Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ic6501 Control Systems: UNIT-1 (2 Mark Q/A)
Uploaded by
Anonymous yO7rcec6vuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ic6501 Control Systems: UNIT-1 (2 Mark Q/A)
Uploaded by
Anonymous yO7rcec6vuCopyright:
Available Formats
IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMS
UNIT-1 (2 mark Q/A)
1. What are the basic elements of a control Systems?
The basic elements in control system are controller, process and feedback path
element and error detector.
2. Define transfer function.
Transfer function is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output
function to the input function with zero initial condition.
3. Why negative feedback is preferred in control systems?
The negative feedback results in better stability in steady state and rejects any
disturbance signals.
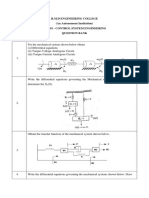
4. Obtain the transfer function X(S) / F(S) the mechanical system shown in fig
below
..
0=Mx Bx Kx K1( x y ) Ms 2 Bs K K1 X (s ) K1Y (s )
F (s )
F (t ) K1( y x ) Y (s ) x(s )
K1
F (s )
Ms 2 Bs K K1 X (s ) K1 x (s )
K1
X (s ) 1
F (s ) Ms Bs K
2
5. What is analogous system?
Systems whose differential equations are of identical form are called analogous
systems.
6. Define resistance and capacitance of thermal system.
The thermal resistance is defined as,
Compiled by Prof.S.Nagammai, HOD/EIE, KLNCE Page 1
IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMS
o
change in temperature difference ( C) 1
R= =
J hA
change in heat flow rate
sec
Where, h - heat transfer co-efficient (J/ m2 sec C)
7. A - Area normal to heat flow (m2)
The thermal capacitance (C) is defined as the ratio of change in heat stored to the
change in temperature.
change in heat stored (J)
C= o
change in temperature ( C)
The thermal capacitance C = mCp
Where, m – mass of the substance considered (kg)
Cp – Specific heat capacity (J/Kg C)
7. Distinguish open loop and closed loop control system.
Open Loop System Closed Loop System
1. Inaccurate and unreliable Accurate and reliable
2. Simple and economical Complex and expensive
3. Changes in output due to external Changes in output due to external
disturbances are not created disturbances are corrected
automatically. automatically.
4. They are generally stable. Greater efforts are needed to design a
stable system.
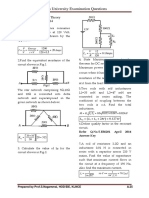
8. Describe the rule for moving a summing point ahead of a block.
Moving a
summing
point
ahead of a
block
9. Obtain C/R ratio of the system shown in Fig below.
Forward path gain P1=2x2x2=8; ∆1=1
Loop gain L1=-2 & L2=-2
Non touching loops L12=4
∆=1-(-2-2)+4=9
C/R= P1∆1/∆=8/9
Compiled by Prof.S.Nagammai, HOD/EIE, KLNCE Page 2
IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMS
10. List out the limitations of transfer function approach.
It is defined under zero initial conditions.
Applicable only to LTIV system.
Highly cumbersome for use with MIMO system.
Provides no information regarding the internal state of the system
11. What is control system?
A system consists of a number of components connected together to perform a
specific function. In a system when the output quantity is controlled by varying the
input quantity then the system is called control system.
12. Define open loop control system.
The control system in which the output quantity has no effect upon the input
quantity is called open loop control system. This means that the output is not
feedback to the input for correction.
13. Define closed loop control system.
The control system in which the output has an effect upon the input quantity so
as to maintain the desired output value is called closed loop control system.
14. What is synchro?
A synchro is an electromagnetic transducer used to convert an angular position
of a shaft into an electric signal.
15. Illustrate with a neat sketch the control of an automobile by the driver and
identify the components of this closed loop control system?
The actual speed is measured by the speedometer and indicated on its deal. The
driver reads the speed visually and compares the actual speed with the desired
one mentally. If there is a deviation of speed, the driver takes the decision to
increase (or) decrease the speed and executed by change in pressure on the
accelerator pedal.
