Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equations: Exposure Calculation Formulas
Uploaded by
agniva dattaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equations: Exposure Calculation Formulas
Uploaded by
agniva dattaCopyright:
Available Formats
3/15/2018 Equations
Equations
Exposure Calculation Formulas
Exposure calculation formulas
Equation Description
Geometric unsharpness:
Ug is the geometric unsharpness in millimeters (mm)
S is the source size in millimeters (mm)
t is the object thickness (or top of object to film distance if film is removed from
object) in millimeters (mm)
d is the source (or focus) to object distance in millimeters (mm)
Source to film distance:
D is the source to film (SFD) or focus to film (FFD) distance
d is the source (or focus) to object distance
t is the object thickness
Reciprocity Law:
I1 is the intensity of X-ray radiation at a tube current of M1 milliampere (mA)
I2 is the intensity of X-ray radiation at a tube current of M2 milliampere (mA)
Reciprocity Law:
I1 is the intensity of gamma radiation at activity A1 Gigabecquerel (GBq)
I2 is the intensity of gamma radiation at activity A2 Gigabecquerel (GBq)
X-ray exposure time:
E is the exposure in milliampere minutes (mAm)
M is the tube current in milliampere (mA)
T is the exposure time in minutes
Gamma ray exposure time:
E is the exposure in Gigabecquerel hours or Gigabecquerel minutes (GBq hours or
GBq minutes)
A is the activity in Gigabecqueres (Gbq)
T is the exposure time in hours or minutes
Exponential decay equation:
At is the activity in time 't' in Gigabecquerels (GBq)
A0 is the initial activity in Gigabecquerels (GBq)
e is the exponential constant (2.718)
t is the age of the source in days/weeks/years
H is the half life in days/weeks/years
Inverse square law:
I1 is the intensity of radiation at distance D1
I2 is the intensity of radiation at distance D2
Distance squared law:
E1 is the exposure at distance D1
E2 is the exposure at distance D2
Equivalent steel thickness:
te is the equivalent steel thickness to be used to determine the exposure from the
X-ray or gamma-ray exposure chart for steel
t0 is the actual thickness to be radiographed
REF is the radiographic equivalence factor
Other equations for Radiographic Testing
http://lrrpublic.cli.det.nsw.edu.au/lrrSecure/Sites/Web/1144B/ndt/content/radiographic/library/equations.htm 1/2
3/15/2018 Equations
Table of equations for Radiographic Testing
Equation Description
Duane-Hunt Law (minimum wavelength):
λ is the shortest wavelength in
metres (m)
V is the applied voltage in volts (V)
Lambert's Law:
It is the intensity of transmitted
(emergent) radiation in millisieverts
per hour (mSv/hr)
I0 is the intensity of incident radiation
in millisieverts per hour (mSv/hr)
e is the exponential constant (2.718)
μ is the absorption coefficient per
millimetre of material at a particular
radiation energy
t is the material thickness in
millimetres (mm)
Film density:
I0 is the incident light intensity
It is the transmitted light intensity
Sensitivity formula for wire type IQI.
Sensitivity formula for step-type IQI.
Sensitivity formula for plaque hole IQI:
A is the thickness of the smallest
plaque image visible, expressed as a
percentage of metal thickness
B is the diameter of the smallest hole
visible, expressed as a percentage of
metal thickness
http://lrrpublic.cli.det.nsw.edu.au/lrrSecure/Sites/Web/1144B/ndt/content/radiographic/library/equations.htm 2/2
You might also like
- Essentials of Radiologic ScienceDocument392 pagesEssentials of Radiologic ScienceKhalil Issaad50% (2)
- 240H - Service Instructions - Ver.5 PDFDocument107 pages240H - Service Instructions - Ver.5 PDFJuan Eladio Lorenzo100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Spectroscopy Method of AnalysisDocument50 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Spectroscopy Method of AnalysisNajmi NasirNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ultrasonic Flaw Sizing of Stress Corrosion Cracking Advanced Ultrasonic PDFDocument4 pagesAdvanced Ultrasonic Flaw Sizing of Stress Corrosion Cracking Advanced Ultrasonic PDFphutd09No ratings yet
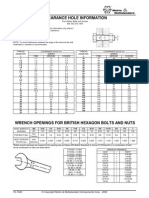
- Clearance Hole ISO 273 1979Document1 pageClearance Hole ISO 273 1979Sachin Verma100% (1)
- 2003 Physics RecallsDocument8 pages2003 Physics RecallsBrian DunfeeNo ratings yet
- Pocket Tutor Chest X-Ray Interpretation 1st PDFDocument233 pagesPocket Tutor Chest X-Ray Interpretation 1st PDFKarthik S100% (1)
- Radiation Safety Exam Preparation Model QuestionsDocument77 pagesRadiation Safety Exam Preparation Model QuestionsAhmed shaban100% (4)
