pagesChapter 9 11Ritik KumarNo ratings yet
- VBT - Theory and IsomerismDocument25 pagesVBT - Theory and Isomerismzuneid-adamoNo ratings yet
- Discussion On:: MBBS Year 1Document9 pagesDiscussion On:: MBBS Year 1Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument3 pagesNutritionDinesh Kumar0% (5)
- BMS Tutorial PDFDocument6 pagesBMS Tutorial PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Session (2020) : Anatomy Practicals Roster Y1Document1 pageSession (2020) : Anatomy Practicals Roster Y1Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- MAHSA Hostel - 2019 InternationalDocument1 pageMAHSA Hostel - 2019 InternationalDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- HEM Tutorial Questions Day 2 (26th June 2020) PDFDocument2 pagesHEM Tutorial Questions Day 2 (26th June 2020) PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Heeeem Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesHeeeem Assignment PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- GIM Block Discussion - 11.06.2020 - With ANSWER PDFDocument12 pagesGIM Block Discussion - 11.06.2020 - With ANSWER PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Gim Discussion 2 19TH June PDFDocument24 pagesGim Discussion 2 19TH June PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Gim Discussion 2 19TH June PDFDocument24 pagesGim Discussion 2 19TH June PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Habitat Operating Hours (MCO & Puasa Month) PDFDocument1 pageHabitat Operating Hours (MCO & Puasa Month) PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument3 pagesHealth Declaration FormDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- HEM Short Formative Assessment - Student Version PDFDocument2 pagesHEM Short Formative Assessment - Student Version PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- MBBS Assignment PDFDocument9 pagesMBBS Assignment PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- International student residence fees 2020Document1 pageInternational student residence fees 2020Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Rwcomposición CorporalDocument21 pagesRwcomposición CorporalJonathan Camilo100% (1)
- The Geekay World School Academic Session 2017 - 2018: Tgws Board ResultsDocument22 pagesThe Geekay World School Academic Session 2017 - 2018: Tgws Board ResultsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sindhu - For MergeDocument20 pagesSindhu - For MergeDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Geekay World School Academic Session 2017 - 2018: Tgws Board ResultsDocument22 pagesThe Geekay World School Academic Session 2017 - 2018: Tgws Board ResultsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS)Document8 pagesBachelor of Surgery (MBBS)Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Thegeekayworldschool Academic Session 2017-2018: Determination of Various Contents of Cold DrinksDocument15 pagesThegeekayworldschool Academic Session 2017-2018: Determination of Various Contents of Cold DrinksDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project PDFHarkritSinghNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project PDFHarkritSinghNo ratings yet
- Project Communication HandbookDocument43 pagesProject Communication Handbookfakhro100% (4)
- 1205 P.A Gautam TransformerDocument27 pages1205 P.A Gautam TransformerDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch16 Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument8 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch16 Chemistry in Everyday LifeDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Communication HandbookDocument43 pagesProject Communication Handbookfakhro100% (4)
- Steps in Balancing Redox ReactionsDocument28 pagesSteps in Balancing Redox ReactionsRUZCHEMISTRYNo ratings yet
- CHM1207 Lab 3 2023 - DRAKES, Tameica (1042436) PDFDocument6 pagesCHM1207 Lab 3 2023 - DRAKES, Tameica (1042436) PDFNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Galvanic Series: Why Metals Corrode?Document7 pagesGalvanic Series: Why Metals Corrode?Rey Francis FamulaganNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Combustion ConversionDocument68 pagesSpontaneous Combustion ConversionRizwan Ullah BaigNo ratings yet
- Performance Based Evaluation of Industrial Grade Resins Duolite ARA-9366 and Duolite A-368Document8 pagesPerformance Based Evaluation of Industrial Grade Resins Duolite ARA-9366 and Duolite A-368misterno2No ratings yet
- Literature Review 26 JuneDocument42 pagesLiterature Review 26 JuneSanjeev NehruNo ratings yet
- Chinese GMP 2010Document115 pagesChinese GMP 2010Atul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1010750-Steam Quality TestingDocument11 pages1010750-Steam Quality TestingHendra Hadriansyah100% (1)
- Is 2986Document9 pagesIs 2986sreenathaNo ratings yet
- ME6008 WELDING TECHNOLOGY Part B IQDocument1 pageME6008 WELDING TECHNOLOGY Part B IQVikram mNo ratings yet
- Organic Name Reactions GuideDocument12 pagesOrganic Name Reactions GuidechinmayaNo ratings yet
- Insect PestsDocument164 pagesInsect PestsKenneth100% (11)
- U15 S1-2 HW KeysDocument6 pagesU15 S1-2 HW KeysRohith GudatiNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics and Thermosetting PlasticDocument24 pagesThermoplastics and Thermosetting PlasticKAPIL SINGHNo ratings yet
- ZeTo RulesDocument30 pagesZeTo RulesRamli Disa100% (5)
- Sunward SWE08B Operator's ManualDocument96 pagesSunward SWE08B Operator's ManualIisakki50% (2)
- Against Water Hummer PDFDocument36 pagesAgainst Water Hummer PDFDenstar Ricardo SilalahiNo ratings yet
- LCGC Europe 2001Document4 pagesLCGC Europe 2001Jhonattan BaezNo ratings yet
- Essay On StalinDocument8 pagesEssay On Stalinfz6zke9m100% (2)
- Johnson Industrial Screens PDFDocument20 pagesJohnson Industrial Screens PDFjaime palenzuela rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Reinforced Concrete - Bond, Development LengthDocument55 pagesLecture 4 - Reinforced Concrete - Bond, Development LengthChristopher PaladioNo ratings yet
- Presentation1. AEC GeoTech LANDFILLDocument22 pagesPresentation1. AEC GeoTech LANDFILLAyan BorgohainNo ratings yet
- 1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance Iedxcel TDocument25 pages1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance Iedxcel TBest ProgressNo ratings yet
- Onions: Vegetable Crops Production Guide For The Atlantic ProvincesDocument8 pagesOnions: Vegetable Crops Production Guide For The Atlantic ProvincesEglNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alkanes and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDocument5 pagesCape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alkanes and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDestinee SullivanNo ratings yet
- S1XBIG58 M500 4 Tech InfoDocument15 pagesS1XBIG58 M500 4 Tech InfoFredy DanielNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cleaning and Shaping in EndodonticsDocument299 pages2 - Cleaning and Shaping in EndodonticsElisabeth MarofNo ratings yet
- PIP PCECV001 Guidelines For Application of Control ValvesDocument39 pagesPIP PCECV001 Guidelines For Application of Control ValvesAndresNo ratings yet
- Identify Hazards and Risks in the WorkplaceDocument7 pagesIdentify Hazards and Risks in the WorkplaceLeah Rizza CabaliwNo ratings yet
- Special Process Audit Check Sheet - PlatingDocument8 pagesSpecial Process Audit Check Sheet - PlatingHariprasanth ChandranNo ratings yet
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryFrom EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionFrom EverandThe History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)


















































![Coordination Compounds Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry [PDF]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/725138012/149x198/dd8b65c9f3/1713690291?v=1)