Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Special Needs Final
Uploaded by
api-3615899180 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesOriginal Title
special-needs-final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesSpecial Needs Final
Uploaded by
api-361589918Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
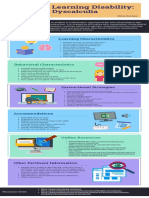
SPECIAL NEEDS
WEEK 10
STRATEGIES FOR STUDENTS WITH
MATHS DIFFICULTIES
Defining Mathematical Symptoms of Mathematical
Difficulties. Difficulties
Dyscalculia: Severe difficulty in making Demonstrate slow or inaccurate recall of basic
arithmetical calculations, as a result of brain arithmetic facts;
disorder. Answer problems impulsively, without
Around half of the students with dyscalculia inhibition;
often suffer from dyslexia. Have difficulty representing mathematical
concepts mentally;
Math Anxiety:
Have poorly developed number sense; and
Cognitive: The cognitive dimension, labeled as
Have difficulty keeping information in their
“worry,” refers to concern about one's
working memory.
performance and the consequences of failure,
Affective: The affective dimension, labeled as Activities in the lesson
“emotionality” refers to nervousness and tension Dyscalculia Screener
in testing situations and respective autonomic Developed by Brian Butterworth, this screener
reactions allows teachers to observe dyscalculia in
students 7-14.
Major Factors of non diagnosed mathematical
Mathematics Assessment interview
difficulties:
Tasks with concrete materials allowing
students to describe their thinking processes
- Ineffective Teaching
Discalculia Perspectives
- Complex Language
Addresses the implications of a life without a
- Symbols have been introduced too early: Lack
of Number sense true sense of numbers and their value.
- Relationship of rational and whole numbers
(Fractions)
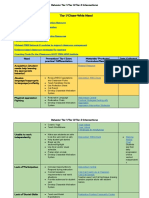
IMPLICATIONS OF
MATH DIFFICULTY
FOR TEACHING
Traditionally, students expected to remember
algorithms, rules & facts without thorough
understandings
Constructivist approaches can only do so much,
partially relying on “incidental learning”
Effective teaching? Investigative activities,
explicit instruction that is teacher-directed,
and plenty of opportunities to practice.
Early intervention & identification will be
crucial, particularly in younger years
LONG TERM IMPLICATIONS STRATEGIES TO
Numeracy is a general capability, per the
Melbourne Declaration students cannot
MANAGE
engage or contribute to society without a CATERING FOR DIVERSITY
functioning sense of numbers and maths.
Direct teaching is essential for those with learning
difficulties (2013)
Global push through TIMSS testing and STEM
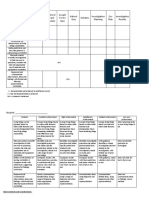
General Class
Thorough planning and sequencing to enable
success
Discussion/sharing ideas and peer teaching or
assistance
Differentiate by group levels or balance out in
tasks i.e. online searches, statistical
spreadsheets and ICT
Assessment
Extra time
Cheat sheets, times tables and charts to
support
Use of calculator except in computation
More space on a page to write and solve
breakdown into sections
Check frequently for understanding
Counting
Comparison of groups, total items vs ordering
of them
Use physical objects, guide movements if need
be for particular disabilities (EA assistance)
Gifted and Talented
Cater to their level/groups like you would
special needs
Strong PCK required (extra PD and
networking)
References Prezi Extra curricular extensions i.e. Tournament of
Minds, Science and Engineering
You might also like
- SLD DyscalculiaDocument1 pageSLD Dyscalculiaapi-558321133No ratings yet
- 1-24-17 Lesson Plan BingoDocument5 pages1-24-17 Lesson Plan Bingoapi-347202641No ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and ASD Part 2Document22 pagesReading Comprehension and ASD Part 2TO ChauNo ratings yet
