Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Approaches in A Qualitiative Research Design
Uploaded by
Hyde Park0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Approaches_QualiRes.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesThe Approaches in A Qualitiative Research Design
Uploaded by
Hyde ParkCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1
John Ryan M. Jacot | 11 – HumSS
An Introduction to Qualitative Research
School Year 2018 – 2019
THE APPROACHES IN A QUALITIATIVE RESEARCH DESIGN
A qualitative research design is a general way of thinking about conducting qualitative research. It describes,
either explicitly or implicitly, the purpose of the qualitative research, the role of the researcher(s), the stages of
research, and the method of data analysis. (Trochim, 2006)
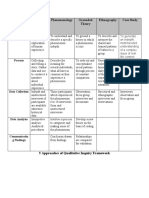
Approach Purpose Method Analysis Outcome
Ethnography To describe a Fieldwork and Detailed and rich “Description of
culture: its immersion in the description of Culture”
characteristics and culture culture
features Key informant
interviews and
observations
Grounded To develop Interviews and “Concept Theory backed by
Theory theories from Observations formation” evidences from
analysis of Data collection “Concept data
patterns, themes and analysis are Development” by
and categories done in parallel. looking into
Data are analyzed literature and
as they come. “sampling of
Patterns and subjects”
themes are “Concept
validated and Modification and
disproved by Integration”
further data
collection.
Phenomenology To describe Seek persons who Classify and rank Findings described
experiences as understand study data from subject’s
they are lived and are willing to Sense of wholeness point-of-view
To examine the express inner Examine Research identifies
uniqueness of feelings and experiences themes
individual’s lived experiences beyond human Structural
situations Describe awareness or that explanation of
To describe that experiences of cannot be findings is
each person has phenomenon communicates developed.
own reality; reality Write experiences
is subjective of phenomenon
Direct Observation
Audio or
Videotape
Narrative To describe Interviews and Analysis of Content Narrative
Analysis experiences observations Looking into form accounts from
Research and function of individual s
participants are stories
encouraged to
share stories.
Discourse To describe Interviews and Analysis of content Discourses that
Analysis discourse present Observations and meaning reflect beliefs,
in a phenomenon behind the principles, and
conversation perspectives
Historical To describe and Formulate idea – Synthesis of all Select means of
Approach examine events of select topic after data; accept and presentation –
the past to reading related reject data; biography,
understand the literature reconcile chronology, issue
present and Develop research conflicting paper
anticipate questions evidence
potential future Develop an
effects inventory of
resources –
archives, private
libraries, papers
Clarify validity and
reliability of data –
primary sources,
authenticity, biases
Develop research
outline to organize
investigative
process
Collect data
Case Study Describe in-depth Direct observation Synthesis of In-depth
the experience of and interaction Experience description of the
one person, family, with the subject experience
group, community
or institution
You might also like
- The Approaches in A Qualitiative Research DesignDocument3 pagesThe Approaches in A Qualitiative Research DesignHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Research Lec1Document2 pagesResearch Lec1angela verayeNo ratings yet
- Qualitative ResearchDocument61 pagesQualitative Researchrmm0415No ratings yet
- Handout On Qualitative ResearchDocument58 pagesHandout On Qualitative Researchchingferdie_111No ratings yet