- Test Bank For Radiation Protection in Medical Radiography 8th Edition by ShererDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Radiation Protection in Medical Radiography 8th Edition by ShererCheryl Tasler100% (24)
- 05 Dr. Sagawa at 22-1 JuneDocument24 pages05 Dr. Sagawa at 22-1 JuneAna SilvaNo ratings yet
- PHY03Document1 pagePHY03ben harrisNo ratings yet
- Sachi SPECTROSCOPY NOTES PDFDocument17 pagesSachi SPECTROSCOPY NOTES PDFarchana giriNo ratings yet
- Ch. 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry: What Is Spectroscopy?Document4 pagesCh. 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry: What Is Spectroscopy?JaiNo ratings yet
- Vector Scalar and Units ReviewDocument43 pagesVector Scalar and Units ReviewGumball DumballNo ratings yet
- Leo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesDocument12 pagesLeo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesVynz JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Basic Optics For Optical MetrologyDocument224 pagesBasic Optics For Optical Metrologyoscar bohorquezNo ratings yet
- GR11 Physics Information SheetsDocument6 pagesGR11 Physics Information Sheetsowamibosch735No ratings yet
- RKS Signals and Systems Lecture 01 03Document18 pagesRKS Signals and Systems Lecture 01 03s.ahmed.2002eeeNo ratings yet
- Fabry Perot Interferometer GovindDocument3 pagesFabry Perot Interferometer Govinddevanarayan2000No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Distance Measurement (Edm)Document11 pagesElectromagnetic Distance Measurement (Edm)Ismail Ben MabroukNo ratings yet
- Error: Absolute Error (X - ) Relative Error (%) 100 (X - )Document26 pagesError: Absolute Error (X - ) Relative Error (%) 100 (X - )Saba AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Practical 13 - Melde's Experiment (Vibrator Generator)Document1 pagePractical 13 - Melde's Experiment (Vibrator Generator)Nasrin SultanaNo ratings yet
- Latin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of MeasureDocument5 pagesLatin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of MeasureChase CampbellNo ratings yet
- Signscsaacsal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The ExperimentDocument9 pagesSignscsaacsal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The Experimentali najatNo ratings yet
- Signal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The ExperimentDocument9 pagesSignal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The Experimentali najatNo ratings yet
- Maths Application SumsDocument36 pagesMaths Application SumsBalakamuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Angle ModulationDocument57 pagesLecture 8 Angle ModulationAwais khanNo ratings yet
- Signscsaacsttal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The ExperimentDocument9 pagesSignscsaacsttal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The Experimentali najatNo ratings yet
- Signscsaacsttgbal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The ExperimentDocument9 pagesSignscsaacsttgbal Expoun Energy and Power: Name of The Experimentali najatNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument24 pagesElectromagnetic WavesBalaji PeddakamNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Fraiber ZambranoDocument5 pagesPre Task - Fraiber ZambranoLugar De La Mancha MuñozNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Signals and Signal Space Spring 2017 IIDocument96 pagesChap 2 Signals and Signal Space Spring 2017 IINayim MohammadNo ratings yet
- (C) 2013 DR JM Fernandez InstanchemDocument91 pages(C) 2013 DR JM Fernandez InstanchemShiroShitenNo ratings yet
- Zurich Principles of Lockin DetectionDocument10 pagesZurich Principles of Lockin DetectionGreen LemonNo ratings yet
- New Method of Data Treatment Related To Induction Machine Bearing Fault Using Axial Vibration Analytic SignalDocument5 pagesNew Method of Data Treatment Related To Induction Machine Bearing Fault Using Axial Vibration Analytic Signallaribi souadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Gamma Cameras For SPECT and PET PDFDocument32 pagesLecture 17 - Gamma Cameras For SPECT and PET PDFFrancesca RivaNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementDocument4 pagesUnits and Measurementsonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Sub Module 2.5 Pyrometery: Radiation FundamentalsDocument17 pagesSub Module 2.5 Pyrometery: Radiation Fundamentalsvikashranjan1987No ratings yet
- Physics of X-Rays and Instrument ParametersDocument46 pagesPhysics of X-Rays and Instrument ParametersVladimir KrzalicNo ratings yet
- Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing BasicsDocument55 pagesThermal Infrared Remote Sensing Basicssoumitra karNo ratings yet
