Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Supply
Uploaded by
michelleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Supply
Uploaded by
michelleCopyright:
Available Formats
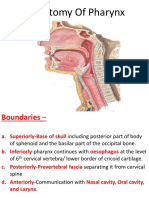
o Blood Supply: Uterine artery (from internal iliac artery); artery crosses above the ureter at the
level of the internal os and ascend along the lateral margin of the uterus within the broad
ligament
o Venous Drainage: Uterine vein > internal iliac vein
o Support: chiefly by levator ani
Subperitoneal condensation of levator ani on the upper surface forming 3 ligaments
Transverse cervical ligament (cardinal ligament/ligament of Mackenrodt): between
the cervix and upper end of the vagina and lateral pelvic walls
Pubocervical: either side of the neck of the urinary bladder, passing from the
posterior surface of the pubis
Sacrocervical: from lower end of sacrum to the upper end of vagina and cervix
o Parts:
Fundus: above the connection of the fallopian tube to the uterus
Body: until the dilatation
Cervix: below the dilatation
Uterine Cavity: triangular space inside fundus and body of uterus
upper angles is formed by uterine opening (uterine os)
lower angle is formed by the internal os
o Relations:
Anteriorly: uterovesical pouch and superior surface of the urinary bladder (body), superior
surface of the urinary bladder (supravaginal part of the cervix), anterior fornix of the vagina
(Vaginal cervix)
Posteriorly: Rectouterine (Douglas) Pouch, with coils of ileum and sigmoid
Laterlally: broad ligament, uterine artery and vein, ureter (supravaginal ureter), lateral
fornix (vaginal cervix)
o Cervical canal: distal continuation of uterine cavity; inferior opening is the external os
o Internal os: communication between uterine cavity and cervical canal
o External os: communication between cervical canal and vaginal canal
o Round ligament of the uterus
fallopian tube: 10 cm long and lies on the upper border of the broad ligament; connects the peritoneal cavity
with the cavity of the uterus
o Receives ovum, and provides site for fertilization; nourishment and transport to the uterine cavity;
conduit along which the sperm travel to reach the ovum
o Blood Supply: Uterine and ovarian artery
o Venous Drainage: Uterine and ovarian veins
o Lymphatics: internal iliac nodes > paraaortic nodes
o Nerve supply: Inferior hypogastric lexus
o Infundibulum: funnel-shaped lateral end that project beyond the broad ligament and overlies the
ovary
Fimbriae: finger-like projections
o Ampulla: the widest part of the tube; the usual site of fertilization
o Isthmus: narrowest part of the tube and lies just lateral to the uterus
o Intramural: most medial part that pierces/embedded in the uterine wall
ovary: 4 x 2 cm, attached to the back of broad ligament, against the lateral pelvic wall in a depression called the
ovarian fossa
o production of ova (female germ cells), production of estrogen and progesterone
o bounded above by external iliac vessels
o bounded behind by internal iliac vessels and ureter
o Blood Supply: ovarian artery (from abdominal artery at L1)
o Venous Drainage: ovarian vein
Left ovarian > Left renal
Right ovarian > Inferior vena cava
o Lymphatics: Paraaortic nodes at L1
o Nerve Supply: aortic plexus
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Pocket Tutor ECG Interpretation PDFDocument165 pagesPocket Tutor ECG Interpretation PDFasri100% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book - Joseph E. MuscolinoDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book - Joseph E. Muscolinonifewedu0% (4)
- Photosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetG Meera Prem Kumar20% (5)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ANATOMY OF PHARYNX (39 CHARACTERSDocument27 pagesANATOMY OF PHARYNX (39 CHARACTERSmichelleNo ratings yet
- Gynecology PDFDocument537 pagesGynecology PDFCrystal Nguyen100% (1)
- Case Presentation of Prostate CA and BPHDocument81 pagesCase Presentation of Prostate CA and BPHJon Gab Paquit100% (8)
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Anatomybayenn100% (3)
- SkullDocument19 pagesSkullMark M. Alipio100% (1)
- General Biology 1: The CellsDocument71 pagesGeneral Biology 1: The CellsPaula Marie Llido100% (2)
- Cap II - Curs 5 - 6 - Somatosensory System - 2014 - 2015 - PDFDocument137 pagesCap II - Curs 5 - 6 - Somatosensory System - 2014 - 2015 - PDFMaria MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems QuizDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems QuizGusthe Jebb AzarconNo ratings yet
- Ellen Shaw DeParedes MD - Atlas of Mammography-LWW (2007)Document703 pagesEllen Shaw DeParedes MD - Atlas of Mammography-LWW (2007)NER CARLO SANTOSNo ratings yet
- CT scan confirms benign mesenteric cystDocument3 pagesCT scan confirms benign mesenteric cystmichelleNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR QUIZDocument2 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR QUIZmichelleNo ratings yet
