Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tut-34.Op Amps
Uploaded by
Booh Own100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
36 views18 pagesoperation amplifier tut. and how to get the profe of op amps
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentoperation amplifier tut. and how to get the profe of op amps
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
36 views18 pagesTut-34.Op Amps
Uploaded by
Booh Ownoperation amplifier tut. and how to get the profe of op amps
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Tutorial: 3-4
Operational Amplifiers
Eng. Sara Rashad
18/3/2018
25/3/2018
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 1
Operational Amplifiers
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 2
Operational Amplifiers 741 OP AMP
Datasheet
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 3
As well as resistors and capacitors, Operational
Amplifiers, or Op-amps as they are more commonly
called, are one of the basic building blocks of Analogue
Electronic Circuits.
Operational amplifiers are linear devices that have all
the properties required for nearly ideal DC amplification
and are therefore used extensively in signal conditioning,
filtering or to perform mathematical operations such as
add, subtract, integration and differentiation.
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 4
An Operational Amplifier, or op-amp for short, is
fundamentally a voltage amplifying device designed
to be used with external feedback components such
as resistors and capacitors between its output and
input terminals.
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 5
An Operational Amplifier is basically a three-
terminal device which consists of :
Inverting Input, marked with a negative or
“minus” sign, ( - ) .
Non-inverting Input, marked with a
positive or “plus” sign ( + ).
The third terminal represents
the Operational Amplifiers output port.
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 6
For all the following types please write the whole prove
to find Vout.
Types of Op Amps
1- Inverting Amplifier
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 7
Types of Op Amps
2- Non Inverting Amplifier
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 8
Types of Op Amps
3- Summing Amplifier
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 9
Types of Op Amps
4- Differential Amplifier
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 10
Types of Op Amps
5- Differentiator
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 11
Types of Op Amps
6- Integrator
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 12
Types of Op Amps
7- summing Integrator
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 13
Types of Op Amps
8- Differential Integrator
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 14
Types of Op Amps
9- Instrumentation Amp.
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 15
Types of Op Amps
9- Instrumentation Amp
may be satisfactory for low impedance sources,
but its input impedance is too low for high-output
impedance sources. Furthermore, if the input
signals are very low level and include noise, the
difference amplifier is unable to extract a
satisfactory difference signal. The solution to this
problem is the instrumentation amplifier. It has
the following characteristics:
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 16
Very high input impedance
Large common mode rejection ratio (CMRR). The CMRR is the
ratio of the difference mode gain to the common mode gain. The
difference mode gain is the amplification factor for the
difference between the input signals, and the common mode
gain is the amplification factor for the average of the input
signals. For an ideal difference amplifier, the common mode gain
is 0, implying an infinite CMRR. When the common mode gain is
nonzero, the output is nonzero when the inputs are equal and
nonzero. It is desirable to minimize the common mode gain to
suppress signals such as noise that are common to both inputs.
Capability to amplify low-level signals in a noisy environment,
often a requirement in differential-output sensor signal-
conditioning applications.
Consistent bandwidth over a large range of gains
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 17
Types of Op Amps
10- Buffer
3/26/2018 Applied Mechatronics 18
You might also like
- Operational AmplifiersDocument37 pagesOperational Amplifiersearl pannilaNo ratings yet
- Designing JFET Audio PreAmplifiersDocument3 pagesDesigning JFET Audio PreAmplifiersganga_ch1No ratings yet
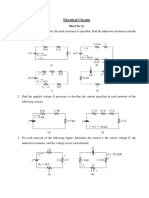
- Electrical Circuits - Sheets - 1Document13 pagesElectrical Circuits - Sheets - 1محمد عجوة100% (1)
- Op-Amp IntegratorDocument5 pagesOp-Amp IntegratorVanja KaranNo ratings yet
- Power Supply DesigningDocument7 pagesPower Supply DesigningmarczzzNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Unit-4Document81 pagesOp-Amp Unit-4ShaktiNo ratings yet
- Arc Flash ProtectionDocument11 pagesArc Flash ProtectionDvmc Zona TacubaNo ratings yet