- Padillo, Bea S. Grade 11 - Leo II Activity 1: Comparison of The Kinds of Qualitative ResearchesDocument2 pagesPadillo, Bea S. Grade 11 - Leo II Activity 1: Comparison of The Kinds of Qualitative ResearchesBea PadilloNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks: Jessline 717182008Document53 pagesPhilosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks: Jessline 717182008melissaacehNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research by J.I. AniDocument23 pagesQualitative Research by J.I. Ani'Yemi AwofalaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Study Phenomenology Grounded Theory Ethnography Case StudyDocument1 pageNarrative Study Phenomenology Grounded Theory Ethnography Case StudyAISHA SOOMRONo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research Designs: 1. PhenomenologyDocument5 pagesQualitative Research Designs: 1. Phenomenologynoramin89No ratings yet
- Advance Qualitative ReserachDocument27 pagesAdvance Qualitative Reserachnestor castanos jrNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 1.2Document8 pagesResearch in Daily Life 1.2Roberto F. JavalNo ratings yet
- PR 1 Module 2Document26 pagesPR 1 Module 2olivaresjirah7No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignsDocument2 pagesQualitative Research DesignsCHRISTINA LLAUDERESNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Researchers Use:: The Characteristics of ResearchDocument5 pagesQualitative Researchers Use:: The Characteristics of ResearchErica Rose RamalesNo ratings yet
- Types of Qualitative ResearchDocument14 pagesTypes of Qualitative ResearchKEAN CHRISTOPHER A NUNEZNo ratings yet
- Navia, Ma. Sharlyn - Activity 3Document2 pagesNavia, Ma. Sharlyn - Activity 3Ma Sharlyn Ariego NaviaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Practical Research 1 PrelimDocument5 pagesReviewer For Practical Research 1 PrelimMaureen ElumbaringNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative StudyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative StudyDr. Muhammad Sofwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research: Methods and Practical Tips: References: Methodology BooksDocument40 pagesQualitative Research: Methods and Practical Tips: References: Methodology Bookska ming chu100% (1)
- Qualitative Research: Asistensi 2Document14 pagesQualitative Research: Asistensi 2Priandi Imaduddin SudarmaNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document6 pagesResearch 1Emmanuelle CalleNo ratings yet
- EPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesEPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - Narratives Research DesignDocument12 pagesGroup 10 - Narratives Research DesignChelsea Chahya NingratNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design - Choosing Among Five Approaches (PDFDrive) - 84-91Document8 pagesQualitative Inquiry & Research Design - Choosing Among Five Approaches (PDFDrive) - 84-91-'aku Cliquers'-No ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 SLHT Week 3Document8 pagesPractical Research 1 SLHT Week 3rodulfo capangpanganNo ratings yet
- Midterm Prac Research Session 3 PDFDocument19 pagesMidterm Prac Research Session 3 PDFCaine de LeonNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Lesson 2 - Qualitative ResearchDocument2 pagesPR1 - Lesson 2 - Qualitative ResearchAnatanya TironaNo ratings yet
- Conducting Qualitative Research: Writing The MethodologyDocument30 pagesConducting Qualitative Research: Writing The MethodologytamiNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Data AnalysisDocument18 pagesQualitative Data Analysisbsunilsilva100% (2)
- Qualitative Vs Quantitative ResearchDocument6 pagesQualitative Vs Quantitative ResearchJelly Mae PeñaNo ratings yet
- A Characteristics of Five Qualitative ApproachesDocument3 pagesA Characteristics of Five Qualitative ApproachestesfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 Ethnographic Research LeCompte Schensul 2010Document15 pagesChapter6 Ethnographic Research LeCompte Schensul 2010LAZET618294No ratings yet
- MPPU 1024 Research Methods in Education: (Comparison Between Grounded Theory, Ethnography, Narrative & Case Study)Document3 pagesMPPU 1024 Research Methods in Education: (Comparison Between Grounded Theory, Ethnography, Narrative & Case Study)Kamarul KhamisNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR1Document3 pagesReviewer PR1daniel.jungwon06No ratings yet
- Research Methods New EditionDocument28 pagesResearch Methods New EditionStiffany Rose Nillama TinambunanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yati Afiyanti, SKP., MN PresentDocument39 pagesDr. Yati Afiyanti, SKP., MN PresenttienNo ratings yet
