Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exceptions in Java: What Is An Exception?
Uploaded by
Probal SilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exceptions in Java: What Is An Exception?
Uploaded by
Probal SilCopyright:
Available Formats
Exceptions in Java
What is an Exception?
An exception is an unwanted or unexpected event, which occurs during the execution of a program i.e at
run time, that disrupts the normal flow of the programs instructions.
Error vs Exception
Error: An Error indicates serious problem that a reasonable application should not try to catch.
Exception: Exception indicates conditions that a reasonable application might try to catch.
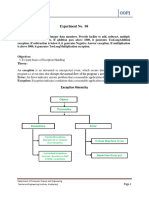
Exception Hierarchy
All exception and errors types are sub classes of class Throwable, which is base class of hierarchy.One
branch is headed by Exception. This class is used for exceptional conditions that user programs should
catch. NullPointerException is an example of such an exception.Another branch, Error are used by the
Java run-time system(JVM) to indicate errors having to do with the run-time environment itself(JRE).
StackOverflowError is an example of such an error.
For checked vs unchecked exception, see Checked vs Unchecked Exceptions
How JVM handle an Exception?
Default Exception Handling : Whenever inside a method, if an exception has occurred, the method
creates an Object known as Exception Object and hands it off to the run-time system(JVM). The exception
object contains name and description of the exception, and current state of the program where exception
has occurred. Creating the Exception Object and handling it to the run-time system is called throwing an
Exception.There might be the list of the methods that had been called to get to the method where exception
was occurred. This ordered list of the methods is called Call Stack.Now the following procedure will
happen.
The run-time system searches the call stack to find the method that contains block of code that can
handle the occurred exception. The block of the code is called Exception handler.
The run-time system starts searching from the method in which exception occurred, proceeds
through call stack in the reverse order in which methods were called.
If it finds appropriate handler then it passes the occurred exception to it. Appropriate handler means
the type of the exception object thrown matches the type of the exception object it can handle.
If run-time system searches all the methods on call stack and couldnt have found the appropriate
handler then run-time system handover the Exception Object to default exception handler ,
which is part of run-time system. This handler prints the exception information in the following format
and terminates program abnormally.
Exception in thread "xxx" Name of Exception : Description
... ...... .. // Call Stack
You might also like
- Ownership and Governance of State Owned Enterprises A Compendium of National Practices 2021Document104 pagesOwnership and Governance of State Owned Enterprises A Compendium of National Practices 2021Ary Surya PurnamaNo ratings yet
- JMeter Interview Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesJMeter Interview Questions and AnswersProbal SilNo ratings yet
- RFCLookup SampleDocument13 pagesRFCLookup SampleProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Java: Programming: Your Step by Step Guide to Easily Learn Java in 7 DaysFrom EverandJava: Programming: Your Step by Step Guide to Easily Learn Java in 7 DaysRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Selenium With C#Document9 pagesSelenium With C#Probal SilNo ratings yet
- IDoc Packaging and Mapping TechniquesDocument20 pagesIDoc Packaging and Mapping TechniquesProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Sample Cracking Microservices InterviewsDocument32 pagesSample Cracking Microservices InterviewsSuhas SettyNo ratings yet
- Java Core Interview in Australia. Questions and Answers. Tech interviewer’s notesFrom EverandJava Core Interview in Australia. Questions and Answers. Tech interviewer’s notesNo ratings yet
- Assignment8-Integration Test Cases For GmailDocument14 pagesAssignment8-Integration Test Cases For GmailVasanth Prasad81% (26)