- Sensors 19 01661Document18 pagesSensors 19 01661Артем ВитальевичNo ratings yet
- ColorimetryDocument33 pagesColorimetryiycbrthoratNo ratings yet
- 7 - SonometerDocument3 pages7 - SonometerIsuru UdaraNo ratings yet
- 3 - Inst Chem Lec Properties of Electromagnetic RadiationPTTDocument11 pages3 - Inst Chem Lec Properties of Electromagnetic RadiationPTTJoudNo ratings yet
- A Units & DimensionsDocument19 pagesA Units & Dimensionsf20230069No ratings yet
- 07-Time of FlightDocument23 pages07-Time of FlightasdfasdfsafdasfsaNo ratings yet
- Wavelength of Mercury Spectrum - SpectrometerDocument3 pagesWavelength of Mercury Spectrum - SpectrometerHarshit Kothala100% (1)
- Vibration Data Acquisition Analysis TechniquesDocument11 pagesVibration Data Acquisition Analysis Techniqueskaran5singh-12No ratings yet
- Determine Wavelength Using Diffraction GratingDocument4 pagesDetermine Wavelength Using Diffraction GratingAditya R GautamNo ratings yet
- Losses in Optical FiberDocument13 pagesLosses in Optical FiberPoonam sawantNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument200 pagesSeminarMudassarNo ratings yet
- 6.1 LThe Wave Nature of LightDocument10 pages6.1 LThe Wave Nature of LightShallimar AlcarionNo ratings yet
- 3.ir Spectroscopy LatestDocument92 pages3.ir Spectroscopy Latestdimitra shenoyNo ratings yet
- Section3 Michelson InterferometerDocument5 pagesSection3 Michelson InterferometerRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- NDT-Basic-FormulaeDocument3 pagesNDT-Basic-FormulaeJayeshNo ratings yet
- Module 3 and 4 Physics 2Document30 pagesModule 3 and 4 Physics 2kyle brian talingtingNo ratings yet
- Kinegram Measurements by Sezad and Shuvo - RCDocument15 pagesKinegram Measurements by Sezad and Shuvo - RCSilence is BetterNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: Signal Space and OrthogonalityDocument75 pagesSignals and Systems: Signal Space and OrthogonalityAli AlluwaimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter No1.PropagationDocument28 pagesChapter No1.PropagationlifeNo ratings yet
- Colloid CharacterizationDocument19 pagesColloid CharacterizationShounak BiswasNo ratings yet
- Rayleigh Scattering: It D Ti y G GDocument34 pagesRayleigh Scattering: It D Ti y G Gmd rokonuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Difraction Grating ResearshDocument8 pagesDifraction Grating ResearshAdham OwiesiNo ratings yet
- Transmission Characteristics of Optical FibersDocument45 pagesTransmission Characteristics of Optical FibersDr Ravi Kumar A VNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive Testing Rm12 01Document32 pagesNon Destructive Testing Rm12 01Urja KaushikNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- 2Document6 pages2agniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical TolerancingDocument12 pagesGeometrical TolerancingItalo Venegas100% (1)
- Norton Saint Gobian AbrasivesDocument2 pagesNorton Saint Gobian Abrasivesagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Bosch and Hitachi Grinder Machine GuideDocument1 pageBosch and Hitachi Grinder Machine Guideagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Tolerancing Pponlinet PDFDocument48 pagesTolerancing Pponlinet PDFagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Carborundum Universal LTDDocument3 pagesCarborundum Universal LTDagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Limits, Fits & CalculationsDocument28 pagesLimits, Fits & Calculationsagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual for Waste Heat Recovery BoilerDocument131 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual for Waste Heat Recovery Boileragniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Bosch and Hitachi Grinder Machine GuideDocument1 pageBosch and Hitachi Grinder Machine Guideagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- 1984 Surf Roughness PGDocument8 pages1984 Surf Roughness PGHussn YazdanNo ratings yet
- Tolerancia y AjusteDocument48 pagesTolerancia y AjusteHeber Esparza CslashNo ratings yet
- Tube-To-tubesheet Joints - ASME (Mechanical) Code Issues - Eng-TipsDocument4 pagesTube-To-tubesheet Joints - ASME (Mechanical) Code Issues - Eng-Tipsagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- ISO Hole Tolerance, ISO Hole Tolerances, Hole Tolerance, ISO 286-2 Hole Tolerances 3mm-400mm PDFDocument3 pagesISO Hole Tolerance, ISO Hole Tolerances, Hole Tolerance, ISO 286-2 Hole Tolerances 3mm-400mm PDFagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Technical Bid 957 PDFDocument108 pagesTechnical Bid 957 PDFagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Ansi B4.1 Fit Chart - Engineering Tolerance - IndustriesDocument1 pageAnsi B4.1 Fit Chart - Engineering Tolerance - Industriesagniva datta0% (1)