16. What is a signal flow graph?
It is a pictorial representation of the simultaneous equations describing the
system. It graphically represents the transmission of signals through the system.
Compiled by Prof.S.Nagammai, HOD/EIE, KLNCE Page 3
IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMS
17. List the analogous quantities in force voltage analogy.
Mechanical Mechanical Force voltage
Translational Rotational analogy
Force (F) Torque (T) Voltage (e)
Mass (M) Moment of inertia (J) Inductance (L)
Viscous friction (B) Viscous friction (f) Resistance (R)
Torsional spring
Spring stiffness (K) Capacitance (C)
stiffness (1/K)
Angular
Displacement (x) Charge (q)
displacement ( )
Velocity ( x ) Angular velocity () Current (i)
18.List the analogous quantities in force current analogy.
Mechanical Mechanical Force current
Translational Rotational analogy
Force (F) Torque (T) Current (i)
Mass (M) Moment of inertia (J) Capacitance (C)
Viscous friction (B) Viscous friction (f) Resistance (R)
Torsional spring
Spring stiffness (K) Inductance (L)
stiffness (1/K)
Angular Flux linkage ( )
Displacement (x)
displacement ( )
Velocity ( x ) Angular velocity () Voltage (e)
19. What is block diagram?
A block diagram of a system is a pictorial representation of the functions performed by
each component of the system and shows the flow of signals. The basic elements of
block diagram are block, branch point and summing point.
20.Write Masons Gain formula
The overall gain of closed loop system can be determined by mason’s gain formula
1
T PK K
K
Where, T → overall (or) closed loop gain
PK → Path gain of Kth forward path
∆ → determinant of the graph.
∆ = 1- (sum of all individual loop gains) + (sum of gain products of all possible
combinations of two non – touching loops) – (sum of gain products of all possible
combinations of 3 non – touching loop)
(ie.) 1 (L1 L2 ........) (L12 L22 ........) (L13 L23 ........)
∆ = The value of ‘∆’ for that part of graph not touching the Kth forward path
Compiled by Prof.S.Nagammai, HOD/EIE, KLNCE Page 4
IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMS
21. What are the types of friction encountered in physical system?
Coulomb friction force: The force of sliding friction between dry surfaces. The force is
substantially constant.
Viscous friction force: The force of friction between solid body and fluid medium.
Force is proportional to velocity.
Stiction: The force required to initiate motion between two contacting surfaces.
22. State the advantages of closed loop system over the open loop system.
i) Accurate
ii) The changes in output due to external disturbances are corrected automatically.
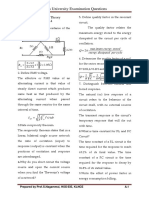
23. Write the force balance equation of ideal dashpot and ideal spring.
The damper element:
x Displacement of moving vehicle w.r.t to reference
F (t ) f (v1 v 2 ) f ( x1 x2 )
f Viscous friction coefficient.
The spring element:
The concept of elastic deformation of a body is symbolized by a helical spring
F (t ) k ( x1 x2 )
K Spring stiffness coefficient
24.What are the advantages and disadvantages of feedback control?
Advantages :
i) Reduction in sensitivity to variations of parameters in the forward path.
ii) Control over the transient response as well as the steady state accuracy by
adjusting the loop gain.
iii) Reduction in the effect of noise or disturbance at the output level.
Disadvantages:
i) The need of additional hardware with consequent increase in cost.
ii) The possibility of instability due to phase lags in the feedback loop.
Compiled by Prof.S.Nagammai, HOD/EIE, KLNCE Page 5
IC6501 CONTROL SYSTEMS
25. What are the applications of synchros?
Synchros are used to transmit torque over a long distance without a rigid mechanical
connection. They are used for operating gates in canals, fire control systems, in military
hardware, motion picture equipments for synchronizing movie cameras and sound
recording equipments.
