Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inglês 4o Bimestre 8o ano
Uploaded by
patriciasairesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inglês 4o Bimestre 8o ano
Uploaded by
patriciasairesCopyright:
Available Formats
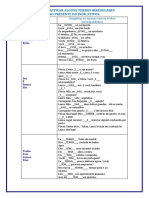
Nome__________________________________________________nº______.
8º.ano “_____” do ensino fundamental
data:______________.
Professora: Francismeiry
TER – 4º BIMESTRE 2014 - INGLÊS
Unit 13
Reading Comprehension
Vocabulary
Indefinite Pronouns p.8, 9
Pronomes Indefinidos (Pronomes Substantivos e Adjetivos) - Indefinite Pronouns
and Adjectives
1. SOME - ALGUM, ALGO, ALGUNS, ALGUMA, ALGUMAS, UM, UNS, UMA,
UMAS, UM POUCO DE
* Some e seus compostos são usados em frases afirmativas. Some também pode ser
usado em frases interrogativas quando se trata de um oferecimento ou pedido ou
quando se espera uma resposta positiva.
Some exercises are difficult to do. (Alguns exercícios são difíceis
de fazer.)
Would you like some tea? (Você gostaria de um pouco de chá?)
2. SOMEBODY/SOMEONE - ALGUÉM
Somebody/Someone is knocking the door. (Alguém está batendo na porta.)
3. SOMETHING - ALGUMA COISA, ALGO
There is something under the bed.
(Há/Tem alguma coisa embaixo da cama.)
4. SOMEWHERE - EM ALGUM LUGAR
I saw your keys somewhere. (Eu vi suas chaves em algum lugar.)
5. ANY - ALGUM, ALGUNS, ALGUMA, ALGUMAS, NENHUM, NENHUMA,
UM, UNS, UMA, UMAS, QUALQUER
*Any é usado em frases interrogativas e negativas. Nas frases afirmativas, any é
usado quando: aparecer após a palavra if; significar qualquer; houver palavra de sentido
negativo na frase como seldom,never, rarely, without, etc.
Do you have any talent for dance? (Você tem algum talento para a dança?)
He didn't have any chance. (Ele não tinha chance alguma.)
If you have any doubt, ask me. (Se você tiver qualquer / alguma dúvida, pergunte-me.)
She rarely has any free weekend.
(Raramente ela tem algum fim de semana livre.)
7. ANYBODY / ANYONE - ALGUÉM, QUALQUER UM, NINGUÉM
There isn't anybody upstairs. (Não há ninguém lá em cima.)
Is there anybody home? (Há alguém em casa?)
8. ANYTHING - ALGUMA COISA, QUALQUER COISA, NADA
I am hungry because I didn't eat anything this morning. (Estou com fome porque não
comi coisa alguma / nada hoje de manhã.)
There isn't anything to do in this city. (Não há coisa alguma / nada para fazer nesta
cidade.)
He may buy anything he wants. (Ele pode comprar qualquer coisa que quiser.)
9. ANYWHERE - EM ALGUM LUGAR, EM QUALQUER LUGAR
Did you see him anywhere? (Você o viu em algum lugar?)
Your shoes must be anywhere. (Seus sapatos podem estar em qualquer lugar.)
10. ANYWAY - DE ALGUMA MANEIRA, DE QUALQUER JEITO
Please, don't tell me what I have to do, anyway, I will only do what I want. (Por favor,
não me diga o que tenho que fazer, de qualquer maneira, farei apenas o que quero.)
I will buy the house anyway. (De qualquer jeito, comprarei a casa.)
11. NO (PRONOME ADJETIVO) - NENHUM,
NENHUMA
I have no money in my wallet. (Não tenho dinheiro
nenhum na minha carteira.)
13. NOBODY / NO ONE - NINGUÉM
Nobody/No one knows what our secret is. (Ninguém sabe qual é o nosso segredo.)
14. NOTHING - NADA
I have nothing to say. (Não tenho nada a dizer.)
There was nothing in the fridge. (Não havia nada na geladeira.)
15. NOWHERE - NENHUM LUGAR
She is nowhere in this park. (Ela não está em lugar nenhum deste parque.)
1)
Put in something, someone, somewhere or anything, anyone, anywhere into the gaps.
1) I've got ___ ___________ in my eye.
2) There is _________________ at the door.
3) We haven't heard _________________ about Peter. Is he ill?
4) Do you live __________________ near Vila Carvalho?
5) ________________ wants to see you.
6) Has _________________ seen my bag?
