Professional Documents
Culture Documents
USPSTF A and B Recommendations: Topic Description Grade
Uploaded by
Santiago Alday0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesLandscape A + B USPSTF recommendations family medicine
Original Title
USPSTF A+B Recs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLandscape A + B USPSTF recommendations family medicine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations: Topic Description Grade
Uploaded by
Santiago AldayLandscape A + B USPSTF recommendations family medicine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
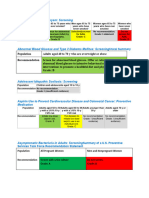
USPSTF A and B Recommendations
Topic Description Grade
Abdominal aortic aneurysm The USPSTF recommends one-time screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm by ultrasonography in men ages 65 to 75 B
screening: men years who have ever smoked.
Alcohol misuse: screening The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen adults age 18 years or older for alcohol misuse and provide persons B
and counseling engaged in risky or hazardous drinking with brief behavioral counseling interventions to reduce alcohol misuse.
Aspirin preventive The USPSTF recommends initiating low-dose aspirin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and B
medication: adults aged 50 to colorectal cancer in adults aged 50 to 59 years who have a 10% or greater 10-year cardiovascular risk, are not at increased
59 years with a ≥10% 10-year risk for bleeding, have a life expectancy of at least 10 years, and are willing to take low-dose aspirin daily for at least 10
cardiovascular risk years.
Bacteriuria screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria with urine culture in pregnant women at 12 to 16 weeks' A
pregnant women gestation or at the first prenatal visit, if later.
Blood pressure screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for high blood pressure in adults aged 18 years or older. The USPSTF recommends A
adults obtaining measurements outside of the clinical setting for diagnostic confirmation before starting treatment.
BRCA risk assessment The USPSTF recommends that primary care providers screen women who have family members with breast, ovarian, B
and genetic tubal, or peritoneal cancer with one of several screening tools designed to identify a family history that may be associated
counseling/testing with an increased risk for potentially harmful mutations in breast cancer susceptibility genes (BRCA1 or BRCA2). Women
with positive screening results should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, BRCA testing.
Breast cancer preventive The USPSTF recommends that clinicians engage in shared, informed decisionmaking with women who are at increased B
medications risk for breast cancer about medications to reduce their risk. For women who are at increased risk for breast cancer and at
low risk for adverse medication effects, clinicians should offer to prescribe risk-reducing medications, such as tamoxifen or
raloxifene.
Breast cancer screening The USPSTF recommends screening mammography for women, with or without clinical breast examination, every 1 to 2 B
years for women age 40 years and older.
Breastfeeding interventions The USPSTF recommends providing interventions during pregnancy and after birth to support breastfeeding. B
Cervical cancer screening The USPSTF recommends screening for cervical cancer every 3 years with cervical cytology alone in women aged 21 to 29 A
years. For women aged 30 to 65 years, the USPSTF recommends screening every 3 years with cervical cytology alone,
every 5 years with high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) testing alone, or every 5 years with hrHPV testing in
combination with cytology (cotesting).
Chlamydia screening: women The USPSTF recommends screening for chlamydia in sexually active women age 24 years or younger and in older women B
who are at increased risk for infection.
Colorectal cancer screening The USPSTF recommends screening for colorectal cancer starting at age 50 years and continuing until age 75 years. A
Dental caries prevention: The USPSTF recommends the application of fluoride varnish to the primary teeth of all infants and children starting at the B
infants and children up to age age of primary tooth eruption in primary care practices. The USPSTF recommends primary care clinicians prescribe oral
5 years fluoride supplementation starting at age 6 months for children whose water supply is fluoride deficient.
Depression screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for major depressive disorder (MDD) in adolescents aged 12 to 18 years. Screening B
adolescents should be implemented with adequate systems in place to ensure accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and appropriate
follow-up.
Depression screening: adults The USPSTF recommends screening for depression in the general adult population, including pregnant and postpartum B
women. Screening should be implemented with adequate systems in place to ensure accurate diagnosis, effective
treatment, and appropriate follow-up.
Diabetes screening The USPSTF recommends screening for abnormal blood glucose as part of cardiovascular risk assessment in adults aged B
40 to 70 years who are overweight or obese. Clinicians should offer or refer patients with abnormal blood glucose to
intensive behavioral counseling interventions to promote a healthful diet and physical activity.
Falls prevention: older adults The USPSTF recommends exercise interventions to prevent falls in community-dwelling adults 65 years or older who are at B
increased risk for falls.