- Brain Breaks: Activity SticksDocument7 pagesBrain Breaks: Activity SticksHayleyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Inclusive Education in Early Childhood SettingsDocument7 pagesModule 2 Inclusive Education in Early Childhood SettingsCalmer LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Sample Behavior PlanDocument7 pagesSample Behavior PlanMelita BezjakNo ratings yet
- Red Flags Early Identification Guide: For Children Aged Birth To Five YearsDocument1 pageRed Flags Early Identification Guide: For Children Aged Birth To Five YearsResza BrotoNo ratings yet
- Reading ManualDocument105 pagesReading Manualapi-202351147No ratings yet
- Dyslexia White PaperDocument7 pagesDyslexia White PaperS Symone WalkerNo ratings yet
- Zones Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesZones Lesson Planapi-334767841No ratings yet
- Play Scotland Play Types Tooolkit Bringing More Play Into The School DayDocument44 pagesPlay Scotland Play Types Tooolkit Bringing More Play Into The School DayGatot SandyNo ratings yet
- Tier II Behavior Intervention Descriptions2Document13 pagesTier II Behavior Intervention Descriptions2api-233605048No ratings yet
- Colourful Semantic DefinitionsDocument3 pagesColourful Semantic Definitionsapi-263123447No ratings yet
- Weekly Behavior Chart Editable FreeDocument8 pagesWeekly Behavior Chart Editable FreeChristine Joy Tanglao AsasNo ratings yet
- Treatments and Interventions for DyslexiaDocument7 pagesTreatments and Interventions for DyslexiaPenelope Danyelle Bohler CruzNo ratings yet
- Teacher Resource Levels Combined yDocument186 pagesTeacher Resource Levels Combined yapi-263662188No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReadingDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ReadingMarin Thompson100% (1)
- Sample Behavior District-Wide Evidence-Based Strategies 2fpractices For BehaviorDocument9 pagesSample Behavior District-Wide Evidence-Based Strategies 2fpractices For Behaviorapi-383588513100% (1)
- Disabilites NotebookDocument5 pagesDisabilites Notebookapi-649553832100% (1)
- RTLB Toolkit Guide to Effective PracticeDocument22 pagesRTLB Toolkit Guide to Effective PracticeEkaterina TrnblNo ratings yet
- Special Education Categories Guide for TeachersDocument16 pagesSpecial Education Categories Guide for TeachersFatima N. LabradorNo ratings yet
- Preventing Adverse Childhood Experiences (Aces) :: Leveraging The Best Available EvidenceDocument40 pagesPreventing Adverse Childhood Experiences (Aces) :: Leveraging The Best Available EvidenceJesse M. MassieNo ratings yet
- Strength Based Student ProfileDocument1 pageStrength Based Student Profileapi-544895801No ratings yet
- Referral For EvaluationDocument4 pagesReferral For Evaluationapi-272673186No ratings yet
- Setting Up A Classroom For 20 Preschool Children: Items QuantitiesDocument12 pagesSetting Up A Classroom For 20 Preschool Children: Items QuantitieschineduNo ratings yet
- Developing and Producing Educational T Oys: Year 10 Materials Technology Unit Outline 2011Document13 pagesDeveloping and Producing Educational T Oys: Year 10 Materials Technology Unit Outline 2011User140035No ratings yet
- Te Pikinga Ki Runga - Principles 26 PracticeDocument2 pagesTe Pikinga Ki Runga - Principles 26 PracticeHeleneNo ratings yet
- Edu356 Fba-2Document4 pagesEdu356 Fba-2api-302319740100% (1)
- Non Word TestDocument1 pageNon Word TestdaroksayNo ratings yet
- Iep Plaafps Information SheetDocument1 pageIep Plaafps Information Sheetapi-335203912No ratings yet
- Parent Handout Email Version 2012Document2 pagesParent Handout Email Version 2012juteauj626No ratings yet
- Elect 2007Document191 pagesElect 2007Erum Syed ImamNo ratings yet
- Response To Intervention Implications For The Proficiency of Early Childhood SpecialDocument8 pagesResponse To Intervention Implications For The Proficiency of Early Childhood Specialapi-300522387No ratings yet
- Welcome To MindUPDocument4 pagesWelcome To MindUPVOLUNTARIA Grupo de VoluntáriosNo ratings yet
