Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lower Limb Orthoses Guide
Uploaded by
mohit durgapalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lower Limb Orthoses Guide
Uploaded by
mohit durgapalCopyright:
Available Formats
22
Lower Limb Orthoses
John R. Fox, William Lovegreen
KEY POINTS
• Lower limb orthoses are the most commonly prescribed type of • Advances in both material science and orthotic design have
orthoses, with ankle–foot orthoses making up 26% of all orthoses resulted in improved functional outcomes for individuals who
provided in the United States,4 and are either prefabricated or require lower limb orthoses.
custom made.
• Lower limb orthoses create biomechanical effects on joints
adjacent to the orthosis.
are also required with high-heel shoes, flip flops, and cowboy boots.
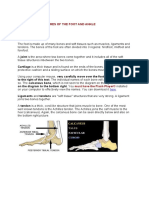
FOOT ORTHOSES
After fitting the patient using the proper shoes, the orthotist reassesses
Foot orthoses (FO) are like the tires on an automobile: They provide the patient’s gait to determine whether goals for alignment, posture,
a critical, biomechanical contact point for the human body, and they pain, and corrections to the foot–ankle complex are being met. Education
can be helpful to correct problems in the foot, knee, hip, and spine. and follow up is key to a successful outcome.11 If the foot–ankle alignment
Prescription foot orthoses are divided into two categories as defined is off biomechanically, it will create a problem with the knee, hip, and
by the American Podiatric Medical Association.2 spine. Returning to the automobile analogy, a bad alignment means
1. Functional orthotics are designed to control abnormal motion. They worn tires, ball joints, and suspension (and a lot of money spent on
may be used to treat foot pain caused by abnormal motion; they replacement parts).17
can also be used to treat injuries such as shin splints or tendinitis.
Functional orthotics are usually crafted of a semirigid material such
as plastic or graphite.
ANKLE–FOOT ORTHOSES
2. Accommodative orthotics are softer and meant to provide additional As the name implies, ankle–foot orthoses (AFOs) are used for problems
cushioning and support. They can be used to treat diabetic foot dealing with foot and ankle issues that are either biomechanical or
ulcers, painful calluses on the bottom of the foot, and other uncom- neurophysiologic in nature. These orthoses include any device that
fortable conditions. passes across the ankle joint but stays distal to the knee joint. Such
Among the two types are custom and noncustom orthoses.5 Custom orthoses are used for diagnoses that range from ankle sprains to stroke
foot orthoses start with a thorough examination of the foot–ankle management. This type of brace could potentially be used for any
complex by a health professional to determine limitations in range of neuromuscular condition requiring support or assistance at the level
motion in both the forefoot and the rear foot, including calcaneal talus of the foot and ankle.
alignment. Once this is done, a gait assessment is performed without AFOs consist of myriad materials, no longer just metal and leather
shoes and socks on, and if there are areas on the foot that need to be (conventional) or plastic. Many current AFO designs comprise a hybrid
unloaded, this is noted. An impression is taken using step-in foam, cast, of different materials. This includes carbon graphite, various plastics,
or a scan (with an optical digitizer) with the foot held in subtalar metal, and various materials for padding. Like FOs, AFOs come in two
neutral. The foot orthotic is made from the positive model of this varieties: custom made for the individual patient or prefabricated (off
impression, and the choice of materials depends on the pathology that the shelf).
is being corrected. Any other type of foot orthosis is noncustom. This The custom AFO builds up from the foot orthosis and is attached
includes the type patients may receive from various outlets claiming to either a shoe or a foot plate (foot orthotic) that is placed into the
custom fit and the type from the big box stores with optical scanners. shoe. It may or may not have an ankle joint that will control ankle
There are many minor foot problems for which noncustom foot orthoses motions in several planes. These motions include plantarflexion,
provide appropriate treatment.3 dorsiflexion, inversion (pronation), and eversion (supination) of the
Successful foot orthotic treatment is dependent on the shoes that foot and varus and valgus of the ankle. Control of the foot–ankle complex