Folic acid supplementation The USPSTF recommends that all women who are planning or capable of pregnancy take a daily supplement containing A
0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 µg) of folic acid.
Gestational diabetes mellitus The USPSTF recommends screening for gestational diabetes mellitus in asymptomatic pregnant women after 24 weeks of B
screening gestation.
Gonorrhea prophylactic The USPSTF recommends prophylactic ocular topical medication for all newborns for the prevention of gonococcal A
medication: newborns ophthalmia neonatorum.
Gonorrhea screening: women The USPSTF recommends screening for gonorrhea in sexually active women age 24 years or younger and in older women B
who are at increased risk for infection.
Healthy diet and physical The USPSTF recommends offering or referring adults who are overweight or obese and have additional cardiovascular B
activity counseling to prevent disease (CVD) risk factors to intensive behavioral counseling interventions to promote a healthful diet and physical activity
cardiovascular disease: for CVD prevention.
adults with cardiovascular risk
factors
Hemoglobinopathies The USPSTF recommends screening for sickle cell disease in newborns. A
screening: newborns
Hepatitis B screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis B virus infection in persons at high risk for infection. B
nonpregnant adolescents and
adults
Hepatitis B screening: The USPSTF strongly recommends screening for hepatitis B virus infection in pregnant women at their first prenatal visit. A
pregnant women
Hepatitis C virus infection The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in persons at high risk for infection. The USPSTF B
screening: adults also recommends offering one-time screening for HCV infection to adults born between 1945 and 1965.
HIV screening: nonpregnant The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen for HIV infection in adolescents and adults ages 15 to 65 years. Younger A
adolescents and adults adolescents and older adults who are at increased risk should also be screened.
HIV screening: pregnant The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen all pregnant women for HIV, including those who present in labor who are A
women untested and whose HIV status is unknown.
Hypothyroidism screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for congenital hypothyroidism in newborns. A
newborns
Intimate partner violence The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen for intimate partner violence in women of reproductive age and provide or B
screening: women of refer women who screen positive to ongoing support services.
reproductive age
Lung cancer screening The USPSTF recommends annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography in adults ages 55 to 80 B
years who have a 30 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years. Screening
should be discontinued once a person has not smoked for 15 years or develops a health problem that substantially limits
life expectancy or the ability or willingness to have curative lung surgery.
Obesity screening and The USPSTF recommends that clinicians offer or refer adults with a body mass index of 30 or higher (calculated as weight B
counseling: adults in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) to intensive, multicomponent behavioral interventions.
Obesity screening: children The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen for obesity in children and adolescents 6 years and older and offer or refer B
and adolescents them to comprehensive, intensive behavioral interventions to promote improvements in weight status.
Osteoporosis screening: B
The USPSTF recommends screening for osteoporosis with bone measurement testing to prevent osteoporotic fractures in
postmenopausal women
postmenopausal women younger than 65 years who are at increased risk of osteoporosis, as determined by a formal
younger than 65 years at
clinical risk assessment tool.
increased risk of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for osteoporosis with bone measurement testing to prevent osteoporotic fractures in B
women 65 years and older women 65 years and older.
Phenylketonuria screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for phenylketonuria in newborns. B
newborns
Preeclampsia prevention: The USPSTF recommends the use of low-dose aspirin (81 mg/d) as preventive medication after 12 weeks of gestation in B
aspirin women who are at high risk for preeclampsia.
Preeclampsia: screening The USPSTF recommends screening for preeclampsia in pregnant women with blood pressure measurements throughout B
pregnancy.
Rh incompatibility screening: The USPSTF strongly recommends Rh (D) blood typing and antibody testing for all pregnant women during their first visit A
first pregnancy visit for pregnancy-related care.
Rh incompatibility screening: The USPSTF recommends repeated Rh (D) antibody testing for all unsensitized Rh (D)-negative women at 24 to 28 weeks' B
24–28 weeks' gestation gestation, unless the biological father is known to be Rh (D)-negative.
Sexually transmitted The USPSTF recommends intensive behavioral counseling for all sexually active adolescents and for adults who are at B
infections counseling increased risk for sexually transmitted infections.
Skin cancer behavioral The USPSTF recommends counseling young adults, adolescents, children, and parents of young children about minimizing B
counseling exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation for persons aged 6 months to 24 years with fair skin types to reduce their risk of skin
cancer.