- General Forms of ResearchDocument25 pagesGeneral Forms of ResearchJa FloresNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks1Document12 pagesPhilosophical Assumptions and Interpretive Frameworks1Rashard AlexanderNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument6 pagesActivityDizon Yevgeny Dre NovalNo ratings yet
- Doing Research in A Way That Counts: Research and The Research ProcessDocument28 pagesDoing Research in A Way That Counts: Research and The Research ProcessArnold Magdalita FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Atlas Ti (DR Ani Munirah)Document14 pagesAtlas Ti (DR Ani Munirah)bNo ratings yet
- Overdue Task Action ResearchDocument19 pagesOverdue Task Action ResearchLuis Cabello DrouetNo ratings yet
- 7 QUALITATIVE DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 26112020 100055am 22062021 042520pmDocument89 pages7 QUALITATIVE DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 26112020 100055am 22062021 042520pmthewarriorprincess02No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignDocument3 pagesQualitative Research DesignBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument7 pagesResearchLoreanne DamascoNo ratings yet
- Prac ResDocument5 pagesPrac Rescuasayprincessnicole4No ratings yet
- Research and Types of ResearchDocument6 pagesResearch and Types of ResearchdatujaiysandiganNo ratings yet
- Practica L Research 2Document22 pagesPractica L Research 2tan2masNo ratings yet
- Narrative Study - Durratu Fakhria N&Parahat AtabayevDocument18 pagesNarrative Study - Durratu Fakhria N&Parahat AtabayevNun100% (1)
- Conceptualization of Research: What? Why? How?Document68 pagesConceptualization of Research: What? Why? How?pragyasimsNo ratings yet
- Doing Qualitative Research - OverviewDocument29 pagesDoing Qualitative Research - OverviewTram AnhNo ratings yet
- L2 NOTES Importance of Quali RSRCH in Daily LifeDocument9 pagesL2 NOTES Importance of Quali RSRCH in Daily Lifecar tadzNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Module 2Document5 pagesPractical Research Module 2Andrielle Keith Tolentino MantalabaNo ratings yet
- Written Texts Across DisciplinesDocument2 pagesWritten Texts Across DisciplinesGlyzeea Lawansi CandidoNo ratings yet
- 02 Qualitative Research MethodsDocument46 pages02 Qualitative Research MethodsAminaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 Q1 M4Document20 pagesPractical Research 1 Q1 M4dv vargasNo ratings yet
- AOBTBCResearch 10 Q1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesAOBTBCResearch 10 Q1 ReviewerReizhelle AbisNo ratings yet
- Summary How To Begin Qualitative Research ProjectDocument4 pagesSummary How To Begin Qualitative Research ProjectHeba MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Day 2 HandoutDocument2 pagesDay 2 HandoutCHRISTINA LLAUDERESNo ratings yet
- Ivan Pavlov'S Theory On Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesIvan Pavlov'S Theory On Classical ConditioningHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Creative Imagination, Especially in The Production of Decorative Objects." However, The ThingDocument4 pagesCreative Imagination, Especially in The Production of Decorative Objects." However, The ThingHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- CreativeNonfiction NotesDocument10 pagesCreativeNonfiction NotesHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Biological EvolutionDocument3 pagesBiological EvolutionHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- The Personal Is SocialDocument2 pagesThe Personal Is SocialHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- JiveDocument10 pagesJiveHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY LITERATURE FROM THE PHILIPPINES AND THE WORLDDocument3 pages21st CENTURY LITERATURE FROM THE PHILIPPINES AND THE WORLDHyde Park50% (4)