7) My teacher asked me ______________________.
8) Can I have ________________ to drink?
9) Don't worry. __________________ can tell you where the post-office in this town is.
10) I don't know __________________ about it.
Unit 14
Verb + verb – ing page 13
Prepositions + verb – ing page 13
Verb Forms:
The - ing Form
The -ing form is also used for gerunds (verbs which are used as nouns).
Gerunds can be used as nouns for subjects and subject complements:
Learning a language isn't easy.
Talking to Bill was a lot of fun.
Communicating by e-mail has become very common.
His hobby is collecting stamps.
______________________________________
Gerunds can also be used as nouns for objects of verbs and prepositions:
They dislike studying.
For exercise, he recommends swimming.
He doesn't care about being on time.
They're tired of listening to you.
Did he succeed in solving the problem?
We use verb+ ing after some verbs like:
Stop - finish - consider - enjoy - miss - avoid - begin
We use verb + ing after prepositions:
After - about - in - at - for - with - by - of
2) Complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in parentheses.
1. Dan enjoys ________________ (read) science fiction.
2. Cheryl suggested __________________ (watch) a movie after work.
3. I miss ________________ (work) in the travel industry. Maybe I can get my old job
back.
4. Do you mind ________________ (help) me translate this letter?
5. If he keeps _________________ (arrive) to work late, he's going to get fired!
6. Debbie began ________________ (think) about travelling abroad next year.
7. I finished _________________ (wash) Jack’s car.
8. The girls insisted on ________________ (go) out with Perry.
9. They are afraid of _________________ (lose) the game.
10. She complains about _______________ (bully)
11. Laura dream of ________________ ( live) on a small island.
12. My friend is good at __________________ (play) volleyball.
Unit 15
Adverbs: perhaps, maybe, possibly, probably, definitely
Modal Verbs: may, might, could, must
Modal Verbs
São verbos modais: can (pode), could (poderia), may(pode, poderia), might (pode,
poderia), should(deveria), must (deve), ought to (precisa) e used to(costumava).
Could: é empregado para expressar habilidade, só que no passado. É usado também com o
sentindo depoderia, em um contexto mais formal.
I could ride a bike when I was 5 years old. (Eu podia/conseguia andar de bicicleta quando tinha
5 anos de idade).
Could you bring me a sandwich and a coke, please? (Você poderia me trazer um sanduíche e
uma coca, por favor?).
May: é usado para expressar uma possibilidade no presente ou no futuro. Também pode ser
usado para pedir permissão, no entanto, may é usado em contextos mais formais que o can.
It may rain tomorrow. (Pode chover amanhã).
May I go to the bathroom? (Eu poderia ir ao banheiro?).
It’s ten o’clock. They might have arrived now.[= Perhaps they have arrived]
They may have arrived hours ago. [= Perhaps they arrived hours ago.]
Might: é usado para expressar possibilidades no passado ou no presente.
She might have come to the party. (Ela poderia ter vindo à festa).
He might have lunch with us tomorrow. (Ele pode vir almoçar com a gente amanhã).
Must: é usado para expressar obrigação.
You must go to school. (Você deve ir à escola).
She must study more. (Ela deve estudar mais).
3) Complete the sentences using the correct modal verb – must, might, may, could -.
1 I'm sure he is here - I can see his car in front of the building.
He ________________ be here. I can see his car in front of the building.
2 They're coming this week but I don't know which day.
They _________________ be coming tomorrow.
3 I'm not sure I'm going to pass the exam. I don't feel very confident.
I _____________________ pass the exam. I don't feel very confident.
4 I've bought a lottery ticket. There's a chance I'll become a millionaire!
I _____________________ become a millionaire!
5 I'm sure she doesn't speak French very well - she's only lived in Paris for a few weeks.
She __________________ speak French very well. She's only lived in Paris for a few
weeks.
6 My key's not in my pocket or on my desk so I'm sure it's in the drawer.
My key's not in my pocket or on my desk so it __________________ be in the drawer.
7 Someone told me that Mark was in Mexico but I saw him yesterday so I'm sure he's not
abroad.
Mark __________________ be abroad.
Unit 16
Vocabulary : Facial Expressions page 23
Tag Questions page 25
A tag question é utilizada no final das sentenças para obter confirmação do que foi dito
anteriormente, e por isso ela é curta e rápida.
VERBOS AUXILIARES
Quando temos o verbo auxiliar na sentença, como o verbo to be, to have, can, could, should, nós
utilizamos esses verbos para formar a tag question. Observe os exemplos:
It is cold today, isn’t it? (Está frio hoje, não está?)