26.Draw the electrical analog of thermometer.
mC p 1
RC where R C mC p
hA hA
27.From the torque-speed characteristics of a two-phase AC servomotor, write the
dynamic equation relating the motor torque and the speed
From the torque speed characteristic we can write,
Where
= torque
= a positive constant = negative of the slope of the torque-speed curve
= a positive constant = torque per unit control voltage at zero speed
= angular displacement
28.State the basic elements for modeling in translational and rotational systems.
Three basic elements of mechanical translational system:
Spring (elastic) element
Damper (frictional) element
Mass (inertia) element
Three basic elements of mechanical rotational system:
Inertia element, spring and friction element.
29. What is the difference between AC servo motor and 2 phase induction motor?
AC servo motor is low power motor while 2 phase induction motor is high power motor.
The AC servo motor has small X/R ratio hence speed torque characteristic is linear
while the 2 phase induction motor has large X/R ratio hence the speed torque
characteristic is non linear.
Compiled by Prof.S.Nagammai, HOD/EIE, KLNCE Page 6
You might also like
- Mathematical ModellingDocument21 pagesMathematical ModellingFhuNo ratings yet
- Control System 2MARKSDocument16 pagesControl System 2MARKSSeekay Alais Karuppaiah CNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Time Response AnalysisDocument29 pagesModeling and Time Response AnalysisPrabhavathi AadhiNo ratings yet
- Analogous SystemDocument19 pagesAnalogous SystemAmit GoriyanNo ratings yet
- Dept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)Document9 pagesDept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)DeepakLingamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Analogous System: Group Discussion ReportDocument12 pagesAnalogous System: Group Discussion ReportAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- EC6405-Control Systems EngineeringDocument12 pagesEC6405-Control Systems EngineeringAnonymous XhmybK0% (1)
- Chap 2Document35 pagesChap 2Temesgen MekonenNo ratings yet
- R.M.D Engineering College (An Autonomous Institution) Ec8391 - Control System Engineering Question BankDocument6 pagesR.M.D Engineering College (An Autonomous Institution) Ec8391 - Control System Engineering Question Bankaarthir88No ratings yet
- Control Engineering Lecture ReviewDocument35 pagesControl Engineering Lecture ReviewpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Department of Electromechanical Engineering Course Title: Control SystemDocument21 pagesDepartment of Electromechanical Engineering Course Title: Control SystemYidersal MarewNo ratings yet
- Linear Control Engineering QBDocument11 pagesLinear Control Engineering QBAkizuki TakaoNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Question BankDocument9 pagesControl Engineering Question Banksathesh waranNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK of Control Systems Engineering PDFDocument12 pagesQUESTION BANK of Control Systems Engineering PDFMouhanit LimbachiyaNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering: Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz UniversityDocument31 pagesCollege of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering: Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz UniversityFawzi RadwanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Ashish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 191ECC302T CSE 2 Marks With Answer-2022Document14 pages191ECC302T CSE 2 Marks With Answer-2022Senthilkumar PandianNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of DC Drive Using PI and PID ControllerDocument4 pagesModelling and Simulation of DC Drive Using PI and PID ControllerOTOMASYON PLCNo ratings yet
- Modeling Circuits and Mechanical Systems in the Frequency DomainDocument15 pagesModeling Circuits and Mechanical Systems in the Frequency DomainZairul IzwanNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Control of Synchronous Generator Under The Condition of Transient Three Phase Short CircuitDocument5 pagesFuzzy Logic Control of Synchronous Generator Under The Condition of Transient Three Phase Short CircuitwilliamNo ratings yet
- Thuật Toán Điều Khiển1Document23 pagesThuật Toán Điều Khiển1Văn Nghĩa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IC6501 Iq PDFDocument13 pagesIC6501 Iq PDFKRISHNA VAMSINo ratings yet
