Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Sample Papers For Class 11 Physics SET C
Uploaded by
ShivangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Sample Papers For Class 11 Physics SET C
Uploaded by
ShivangCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Physics SET C
1. Convert 1 kWh in joule. (HOTS)
2. Define thrust ?
3. What is the equation and work done in an adiabatic process ?
4. What is odour ?
5. Which of the following conditions is not sufficient for S.H.M. and why ?
(i) acceleration ∝ displacement.
(ii) restoring force displacement. (HOTS)
6. “A more precise measurement has to be more accurate.” Comment.
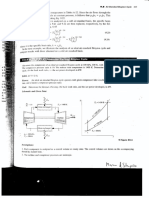
7. What can be represented by the graph given below, where h is height and v is velocity ?
8. The sum and difference of two vectors are perpendicular to each other. Prove that the vectors are equal in
magnitude.
Or
Why a horse has to apply more force to start a cart than to keep it moving ? Explain.
9. (a) What is the physical significance of M.I. ?
(b) Define M.I. of a body rotating about an axis.
10. Define undamped and damped oscillations.
11. In an experiment, on determining the density of a rectangular block, the dimensions of the block are
measured with a vernier caliper (with a least count of 0.01 cm) and its mass is measured with a beam
balance of least count 01 g. How do we report our result for the density of the block ? (HOTS)
12. A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 291 ms-1.
(a) What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball ?
(b) What is the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point of its motion ?
(c) Choose the x = 0 m and t = 0 s to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point, vertically
downward direction to the positive direction of x-axis and give the signs of position, velocity and
acceleration of the ball during its upward and downward motion.
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
(d) To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player’s hand? (Take g =
9.8 ms-2 and neglect air resistance)
13. The celling of a long hall is 25 m high. What is the maximum horizontal distance that a ball thrown with
a speed of 40 ms-1 can go without hitting the celling of the hall ?
14. Two bodies A and B of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth horizontal surface are tied
to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to (a) A, (b) B along the direction of
string. What is the tension in the string in each case ?
15. A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with speed 200 ms-1 and angle 30° with the normal
and rebounds with the same speed. Is momentum conserved in the collision ? Is the collision elastic or
inelastic ?
16. Show that centre of mass of a system of two particles lies on the straight line joining them.
17. Suppose there existed a planet that went around the sun twice as fast as the earth. What would be its
orbital size as compared to that of earth.
18. Figure (a) shows a spring of force constant K clamped rigidly at one end and a mass m attached to its
free end. A force applied at the free end stretches the spring.
Figure (b) shows the same spring with both ends free and attached to a mass m at either end. Each end of the
spring in figure (b) is stretched by the same force F.
(i) What is the maximum extension of the spring in the two cases?
(ii) If the mass in figure (a) and the two masses in fig. (b) are released free. What is the period of oscillations
in each case?
Or
What are nodes and antinodes ? Do they coincide with pressure nodes and antinodes ? In terms of X, what is
the separation of a node from the nearest antinode ? What is the phase difference between points separated
by X/10 in stationary waves ?
19. Define Pascal law and give its particle applications.
20. (a) Define stream line.
(b) Write any two properties of streamlines. (KVS 2008)
21. Give a brief account of Joule’s experimant ?
22. (a) State second law of thermodynamics.
(b) What is coefficient of performance of a refrigerator ?
23. The Physics Teacher of class XI has assigned the work of finding the resultant spring constant when two
springs of spring constants k1, k2 are joined in series. Two students Sabita and Shirin. Sabita made a
theoretical study as well as verified experimentally. Whereas Shirin could not complete the work. When the
teacher enquired the next day Sabita could give the answer. Whereas Shirin could not :
(a) comment upon the qualities of Sabita.
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
Bookmark – LearnCBSE.in
Open a Bookmark – LearnCBSE.in
1. On your computer, open Chrome.
2. At the top right, (3 dots) click More Bookmarks.
3. Find and click on your favorite LearnCBSE.in Bookmark.
To open bookmarks faster, use the bookmarks bar. Your bookmarks will show under the address bar. Click
a bookmark to open it. To turn the bookmarks bar on or off, click More Bookmarks Show Bookmarks
Bar.
How to Search in Google, to access NCERT Solutions Faster.