Fernanda is a good girl, isn’t she? (Fernanda é uma boa garota, não é?)
David was there, wasn’t he? (David estava lá, não estava?)
They were friends, weren’t they? (Eles eram amigos, não eram?)
She has a car, hasn’t she? (Ela tem um carro, não tem?)
My parents can’t run, can they? (Meus pais não podem correr, podem?)
My sister could travel, couldn’t she? (Minha irmã poderia viajar, não poderia?)
The teacher should do this, shouldn’t he? (O professor deveria fazer isso, não deveria?)
VERBOS NÃO AUXILIARES
Quando não temos o verbo auxiliar na sentença, nós utilizamos outras formas verbais para
formar a tag question, como: do, does, don’t, doens’t – para o presente – e did ou didn’t – para
o passado. Devemos relembrar que se a primeira parte está na forma positiva, a segunda deve
estar na negativa e vice-versa. Observe os exemplos:
You understand English, don’t you? (Você entende inglês, não entende?)
You don’t live here, do you? (Você não mora aqui, mora?)
She doesn’t cook very well, does she? (Ela não cozinha muito bem, cozinha?)
You went to Salvador last week, didn’t you? (Você foi a Salvador semana passada, não foi?)
Raquel didn’t go to school, did she? (Raquel não foi à escola, foi?)
FUTURE AND CONDITIONAL
Para o futuro se usa o auxiliar will, na forma afirmativa, e won’t na forma negativa;
ou would para expressar condição, na forma afirmativa, e wouldn’t, na forma negativa.
Observe os exemplos:
You will travel to Buenos Aires, won’t you? (Você irá viajar para Buenos Aires, não vai?)
He won’t arrive on time, will he? (Ele não chegará a tempo, chegará?)
Marcela would arrive, wouldn’t she? (Marcela iria chegar, não iria?)
The players wouldn’t go, would they? (Os jogadores não iriam, iriam?)
Observação:
Para a 1º pessoa do singular I, a tag question tem uma forma irregular.
Ex.: I am your friend, aren't I?
4) Instructions: Add a suitable question tag to the following sentences. In each case the
speaker wants clarification that what he is saying is correct.
1There wasn't enough paper in the printer , ___________________?
2If he spoke better English he would look for a job abroad, _____________________ ?
3They've already sent you the invitation, _____________________ ?
4We should invite them to our party, ______________________?
5You had to sell some shares, _____________________ ?
6You were disappointed when you got your exam results, ______________________ ?
7We won't have to work tomorrow, _____________________ ?
8We'll have to finish the project before next week, _____________________ ?
You might also like
- Inglês 9ºanoDocument2 pagesInglês 9ºanoMax Portela RywaNo ratings yet
- Colégio Estadual Nestor Victor - Atividade de Inglês: Adjectives ComparativesDocument6 pagesColégio Estadual Nestor Victor - Atividade de Inglês: Adjectives ComparativesTatiane MendonçaNo ratings yet
- Nome: DataDocument8 pagesNome: DataNicolly FreireNo ratings yet
- Modos Verbais - Verbo TerDocument15 pagesModos Verbais - Verbo TerSmart AcademyNo ratings yet
- Past Simple (Passado Simples)Document10 pagesPast Simple (Passado Simples)Matheus ZamboniNo ratings yet
- Ucv Pos PT IiiDocument43 pagesUcv Pos PT IiiDANIEL ELIAS CHERRES GARCIANo ratings yet
- Guia de gramática e dicas de inglêsDocument84 pagesGuia de gramática e dicas de inglêsSamira Liliane de Freitas100% (1)
- Livro Muito Prazer Portugues Gramatica-Unidade8Document8 pagesLivro Muito Prazer Portugues Gramatica-Unidade8Camila TribessNo ratings yet
- Conteudo e Atividade - 2º Ano - Present PerfectDocument4 pagesConteudo e Atividade - 2º Ano - Present PerfectEduardo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Modal Perfect situaçõesDocument10 pagesModal Perfect situaçõesandreNo ratings yet
- Exercícios para RevisãoDocument17 pagesExercícios para Revisãoatconasce100% (1)
- Mãe Não TrabalhaDocument5 pagesMãe Não Trabalhampetrini31No ratings yet