Statin preventive medication: The USPSTF recommends that adults without a history of cardiovascular disease (CVD) (i.e., symptomatic coronary artery B
adults ages 40–75 years with disease or ischemic stroke) use a low- to moderate-dose statin for the prevention of CVD events and mortality when all of
no history of CVD, 1 or more the following criteria are met: 1) they are ages 40 to 75 years; 2) they have 1 or more CVD risk factors (i.e., dyslipidemia,
CVD risk factors, and a diabetes, hypertension, or smoking); and 3) they have a calculated 10-year risk of a cardiovascular event of 10% or
calculated 10-year CVD event greater. Identification of dyslipidemia and calculation of 10-year CVD event risk requires universal lipids screening in adults
risk of 10% or greater ages 40 to 75 years.
Syphilis screening: A
The USPSTF recommends screening for syphilis infection in persons who are at increased risk for infection.
nonpregnant persons
Syphilis screening: pregnant A
The USPSTF recommends early screening for syphilis infection in all pregnant women.
women
Tobacco use counseling and The USPSTF recommends that clinicians ask all adults about tobacco use, advise them to stop using tobacco, and provide A
interventions: nonpregnant behavioral interventions and U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved pharmacotherapy for cessation to adults
adults who use tobacco.
Tobacco use counseling: The USPSTF recommends that clinicians ask all pregnant women about tobacco use, advise them to stop using tobacco, A
pregnant women and provide behavioral interventions for cessation to pregnant women who use tobacco.
Tobacco use interventions: The USPSTF recommends that clinicians provide interventions, including education or brief counseling, to prevent initiation B
children and adolescents of tobacco use in school-aged children and adolescents.
Tuberculosis screening: The USPSTF recommends screening for latent tuberculosis infection in populations at increased risk. B
adults
Vision screening: children The USPSTF recommends vision screening at least once in all children ages 3 to 5 years to detect amblyopia or its risk B
factors.
You might also like
- USPSTF A and B RecommendationsDocument4 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendationsstarblue265No ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations SummaryDocument2 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations SummarylamaNo ratings yet
- Preventive Screenings Coverd Under The Affordable Care ActDocument2 pagesPreventive Screenings Coverd Under The Affordable Care Actjacques2900No ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations for Preventive ServicesDocument2 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations for Preventive ServicesHuner GillNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations Screening GuideDocument5 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations Screening GuidehectorNo ratings yet
- A and B Recommendations United States Preventive Services TaskforceDocument8 pagesA and B Recommendations United States Preventive Services TaskforceHassan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A and B Recommendations United States Preventive Services TaskforceDocument7 pagesA and B Recommendations United States Preventive Services TaskforcejonNo ratings yet
- Preventive Services in Primary Health CareDocument19 pagesPreventive Services in Primary Health CareAhmad AltarefeNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A & B RecommendationsDocument7 pagesUSPSTF A & B RecommendationsDavid CheNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations for Preventive ServicesDocument5 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations for Preventive ServicesVishala MishraNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations by DateDocument3 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations by DateMonica LeeNo ratings yet
- 9-Health Maintenance Screening + Adult ImmunizationDocument60 pages9-Health Maintenance Screening + Adult Immunizationalmho0y2No ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations by DateDocument4 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations by DateAnonymous GkOBsFLvuNo ratings yet
- 12.14.11 Geriatric Immunization & ScreeningDocument6 pages12.14.11 Geriatric Immunization & ScreeningDiana HyltonNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening TestsDocument3 pagesCancer Screening TestsVijaya AcharNo ratings yet