- Into The World of ChristianityDocument15 pagesInto The World of ChristianityHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- UCSP ReviewDocument2 pagesUCSP ReviewHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Topic: Decision Making 1. SWOT AnalysisDocument10 pagesTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Topic: Decision Making 1. SWOT AnalysisHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument5 pagesOrigin of LifeHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Study: Practical Research 1 2018 - 2019Document14 pagesSignificance of The Study: Practical Research 1 2018 - 2019Hyde ParkNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument2 pagesQualitativeHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and GovernanceDocument5 pagesPhilippine Politics and GovernanceHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- OralComm NotesDocument3 pagesOralComm NotesHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- ACCA Qualification Recognition StatusDocument14 pagesACCA Qualification Recognition StatusRuxandraBalanescuNo ratings yet
- University of Washington (Foster School of Business)Document5 pagesUniversity of Washington (Foster School of Business)Sumanta SinhatalNo ratings yet
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West BengalDocument1 pageMaulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengalbiswajit dasNo ratings yet
- System Audit RequirementDocument37 pagesSystem Audit Requirementavinashbatra171% (7)
- Certified Professional in Supply Management: CPSM Exam OverviewDocument1 pageCertified Professional in Supply Management: CPSM Exam OverviewmsajanjNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Chem3472.002.07s Taught by Lynn Melton (Melton)Document12 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Chem3472.002.07s Taught by Lynn Melton (Melton)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- 211 IFE Level 3 Certificate in Fire InvestigationDocument14 pages211 IFE Level 3 Certificate in Fire InvestigationVivek ParitNo ratings yet
- Student Handbook Part 1Document46 pagesStudent Handbook Part 1LOUISE ANNE NAGALNo ratings yet
- Students Feedback Form LaboratoryDocument2 pagesStudents Feedback Form LaboratoryRonald Candy LasatenNo ratings yet
- 08 Kumiko Takahara PDFDocument12 pages08 Kumiko Takahara PDFtengku trishaNo ratings yet
- STAT 512: Applied Regression Analysis: Fall 2018Document7 pagesSTAT 512: Applied Regression Analysis: Fall 2018Gurkreet SodhiNo ratings yet
- Makaut University Notice For Backlog Fill UpDocument1 pageMakaut University Notice For Backlog Fill UpSourav PandaNo ratings yet
- Bonar N Lowes1990Document7 pagesBonar N Lowes1990muhromNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesChapter Three Research MethodologyAdediran Dolapo50% (2)
- CCISO PresentationDocument16 pagesCCISO PresentationPRASHANTH B S50% (2)
- CASP Systematic Reviews PDFDocument2 pagesCASP Systematic Reviews PDFwidthewitchNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee: Application For Admission ToDocument2 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Roorkee: Application For Admission Tohimanshi khivsaraNo ratings yet
- MS Medical PhysicsDocument2 pagesMS Medical PhysicsHofstraUniversityNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Counseling Theories and TechniquesDocument10 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Counseling Theories and TechniquesKate Arzaga San JoseNo ratings yet
- Coaching Model: Jean Biacsi The SUCCESSDocument4 pagesCoaching Model: Jean Biacsi The SUCCESSCoach CampusNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Cacm 11001 007 Spring 2010Document4 pagesSyllabus Cacm 11001 007 Spring 2010Muhammad Saad AyubNo ratings yet
- Fallacies of LogicDocument5 pagesFallacies of LogicCrisanta MarieNo ratings yet
- Omnibus Certification and Autheticity and Veracity of DocumentsDocument1 pageOmnibus Certification and Autheticity and Veracity of DocumentsFrancis NicorNo ratings yet
- Official Florida Driver's Handbook 2008Document64 pagesOfficial Florida Driver's Handbook 2008Ricardo MacariNo ratings yet
- Transformation of SentencesDocument30 pagesTransformation of SentencesSasa Milosevic100% (9)
- My Teen Romantic Comedy Snafu (Volume 10.5)Document142 pagesMy Teen Romantic Comedy Snafu (Volume 10.5)YudhistiraAgungPNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in EnglishJudelyn DomingoNo ratings yet
- NBCC (India) Limited: Personal DetailsDocument2 pagesNBCC (India) Limited: Personal DetailsNeeraj JoshiNo ratings yet
- PNP QS For All Ranks (February 2010)Document2 pagesPNP QS For All Ranks (February 2010)Leon GuerreroNo ratings yet
- MBTI Distribution RateDocument54 pagesMBTI Distribution RateVania FlorensiaNo ratings yet