- Utilizando “SOME”, “ANY” ou “NO” para expressar quantidadeDocument3 pagesUtilizando “SOME”, “ANY” ou “NO” para expressar quantidadeAntonio Marco CastilhoNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect em inglêsDocument8 pagesPresent Perfect em inglêsLucas TvsNo ratings yet
- Gramática português BRDocument6 pagesGramática português BRCamila Tribess100% (1)
- PET 7 - Plano de estudo de inglês para aluno do 6o anoDocument8 pagesPET 7 - Plano de estudo de inglês para aluno do 6o anofabioNo ratings yet
- Exercícios de Gramática Do Uso Da Língua Portuguesa Do BrasilDocument4 pagesExercícios de Gramática Do Uso Da Língua Portuguesa Do BrasilLuiz Ricardo DuarteNo ratings yet
- Português Estrangeira UFAMDocument16 pagesPortuguês Estrangeira UFAMValeria Moisin De AraujoNo ratings yet
- Inglês MaterialDocument8 pagesInglês MaterialAlice BarretoNo ratings yet
- Autorregulada 7º AnoDocument5 pagesAutorregulada 7º AnoHemerson Carvalho ValentimNo ratings yet
- Exercícios ELEMENTAR 3Document32 pagesExercícios ELEMENTAR 3ISMAEL FERNANDEZ R.No ratings yet
- 2 ATIVIDADE DE INGLÊS - Verb To Be - PROF TAIS SALBEDocument5 pages2 ATIVIDADE DE INGLÊS - Verb To Be - PROF TAIS SALBEIsrael LemosNo ratings yet
- Exercícios ELEMENTAR 3Document33 pagesExercícios ELEMENTAR 3ISMAEL FERNANDEZ R.No ratings yet
- Ensino Fundamental e Médio no Colégio FAATDocument15 pagesEnsino Fundamental e Médio no Colégio FAATpatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Tense Exercises3Document8 pagesPast Simple Tense Exercises3martimdinisNo ratings yet
- Funções Sintáticas FI e FTDocument6 pagesFunções Sintáticas FI e FTCatarina CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Tempos verbais simples no 5o ano de escolaridadeDocument2 pagesTempos verbais simples no 5o ano de escolaridadeMargaridaNo ratings yet
- Ensino Médio Módulo 1Document9 pagesEnsino Médio Módulo 1Rose CunhaNo ratings yet
- Apostila 7º Ano Inglês 2023Document11 pagesApostila 7º Ano Inglês 2023janielNo ratings yet
- To Be no Presente SimplesDocument2 pagesTo Be no Presente SimplesNamarka InterioresNo ratings yet
- Verbos irregulares - exercícios extras 8o anoDocument3 pagesVerbos irregulares - exercícios extras 8o anobimachobiNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument14 pagesModal VerbsLua BilhalvaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument8 pagesModal VerbsGabriel Portela100% (1)
- Exercicios Semana 1 PDFDocument23 pagesExercicios Semana 1 PDFMagally Vasquez R.100% (1)
- Worksheet 7 - Verb There To Be (Present Simple)Document2 pagesWorksheet 7 - Verb There To Be (Present Simple)André100% (2)
- Ensino Médio 1Document9 pagesEnsino Médio 1Raquel Francisca CostaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs in Portuguese - Dizer e Fazer Author MiaDocument1 pageIrregular Verbs in Portuguese - Dizer e Fazer Author MiasparklewiccaNo ratings yet
- Apostila 7º Ano - Língua Inglesa - 1º TrimestreDocument17 pagesApostila 7º Ano - Língua Inglesa - 1º TrimestreThainá Cardoso100% (1)
- Evangelina-Repassando - 2Document12 pagesEvangelina-Repassando - 2María Regina Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Aula 4 - 6º LI - Simple Present and Present ContinuousDocument12 pagesAula 4 - 6º LI - Simple Present and Present ContinuousCARMELIA MARIA TAVARES DE BARROSNo ratings yet
- Diferença entre Pretérito Perfeito e Pretérito ImperfeitoDocument2 pagesDiferença entre Pretérito Perfeito e Pretérito ImperfeitoPam Padilla CruzadoNo ratings yet
- English - Apostila Basic English Concurso MBorgesDocument63 pagesEnglish - Apostila Basic English Concurso MBorgesBbook One100% (6)
- English Verbos ModaisDocument14 pagesEnglish Verbos ModaisNena Garuzzi100% (1)
- Aula de português sobre o uso de há e aDocument6 pagesAula de português sobre o uso de há e aLuciana NoronhaNo ratings yet
- 12º Caderno de Exercícios Dos EstudantesDocument8 pages12º Caderno de Exercícios Dos EstudantesRosa Rodriguez VillarNo ratings yet
- Weekly English lessons summaryDocument77 pagesWeekly English lessons summaryBruna Bruna100% (1)