- Control Systems Systems and Their Representations Unit-1: Ms. P. Geethanjali Asst. Professor (SR) SelectDocument72 pagesControl Systems Systems and Their Representations Unit-1: Ms. P. Geethanjali Asst. Professor (SR) SelectVijay IndukuriNo ratings yet
- Exp01 EEE318Document7 pagesExp01 EEE318Abid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Transfer Function - by AnalogyDocument22 pagesTransfer Function - by AnalogyMohd Ridzuan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Matlab and Simulink For Modeling and Control DC MotorDocument14 pagesMatlab and Simulink For Modeling and Control DC MotorGhaleb AlzubairiNo ratings yet
- 2018 EE305 New SolutionDocument25 pages2018 EE305 New SolutionJasa R ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Modeling Using MATLABDocument10 pagesDC Motor Modeling Using MATLABmuhmad almtrabieNo ratings yet
- Digital Control of a Single-Phase PWM Inverter Using GPCDocument3 pagesDigital Control of a Single-Phase PWM Inverter Using GPCsa920189No ratings yet
- VMU Aarupadai Veedu Institute of Technology Question Bank for Control SystemsDocument10 pagesVMU Aarupadai Veedu Institute of Technology Question Bank for Control SystemsSagaraptor RexNo ratings yet
- Control Systems OverviewDocument2 pagesControl Systems OverviewSornagopal VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Control Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud) PDFDocument183 pagesControl Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud) PDFShakil Ahmed100% (1)
- Control Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud)Document183 pagesControl Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud)Anik PaulNo ratings yet
- Control ActionDocument11 pagesControl ActionfaizNo ratings yet
- Applied Marine Control Systems and AutomationDocument15 pagesApplied Marine Control Systems and AutomationSrinivasan PrakashNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Unitwise Important Questions Unit 1 Part ADocument10 pagesControl Systems Unitwise Important Questions Unit 1 Part AChandra shekarNo ratings yet
- ME 304 Control Systems ExercisesDocument58 pagesME 304 Control Systems ExercisesmjdaleneziNo ratings yet
- EE 312 Lecture 1Document12 pagesEE 312 Lecture 1دكتور كونوهاNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Modeling and Analysis of Synchronverters: Zhou Wei, Chen Jie and Gong ChunyingDocument5 pagesSmall Signal Modeling and Analysis of Synchronverters: Zhou Wei, Chen Jie and Gong ChunyingEnimien AymenNo ratings yet
- Cs 2 MarksDocument23 pagesCs 2 Markshemalatha10No ratings yet
- Control Systems: Module: Modelling of SystemsDocument32 pagesControl Systems: Module: Modelling of Systemsee210002004No ratings yet
- EEN 407 Sample QuestionsDocument41 pagesEEN 407 Sample QuestionsAbu SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Control of A Single-Link Flexible Joint Manipulator Using Differential FlatnessDocument6 pagesNonlinear Control of A Single-Link Flexible Joint Manipulator Using Differential Flatnessanon_93685582No ratings yet
- IAT SolutionsDocument13 pagesIAT Solutionsjay mehtaNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Nonlinear Control SystemsDocument99 pagesExercises in Nonlinear Control SystemsSteve DemirelNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Levitation System: An Experimental ApproachDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Levitation System: An Experimental Approachsh1n00b1No ratings yet
- Mech3418 Ca 2016Document4 pagesMech3418 Ca 2016Barry PoonNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - PART - ADocument12 pagesControl Systems - PART - Aaarthir88100% (1)
- Modeling and Simulation of A Series Resonant InverterDocument6 pagesModeling and Simulation of A Series Resonant InverterkaaisNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Several Control Techniques Applied To A Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study of Several Control Techniques Applied To A Boost ConverterulaganathanNo ratings yet
- Model and Observer-Based Controller Design For A Quanser Helicopter With Two DOFDocument5 pagesModel and Observer-Based Controller Design For A Quanser Helicopter With Two DOFosdacavNo ratings yet
- New Rich Text DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Rich Text DocumentbhaskarNo ratings yet
- DoxsDocument14 pagesDoxsTALHA SALEEMNo ratings yet
- 2 1 2 08 ProofDocument12 pages2 1 2 08 ProofMongiBESBESNo ratings yet