- New Japa Retreat NotebookDocument48 pagesNew Japa Retreat NotebookRob ElingsNo ratings yet
- C++ NotesDocument129 pagesC++ NotesNikhil Kant Saxena100% (4)
- CS3391 Oops Unit 3Document31 pagesCS3391 Oops Unit 3Sakkaravarthi SNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Delivering A Memorized SpeechDocument9 pagesOrganizing and Delivering A Memorized SpeechJanice L. Langit100% (4)
- Writing Simple Sentences to Describe ScenariosDocument5 pagesWriting Simple Sentences to Describe Scenariosepol67% (3)
- ExceptionsDocument3 pagesExceptionsdeniseNo ratings yet
- Java Exceptions ExplainedDocument3 pagesJava Exceptions ExplainedBogdan CocuNo ratings yet
- Exception in JavaDocument42 pagesException in Javadisha2001No ratings yet
- Chapter_-5_Exception_handling__multithreaded_programmingDocument24 pagesChapter_-5_Exception_handling__multithreaded_programmingxitekol233No ratings yet
- Exception Handling: Maintain FlowDocument105 pagesException Handling: Maintain FlowTechVeerendra's Software SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Exception:: Exception Handling-UNIT-3-PART-1Document19 pagesException:: Exception Handling-UNIT-3-PART-1dil rockNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling in Java: What Are Exceptions?Document5 pagesException Handling in Java: What Are Exceptions?octavesNo ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument24 pagesException HandlingSENTHILNAATHAN KANNAPPANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Multi Threading and Exception HandlingDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Multi Threading and Exception Handlingsmrt00783% (6)
- Exception Handling in JavaDocument4 pagesException Handling in Javaarun yadavNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling in .NETDocument14 pagesException Handling in .NETWechuli PaulNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument13 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesEdenmay VerNo ratings yet
- JAVA EXCEPTION HANDLINGDocument23 pagesJAVA EXCEPTION HANDLINGldp100476No ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument27 pagesException HandlingAkshItha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument21 pagesException HandlingMadhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 - Exception HandlingDocument26 pagesChapter 09 - Exception HandlingTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Managing Errors and Exceptions in JavaDocument21 pagesManaging Errors and Exceptions in JavaGeneral Zorawar SinghNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling-Converted1Document28 pagesException Handling-Converted1Madhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Exception Handling 2023Document20 pagesChapter Five Exception Handling 2023tinsaie berhanuNo ratings yet
- What Is An ExceptionDocument29 pagesWhat Is An ExceptionSujit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming-Lecture No 9Document14 pagesObject Oriented Programming-Lecture No 9Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- 53 16sccit4-16sccca3-16scccs3 2020051902155688Document16 pages53 16sccit4-16sccca3-16scccs3 2020051902155688sathyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ExceptionHandlingDocument8 pagesChapter 7 ExceptionHandlingmbiruk118No ratings yet
- Java ExceptionDocument15 pagesJava ExceptionDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling 1Document32 pagesException Handling 1Manoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- Exception HadlingDocument26 pagesException HadlingSushíl kanikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five - Exception HandlingDocument6 pagesChapter Five - Exception HandlingKene BirhanuNo ratings yet
- CSEC 313: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Exception HandlingDocument24 pagesCSEC 313: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Exception HandlingxuoNo ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument12 pagesException HandlingKousik mannaNo ratings yet
- Exceptional Handling in JavaDocument11 pagesExceptional Handling in Javajasmine serraoNo ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument11 pagesException HandlingBadal RorNo ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument11 pagesException HandlingSowjanya BalagaNo ratings yet
