Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 57
Uploaded by
MarcTnnOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 57
Uploaded by
MarcTnnCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
Lesson: Lattice Energy
Aim :
To study the determination of the lattice energy of an ionic compound using a Born-Haber
cycle.
Learning Outcomes :
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to :
1. define : lattice energy, standard enthalpy change of atomisation, ionisation energy
and electron affinity.
2. draw and use a Born-Haber cycle to determine the lattice energy of an ionic
compound.
3. list the factors that affect the lattice energy of an ionic compound.
4. define standard enthalpy change of hydration and solution.
5. relate the solubility of an ionic compound with its standard enthalpy change of
solution.
Assumed prior knowledge :
Students should already be familiar with :
1. the concept of enthalpy changes.
2. the definitions of ionisation energy and lattice structure.
Underlying Principles
1. Making the invisible, visible.
2. Enabling students to know what to look for.
Time taken to complete the activities : 80 minutes
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 1 of 4
Differentiation
Questions in the student notes are designed to enable all students to complete the activity.
The pop-up answers are provided for the students to view when they have considered their
responses. Worksheet questions include questions that require recall, understanding and
application of the new concepts learned.
Development of Lesson :
No. Steps Strategy Resources
1 Set Induction. • Teacher to quiz student to ensure that
(Ascertaining prior they have the necessary background
knowledge and knowledge.
introducing lesson
topic for the day). Teacher to point out lesson objectives for
the day.
2 Student Activity Teacher to go through Activities 1 - 3 • Courseware
with the students.
• Activity 1 : Lattice energy
Students are introduced to the definition
of lattice energy and the processes
involved in the formation of a lattice
structure of an ionic compound.
• Activity 2 : Factors affecting lattice
energy
Students are shown how the lattice
energy of an ionic compound depends on
the ionic radius and the ionic charge of
the ions involved.
• Activity 3 : Standard enthalpy change
of solution.
Students are shown how to calculate the
standard enthalpy change of solution.
3 Evaluation • Students to answer questions in the • Worksheet
student worksheet on their own.
4 Extension activity • Students to go through the extension • Websites
activities on their own. • Reference
books.
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 2 of 4
Worksheet answers
1. Lattice energy.
1.1 a. Lattice energy is the heat released when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is
formed from its gaseous ions.
2. Factors affecting lattice energy
2.1 a. KI < MgCl2 < CaO
b. Ionic charge, Ionic radius.
3. Standard enthalpy change of solution
3.1 a. Hydration energy is the energy liberated when 1 mol of gaseous ions become
hydrated at infinite dilution.
b. The enthalpy changes involved in dissolving an ionic solid are:
i. lattice energy is absorbed
ii. enthalpy change of hydration is liberated
c.
Hsolution
NaCl(s) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
absorbs lattice energy liberates hydration energy
Na+(g) + Cl-(g)
3.2 a. The factors affecting enthalpy change of hydration are:
i. ionic charge
ii. ionic size
b. The enthalpy change of hydration decreases down the group.
c. The size of the Cl- ions is bigger than that of the F- ion. The lattice energy of
CaCl2 is less than that of CaF2. The enthalpy change of hydration of CaCl2 is
also less than that of CaF2. For both CaCl2 and CaF2, the enthalpy change of
hydration is greater than the lattice energy but the difference is bigger for
CaCl2. Hence, CaCl2 is more soluble.
