Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hematology Diseases
Uploaded by
Leonida Dalugdog0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesSummarized hematology reviewer
Original Title
hematology Diseases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSummarized hematology reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesHematology Diseases
Uploaded by
Leonida DalugdogSummarized hematology reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
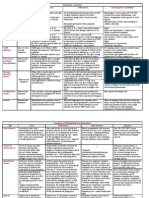
Myeloid Line
Toxic Granulation Persistent staining of primary granules
Toxic Vacuolation Indicates phagocytic activity and deganulation
Dohle bodies RNA remnants
Shift to the Left increase myelo, meta, stabs @ pb
Functional Disorder
Chronic Granulomatous Dse granules fail to degranulate
Chediak- Higashi Syndrome abnormal fusion of primary and secondar granules
Nuclear Disorder
Hypersegmention
Pelger-Huet Anomaly nucleus does not mature past 2 lobes, peanut shaped
Pseudo Pelger-Huet nucleus appears round
Cytoplasmic
May-Hegglin Anomaly has crystalline cigar-shaped Dohle-like incusions
Alder-Reily Anomaly azurphilic granules in cytoplasm of all or only one cell line
Lipid Storage Disorders for Monocytes
Gauchers Disease deficiency in glucocerebrosidase causing glucocerebroside to accumulate
Niemann- Pick Disease deficiency in sphingomyelinase causing sphingomyelin to accumulate in
Sea-blue Histiocytosis unknown deficiency. Sea-blue colored macrophages
Non-malignant Lymphocytosis
Infectious mononucleosis Epstein-Barr virus infects B cells ; (+) heterophile Ab; T lymph attacks affected
B cells
Cytomegalovirus symptoms same with Infectious mono but (-) heterophile Ab
Infectious lymphocytosis assoc. With adenovirus and Coxsackie A
Acute Lymphoproliferative Disorders
FAB L1 most common childhood leuk. best prognosis, small,homogenous, most ALLs
FAB L2 most common in adults, large blasts w/ heterogenous appearance
FAB L3 lympoblasts are uniform and large, w/ prominent nucleoli, infects B-cell line
poor prognosis. Leukemic phase of Burkitt lymphoma
Burkitt Lyphoma High-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma phase, presents w/ abd. Mass,
t(8:14) rearrangement of MYC oncogene
Chronic Lymphoproliferative DO
Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in adults over 60yo. Hypercellular bm w/ abs. Lymphocytosis, (B-cell Malig.)
Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL) massive splenomegaly w/ pancytopenia. Lymphs show hair-like projections
Prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL) >100 x10/L lymphocytosis w/ many prolymphs and thrombocytopenia
Other Lymphoid malignancies
Multiple Myeloma b-cells produce excessive IgG/IgA with decrease prod. Of other globulins.. Inc.
bld. Viscosity with M-spike on gamma region on electrophoresis. Bence-Jones
CHONS in urine.
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia same with MM except excessive IgM with lymphadenopathy and hepato-
splenomegaly
Hodgkin Lymphoma malignant cells in lymphatic tissue. Reed-Sternberg cells(B-cell lineage)
Hon-Hodgkin Lymphoma without RS cells
Mycosis fungoides T/NK cell neoplasm. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; Sezary Syndrome
Acute Myeloproliferative Disorders
Acute myelogenous leukemia
FAB MO blasts exhibit myeloid markers but stain negatively
FAB M1 AML without maturation. 90% or more marrow myeloblasts
FAB M2 AML with maturation. <90% m marrow myeloblasts
FAB M3 Acute promyelocytic leuk; DIC (promyelocytes are procoagulant) w/ auer rods
FAB M4 Acute myelomonocytic leukemia
FAB M5 Acute monocytic leukemia
FAB M6 (Di Guglielmo syndrome) Acute erythroleukemia; >50 dysplastic marrow normoblasts
FAB M7 Acute megakaryocytic leuk. Blasts have cytoplasmic. blebs, w/ pancytopenia
Bilineage Leukemia 2 cell populations, myeloid and lymphoid
Biphenotypic leukemia when myeloid and lymphoid Ag are expressed on the same cell
Chronic Myeloproliferative Disorders
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia proliferation of granulocytes, Philapdelphia (t;22) chromosome
Essemtial Thrombocythemia proliferaton of megakaryocytes; plt count >1000
Polycythemia Vera increase in all lines esp. Red cells despite decrease erythropoietin
Chronic Idiopathic myelofibrosis proliferation of erythroid, myeloid, granulocytic & megakaryocytc precursors
in bm with dyspoiesis; progressive marrow fibrosis
Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Refractory Anemia anemia that is not responsive to therapy
Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia the only one that presents with leukocytosis
Refractory Anemia w/ excess blasts trilineage cytopenias common. No abs. Monocytosis
Hemolytic Anemia due to Extrinsic/Non-Immune Defects (normocytic, normochromic)
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemias
a. DIC sytemic clotting due to 1) act. of coag. Cascade 2) fibrin in vessels
b. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in children following gastrointestinal inf. ; renal damaga
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Pur. def. In enzyme ADAMTS13 resp. for breakdown of vWF
March hemoglobinuria forceful contact of body with hard surfaces. (sa mga players)
Hemoglobinopathies
Sickle cell Dse. Valine replaces glutamic acid @ 6th position on both beta chains
Sicke Cell Trait Valine replaces glutamic acid @ 6th position on one beta chain
Hgb C Lysine replaces glutamic acid @ 6th position on both beta chains
Hgb SC One sickle gene from one parent and one Hgb C gene fro another parent
Hgb E Lysine replaces glutamic acid @ 26th position on beta chain
Hgb D Glycine replaces glutamic acid @ 121st position on beta chains
Thallasemias
Major B/Homozygo/Cooley anemia absence of both beta chains
Minor B/heterozyhous absence of one beta chain
Major A/ Hydrops fetalis absence of four alpha chains; 80% Hbg Barts(γ4), incompatible w/ life
Hgb H Dse Three alpha genes are deleted
Minor/ trait two alpha genes deleted.
Silent carrier one alpha gene deleted
Dse. Assoc. w/ the Vascular System
Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia thin vessel walls cause mucous membrane bleeding
Ehlers- Danlos abn collargen prod. Causing hyperelastic skin and joint abn
Hereditary Adhesion Defects
vonWillebrand Dse lack vW factor unabling plts to adhere to collagen
Bernard-Soulier lack glycoprotein Ib receptor
Hereditary Aggregation & Clot Retraction
Glanzmann Thrombasthenia lack glycoprotein Iib/IIIa, the fibrinogen binding receptor; lack of throm-
basthenin/actomyosin causes clot-retraction defect
Storage Pool Defects
Gray-platelet syndrome large plt, thrombocytopenia, and absenc of alpha ganules
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome small plts, thrombocytopenia and decreased alpha granules & dense bodies
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome lacks dense body granules. Px exhibits oculocutaneous albinism
QUANTITATIVE Platelet Disorders
Primary Thrombocytosis uncontrolled malignant proliferation, NOT in response to thrombopoietin
>1000 x 10^9 /L
Secondary (Reactive) Thrombocytosis increased plt prod. In response to thrombopoietin : <1000 x 10^9 /L
You might also like
- Hema PointrDocument4 pagesHema PointrLeonida DalugdogNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative DisorderDocument36 pagesMyeloproliferative DisorderKalpana ShahNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis and Clinical ApplicationDocument47 pagesHaemopoiesis and Clinical ApplicationPrashantTiwariNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledSandeep m rNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - LecturioDocument17 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - LecturioCornel PopaNo ratings yet
- Summary of All AnemiaDocument2 pagesSummary of All Anemiabenlarsena93% (14)
- SBRC HematologyOncology 2Document80 pagesSBRC HematologyOncology 2dalia khamoNo ratings yet
- Heme Malignancy Review 2020Document163 pagesHeme Malignancy Review 2020Anna StacyNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia DiagnosisDocument4 pagesChronic Myeloid Leukemia DiagnosisKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Sh. Silmi MSC Haematology, FIBMSDocument63 pagesAhmad Sh. Silmi MSC Haematology, FIBMSHadi AdamNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis and Clinical ApplicationDocument42 pagesHaemopoiesis and Clinical Applicationtamer273No ratings yet
- SGL 2 (Hemolytic Anemia & Hemoglobinopathies)Document53 pagesSGL 2 (Hemolytic Anemia & Hemoglobinopathies)raman mahmudNo ratings yet
- Benign Disorders of The WBCsDocument2 pagesBenign Disorders of The WBCsHo Yong WaiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Leukaemia 111Document15 pagesChronic Leukaemia 111Razib HasanNo ratings yet