- Op AmpDocument106 pagesOp AmpAneela PathanNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Differential Amplifier Circuit Age SubtractorDocument9 pagesOp Amp Differential Amplifier Circuit Age SubtractorSai Arja SaiNo ratings yet
- EC-8453 Linear Integrated Circuits QA BankDocument7 pagesEC-8453 Linear Integrated Circuits QA Banksanthosh sekarNo ratings yet
- Negative Feedback CircuitsDocument21 pagesNegative Feedback CircuitsSourya DewanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Simulation Lab 3rd SemDocument41 pagesCircuit Simulation Lab 3rd SemSUNIL MAURYANo ratings yet
- AC-DC - Fabrication 2Document191 pagesAC-DC - Fabrication 2VinayakNo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning Op-AmpsDocument41 pagesSignal Conditioning Op-AmpsSaleem Haddad100% (1)
- PC2193 Basic Electronics Introduction To The OscilloscopeDocument7 pagesPC2193 Basic Electronics Introduction To The OscilloscopeddyzleeNo ratings yet
- Input-Output Impedance and Reverberation Decay TimeDocument6 pagesInput-Output Impedance and Reverberation Decay Timerythmaccount100% (1)
- Introduction To Power-Amplifiers PDFDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Power-Amplifiers PDFmrana_56No ratings yet
- EC8453 OPAMP Applications GuideDocument6 pagesEC8453 OPAMP Applications GuideShanilDayalanNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier - The Voltage SubtractorDocument6 pagesDifferential Amplifier - The Voltage SubtractorRing MasterNo ratings yet
- Applications of Sample and Hold Amps 1314747719Document5 pagesApplications of Sample and Hold Amps 1314747719janani murugesanNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and Inductance MeasurementDocument24 pagesCapacitance and Inductance MeasurementDina GaranNo ratings yet
- Transformer Coupled AmplifierDocument6 pagesTransformer Coupled AmplifierXyrex CalangNo ratings yet
- شرح الكترونيات 1 AmplifiersDocument43 pagesشرح الكترونيات 1 AmplifiersAboodA.KhraishiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Differential Amplifiers 2nd LectureDocument35 pagesChapter Two Differential Amplifiers 2nd LectureTemesgen MekonenNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: DC AnalysisDocument5 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: DC Analysishemanshu_abbey100% (2)
- Bipolar Transistor BiasingDocument8 pagesBipolar Transistor BiasingGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- Intercom Project Assembly GuideDocument3 pagesIntercom Project Assembly GuideJohn OrokNo ratings yet
- Dual Tracking RegulatorDocument2 pagesDual Tracking RegulatorJCMNo ratings yet
- JFETsDocument78 pagesJFETsLai Yon Peng100% (2)
- Capacitor PDFDocument5 pagesCapacitor PDFsathyakalyanNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits - EC2254Document77 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits - EC2254Muthu LakiNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current DividersDocument6 pagesVoltage and Current DividersRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit 1 ManualDocument44 pagesElectronic Circuit 1 ManualEr AnandNo ratings yet
- A Class-A Amplifier For Home Constructors: PART ONE - Design Considerations and A Circuit DescriptionDocument7 pagesA Class-A Amplifier For Home Constructors: PART ONE - Design Considerations and A Circuit DescriptionisaijhabinNo ratings yet
- Design of Instrumentation Amplifier For Small Signal Measurements: A Case StudyDocument5 pagesDesign of Instrumentation Amplifier For Small Signal Measurements: A Case StudyAnuradha GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Blue Book 2017: Code of Practice On Electrical Safety For The Work On or Near High Voltage Electrical ApparatusDocument70 pagesThe Blue Book 2017: Code of Practice On Electrical Safety For The Work On or Near High Voltage Electrical ApparatusandyhilbertNo ratings yet
- Types of DiodeDocument34 pagesTypes of DiodeAfolabiNo ratings yet
- Feedback Amplifiers: EMT 212/4 - Analog Electronic IIDocument54 pagesFeedback Amplifiers: EMT 212/4 - Analog Electronic IIJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Electronics Mini Dictionary by GadgetronicxDocument49 pagesElectronics Mini Dictionary by GadgetronicxObby JhonNo ratings yet
- 12 Mosfet BiasingDocument18 pages12 Mosfet BiasingManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier GuideDocument56 pagesOperational Amplifier GuideVedang PavanjeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Code and Transistor HistoryDocument44 pagesBasic Electronics Code and Transistor HistoryNidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Harris SX-1 AM Transmitter Manual-1 PDFDocument320 pagesHarris SX-1 AM Transmitter Manual-1 PDFJULIO ALVAREZ FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifiersDocument45 pagesFeedback Amplifiersحافظ حمزہ اعوانNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Properties of The Op-Amp 1 (Buffer Non Inverting Op-Amp)Document9 pagesLab 4 - Properties of The Op-Amp 1 (Buffer Non Inverting Op-Amp)Alia Atikah100% (1)