• In Google Assistant Voice Search LearnCBSE.in to Get Best NCERT Solutions
• Add to Favorites - Bookmark in Google browser to Access Faster
• In Google Search bar You can search
Ex: (i) LearnCBSE.in Class 11 Maths ch 1 Ex 1.1 Q1,
(ii) LearnCBSE.in Class 11 Physics,
(iii) Any Question (LearnCBSE.in + Type your Question in Google Search bar)
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
(b) Two springs are joined in series and connected to a mass m as shown in fig. If spring constants are k1
and k2, calculate the period of oscillation of mass m. (V.B.Q.)
24. State and prove parallelogram law of vector addition. Discuss some special cases.
Or
(a) Discuss the problem of a swimmer, who want to cross the river in the shortest time.
(b) Define null vector. What are its properties and physical significance.
25. Prove the relation between torque and momentum of inertia. (HOTS)
Or
Derive an expression for K.E. of rotation.
26. By using Stoke’s law derive an expression of terminal velocity. On what factors it depends ?
Or
Explain surface energy. Establish its relation with surface tension.
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
LearnCBSE.in Class 11 Physics
NCERT Exemplar Problems with
NCERT Solutions CBSE Notes
Solutions
Chapter 1 Physical World Physical World Chapter 1: Units and Measurements
Chapter 2 Units and Measurements Units and Measurements Chapter 2: Motion in a Straight Line
Chapter 3 Motion in a Straight Line Motion in a Straight Line Chapter 3: Motion in a Plane
Chapter 4 Motion in a plane Motion in a plane Chapter 4: Laws of Motion
Chapter 5 Laws of motion Laws of motion Chapter 5: Work, Energy and Power
Chapter 6: System of Particles and
Chapter 6 Work Energy and power Work Energy and power
Rotational Motion
Chapter 7 System of particles and System of particles and
Chapter 7: Gravitation
Rotational Motion Rotational Motion
Chapter 8: Mechanical Properties of
Chapter 8 Gravitation Gravitation
Solids
Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties Of Chapter 9: Mechanical Properties of
Mechanical Properties Of Solids
Solids Fluids
Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties Of Chapter 10: Thermal Properties of
Mechanical Properties Of Fluids
Fluids Matter
Chapter 11 Thermal Properties of matter Thermal Properties of matter Chapter 11: Thermodynamics
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Chapter 12: Kinetic Theory
Chapter 13 Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory Chapter 13: Oscillations
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Chapter 14: Waves
Chapter 15 Waves Waves
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
CBSE Class 11 Physics Practical Lab Manual
LearnCBSE.in HC Verma Solutions
Concept 33: Thermal and Chemical
Concept 1: Introduction to Physics Concept 17: Light Waves
Effects of current
Concept 2: Physics and Mathematics Concept 18: Geometrical Optics Concept 34: Magnetic field
Concept 3: Rest and Motion: Concept 35: Magnetic field due to a
Concept 19: Optical Instruments
Kinematics current
Concept 20: Dispersion and
Concept 4: The Forces Concept 36: Permanent Magnets
Spectra
Concept 37: Magnetic properties of
Concept 5: Newton’s Laws of Motion Concept 21: Speed of Light
matter
Concept 6: Friction Concept 22: Photometry Concept 38: Electromagnetic Induction
Concept 23: Heat and
Concept 7: Circular Motion Concept 39: Alternating current
Temperature
Concept 24: Kinetic Theory of
Concept 8: Work and Energy Concept 40: Electromagnetic Waves
gases
Concept 9: Centre of Mass, Linear Concept 41: Electric Current through
Concept 25: Calorimetry
Momentum, Collision gases
Concept 26: Law of Concept 42: Photoelectric Effect and
Concept 10: Rotational Mechanics
thermodynamics Wave Particle Duality
Concept 27: Specific heat Concept 43: Bohr’s Model and Physics of
Concept 11: Gravitation
Capacities of gases the Atom
Concept 12: Simple Harmonic Motion Concept 28: Heat Transfer Concept 44: X-rays
Concept 29: Electric field and Concept 45: Semiconductors and
Concept 13: Fluid Mechanics
potential Semiconductor Devices
Concept 14: Some Mechanical
Concept 30: Gauss’s Law Concept 46: The Nucleus
Properties of Matter
Concept 15: Wave Motion and Waves Concept 47: The Special Theory of
Concept 31: Capacitors
on a String Relativity
Concept 32: Electric current in
Concept 16: Sound Waves
conductors
LearnCBSE.in JEE Main Physics
Units , Dimensions and Errors Gravitation Electromagnetism
Practical Physics Properties of Matter Electromagnetic Induction
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
Kinematics Heat And Thermodynamics Optics
Laws of Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Modern Physics
Work ,Energy And Power Waves Semiconductor Devices