- Vasile Musteata, MD, PHD, MPH, Associate Professor Discipline of Hematology, State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "N. Testemitanu"Document49 pagesVasile Musteata, MD, PHD, MPH, Associate Professor Discipline of Hematology, State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "N. Testemitanu"AlbuNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Leukemia FinalDocument68 pagesAcute and Chronic Leukemia FinalHannah LeiNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Disorders 18th Oct 2010Document62 pagesMyeloproliferative Disorders 18th Oct 2010saint5470No ratings yet
- MDT 100 Study GuideDocument7 pagesMDT 100 Study GuideSatori NoëlNo ratings yet
- Lymphadenitis Classification and EtiologyDocument43 pagesLymphadenitis Classification and EtiologyMuhammad Harmen Reza SiregarNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia: Dimas Bayu Tutik Harjianti A. FachruddinDocument41 pagesAcute Leukemia: Dimas Bayu Tutik Harjianti A. FachruddinFI 034 Mega Rahmawati MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Disorders of Leukocytes: Supachai A. Basit, RMT, PHDDocument109 pagesMalignant Disorders of Leukocytes: Supachai A. Basit, RMT, PHDChatie PipitNo ratings yet
- The LeukemiasDocument52 pagesThe Leukemiasمصطفي خندقاوي100% (1)
- WBC DisordersDocument114 pagesWBC DisordersNdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- 20 Lymphomas and LeukemiastextsDocument40 pages20 Lymphomas and LeukemiastextsArief SeptianurNo ratings yet
- Chronic LeukemiasDocument26 pagesChronic LeukemiasNasser SalahNo ratings yet
- 3-T and Sicke Cell Disease 2016Document68 pages3-T and Sicke Cell Disease 2016ThaveeshaLindsayWhiteNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoid Leukemia (Airway Management)Document48 pagesAcute Lymphoid Leukemia (Airway Management)Ankita SamantaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Smear Examination PDFDocument91 pagesPeripheral Smear Examination PDFtufis02No ratings yet
- Acute Leukaemia-Update: DR Niranjan N. RathodDocument89 pagesAcute Leukaemia-Update: DR Niranjan N. RathodratanNo ratings yet
- LYMPH NODE CANCERDocument190 pagesLYMPH NODE CANCERNinna Isabel VictorioNo ratings yet
- The Complete Hematopathology Guide Web Sample Long1 PDFDocument11 pagesThe Complete Hematopathology Guide Web Sample Long1 PDFAmina RichardsonNo ratings yet
- WHO 2022 For Undergraduate 2022-2023Document10 pagesWHO 2022 For Undergraduate 2022-2023DING TIAN YUNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument171 pagesHematologyDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- Hematolocical Clonal Disorders (Malignancies) : Lympho-Proliferative Disorders Myeloid DisordersDocument50 pagesHematolocical Clonal Disorders (Malignancies) : Lympho-Proliferative Disorders Myeloid DisordersAngelica CoppolaNo ratings yet
- WaloDocument67 pagesWaloyepNo ratings yet
- MRCPass Notes For MRCP 1 - HEMATOLOGYDocument9 pagesMRCPass Notes For MRCP 1 - HEMATOLOGYsabdali100% (1)
- Leukemias & Lymphomas - HY USMLEDocument87 pagesLeukemias & Lymphomas - HY USMLEMatt McGlothlinNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Disorders (Bhs Inggris)Document57 pagesMyeloproliferative Disorders (Bhs Inggris)Denny DedenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsDocument16 pagesChapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsOmar100% (1)
- Blood DiseasesDocument22 pagesBlood Diseases96k7z7khz7No ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of LymphomasDocument17 pagesPa Tho Physiology of LymphomasKent MasadoNo ratings yet
- BoardReviewPart2B MalignantHemePathDocument207 pagesBoardReviewPart2B MalignantHemePathMaria Cristina Alarcon NietoNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lecture 2nd CourseDocument128 pagesPathology Lecture 2nd CourseAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- MK Hematology-LeukemiasDocument35 pagesMK Hematology-LeukemiasMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia Types and TreatmentDocument22 pagesAcute Leukemia Types and TreatmentFelix Allen100% (1)
- Hodgkins and Non Hodgkins LymphomaDocument5 pagesHodgkins and Non Hodgkins LymphomakakuNo ratings yet
- Chronic Leukemia: Rahmawati Minhajat A. Fachruddin BenyaminDocument24 pagesChronic Leukemia: Rahmawati Minhajat A. Fachruddin BenyaminMJ PutraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Leukaemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Leukaemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentArnab Ghosh100% (1)
- Pathology of Castleman DiseaseDocument16 pagesPathology of Castleman DiseaseAbsalom MwazhaNo ratings yet