- Modal VerbsDocument34 pagesModal Verbsinaldotorres1No ratings yet
- Portugues JuridicoDocument6 pagesPortugues JuridicoMotormax Compressores LTDANo ratings yet
- Teste de audibilizaçãoDocument6 pagesTeste de audibilizaçãoMaria Bernadete Lizareli WippichNo ratings yet
- 9o. A 12 Semana - To Be in The Simple Present - Aff and Neg FormDocument6 pages9o. A 12 Semana - To Be in The Simple Present - Aff and Neg FormfabioNo ratings yet
- Lista de exercícios sobre pronomes indefinidosDocument5 pagesLista de exercícios sobre pronomes indefinidosProfessora Kariny OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Exercícios Com Advérbios de FrequênciaDocument2 pagesExercícios Com Advérbios de FrequênciapatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Prova 2º Ano 2º BimestreDocument2 pagesProva 2º Ano 2º BimestrepatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Semana 17: Crédito: Portal Academico CCHDocument3 pagesSemana 17: Crédito: Portal Academico CCHpatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- 8º C - Future Going ToDocument2 pages8º C - Future Going TopatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Test Your English 5Document24 pagesTest Your English 5patriciasaires80% (5)
- Ensino de Inglês com músicaDocument37 pagesEnsino de Inglês com músicapatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Voz Passiva em 40Document2 pagesVoz Passiva em 40Regiane Santos0% (1)
- 8 Ano InglêsDocument11 pages8 Ano InglêsClebson Morais de AssunçãoNo ratings yet
- Atividades Complementares 11 3 Semana de Junho 801 PDFDocument1 pageAtividades Complementares 11 3 Semana de Junho 801 PDFpatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- 6o Ano Estudo Dirigido de InglêsDocument5 pages6o Ano Estudo Dirigido de Inglêspatriciasaires100% (1)
- Língua Estrangeira: BimestreDocument2 pagesLíngua Estrangeira: BimestrepatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Escola Fundamental Aleluia MadureiraDocument4 pagesEscola Fundamental Aleluia MadureirapatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Voo Natal-RioDocument1 pageVoo Natal-RiopatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Roteiro de AulaDocument2 pagesConditional Sentences Roteiro de AulapatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Material de EstudoDocument5 pagesModal Verbs Material de EstudopatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Jane Austen publicou dois romances após sua morteDocument1 pageJane Austen publicou dois romances após sua mortepatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Amor da Minha VidaDocument1 pageAmor da Minha VidapatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- 2ano 0704 InglesDocument2 pages2ano 0704 InglespatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Atividades de música em inglês para identificar gêneros e completar letrasDocument3 pagesAtividades de música em inglês para identificar gêneros e completar letraspatriciasaires100% (3)
- L. Inglesa - Carina e Manoela - 7º AnoDocument14 pagesL. Inglesa - Carina e Manoela - 7º AnopatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- ROTEIRO DE RECUPERAÇÃO DE INGLÊS 6o ANODocument7 pagesROTEIRO DE RECUPERAÇÃO DE INGLÊS 6o ANOpatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- 7 - 47 - 124 - 2013 - 2° Simulado Objetivo - 7°ano - 20-08 - GABARITADO PDFDocument16 pages7 - 47 - 124 - 2013 - 2° Simulado Objetivo - 7°ano - 20-08 - GABARITADO PDFAlexandre PereiraNo ratings yet
- 07-Lesson 7 Present ContinuousDocument4 pages07-Lesson 7 Present ContinuousWerner Borges100% (7)
- Roteiro de Recuperação de InglêsDocument6 pagesRoteiro de Recuperação de InglêspatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Estrangeirismos na música 'Samba do Approach' de Zeca BaleiroDocument13 pagesEstrangeirismos na música 'Samba do Approach' de Zeca BaleiroNarraque GarciaNo ratings yet
- Educação de Jovens e Adultos Leitura em InglêsDocument2 pagesEducação de Jovens e Adultos Leitura em Inglêspatriciasaires100% (1)