are used in conjunction with the orthosis. If a person brings in a shoe provides control of the tibia’s progression over the ankle and of the
that barely accommodates his or her feet (too tight or too worn), then knee’s flexion and extension moments during the stance phase parts
placing a foot orthotic into it will lead to failure. Special considerations of the gait cycle. The AFO can also control toe-off (push off) and swing
239
You might also like
- Orthosis LectureDocument11 pagesOrthosis LecturenurubashNo ratings yet
- Shoe Modification and The Use of Orthoses in The Treatment of Foot and Ankle PathologyDocument7 pagesShoe Modification and The Use of Orthoses in The Treatment of Foot and Ankle PathologyMuhammad TahirNo ratings yet
- Orthotic in The Treatment of Rearfoot ProblemsDocument14 pagesOrthotic in The Treatment of Rearfoot ProblemstommygarnierNo ratings yet
- Design, Manufacture, and Selection of Ankle-Foot-Orthoses: January 2018Document19 pagesDesign, Manufacture, and Selection of Ankle-Foot-Orthoses: January 2018alejasoto17No ratings yet
- OrtesisDocument15 pagesOrtesisTito IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Basis of Foot Orthotic PrescriptionDocument6 pagesBiomechanical Basis of Foot Orthotic PrescriptionDusan OrescaninNo ratings yet
- KAFO and KO Guide for Lower Limb StabilizationDocument35 pagesKAFO and KO Guide for Lower Limb StabilizationMaryam KhalidNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in Perfomance Shoes 1Document15 pagesBiomechanics in Perfomance Shoes 1Shivani Jayanth100% (1)
- Knee Joint Materials and Components: by M.L. Stills, C ODocument4 pagesKnee Joint Materials and Components: by M.L. Stills, C OSusan KNo ratings yet
- Foot Orthosis and Lower Limb Bracing GuideDocument25 pagesFoot Orthosis and Lower Limb Bracing GuideAbdul Al-FattahNo ratings yet
- Active Ankle-Foot Orthoses DevelopmentDocument6 pagesActive Ankle-Foot Orthoses DevelopmentRahisya MentariNo ratings yet
- 0868 Upper Limb OrthosesDocument68 pages0868 Upper Limb OrthosesJose Jaramillo100% (1)
- OrthosisDocument35 pagesOrthosissinghmenkaNo ratings yet
- Custom Orthotics for Unique Foot SupportDocument1 pageCustom Orthotics for Unique Foot SupportRoxana RascaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Orthotics ANUMDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Orthotics ANUMMaryam KhalidNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Orthosis: Dr. Sumit Raghav, PT Assistant Professor Jyotirao Subharti College of PhysiotherapyDocument56 pagesLower Limb Orthosis: Dr. Sumit Raghav, PT Assistant Professor Jyotirao Subharti College of PhysiotherapyKavya Mittal100% (2)
- Knee Joint Functions and Knee Orthosis TypesDocument40 pagesKnee Joint Functions and Knee Orthosis TypesAlfred JacksonNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing of Custom Orthoses and Prostheses - A ReviewDocument7 pagesAdditive Manufacturing of Custom Orthoses and Prostheses - A ReviewÖzgeSevinKeskinNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Orthotics KCDocument14 pagesLower Extremity Orthotics KCLuca CristianNo ratings yet
- Artikel BunionDocument6 pagesArtikel BunionIsmi SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminationDocument6 pagesClinical Examinationarvind appNo ratings yet
- Knee Joint ThesisDocument5 pagesKnee Joint Thesisamywashingtonpittsburgh100% (2)
- Splints BracesDocument18 pagesSplints BracesvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- PONSETTI METHOD FOR CLUBFOOT CORRECTIONDocument5 pagesPONSETTI METHOD FOR CLUBFOOT CORRECTIONIjaz KhanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Different Dephts of Medial Heel Skive On Plantar PressuresDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Different Dephts of Medial Heel Skive On Plantar PressuresAlberto Jesús CamposNo ratings yet
- Introductio To OrthoticsDocument8 pagesIntroductio To OrthoticsGopi Krishnan100% (1)
- SHAHMEERDocument29 pagesSHAHMEERMosa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Gastrocnemius Operating Length With Ankle Foot Orthoses in Cerebral PalsyDocument2 pagesGastrocnemius Operating Length With Ankle Foot Orthoses in Cerebral PalsyAmr Mohamed GalalNo ratings yet
- 3D Printed Food OrthoseDocument6 pages3D Printed Food OrthoseIKFR UNDIP 77No ratings yet
- Orthotics 121208142340 Phpapp01Document94 pagesOrthotics 121208142340 Phpapp01Raghu Nadh100% (1)
- AGUADO - Diseño de Órtesis en Impresión 3D PDFDocument84 pagesAGUADO - Diseño de Órtesis en Impresión 3D PDFJoel Kevin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Joint Movements Inside Orthoses For Children With Spastic CPDocument6 pagesFoot and Ankle Joint Movements Inside Orthoses For Children With Spastic CPClaraNo ratings yet