- The Incredible Years Parentling Program in Ireland A Qualitative Analysis of The Experience of Disadvantaged ParentsDocument16 pagesThe Incredible Years Parentling Program in Ireland A Qualitative Analysis of The Experience of Disadvantaged ParentsMyraChNo ratings yet
- Fba and PBSPDocument32 pagesFba and PBSPapi-313773740No ratings yet
- AUTISM 101: A Psychoeducational Intervention For Parents of Newly Diagnosed Children With Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument1 pageAUTISM 101: A Psychoeducational Intervention For Parents of Newly Diagnosed Children With Autism Spectrum DisorderAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Incredible Years Classroom Management Teacher Training Program Content Methods and ProcessDocument47 pagesThe Incredible Years Classroom Management Teacher Training Program Content Methods and ProcesscamcromanceNo ratings yet
- 8 SLD Considerations Document 2011Document59 pages8 SLD Considerations Document 2011Mac YmacNo ratings yet
- ESF Reading Scope and SequenceDocument6 pagesESF Reading Scope and SequenceStu LoweNo ratings yet
- Behaviour Tracking Form Template Fillable Form EecdDocument2 pagesBehaviour Tracking Form Template Fillable Form Eecdapi-249399814No ratings yet
- Hands, Feet, Body To Self Social StoryDocument8 pagesHands, Feet, Body To Self Social StoryHailey MichelleNo ratings yet
- Calmer-Classrooms-Guide - Professional Reading To Help Student UnderstandingDocument42 pagesCalmer-Classrooms-Guide - Professional Reading To Help Student Understandingapi-417829366No ratings yet
- Beat Dyslexia: Bk. 2: A Step-By-Step Multi-Sensory Literacy Programme - LiteracyDocument4 pagesBeat Dyslexia: Bk. 2: A Step-By-Step Multi-Sensory Literacy Programme - LiteracylorylecuNo ratings yet
- Social motivation theory of autism focuses on impaired reward processingDocument10 pagesSocial motivation theory of autism focuses on impaired reward processingChrysoula Gkani100% (1)
- Dibels 8 Benchmark K Scoring 2019Document16 pagesDibels 8 Benchmark K Scoring 2019api-424731280No ratings yet
- Parent Interview of Social FunctioningDocument2 pagesParent Interview of Social FunctioningMiyNo ratings yet
- Child Developmental MilestonesDocument11 pagesChild Developmental MilestonesLassanah KeitaNo ratings yet
- Collaborating With Children For Effective ProgrammingDocument14 pagesCollaborating With Children For Effective ProgrammingSally MengNo ratings yet
- Teaching PhilosophyDocument3 pagesTeaching Philosophyapi-356514016No ratings yet
- CICMH Mental Health Crisis Response On Campus ToolkitDocument34 pagesCICMH Mental Health Crisis Response On Campus ToolkitProyecto IMABIS100% (1)
- Common Questions About Oppositional Defiant Disorder - American Family PhysicianDocument12 pagesCommon Questions About Oppositional Defiant Disorder - American Family Physiciando lee100% (1)
- Cowen School Counseling PhilosophyDocument4 pagesCowen School Counseling Philosophyapi-249878488No ratings yet
- MockiepDocument12 pagesMockiepapi-214642370No ratings yet
- Guidance For Children and Young People With Social and Emotional and Behavioural DifficultiesDocument4 pagesGuidance For Children and Young People With Social and Emotional and Behavioural DifficultiesfionaphimisterNo ratings yet
- Writing Sel Based Learning Unit PlanDocument19 pagesWriting Sel Based Learning Unit Planapi-524241370100% (1)
- TALK MilestonesDocument10 pagesTALK MilestonesDEAN MIKO BULLONo ratings yet
- Defining Challenging Behavior by Milkyas SolomonDocument52 pagesDefining Challenging Behavior by Milkyas SolomonVerity SplendourNo ratings yet
- The Teacher's Guide to Intervention and Inclusive Education: 1000+ Strategies to Help ALL Students Succeed!From EverandThe Teacher's Guide to Intervention and Inclusive Education: 1000+ Strategies to Help ALL Students Succeed!No ratings yet