- Ty Cse: Experiment No. 08Document3 pagesTy Cse: Experiment No. 08sardarNo ratings yet
- jpr-ch4Document19 pagesjpr-ch4xboyxman1000No ratings yet
- Module 4Document28 pagesModule 4Sheela MaharajpetNo ratings yet
- ch-3 ExceptionDocument31 pagesch-3 ExceptionMarkos MathewosNo ratings yet
- Java Exception HandlingDocument14 pagesJava Exception HandlingDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Chap 5, Exceptn HandDocument12 pagesChap 5, Exceptn Handbirhanu gebisaNo ratings yet
- Exceptions Tutorial Which Covers AllDocument11 pagesExceptions Tutorial Which Covers AllLakshmanNo ratings yet
- Exceptions Handling Constructs: ErrnoDocument5 pagesExceptions Handling Constructs: ErrnoJayesh TrimbakkarNo ratings yet
- Java Unit-3Document61 pagesJava Unit-3syeda husnaNo ratings yet
- Unit3exception HandlingDocument3 pagesUnit3exception Handlingmadani hussainNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 JavaDocument3 pagesPresentation 1 JavapratikNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling in JavaDocument7 pagesException Handling in JavaTechnical LobbyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Java ExceptionsDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Java ExceptionsHaymanot MatebieNo ratings yet
- Managing Errors and ExceptionDocument12 pagesManaging Errors and ExceptionShanmuka Sreenivas100% (1)
- QB104343Document7 pagesQB104343Viswanathkani TNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Exception HandlingDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Java Exception HandlingUday KumarNo ratings yet
- Cs8392 Object Oriented Programming: Unit Iii Exception Handling and I/ODocument43 pagesCs8392 Object Oriented Programming: Unit Iii Exception Handling and I/OmahalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3.1Document18 pagesLecture-3.1gdgdNo ratings yet
- Exception-Handling Fundamentals: Learn Key Concepts Like try, catch, throw, throws & finallyDocument31 pagesException-Handling Fundamentals: Learn Key Concepts Like try, catch, throw, throws & finallyviji90kuNo ratings yet
- PR - 9 - Exception HandlingDocument4 pagesPR - 9 - Exception HandlingRohan RahalkarNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling and SuperDocument3 pagesException Handling and Super1DT19CS049 Gurijala PranathiNo ratings yet
- PROG-J - M03 - C02 - SLM - Exceptions and Exception HandlingDocument32 pagesPROG-J - M03 - C02 - SLM - Exceptions and Exception HandlingYogesh sNo ratings yet
- Java ExceptionDocument19 pagesJava ExceptionMihaiDurneaNo ratings yet
- uUNIT-III OOPC JAVADocument24 pagesuUNIT-III OOPC JAVAamancha SANJANANo ratings yet
- Description: Exception-Handling FundamentalsDocument2 pagesDescription: Exception-Handling Fundamentalsnavita08No ratings yet
- Plug in ExtensionDocument13 pagesPlug in ExtensionProbal SilNo ratings yet
- SOAP UI - Data SourceDocument5 pagesSOAP UI - Data SourceProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Selenium With C# - Session04Document8 pagesSelenium With C# - Session04Probal SilNo ratings yet
- Gateway Training 01Document22 pagesGateway Training 01Probal SilNo ratings yet
- Sap Ui5Document6 pagesSap Ui5Probal SilNo ratings yet
- Selenium With C# - Session03Document16 pagesSelenium With C# - Session03Probal SilNo ratings yet
- Selenium With C# - Session02Document12 pagesSelenium With C# - Session02Probal SilNo ratings yet
- Modern Compiler Design Java TutorialDocument54 pagesModern Compiler Design Java TutorialProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Groovy - Agile dynamic language for JavaDocument69 pagesIntroduction to Groovy - Agile dynamic language for Javavivek558100% (1)
- Sample Quality Assurance ResumeDocument2 pagesSample Quality Assurance ResumeProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Penetration Testing: From Enumeration to Code ExecutionDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Penetration Testing: From Enumeration to Code ExecutionProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Hana NotesDocument1 pageHana NotesProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Group - e Financial Management 01Document26 pagesGroup - e Financial Management 01Probal SilNo ratings yet