- The Neurophysiological Ankle Foot OrthosisDocument32 pagesThe Neurophysiological Ankle Foot OrthosisSanket RoutNo ratings yet
- ORTHOTIC BASICSDocument94 pagesORTHOTIC BASICSAkbar AziziNo ratings yet
- Orthosis 130814094004 Phpapp02Document23 pagesOrthosis 130814094004 Phpapp02Anisha KhanalNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Orthosis Types and UsesDocument44 pagesLower Limb Orthosis Types and UsesRakesh shahNo ratings yet
- Handbook KafoDocument36 pagesHandbook KafoDillip Kumar SAhooNo ratings yet
- KAFODocument34 pagesKAFOBedo GikryNo ratings yet
- Foot Orthoses NotesDocument3 pagesFoot Orthoses NotesSangeetha GnaneswaranNo ratings yet
- MOC Notes 2011 NewDocument181 pagesMOC Notes 2011 NewMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Orthotic Care of The Denervated Foot in Hansen'S DiseaseDocument7 pagesThe Orthotic Care of The Denervated Foot in Hansen'S DiseaseImro SolihaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Foot Characteristics: Lecture Four Artificial Organs 1 Dr. Waleed JasimDocument12 pagesProsthetic Foot Characteristics: Lecture Four Artificial Organs 1 Dr. Waleed Jasimزهراء حيدر ميريNo ratings yet
- 09 AfoDocument107 pages09 AfonovitaNo ratings yet
- E-Book AFODocument107 pagesE-Book AFOmilaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Foot Orthoses On Foot Mobility Magnitude and Arch Height Index in Adults With Flexible Flat FeetDocument7 pagesThe Influence of Foot Orthoses On Foot Mobility Magnitude and Arch Height Index in Adults With Flexible Flat FeetFahim Abrar KhanNo ratings yet
- Orthotics - Ul & LLDocument48 pagesOrthotics - Ul & LLReena PremNo ratings yet
- Orthotic Devices: Diagnosis Recommended Orthotic Device Bunions And/or BunionettesDocument3 pagesOrthotic Devices: Diagnosis Recommended Orthotic Device Bunions And/or BunionettesAngela PascarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Foot Orthoses With Medial Arch Support and Lateral Wedge On Knee Adduction Moment in Patients With Medial Knee OsteoarthritisDocument8 pagesEffects of Foot Orthoses With Medial Arch Support and Lateral Wedge On Knee Adduction Moment in Patients With Medial Knee OsteoarthritisHusna LathiifaNo ratings yet
- Pedorthic and Orthotic Management of The Diabetic Foot: Dennis J. Janisse, Cped, Erick J. Janisse, Cped, CoDocument18 pagesPedorthic and Orthotic Management of The Diabetic Foot: Dennis J. Janisse, Cped, Erick J. Janisse, Cped, CoAnonymous kdBDppigENo ratings yet
- Evaluation Procedures For Lower Limb OrthosesDocument19 pagesEvaluation Procedures For Lower Limb OrthosesMaryam KhalidNo ratings yet
- Partial Foot AmputationDocument38 pagesPartial Foot AmputationVandana SinghNo ratings yet
- InTech-Lower Limb Wearable ExoskeletonDocument28 pagesInTech-Lower Limb Wearable ExoskeletonJuan Guillermo Patiño VengoecheaNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Orthotics - 2023 - SVDocument86 pagesLower Extremity Orthotics - 2023 - SVashlyn granthamNo ratings yet
- Chirurgia Piciorului ºi GlezneiDocument28 pagesChirurgia Piciorului ºi GlezneiAngela PascarNo ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes EquinovarusDocument25 pagesCongenital Talipes EquinovarusArlyn MillanesNo ratings yet
- Bicomechanical Evaluation of Ability of Casts and Braces To Immobilize The Ankle and HindfootDocument6 pagesBicomechanical Evaluation of Ability of Casts and Braces To Immobilize The Ankle and HindfootdewNo ratings yet
- Orthhotic FunctionDocument1 pageOrthhotic Functionsurbhi voraNo ratings yet
- FWD - 102 - Learning Material - 2Document8 pagesFWD - 102 - Learning Material - 2Sbl IrvNo ratings yet
- OrthothicsDocument32 pagesOrthothicsRafael Miguel MallillinNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Biomechanics in Sports MedicineFrom EverandOrthopaedic Biomechanics in Sports MedicineJason KohNo ratings yet
- Control Systems K-NotesDocument35 pagesControl Systems K-NotesAkashGaurav100% (1)
- Get 20 2019Document2 pagesGet 20 2019mohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Dual Converter: High Speed Response with Circulating CurrentDocument5 pagesDual Converter: High Speed Response with Circulating Currentmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Chopper (DC-DC Converter) PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 02 Chopper (DC-DC Converter) PDFmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Format For Acceptance of Offer of EngagementDocument1 pageFormat For Acceptance of Offer of Engagementmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Mtnotice291t67Document1 pageMtnotice291t67RajeshKumarSahuNo ratings yet