- Hass Presentation RecoveredDocument17 pagesHass Presentation Recoveredapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Mock Assessment and RationaleDocument4 pagesMock Assessment and Rationaleapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Assessment and Increased Achievement With ReferencesDocument6 pagesAssessment and Increased Achievement With Referencesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Creating Your Own Medallion StepsDocument1 pageCreating Your Own Medallion Stepsapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Summative Assess Whole UnitDocument2 pagesSummative Assess Whole Unitapi-361589918No ratings yet
- RationaleDocument3 pagesRationaleapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Wonka FPDDocument6 pagesWonka FPDapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Y4 Angles Sir CumferenceDocument3 pagesY4 Angles Sir Cumferenceapi-361589918No ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument3 pagesReflectionapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Presentation Lesson FPDDocument3 pagesPresentation Lesson FPDapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Mathematical Difficulties Essay 2Document8 pagesMathematical Difficulties Essay 2api-361589918No ratings yet
- Sample StrategyDocument1 pageSample Strategyapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Planning Template PromptedDocument1 pagePlanning Template Promptedapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Zoo ContentsDocument3 pagesZoo Contentsapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Investigation RubricDocument1 pageInvestigation Rubricapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Weebly 1science Fpd-Feathers Fur or LeavesDocument1 pageWeebly 1science Fpd-Feathers Fur or Leavesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Zoo PlanDocument1 pageZoo Planapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Weebly 5science Fpd-Feathers Fur or LeavesDocument1 pageWeebly 5science Fpd-Feathers Fur or Leavesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- 11 Animal Images Creative CommonsDocument6 pages11 Animal Images Creative Commonsapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Weebly 4science Fpd-Feathers Fur or LeavesDocument1 pageWeebly 4science Fpd-Feathers Fur or Leavesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Aim/Question of Investigation: Variables I Will Keep The Same (Measure) : Only Variable I Will ChangeDocument1 pageAim/Question of Investigation: Variables I Will Keep The Same (Measure) : Only Variable I Will Changeapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Debate Table ChecklistDocument1 pageDebate Table Checklistapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Weebly 3science Fpd-Feathers Fur or LeavesDocument1 pageWeebly 3science Fpd-Feathers Fur or Leavesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Weebly 2science Fpd-Feathers Fur or LeavesDocument1 pageWeebly 2science Fpd-Feathers Fur or Leavesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Word Wall Placement ChecklistDocument1 pageWord Wall Placement Checklistapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Design-Brief FinalDocument1 pageDesign-Brief Finalapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Word Doc TableDocument1 pageWord Doc Tableapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Weeblyscience Fpd-Feathers Fur or LeavesDocument5 pagesWeeblyscience Fpd-Feathers Fur or Leavesapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Teachmeet PD CertDocument1 pageTeachmeet PD Certapi-361589918No ratings yet
- Chromatography Viva Questions & Answers GuideDocument4 pagesChromatography Viva Questions & Answers GuidedhruvNo ratings yet
- EMship Course ContentDocument82 pagesEMship Course ContentBecirspahic Almir100% (1)
- Signals SyllabusDocument1 pageSignals SyllabusproNo ratings yet
- Week4.pdf 82849 1 1583836882000 PDFDocument17 pagesWeek4.pdf 82849 1 1583836882000 PDFsssmmm8No ratings yet