- Parte V - Atividades Multidisciplinares - 7º AnoDocument23 pagesParte V - Atividades Multidisciplinares - 7º AnopatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- 1 Ano InglesDocument52 pages1 Ano InglesManoel MattosNo ratings yet
- Expressing Yourself in a DiaryDocument16 pagesExpressing Yourself in a Diarypatriciasaires33% (3)
- Some AnyDocument9 pagesSome AnypatriciasairesNo ratings yet
- Latim A Arte de RaciocinarDocument109 pagesLatim A Arte de RaciocinarMarlon SapatiniNo ratings yet
- Formação de palavras: processos e exemplosDocument9 pagesFormação de palavras: processos e exemplosjoao sales100% (1)
- Termos Integrantes Da OraçãoDocument10 pagesTermos Integrantes Da OraçãoAnita CairoNo ratings yet
- Singular e Plural - Formação do plural em portuguêsDocument3 pagesSingular e Plural - Formação do plural em portuguêskarolsilva_1994No ratings yet
- Arte Da Lingua de AngolaDocument68 pagesArte Da Lingua de AngolaIcaro RochaNo ratings yet
- VERBOS E SUAS CONJUGACÕESDocument15 pagesVERBOS E SUAS CONJUGACÕESLeticia NobregaNo ratings yet
- Tempos e Modos Verbais 2Document11 pagesTempos e Modos Verbais 2Vinícius Chiquetto FariaNo ratings yet
- Morfologia e sintaxe: preposiçõesDocument9 pagesMorfologia e sintaxe: preposiçõesDebora DeusNo ratings yet
- Formas nominais: infinitivo, gerúndio e particípioDocument3 pagesFormas nominais: infinitivo, gerúndio e particípioManuh Lima100% (1)
- Advérbios e conjunções em latim e portuguêsDocument22 pagesAdvérbios e conjunções em latim e portuguêsArthur MotaNo ratings yet
- Morfossintaxe: classes gramaticais e funções sintáticasDocument2 pagesMorfossintaxe: classes gramaticais e funções sintáticasdfdfdsfdsfdg100% (8)
- Concordância nominal e de adjtivos em gramáticaDocument3 pagesConcordância nominal e de adjtivos em gramáticaCris Campedeli BarneziNo ratings yet
- Relações Textuais Entre Orações, Períodos, Parágrafos Ou Blocos Maiores Do Texto, Por Meio de Expressões ConectorasDocument35 pagesRelações Textuais Entre Orações, Períodos, Parágrafos Ou Blocos Maiores Do Texto, Por Meio de Expressões ConectorasClaudiaLazzarottoNo ratings yet
- Aula 06Document80 pagesAula 06Anonimo100% (1)
- Aula 3 Verbos RegularesDocument6 pagesAula 3 Verbos RegularesGrace BritoNo ratings yet
- Lista de Exercícios PortuguesDocument3 pagesLista de Exercícios PortuguesFabio BarrosNo ratings yet
- Exercícios de preparação para o 9.o ano - IIDocument4 pagesExercícios de preparação para o 9.o ano - IIManuela TavaresNo ratings yet
- Conjunções: tipos e funçõesDocument3 pagesConjunções: tipos e funçõesMaria Carolina OriáNo ratings yet
- MorfologiaDocument20 pagesMorfologiaJairyo PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Alemão A1 - Declinação Dos SubstantivosDocument6 pagesAlemão A1 - Declinação Dos SubstantivosMJoãoViceNo ratings yet
- Morfossintaxe: análise de palavras e funçõesDocument15 pagesMorfossintaxe: análise de palavras e funçõesGigi CicoteNo ratings yet
- Verbos - Tempos do indicativo em portuguêsDocument1 pageVerbos - Tempos do indicativo em portuguêsAndreia CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Guia de Estudos MorfologiaDocument78 pagesGuia de Estudos MorfologiaAndré França100% (1)
- VERBOS E TEMPOS VERBAIS EM PORTUGUÊSDocument25 pagesVERBOS E TEMPOS VERBAIS EM PORTUGUÊSMilaJoiaNo ratings yet
- Formação de Palavras Exercicios EnsinofundamentalDocument3 pagesFormação de Palavras Exercicios EnsinofundamentalamaraladriNo ratings yet
- Formação do plural de substantivos em PortuguêsDocument3 pagesFormação do plural de substantivos em Portuguêskeyde1No ratings yet
- MorfossíntaxeDocument1 pageMorfossíntaxeCATIA SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Flexão de Número Do SubstantivoDocument1 pageFlexão de Número Do SubstantivoRegiane MachadoNo ratings yet
- Brave, Honest and Beautiful - Fifth Harmony Lyrics QuizDocument4 pagesBrave, Honest and Beautiful - Fifth Harmony Lyrics QuizLan ElaineNo ratings yet