- Bhopal: Technical Specification For Drilling of Tube Holes in SS-overlayed Tube PlatesDocument2 pagesBhopal: Technical Specification For Drilling of Tube Holes in SS-overlayed Tube Platesagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Hole Quality Defined - CompositesWorldDocument3 pagesHole Quality Defined - CompositesWorldagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- METRIC STANDARDS For Worldwide Manufacturing SummariesDocument123 pagesMETRIC STANDARDS For Worldwide Manufacturing Summariescicero220358100% (2)
- General ISO Geometrical Tolerances Per. ISO 2768 - GD&T Tolerances - ISO G&T Tolerances - Engineers EdgeDocument4 pagesGeneral ISO Geometrical Tolerances Per. ISO 2768 - GD&T Tolerances - ISO G&T Tolerances - Engineers Edgeagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Limit and Fit - ISO Hole Chart - ToleranceDocument2 pagesLimit and Fit - ISO Hole Chart - Toleranceagniva datta100% (2)
- Engineering, Manufacturing Tolerance Limits Fits Charts - ISO 286 Tolerances - Metric Tolerance Chart - Engineers EdgeDocument12 pagesEngineering, Manufacturing Tolerance Limits Fits Charts - ISO 286 Tolerances - Metric Tolerance Chart - Engineers Edgeagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Amazon - in - Drilling Holes Tolerance Books PDFDocument3 pagesAmazon - in - Drilling Holes Tolerance Books PDFagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Absorption of γ-Rays: Determining Half-Value ThicknessDocument19 pagesAbsorption of γ-Rays: Determining Half-Value ThicknessAbhrajit MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Radiation Health Protection ManualDocument58 pagesRadiation Health Protection Manualgangzhu liangNo ratings yet
- RPII Code Design Medical Facilities 09Document112 pagesRPII Code Design Medical Facilities 09Muhammad IkbarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear MedicineDocument11 pagesNuclear MedicineJose NicoliellyNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety Procedure Rev.08Document41 pagesRadiation Safety Procedure Rev.08manz29No ratings yet
- Icrp 94 Radiological ProtectionDocument84 pagesIcrp 94 Radiological ProtectionBudi ArifNo ratings yet
- User Guide Epsilon4 enDocument59 pagesUser Guide Epsilon4 ennabbatahabba habsteinNo ratings yet
- RPDIR-L04 Internat System WEBDocument43 pagesRPDIR-L04 Internat System WEBAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- Cs137 MSDSDocument3 pagesCs137 MSDSFrancisco CanoNo ratings yet
- Semi SourceDocument14 pagesSemi SourceMouneeshNo ratings yet
- RPP Study MaterialDocument14 pagesRPP Study MaterialKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- SafeRad SCAR PresentationDocument280 pagesSafeRad SCAR PresentationnathgsurendraNo ratings yet
- Asme B16.34Document15 pagesAsme B16.34Achraf Ismail100% (1)
- 2.37 Rso Training Standard Syllabi For Training Courses On Radiological SafetyDocument96 pages2.37 Rso Training Standard Syllabi For Training Courses On Radiological SafetyashwiniNo ratings yet
- VIP Radiation PhysicsDocument102 pagesVIP Radiation PhysicsgetachewNo ratings yet
- Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Children Clinical Effectiveness and Cancer Risk Due To Radiation Exposure 2019Document6 pagesDental Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Children Clinical Effectiveness and Cancer Risk Due To Radiation Exposure 2019Meris JugadorNo ratings yet
- Shielding GuidelineDocument40 pagesShielding Guidelinemax_schofieldNo ratings yet
- P 119 JAICRP 41(s) Compendium of Dose Coefficients Based On ICRP Publication 60 PDFDocument132 pagesP 119 JAICRP 41(s) Compendium of Dose Coefficients Based On ICRP Publication 60 PDFFlorentin DumitruNo ratings yet
- Occupational Radiation Safety: Directed Readings in The ClassroomDocument54 pagesOccupational Radiation Safety: Directed Readings in The ClassroomErick Calcaligong100% (1)
- Datasheet Stratos DR DMS GroupDocument9 pagesDatasheet Stratos DR DMS GroupDigo OtávioNo ratings yet
- Vrdose Overview 1.1Document25 pagesVrdose Overview 1.1hyoung65No ratings yet
- Terra P Operating ManualDocument55 pagesTerra P Operating ManualosecaloNo ratings yet
- 1999 Criticality Accident at The Fuel Conversion Plant in Tokaimura in JapanDocument29 pages1999 Criticality Accident at The Fuel Conversion Plant in Tokaimura in JapannaoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and Energy Chapter OverviewDocument54 pagesNuclear Chemistry and Energy Chapter OverviewBruce MendozaNo ratings yet