- USPSTF Cancer and Heart Disease Screening GuidelinesDocument12 pagesUSPSTF Cancer and Heart Disease Screening GuidelinesMoliNo ratings yet
- 2021 Adult Preventive Health GuidelinesDocument8 pages2021 Adult Preventive Health GuidelinesAnthony El HageNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening GuideDocument3 pagesCancer Screening Guidebond0071993No ratings yet
- GuidelinesDocument7 pagesGuidelinesAshish GuragainNo ratings yet
- 2019AdultPreventiveHealthGuidelines PDFDocument7 pages2019AdultPreventiveHealthGuidelines PDFvesvNo ratings yet
- Clinical Internal Medicine Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2From EverandClinical Internal Medicine Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2No ratings yet
- FM CasesDocument16 pagesFM CasesJameson87No ratings yet
- Affordable Care Act - USPSTF A and B Recommendations PDFDocument5 pagesAffordable Care Act - USPSTF A and B Recommendations PDFSunil UpadhayaNo ratings yet
- Health Maintenance Guidelines PDFDocument2 pagesHealth Maintenance Guidelines PDFWin MuliadiNo ratings yet
- Aquifer Case - Summary - FamilyMedicine17 - 55-YDocument9 pagesAquifer Case - Summary - FamilyMedicine17 - 55-YHyunsoo EllisNo ratings yet
- Health Maintenance: Guidelines For AdultsDocument6 pagesHealth Maintenance: Guidelines For AdultsgurneeNo ratings yet
- CPG PerinatalDocument7 pagesCPG PerinatalReuter Lloyd MarianoNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening Guidelines: Prepared By: DR. Hanan AbbasDocument35 pagesCancer Screening Guidelines: Prepared By: DR. Hanan AbbashanfmhananfmhanNo ratings yet
- ACOG Perinatal Care Guideline Summary 7th EditionDocument6 pagesACOG Perinatal Care Guideline Summary 7th EditionpolygoneNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Shelf Review - PPTX (Read-Only)Document142 pagesFamily Medicine Shelf Review - PPTX (Read-Only)Alejandro Bocanegra Osuna58% (19)
- Task Force CA CervicalDocument13 pagesTask Force CA CervicalLuis Andres Carrero TovarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Task ForceDocument13 pagesClinical Task ForcePriscillitapp JimenezNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Shelf Review: Vaccinations and Screening GuidelinesDocument69 pagesFamily Medicine Shelf Review: Vaccinations and Screening GuidelinesShayn100% (14)
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsFrom EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Family Medicine Shelf Review: Vaccination and Screening GuidelinesDocument142 pagesFamily Medicine Shelf Review: Vaccination and Screening GuidelinesAnonymous kOPWA2s0% (1)
- Guidelines Screening USADocument2 pagesGuidelines Screening USAAyu RahmaNo ratings yet
- Mqic Adult Preventive Services Ages 18 To 49 CPGDocument1 pageMqic Adult Preventive Services Ages 18 To 49 CPGjetiradoNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care Guideline Provides Comprehensive OverviewDocument14 pagesAntenatal Care Guideline Provides Comprehensive OverviewYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Shelf ReviewDocument69 pagesFamily Medicine Shelf ReviewnomansnNo ratings yet
- Nurses As Cancer InsurgentsDocument7 pagesNurses As Cancer InsurgentsNick RealinoNo ratings yet
- USPSTF Summary For ScreeningDocument22 pagesUSPSTF Summary For ScreeningEmirhan llkhanNo ratings yet
- USPSTF RecommendationsDocument3 pagesUSPSTF RecommendationsKevinMathewNo ratings yet
- Docslide - Us Family Medicine Shelf Reviewpptx Read OnlyDocument142 pagesDocslide - Us Family Medicine Shelf Reviewpptx Read OnlyDavid DengNo ratings yet
- Health ScreeningDocument27 pagesHealth ScreeninglilydariniNo ratings yet
- Community and Preventative MedicineDocument1 pageCommunity and Preventative MedicineToolMoodNo ratings yet
- Cancer Facts: For WomenDocument6 pagesCancer Facts: For WomenShanntha JoshittaNo ratings yet
- What Women Should Know About CancerDocument20 pagesWhat Women Should Know About CancerAnonymous c4GVTgkvNo ratings yet
- Perspective: New England Journal MedicineDocument3 pagesPerspective: New England Journal MedicineYosua_123No ratings yet
- Prevention Case StudyDocument6 pagesPrevention Case StudyllukelawrenceNo ratings yet
- FAMMED - Principle of ScreeningDocument24 pagesFAMMED - Principle of ScreeningWan Razin Wan HassanNo ratings yet
- Oncology and Palliative Care 2023 FinalDocument99 pagesOncology and Palliative Care 2023 FinalBelinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Screening StuffDocument3 pagesCervical Cancer Screening Stuffyasir saeedNo ratings yet