- Advanced Single-Loop Discrete-Time Control For T-Type Voltage Source InverterDocument21 pagesAdvanced Single-Loop Discrete-Time Control For T-Type Voltage Source InverterBá Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Block Diagram GuideDocument86 pagesControl Systems Block Diagram Guidenaughty dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Electrical-Mechanical Analogy ExplainedDocument14 pagesElectrical-Mechanical Analogy ExplainedAvinash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- MF2030 Final Exam Solution HT10Document12 pagesMF2030 Final Exam Solution HT10Athul_V_Dev_1688No ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- Energetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandEnergetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- 5.ee6201 May 2016Document9 pages5.ee6201 May 2016Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Anna University Examination Questions: EE6201-Circuit Theory NOV - 2015Document9 pagesAnna University Examination Questions: EE6201-Circuit Theory NOV - 2015Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Anna University Circuit Theory QuestionsDocument8 pagesAnna University Circuit Theory QuestionsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- 6.TR Nov'2017Document2 pages6.TR Nov'2017Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- DSBSC NotesDocument17 pagesDSBSC NotesAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- 2.EI 6401 - Nov 15 - TR KeyDocument17 pages2.EI 6401 - Nov 15 - TR KeyAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- 1.EI 6401 - April 15 - TR KeyDocument26 pages1.EI 6401 - April 15 - TR KeyAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Anna University Circuit Theory QuestionsDocument7 pagesAnna University Circuit Theory QuestionsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Anna University Examination Questions: EE6201-Circuit Theory May - 2014Document8 pagesAnna University Examination Questions: EE6201-Circuit Theory May - 2014Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAM TRANSDUCER ENGINEERING APR/MAY 2017Document2 pagesB.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAM TRANSDUCER ENGINEERING APR/MAY 2017Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Ei 6602 PC April 2017Document12 pagesEi 6602 PC April 2017Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- 2.EI6602 PC Nov'2016Document23 pages2.EI6602 PC Nov'2016Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Transducer Engineering Measurement SystemDocument13 pagesTransducer Engineering Measurement SystemAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Anna University Communication Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesAnna University Communication Engineering Questions and AnswersAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- EC COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EXAM QUESTIONSDocument18 pagesEC COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EXAM QUESTIONSAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- EI 8352 TR - Nov 17Document2 pagesEI 8352 TR - Nov 17Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics - Mumbai Univ - Sem 8 ElexDocument10 pagesMechatronics - Mumbai Univ - Sem 8 Elex111ashwinNo ratings yet
- 1.EI 6602 PC April 16 - KeyDocument25 pages1.EI 6602 PC April 16 - KeyAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- EC8351 Electronics Devices and CircuitsDocument1 pageEC8351 Electronics Devices and CircuitsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Process Control Question Paper Code 20480Document2 pagesProcess Control Question Paper Code 20480Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Ei6801 - Computer Control of Process Part-A Answer All Questions (5x2 10)Document7 pagesEi6801 - Computer Control of Process Part-A Answer All Questions (5x2 10)Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Aptitude QuestionsDocument9 pagesAptitude QuestionsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- K L N College of Engineering Pottapalaym: 1 Gshs S 100Document2 pagesK L N College of Engineering Pottapalaym: 1 Gshs S 100Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Name: Digital Logic Circuits (Common To ICE) Part A (20X2 40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesName: Digital Logic Circuits (Common To ICE) Part A (20X2 40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- IC6701 May 18 With KeyDocument14 pagesIC6701 May 18 With KeyAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- DTSSP 2mark Q&ADocument31 pagesDTSSP 2mark Q&AAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- CS ASS2 (13-17batch)Document3 pagesCS ASS2 (13-17batch)Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Aptitude QuestionsDocument9 pagesAptitude QuestionsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- CS ASS2 (13-17batch)Document3 pagesCS ASS2 (13-17batch)Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Signal Degradation in Optical Fiber: AttenuationDocument42 pagesSignal Degradation in Optical Fiber: AttenuationDevLaxmanNo ratings yet