- Unable To See Pipe Line Steps in The... : Muniyappan MarasamyDocument2 pagesUnable To See Pipe Line Steps in The... : Muniyappan MarasamyProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Sample Quality Assurance ResumeDocument2 pagesSample Quality Assurance ResumeProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Map Values Using XI Graphical EditorDocument4 pagesMap Values Using XI Graphical EditorProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Java MappingDocument10 pagesJava MappingProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Sunil CVDocument5 pagesSunil CVapi-3731110No ratings yet
- Steps To Use External DefinitionDocument2 pagesSteps To Use External DefinitionProbal SilNo ratings yet
- SeleniumDocument17 pagesSeleniumProbal SilNo ratings yet
- File To RFC Without BPMDocument7 pagesFile To RFC Without BPMapi-3722276100% (2)
- Advanced user-defined functions import contexts or queuesDocument4 pagesAdvanced user-defined functions import contexts or queuesProbal SilNo ratings yet
- Linux / UNIX: Check If File Is Empty or Not Using Shell ScriptDocument2 pagesLinux / UNIX: Check If File Is Empty or Not Using Shell ScriptProbal SilNo ratings yet
- S 212 Pre Course WorkDocument5 pagesS 212 Pre Course Workafiwierot100% (2)
- Biomérieux 21342 Vitek 2 GP: Intended UseDocument19 pagesBiomérieux 21342 Vitek 2 GP: Intended UserezaNo ratings yet
- Remembrance 23 Names PDFDocument1 pageRemembrance 23 Names PDFJennifer ThuncherNo ratings yet
- Stmma-Fd: Zhejiang Castchem New Material Co.,Ltd&Castchem (Hangzhou), IncDocument2 pagesStmma-Fd: Zhejiang Castchem New Material Co.,Ltd&Castchem (Hangzhou), IncYash RaoNo ratings yet
- Asian Studies For Filipinos The Philippines in The Asian CenturyDocument15 pagesAsian Studies For Filipinos The Philippines in The Asian CenturyGlaizza QuintonNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVADocument7 pagesRecent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVAcal2_uniNo ratings yet
- Mini Centre CatalogDocument26 pagesMini Centre CatalogJohn EarleyNo ratings yet
- 6470b0e5f337ed00180c05a4 - ## - Atomic Structure - DPP-01 (Of Lec-03) - Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pages6470b0e5f337ed00180c05a4 - ## - Atomic Structure - DPP-01 (Of Lec-03) - Arjuna NEET 2024Lalit SinghNo ratings yet
- Jeremy Hughes ReviewDocument5 pagesJeremy Hughes ReviewgracecavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2maxamed0% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesDocument21 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesRashdan HarunNo ratings yet
- Tendernotice 2Document20 pagesTendernotice 2VIVEK SAININo ratings yet
- Institutional Competency Assessment Instrument (ICAI)Document12 pagesInstitutional Competency Assessment Instrument (ICAI)Bea EtacNo ratings yet
- Complete Approval List by FSSAIDocument16 pagesComplete Approval List by FSSAIAnkush Pandey100% (1)
- Intraoperative Nursing Care GuideDocument12 pagesIntraoperative Nursing Care GuideDarlyn AmplayoNo ratings yet
- Acid content in fruitsDocument2 pagesAcid content in fruitsbone fire100% (1)
- Administrations whose CoCs are accepted for CECDocument1 pageAdministrations whose CoCs are accepted for CECGonçalo CruzeiroNo ratings yet
- Journal 082013Document100 pagesJournal 082013Javier Farias Vera100% (1)
- 4 Exploring Your Personality Q and Scoring Key (Transaction Analysis)Document3 pages4 Exploring Your Personality Q and Scoring Key (Transaction Analysis)Tarannum Yogesh DobriyalNo ratings yet
- Product Manual 82434 (Revision C) : Generator Loading ControlDocument26 pagesProduct Manual 82434 (Revision C) : Generator Loading ControlAUGUSTA WIBI ARDIKTANo ratings yet
- Preparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimDocument9 pagesPreparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimslightlyguiltyNo ratings yet
- Leks Concise Guide To Trademark Law in IndonesiaDocument16 pagesLeks Concise Guide To Trademark Law in IndonesiaRahmadhini RialiNo ratings yet
- D2DDocument2 pagesD2Dgurjit20No ratings yet
- L P 10Document13 pagesL P 10Bình Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id26238Document21 pagesSSRN Id26238Ayame KusuragiNo ratings yet