- Analog Ee-1 PDFDocument264 pagesAnalog Ee-1 PDFmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- RrbjeDocument3 pagesRrbjemohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Sel1920 06 ELECTRICAL PDFDocument1 pageSel1920 06 ELECTRICAL PDFmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- 37 - 19 Engineer Civil Regular AdDocument6 pages37 - 19 Engineer Civil Regular Adshubham SainiNo ratings yet
- Cur Affairs MayDocument126 pagesCur Affairs MayRaja huliNo ratings yet
- Starting Pages - New NAS WBDocument10 pagesStarting Pages - New NAS WBmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- FilingDocument2 pagesFilingmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- BTECH EE Theory SyllabiDocument33 pagesBTECH EE Theory Syllabimohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Ps SampleDocument38 pagesPs Samplemohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Starting Pages - New NAS WBDocument10 pagesStarting Pages - New NAS WBmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Starting Pages - New NAS WBDocument10 pagesStarting Pages - New NAS WBmohit durgapalNo ratings yet
- Trauma: © Physio Tools LTDDocument1 pageTrauma: © Physio Tools LTDFangYeeNo ratings yet
- The Regions of The Inferior LimbDocument30 pagesThe Regions of The Inferior LimbSaeed Hreiz100% (1)
- Reviewer in PeDocument8 pagesReviewer in PeKay ZeeNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Internal Martial ArtsDocument9 pagesFoundation of Internal Martial ArtsJim WeaverNo ratings yet
- 2016 Taylor-Spann ThesisDocument228 pages2016 Taylor-Spann ThesisJoanna Angela Lee100% (1)
- Nimbleness Boxing (Jie Quan) : Brennan TranslationDocument37 pagesNimbleness Boxing (Jie Quan) : Brennan TranslationPavelNo ratings yet
- 1 Learning To Walk The Circle - Circle Walking Basics PDFDocument35 pages1 Learning To Walk The Circle - Circle Walking Basics PDFStasha100% (5)
- Lower Extremity Amputation PreventionDocument1 pageLower Extremity Amputation PreventionEvaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PFDocument7 pagesDaftar Pustaka PFNadia RahmayantiNo ratings yet
- DRILL CHEATSHEET FOR BASEBALL PITCHERSDocument1 pageDRILL CHEATSHEET FOR BASEBALL PITCHERServoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 8th Edition Marieb Test BankDocument21 pagesHuman Anatomy 8th Edition Marieb Test Bankrhythmerossianic.lo93o100% (24)
- MCQ Question BankDocument102 pagesMCQ Question BankdrmadaanpiyushNo ratings yet
- Physics EntertainmentDocument124 pagesPhysics EntertainmentthryeeNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spine ExaminationDocument6 pagesLumbar Spine ExaminationSaddam Kanaan100% (1)
- Basics of Steps AerobicsDocument7 pagesBasics of Steps AerobicsJohn Marlo Catibog100% (1)
- Part of Body & Istilah Medis KeperawatanDocument61 pagesPart of Body & Istilah Medis KeperawatanFholsen FrohansenNo ratings yet
- Suspension Training Student Manual Secure PDFDocument56 pagesSuspension Training Student Manual Secure PDFzeggari azzedineNo ratings yet
- Mike Sanders - Idiot's Guides Drawing Manga 2013Document227 pagesMike Sanders - Idiot's Guides Drawing Manga 2013BullBlue100% (8)
- Week 5 Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesWeek 5 Skeletal SystemKimberly Faye JuevesNo ratings yet
- Ankle N Foot 3Document63 pagesAnkle N Foot 3YusraNo ratings yet
- Dance Terms With Foreign Origin and Filipino Dance Terms Used in Filipino DancesDocument5 pagesDance Terms With Foreign Origin and Filipino Dance Terms Used in Filipino DancesRyan Paolo DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Seated Elastic Band Exercise For Foot DropDocument2 pagesSeated Elastic Band Exercise For Foot DropDennis Diaz AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Leg and Foot PDFDocument7 pagesLeg and Foot PDFStephen Subiera MiayoNo ratings yet
- Medical Disclaimer for Building Muscle 101 Exercise GuideDocument96 pagesMedical Disclaimer for Building Muscle 101 Exercise GuidePavelSporish100% (3)
- Peripheral Nerves and Plexus. QuestionsDocument33 pagesPeripheral Nerves and Plexus. QuestionsAmanuelNo ratings yet
- Booty Burner GuideDocument26 pagesBooty Burner GuideJB100% (1)
- Physical Education module explores folk danceDocument11 pagesPhysical Education module explores folk danceCryzel MuniNo ratings yet
- Legs To Sing On: A Practical Guide For Singers and Voice TeachersDocument8 pagesLegs To Sing On: A Practical Guide For Singers and Voice Teachers小羊No ratings yet
- PE 2 Dances GuideDocument8 pagesPE 2 Dances GuideMin Hye JinNo ratings yet
- 7 Free Sock Knitting PatternsDocument25 pages7 Free Sock Knitting PatternsHaniBrombachScottBoeck100% (1)