- Friction - Engineering Mechanics ReviewDocument5 pagesFriction - Engineering Mechanics Reviewleonard dela cruz100% (1)
- Liquid Flowmeters: Reynolds NumbersDocument12 pagesLiquid Flowmeters: Reynolds NumbersAsaithambi DorairajNo ratings yet
- MENG375 Machine Element I: Torsion & Static Failure TheoriesDocument21 pagesMENG375 Machine Element I: Torsion & Static Failure TheoriesiSMAİL ekenNo ratings yet
- Examen PE GeotecniaDocument38 pagesExamen PE GeotecniaMario Berti100% (2)
- Kohn-Sham Equations For DFTDocument15 pagesKohn-Sham Equations For DFTRikardo Pino RiosNo ratings yet
- 3D Rendered View of House Structure Analysis in STAAD ProDocument34 pages3D Rendered View of House Structure Analysis in STAAD ProMochammad Su'udNo ratings yet
- Oxo Aqa16 p10cs xm01 XxaannDocument2 pagesOxo Aqa16 p10cs xm01 Xxaannoliwierwojciechowski603No ratings yet
- Open Ended Assignment ESEDocument2 pagesOpen Ended Assignment ESEParas kapoorNo ratings yet
- Structural Assessment of Stainless Steel Stiffened PanelsDocument17 pagesStructural Assessment of Stainless Steel Stiffened PanelsMariana PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Phys For Engineers Quiz 5Document4 pagesPhys For Engineers Quiz 5Joforce Karl Malana0% (1)
- FOUNDATIONS FOR SHALLOW STRUCTURESDocument29 pagesFOUNDATIONS FOR SHALLOW STRUCTURESBuoyancyNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis of StructuresDocument136 pagesPlastic Analysis of StructuresMarcos SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of The Ultrasonic Cavitating AtomizerDocument512 pagesNumerical Simulation of The Ultrasonic Cavitating Atomizervedanth_sNo ratings yet
- Punching Shear and One Way Shear Check.Document2 pagesPunching Shear and One Way Shear Check.ElancheliyanNo ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Ch4Document200 pagesAP Phys1 Ch4Raja DanialNo ratings yet
- StringpapertpDocument20 pagesStringpapertpapi-237181799No ratings yet
- Settlement Analysis For Foundations: S D D E Q B' (1 - ) IDocument2 pagesSettlement Analysis For Foundations: S D D E Q B' (1 - ) IankitNo ratings yet
- 3) M2 Work, Energy and PowerDocument44 pages3) M2 Work, Energy and Powermath magicNo ratings yet
- PRYING9.xls AISC Prying Action AnalysisDocument5 pagesPRYING9.xls AISC Prying Action AnalysisCarlos Valverde PortillaNo ratings yet
- The Special Theory of Relativity A Critical Analysis Louis Essen DigitizedDocument27 pagesThe Special Theory of Relativity A Critical Analysis Louis Essen DigitizedStanley V Byers100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument73 pagesPhysicsVikash KotteeswaranNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics - Spectroscopy Video WorksheetDocument3 pagesAstrophysics - Spectroscopy Video WorksheetJake NadrezNo ratings yet
- Clutch Lab Sheet 2018Document6 pagesClutch Lab Sheet 2018Gabriel VaughnNo ratings yet
- A Curious Observer's Guide To Quantum Mechanics, Pt. 5 - Catching A Wave - Ars TechnicaDocument5 pagesA Curious Observer's Guide To Quantum Mechanics, Pt. 5 - Catching A Wave - Ars TechnicasiesmannNo ratings yet
- 5 Propeller Theory - ExamplesDocument4 pages5 Propeller Theory - ExamplesVăn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machines Lecture on Isolation and TransmissibilityDocument17 pagesDynamics of Machines Lecture on Isolation and TransmissibilityNeelesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Representation of Vectors Using Rectangular ComponentsDocument12 pagesRepresentation of Vectors Using Rectangular ComponentsGherico MojicaNo ratings yet
- Corollary of 2nd Law of ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesCorollary of 2nd Law of ThermodynamicsHusnain A Ali75% (4)
- Determination of Dynamic Ballast Characteristics Under Transient Impact LoadingDocument18 pagesDetermination of Dynamic Ballast Characteristics Under Transient Impact Loadingomar cNo ratings yet