- Sid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd1.avi Sid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd2.aviDocument27 pagesSid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd1.avi Sid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd2.avisheena2saNo ratings yet
- Shukr Thankfulness To Allah Grade 12Document21 pagesShukr Thankfulness To Allah Grade 12Salman Mohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Júlia Morell Gagnum, Group 2BDocument9 pagesJúlia Morell Gagnum, Group 2BJulia Lena MorellNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Lifespan Development in Context A Topical Approach 1st Edition Tara L KutherDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Lifespan Development in Context A Topical Approach 1st Edition Tara L Kutherzoundsstriklegnth100% (49)
- Optimum Design of Cyclone Separator: SeparationsDocument5 pagesOptimum Design of Cyclone Separator: SeparationsJeyakumar RajaNo ratings yet
- 5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsDocument5 pages5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsSendhil RevuluriNo ratings yet
- Sylviane Granger, Gaëtanelle Gilquin, Fanny Meunier - The Cambridge Handbook of Learner Corpus Research-Cambridge University Press (2015)Document618 pagesSylviane Granger, Gaëtanelle Gilquin, Fanny Meunier - The Cambridge Handbook of Learner Corpus Research-Cambridge University Press (2015)Joyce CheungNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Le Juge Administratif Et Le Droit InternationalDocument8 pagesDissertation Le Juge Administratif Et Le Droit InternationalPayPeopleToWritePapersWestValleyCityNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ErgonomicsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Ergonomicsnatrix029No ratings yet
- SF3 - 2022 - Grade 8 SAMPLEDocument2 pagesSF3 - 2022 - Grade 8 SAMPLEANEROSE DASIONNo ratings yet
- Akhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihDocument44 pagesAkhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihSauri ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- English Language (1122)Document26 pagesEnglish Language (1122)TD X Mzinda100% (1)
- Scitech 101 Course Pack Final Revision Edited 8-11-2021Document111 pagesScitech 101 Course Pack Final Revision Edited 8-11-2021Zendee Jade MaderaNo ratings yet
- The Experiences and Challenges Faced of The Public School Teachers Amidst The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study in The PhilippinesDocument21 pagesThe Experiences and Challenges Faced of The Public School Teachers Amidst The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Study in The PhilippinesDE LOS REYES MARY ZEALANo ratings yet
- 4-23-18 DktEnt 138 Petitions Rehearing Enbanc PDFDocument103 pages4-23-18 DktEnt 138 Petitions Rehearing Enbanc PDFArek FressadiNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Technician: Semiconductor ComponentsDocument253 pagesElectronics Engineering Technician: Semiconductor Componentsnagsanthosh3No ratings yet
- QDEGNSWDocument2 pagesQDEGNSWSnehin PoddarNo ratings yet
- SkipTheFlip Physical PDFDocument230 pagesSkipTheFlip Physical PDFSebi100% (4)
- Case 6 Solved by Iqra's GroupDocument11 pagesCase 6 Solved by Iqra's GroupIqra -Abdul ShakoorNo ratings yet
- Writing Essays B1Document6 pagesWriting Essays B1Manuel Jose Arias TabaresNo ratings yet
- BCG X Meta India M&E 2023Document60 pagesBCG X Meta India M&E 2023Никита МузафаровNo ratings yet
- Ass. 2 English Revision WsDocument3 pagesAss. 2 English Revision WsRishab ManochaNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract ActDocument26 pagesThe Indian Contract ActJinkalVyas100% (2)
- Determinants of Cash HoldingsDocument26 pagesDeterminants of Cash Holdingspoushal100% (1)
- A Study on Student Budgeting HabitsDocument41 pagesA Study on Student Budgeting Habitsbornak BonalasNo ratings yet
- Aspen FLARENET Getting StartedDocument62 pagesAspen FLARENET Getting StartedAde Nurisman100% (7)