- Learnin ObjectiveDocument19 pagesLearnin ObjectivemadeNo ratings yet
- Approach To HemoglobinopathiesDocument37 pagesApproach To Hemoglobinopathiesabo slo0hNo ratings yet
- Curs5 Hematologie AnvDocument59 pagesCurs5 Hematologie AnvRaluca PăunaNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnaemiaDocument60 pagesHemolytic AnaemiaAthul GurudasNo ratings yet
- Disease Chart I3-1 (Emmeline)Document20 pagesDisease Chart I3-1 (Emmeline)ivankcurryNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia: Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument52 pagesAcute Leukemia: Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and ManagementJamilNo ratings yet
- Neonatal DXDocument10 pagesNeonatal DXkendall_polirer_9056No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Diseases and Thalasemia Asma2Document60 pagesSickle Cell Diseases and Thalasemia Asma2Female calmNo ratings yet
- 2010-11meridian Catalog6aDocument16 pages2010-11meridian Catalog6aJuanPerez555No ratings yet
- EENT Exam 2Document3 pagesEENT Exam 2Beda MalecdanNo ratings yet
- GP Exam Questions on Infectious DiseasesDocument34 pagesGP Exam Questions on Infectious DiseasesRichard EdgeNo ratings yet
- Common Viral Infections in The Oral Cavity: 1. Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis DNA VirusDocument6 pagesCommon Viral Infections in The Oral Cavity: 1. Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis DNA VirusChristineMartinNo ratings yet
- GBS Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument4 pagesGBS Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentJohn Paul NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Mono nUkLeosisDocument1 pageMono nUkLeosisTitis Mustika HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacy Practice and Simulation: PHAR456Document82 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacy Practice and Simulation: PHAR456Hassan El HajjNo ratings yet
- MBChB Year 4 & 5 Past Papers + Answers for Respiratory, Gastrointestinal, Neurology and MoreDocument172 pagesMBChB Year 4 & 5 Past Papers + Answers for Respiratory, Gastrointestinal, Neurology and MoreHariharan NarendranNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Virology NotesDocument7 pagesMtap - Virology NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Vircell Product Catalogue 2011Document20 pagesVircell Product Catalogue 2011Yeni AzamarNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases EmqDocument24 pagesInfectious Diseases Emqfrabzi100% (1)
- Chronic Fatigue SyndromeDocument3 pagesChronic Fatigue Syndromereinfabz13No ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases of Oral CavityDocument21 pagesInfectious Diseases of Oral CavityhunarsandhuNo ratings yet
- Pyrexia of Unknown OriginDocument55 pagesPyrexia of Unknown OriginsanjeevNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy CuresDocument18 pagesHomeopathy CureschampakNo ratings yet
- Athletic Physical and Consent FormsDocument4 pagesAthletic Physical and Consent FormsJohnny TuNo ratings yet
- Herpetic Mucocutaneous Infections: HSV (HSV 1 & 2) & VZVDocument32 pagesHerpetic Mucocutaneous Infections: HSV (HSV 1 & 2) & VZVJaneNo ratings yet
- NBME 3 BLOCK 1-4 (With Answers)Document204 pagesNBME 3 BLOCK 1-4 (With Answers)sarah50% (2)
- The Mononucleosis SyndromesDocument9 pagesThe Mononucleosis SyndromesbencleeseNo ratings yet
- Blood CancerDocument22 pagesBlood CanceranjanaNo ratings yet
- Non Malignant Reactive Disorders of LymphocytesDocument8 pagesNon Malignant Reactive Disorders of LymphocytesGilo IlaganNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument98 pagesOral RevalidaJay ArNo ratings yet
- Herpes Viruses LectureDocument46 pagesHerpes Viruses Lectureapi-19969058100% (1)
- 7 Natural Remedies For Epstein Barr VirusDocument40 pages7 Natural Remedies For Epstein Barr VirusDraganescu Violeta33% (3)
- CytomegalovirusDocument25 pagesCytomegalovirustummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Icd - 10 (2017)Document4,278 pagesIcd - 10 (2017)Rakhmat DarainiNo ratings yet
- LimfadenopatiDocument7 pagesLimfadenopatiLestari Santika DewiNo ratings yet
- 01.02 - Organizing Knowledge and InformationDocument12 pages01.02 - Organizing Knowledge and InformationDaphne DunneNo ratings yet
- Viral Infections of HumansDocument89 pagesViral Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet
- EBV Infection and Infectious MononucleosisDocument70 pagesEBV Infection and Infectious Mononucleosisminerva_stanciuNo ratings yet