- The Mode of Action of Electrical High Frequency ST PDFDocument10 pagesThe Mode of Action of Electrical High Frequency ST PDFmichelleNo ratings yet
- Cancer in Children and Adolescents: Epidemiology and Risk FactorsDocument115 pagesCancer in Children and Adolescents: Epidemiology and Risk FactorsmichelleNo ratings yet
- Analytical Reasoning BDocument2 pagesAnalytical Reasoning BmichelleNo ratings yet
- ZJRMS v16n1p51 Fa PDFDocument4 pagesZJRMS v16n1p51 Fa PDFmichelleNo ratings yet
- Bioethics - CompassionDocument5 pagesBioethics - CompassionmichelleNo ratings yet
- Analytical Reasoning ADocument1 pageAnalytical Reasoning AmichelleNo ratings yet
- Synthof THDocument1 pageSynthof THmichelleNo ratings yet
- Analytical Reasoning CDocument1 pageAnalytical Reasoning CmichelleNo ratings yet
- Foot UlcerDocument1 pageFoot UlcermichelleNo ratings yet
- Endocrin Sim Lab KeyDocument6 pagesEndocrin Sim Lab KeyapriliatriwahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- HypercholesterolemiaDocument5 pagesHypercholesterolemiamichelleNo ratings yet
- Acasestudyoncirrhosisofliver 160424143748Document48 pagesAcasestudyoncirrhosisofliver 160424143748michelleNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Physical Processes of DigestionDocument59 pagesChemical and Physical Processes of DigestionmichelleNo ratings yet
- Neck LectureDocument10 pagesNeck Lectureapi-3812135No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemmichelleNo ratings yet
- PhyEx 8 1&2Document3 pagesPhyEx 8 1&2michelleNo ratings yet
- Ascietes by DR Naila MasoodDocument45 pagesAscietes by DR Naila MasoodmichelleNo ratings yet
- Persistent Impairment of Taste Associated With Terbinafine: Case ReportDocument2 pagesPersistent Impairment of Taste Associated With Terbinafine: Case ReportmichelleNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids - 20180412195233Document59 pagesNucleotides and Nucleic Acids - 20180412195233michelleNo ratings yet
- 1 EyelidsDocument2 pages1 EyelidsmichelleNo ratings yet
- Liv CirrDocument1 pageLiv CirrmichelleNo ratings yet
- Regina Hansen 1A EndocrineDocument4 pagesRegina Hansen 1A EndocrinemichelleNo ratings yet
- Acasestudyoncirrhosisofliver 160424143748Document48 pagesAcasestudyoncirrhosisofliver 160424143748michelleNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument41 pagesHead and Neckdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemmichelleNo ratings yet
- Symp FibDocument1 pageSymp FibmichelleNo ratings yet
- A104 Biology Problem 1: Same Yet DifferentDocument179 pagesA104 Biology Problem 1: Same Yet Differentben ooNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: SubtitleDocument89 pagesThe Respiratory System: SubtitleAaaNo ratings yet
- 2021 ISFM Consensus Guidelines On The Collection and Administration of Blood and Blood Products in CatsDocument23 pages2021 ISFM Consensus Guidelines On The Collection and Administration of Blood and Blood Products in CatsNurul Izzatul AnnisaNo ratings yet
- External Nose AnatomyDocument17 pagesExternal Nose AnatomyAnonymous avOsNPcNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument5 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityYda Maxine PalmaNo ratings yet
- Paradox of ChoiceDocument2 pagesParadox of ChoiceCarelessNo ratings yet
- Protocol Book BWCT DominiqueS 2Document126 pagesProtocol Book BWCT DominiqueS 2N AaNo ratings yet
- Pre Transfusion TestingDocument67 pagesPre Transfusion TestingPaulino GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Structure and Function of SkinDocument10 pagesThe Integumentary System: Structure and Function of SkinDonto KonoNo ratings yet
- The Neuroendocrine System of InvertebratesDocument16 pagesThe Neuroendocrine System of InvertebratesRoxy Destiny100% (1)
- Electrolyte&Fluid Balance Simple DR - Dicky, SPPDDocument38 pagesElectrolyte&Fluid Balance Simple DR - Dicky, SPPDGhadiz Fhydhya FadhillaNo ratings yet
- The Cell as a Biological SystemDocument37 pagesThe Cell as a Biological SystemNacu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Class Notes For Upper Biology MasterclassDocument2 pagesClass Notes For Upper Biology MasterclassYehia Khaled Essam Fawaz ICSBR1No ratings yet
- Survey A&P Lab 1 GuideDocument7 pagesSurvey A&P Lab 1 Guidegabriella IrbyNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEM REVIEWERDocument8 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEM REVIEWERJames Russel MariNo ratings yet
- Caring For The Patient With Cerebrovascular Disease Super FinalDocument84 pagesCaring For The Patient With Cerebrovascular Disease Super FinalDexter Niel Ortilano CPAC-SNNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 3 Life Unit 3L1Document22 pagesScience Grade 3 Life Unit 3L1Cristina Isabel Saavedra CuellesNo ratings yet
- Biology WAEC Likely Questions PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesBiology WAEC Likely Questions PDF DownloadCharles Obaleagbon100% (1)
- Abdominal Compartment SyndromeDocument12 pagesAbdominal Compartment SyndromeAltus GoldenNo ratings yet