Centre of Mass, Momentum & Impulse Electrostatics
Rotational Motion Current Electricity
LearnCBSE.in Class 11
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Hindi
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Hindi Aroh (आरोह
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics भाग 1)
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Hindi Vitan (वितान
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry भाग 1)
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English Woven Words Short
Stories NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English Woven Words Essay NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English Woven Words Poetry Class 11 Indian Economic Development
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English Snapshots (Python)
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English Hornbill
CBSE Sample Papers NCERT Solutions LearnCBSE.in
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 02 Common Converstion FactorsDocument1 page02 Common Converstion FactorsDarleen PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Eldom Fisa TehnicaDocument1 pageEldom Fisa TehnicadoggovyNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication and Testing of A Steam Generator: November 2010Document78 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Testing of A Steam Generator: November 2010Vignesh AlagesanNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Heat and Temperature ConceptsDocument37 pagesModule 13 Heat and Temperature ConceptsMelvin Cabonegro100% (2)
- Eng Komolafe Thermodynamics Lecture Note. (Module 1-4) DocxDocument35 pagesEng Komolafe Thermodynamics Lecture Note. (Module 1-4) DocxOyedotun Tunde100% (1)
- Advanced Thermodynamics: OutlineDocument10 pagesAdvanced Thermodynamics: Outlinexx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxNo ratings yet
- Continuous Distillation Lab ExperimentDocument3 pagesContinuous Distillation Lab ExperimentHusna Hafiza Bt. R.AzamiNo ratings yet
- CHM 650: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications To ChemistryDocument2 pagesCHM 650: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications To ChemistrySorayaNo ratings yet
- Oil Cooler (LT Cooler - Water Cooled Type) : NomenclatureDocument3 pagesOil Cooler (LT Cooler - Water Cooled Type) : NomenclatureEko hari PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Conduction MCQsDocument4 pagesConduction MCQsyogesh shindeNo ratings yet
- DATA SHEET VCM Condenser No 2Document1 pageDATA SHEET VCM Condenser No 2nabila OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Da Manual PDFDocument4 pagesDa Manual PDFJer SowNo ratings yet
- Fisa Tehnica CMTDocument2 pagesFisa Tehnica CMTAnonymous ZPTCAz9No ratings yet
- 09-Ap 1Document5 pages09-Ap 1mostafaabdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Ignitability and Explosibility of Gases and VaporsDocument230 pagesIgnitability and Explosibility of Gases and VaporsKonstantinKot100% (3)
- CPT-325 - 13 - Model of A 3-Zone FW HeaterDocument21 pagesCPT-325 - 13 - Model of A 3-Zone FW HeaterJeeEianYannNo ratings yet
- ME 307 2013-2014 Fall Week 7th RecitationDocument14 pagesME 307 2013-2014 Fall Week 7th RecitationYeiner MachadoNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Quick Calculation of Refrigeration Load For RoomsDocument3 pagesHVAC - Quick Calculation of Refrigeration Load For Roomswisnu_bayusaktiNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT - ConvectionDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT - ConvectionShiva DasNo ratings yet
- 526134ijsetr1276 445 PDFDocument6 pages526134ijsetr1276 445 PDFkhurramNo ratings yet
- MG Cu yDocument13 pagesMG Cu yAnonymous 73gEYyEtLNo ratings yet
- TIPERs Sensemaking Tasks For Introductory Physics 1st Edition Hieggelke Solutions Manual 1Document74 pagesTIPERs Sensemaking Tasks For Introductory Physics 1st Edition Hieggelke Solutions Manual 1Arturo Newman100% (35)
- Performance Analysis of The Vehicle Diesel EngineDocument20 pagesPerformance Analysis of The Vehicle Diesel EnginePHI TRUONGNo ratings yet
- Solar Air Conditioning ThesisDocument7 pagesSolar Air Conditioning Thesisjjvveqvcf100% (2)
- Application 14101 PDFDocument5 pagesApplication 14101 PDFElenaPeñarandaNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM CombustionDocument5 pagesFINAL EXAM CombustionJepoy torresNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument43 pagesFluid MechanicsVinodh Kumar LNo ratings yet
- ALPEMA Standards Rev1Document8 pagesALPEMA Standards Rev1nattusharanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - FullDocument68 pagesUnit-1 - FullMohammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency in BuildingsDocument72 pagesEnergy Efficiency in Buildingsahtin618100% (1)