- Breastcanscrfinalrs PDFDocument19 pagesBreastcanscrfinalrs PDFPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Screening - Patient Information (CDC)Document2 pagesBreast Cancer Screening - Patient Information (CDC)kneovncrvNo ratings yet
- Online MedEd For Bioethics, Biostats, EtcDocument2 pagesOnline MedEd For Bioethics, Biostats, EtcjohntheuglyllamaNo ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument3 pagesPrenatal CareYolanda Dwi OktaviyaniNo ratings yet
- Preventive Care Guidelines by AgeDocument3 pagesPreventive Care Guidelines by Agecielo vanNo ratings yet
- Pco RcogDocument15 pagesPco RcogganotNo ratings yet
- General Screening GuidelinesDocument2 pagesGeneral Screening GuidelinesStormNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 1: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3From EverandClinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 1: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2015 UTI Complicated PDFDocument222 pages2015 UTI Complicated PDFLuis CoNo ratings yet
- Data Formulasi Tugas Kuis Teknologi Sediaan SolidaDocument11 pagesData Formulasi Tugas Kuis Teknologi Sediaan SolidaRiswan Genesis DeadsquadNo ratings yet
- California school immunization recordDocument2 pagesCalifornia school immunization recordWillNo ratings yet
- Meningitis CausesDocument6 pagesMeningitis CausesAgustinNo ratings yet
- TramadolDocument1 pageTramadolmilesminNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument24 pagesCardiomyopathyapi-462914447No ratings yet
- ABC Practice Test PregnancyDocument11 pagesABC Practice Test PregnancyMarcus, RN80% (10)
- ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, AND CAUSESDocument10 pagesACUTE KIDNEY INJURY SIGNS, SYMPTOMS, AND CAUSESYanti TandjungNo ratings yet
- ImciDocument3 pagesImciJohn Benzon0% (1)
- CefuroximeDocument14 pagesCefuroximeBentoys StreetNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Across Age GroupsDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Across Age GroupsBillyNicolasNo ratings yet
- Henoch-Schonlein Purpura, Atopic Dermatitis, Seborrheic Dermatitis & Oral Isotretinoin TherapyDocument5 pagesHenoch-Schonlein Purpura, Atopic Dermatitis, Seborrheic Dermatitis & Oral Isotretinoin TherapyJoan ChoiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: New Normal Health Assessment Form For LearnersDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: New Normal Health Assessment Form For LearnersCristilyn SaagundoNo ratings yet
- Hypomagnesemia & HypermagnesemiaDocument18 pagesHypomagnesemia & HypermagnesemiaLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Master DDD 2017Document904 pagesMaster DDD 2017Ainul YuyunNo ratings yet
- Anti-Tuberculosis AgentsDocument15 pagesAnti-Tuberculosis AgentsNick van ExelNo ratings yet
- DR Swamy PLAB Courses LTD.: Plab 1 Mock Test: 5 March 2019 Time Allowed: 3HrsDocument31 pagesDR Swamy PLAB Courses LTD.: Plab 1 Mock Test: 5 March 2019 Time Allowed: 3HrsSualeha SohailNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument1 pageAppendicitisvaleriaNo ratings yet
- Reduce MTCT of HIV in PregnancyDocument44 pagesReduce MTCT of HIV in PregnancyAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Cross-Sensitivity ChartDocument1 pageAntibiotic Cross-Sensitivity ChartAji YudhaNo ratings yet
- National Safe Motherhood Program ReviewDocument12 pagesNational Safe Motherhood Program ReviewFerzada SajiranNo ratings yet
- Clinic Drugs Preferred Supplier ListDocument6 pagesClinic Drugs Preferred Supplier ListKojo EgyirNo ratings yet
- Daftar AntibiotikDocument448 pagesDaftar AntibiotikevaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics History ExampleDocument3 pagesObstetrics History ExampleMohamed Elprince Adel100% (3)
- Ciprofloxacin drug information: indications, dosage, side effectsDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin drug information: indications, dosage, side effectsRina Jean SuicoNo ratings yet
- ECG Changes Due To Electrolyte Imbalance (Disorder) - ECG LearningDocument1 pageECG Changes Due To Electrolyte Imbalance (Disorder) - ECG LearningRadhika MNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac (Drug Study)Document2 pagesKetorolac (Drug Study)Cassandra Grace Labial Paynter89% (18)
- Med Dermatology Questions-75Document67 pagesMed Dermatology Questions-75Khalifa AL-Wishahi75% (4)
- Pinkeye Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment for Sore EyesDocument21 pagesPinkeye Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment for Sore EyesDiana MaeNo ratings yet
- Rundown SOC HF 16-17.nov.2019Document2 pagesRundown SOC HF 16-17.nov.2019More Than WordsNo ratings yet