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 3 of 4
1
3.3 a. i. Mg(s) + O2(g) MgO(s)
2
ii. Mg2+(g) + O2-(g) MgO(s)
b. Born-Haber cycle
Mg2+(g) + O2-(g)
IE EA2
Mg+(g) + O-(g)
IE EA1
Mg(g) + O(g)
Hlattice
Energy
Hatom Hatom
1
Mg(s) + O2(g)
2
Hf
MgO(s)
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Physics and Technology For Engineers... 2023Document546 pagesPhysics and Technology For Engineers... 2023david floresNo ratings yet
- Asme BPVC - Ssc.i.ii.v.ix - Xiii-2023Document42 pagesAsme BPVC - Ssc.i.ii.v.ix - Xiii-2023mmendozagNo ratings yet
- Van de GraaffDocument4 pagesVan de GraaffMaeka SanvictoresNo ratings yet
- CFD Csa A23.3 14Document76 pagesCFD Csa A23.3 14putra wiraNo ratings yet
- Nexans MV Cables UK Brochure - 1Document48 pagesNexans MV Cables UK Brochure - 1Ra'fat HerzallahNo ratings yet
- B 549 - 13 PDFDocument8 pagesB 549 - 13 PDFTuanbk Nguyen0% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Dair First Sem ScheduleDocument1 pageDair First Sem ScheduleMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Heat Energy ChangeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Heat Energy ChangeMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Dun DownloadDocument1 pageDun DownloadMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 48Document3 pagesLesson 48MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of ElectrolysisMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 49Document3 pagesLesson 49MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 50Document3 pagesLesson 50MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Partition LawDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: The Partition LawMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Separation of Ideal MixturesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Separation of Ideal MixturesMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Non-Ideal SolutionsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Non-Ideal SolutionsMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 42Document4 pagesLesson 42MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (I)Document4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (I)MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 45Document4 pagesLesson 45MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 40Document5 pagesLesson 40MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 41Document4 pagesLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)Document4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: K and K For Heterogeneous SystemDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: K and K For Heterogeneous SystemMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Acid-Base TitrationDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Acid-Base TitrationMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Acid Dissociation ConstantDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: The Acid Dissociation ConstantMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Introduction To Ionic EquilibriumDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Introduction To Ionic EquilibriumMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: PH and pOHDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: PH and pOHMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- AWS Weld Detail LegendDocument2 pagesAWS Weld Detail LegendGerardo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Vane Pump Article WearDocument7 pagesVane Pump Article WearDirk DreesNo ratings yet
- Roark's Formula 7Document1 pageRoark's Formula 7Jay CeeNo ratings yet
- Manganese Bronze Data SheetDocument10 pagesManganese Bronze Data SheetKapil HarchekarNo ratings yet
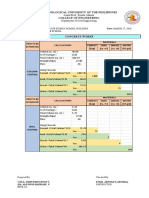
- 2 Concrete Works CompuDocument14 pages2 Concrete Works CompuALFONSO RAPHAEL SIANo ratings yet
- Non Aqeuous TitrationDocument7 pagesNon Aqeuous Titrationsurabhi tadeNo ratings yet
- Elementary Solid State Physics Omar PDF Free Halaman 15 46Document32 pagesElementary Solid State Physics Omar PDF Free Halaman 15 46Ihsania Ikrima KinantiNo ratings yet
- Reactive Wetting, Evolution of Interfacial and Bulk IMCs and Their Effect On Mechanical PDFDocument32 pagesReactive Wetting, Evolution of Interfacial and Bulk IMCs and Their Effect On Mechanical PDFeid elsayedNo ratings yet
- CgtophDocument2 pagesCgtophcristian orihuelaNo ratings yet
- Duremax GPE: General Purpose Epoxy CoatingDocument4 pagesDuremax GPE: General Purpose Epoxy CoatinglivefreakNo ratings yet
- LJF Installation Manual ACQA36-00270Document11 pagesLJF Installation Manual ACQA36-00270Raymundo Rangel RdzNo ratings yet
- Handrail & Baluster DRAFT-1Document2 pagesHandrail & Baluster DRAFT-1jijinjohnNo ratings yet
- Series 46 V9Document6 pagesSeries 46 V9Process Controls & ServicesNo ratings yet
- On-Site Electrolytic Chlorination Skid-Mounted OSEC B-Pak SystemDocument4 pagesOn-Site Electrolytic Chlorination Skid-Mounted OSEC B-Pak SystemgohviccNo ratings yet
- B LineDocument29 pagesB Linehesham3bbasNo ratings yet
- Carriers of The Protective Effectiveness of Used Motor OilsDocument4 pagesCarriers of The Protective Effectiveness of Used Motor OilsChristian D JiménezNo ratings yet
- Resistência Da Cor Ao Calor Prensagem A Quente - AATCC 133-2010Document2 pagesResistência Da Cor Ao Calor Prensagem A Quente - AATCC 133-2010raissaNo ratings yet
- Science Answer Key Class IxDocument7 pagesScience Answer Key Class IxLakshay BansalNo ratings yet
- IES Mechanical Engineering Paper II 2013 PDFDocument20 pagesIES Mechanical Engineering Paper II 2013 PDFBalvinderNo ratings yet
- Strength-Durability Correlation of OsteosynthesisDocument17 pagesStrength-Durability Correlation of OsteosynthesisdeniNo ratings yet
- Mech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) NotesDocument45 pagesMech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) Notesnikhil0% (1)
- Cmos Process FlowDocument25 pagesCmos Process FlowSHAIK MUSTHAFANo ratings yet
- Asphalt Rejuvenators Fact or FableDocument17 pagesAsphalt Rejuvenators Fact or FableAramisFariasNo ratings yet
- Evonik-Ancamine 2803Document2 pagesEvonik-Ancamine 2803AceVũNo ratings yet