- NIT Karnataka CMUT Design Improves Using Piston-Shaped MembranesDocument7 pagesNIT Karnataka CMUT Design Improves Using Piston-Shaped MembranesAdityaNo ratings yet
- Single-Stage OpAmp Topologies GuideDocument74 pagesSingle-Stage OpAmp Topologies Guidepalagani muralibabuNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Circuit by CorcoranDocument598 pagesAlternating Current Circuit by CorcoranMahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifiersDocument21 pagesFeedback AmplifiersNon Artists100% (1)
- ECD Lab EEC 752Document17 pagesECD Lab EEC 752juhi99360% (5)
- Operational AmplifierDocument17 pagesOperational AmplifierDan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument60 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorDfm-Crisna RadityaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Complete - 2Document38 pagesChapter 4 Complete - 2Danish UttraNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.776 High Speed Communications Circuits Spring 2005Document29 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.776 High Speed Communications Circuits Spring 2005adi3443No ratings yet
- DC Motor DrivesDocument39 pagesDC Motor DrivesAnuar Nuafzan100% (1)
- Jyri Pakarinen, David T. Yeh A Review of Digital Techniques For Modeling Vacuum-Tube Guitar AmplifiersDocument16 pagesJyri Pakarinen, David T. Yeh A Review of Digital Techniques For Modeling Vacuum-Tube Guitar AmplifiersMišo KovačNo ratings yet
- Our Edublog: Stumbleupon SubmitDocument4 pagesOur Edublog: Stumbleupon SubmitNeha AnisNo ratings yet
- Design Differentiator Circuit Using OP-AMP LargeDocument18 pagesDesign Differentiator Circuit Using OP-AMP Largeamit davaNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument51 pagesAnalog Electronicssaiganeah884No ratings yet
- HIGH EFFICIENCY MULTICRYSTAL SOLAR MODULESDocument2 pagesHIGH EFFICIENCY MULTICRYSTAL SOLAR MODULESAnonymous 7kJDSaNo ratings yet
- Plant specification and bill of quantityDocument4 pagesPlant specification and bill of quantitylewgne08No ratings yet
- Equipment Cross Reference GuideDocument22 pagesEquipment Cross Reference GuideizmitlimonNo ratings yet
- Mil HDBK 1553Document678 pagesMil HDBK 1553Lyster100% (1)
- Power System Protection Engineer ResumeDocument4 pagesPower System Protection Engineer ResumeMuthuRajNo ratings yet
- Pickup Wiring 1 ConductorDocument5 pagesPickup Wiring 1 ConductorJD HNo ratings yet
- Sel 321Document33 pagesSel 321John AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 6G Wireless CommunicationDocument6 pages6G Wireless CommunicationMUHAMMAD BADAR ASHRAF RANANo ratings yet
- MPPT Using Sepic ConverterDocument109 pagesMPPT Using Sepic ConverterSandhya RevuriNo ratings yet
- 1552 Link Calculator V1Document26 pages1552 Link Calculator V1shripalNo ratings yet
- Delta VFD E Series User ManualDocument399 pagesDelta VFD E Series User ManualTendai AlfaceNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 03Document29 pagesLecture Notes 03stephen562001No ratings yet
- Apar Transformer Oil PDS - To 1020 60 U PDFDocument1 pageApar Transformer Oil PDS - To 1020 60 U PDFmaa vaishnavi ventureNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5Document2 pagesProblem Set 5Saied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Iq2 MidiDocument49 pagesIq2 MidiJose Angel Avila MaciasNo ratings yet
- Dual PowersupplyDocument21 pagesDual Powersupplyrakeshcusat89100% (6)
- Intel® Desktop Board D102GGC2Document64 pagesIntel® Desktop Board D102GGC2Nataniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assemble Electrical Circuit ComponentsDocument9 pagesAssemble Electrical Circuit ComponentsAnvi MantriNo ratings yet
- COOLER MASTER - RS-850-AFBA-G1 - 850W - ECOS 3494 - ReportDocument1 pageCOOLER MASTER - RS-850-AFBA-G1 - 850W - ECOS 3494 - ReportSat.Narkoba Polres EndeNo ratings yet
- Rotordynamic Design Considerations For A 23 MW Compressor With Magnetic BearingsDocument15 pagesRotordynamic Design Considerations For A 23 MW Compressor With Magnetic Bearingsmghgol100% (1)
- VR-500 BrochureDocument2 pagesVR-500 Brochuresdelpi5146No ratings yet
- Canon IR Advance C5030 Trouble Error CodesDocument73 pagesCanon IR Advance C5030 Trouble Error Codesnafees100% (8)
- CS1U-400|405|410|415|420MS HiDM ModuleDocument2 pagesCS1U-400|405|410|415|420MS HiDM ModuleEdgar Molina RiveraNo ratings yet
- 9.1.3 Product Description For BTS 3606EDocument73 pages9.1.3 Product Description For BTS 3606Ealpha74uNo ratings yet
- AH 480 DeviceList 20210719Document456 pagesAH 480 DeviceList 20210719Yu FelixNo ratings yet
- 2005 Mazda 3Document8 pages2005 Mazda 3Josmar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lab 9Document13 pagesLab 9Hassaan SaeedNo ratings yet
- XRF ManualDocument160 pagesXRF Manualsaiful islamNo ratings yet
- Colwood-Trim Pot InstructionsDocument1 pageColwood-Trim Pot InstructionsEdwin HarrisNo ratings yet
- Objective Question - 1 (Information Theory and Coding)Document11 pagesObjective Question - 1 (Information Theory and Coding)suganyamachendran66% (32)