Professional Documents
Culture Documents
USII Final Guide
Uploaded by
mrsorleckOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
USII Final Guide
Uploaded by
mrsorleckCopyright:
Available Formats
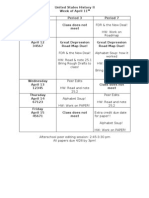
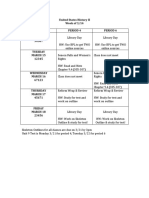
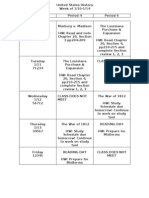
USII-Level 1/Honors 2011 Final Review Guide
Orleck
Format: Your midterm exam will be a cumulative exam covering all the material we have done up to this point. This will be a scan-tron exam that will consist of multiple choice, true/false, matching/identifications, map analysis, as well as a written response. Please note that your exam will include new material from our Imperialism unit. Review: Preparation is the absolute key to successfully preparing for cumulative exams. We will review in class during Reading Days, but you absolutely MUST be disciplined and create a multi-day study plan and schedule. If you would like help with study skills, please do not hesitate to see me. Organization: I expect you to create tangible study materials for this exam. Simply reading over notes is not enough. You should have ALL materials from the year organized. Expect your study guide to be checked at random intervals in the time leading up to the exam. Unit I: Western Migration Unit Essential Question: What were the motivations for westward expansion? Why did the United States feel they had a right to assimilate and Native Americans as they pushed west? Key Questions: In what ways did the U.S. try to assimilate Native Americans? What was the source of conflict among the U.S. government, white settlers and Native Americans? How did the Native Americans resist and protest the treatment by the U.S. government and soldiers? What types of economic incentives did the United States government provide to settlers in the west to encourage growth of private property ownership? What technological advancements helped make farming profitable? How did cattle ranching and mining expand opportunities for settlement? Do you think the federal government had the right to give away land on which Native Americans already live? Was the "free land" offered by the Homestead Act really free? How does a government get people to move to an area where few people live? Having suffered slavery and oppression themselves, how do you think the buffalo soldiers justified supporting the government's oppression of the Native Americans? Terms: Homestead Act Bureau for Indian Affairs Sand Creek Massacre Battle at Wounded Knee Ghost Dance General Custer Sitting Bull Treaty of Medicine Lodge Crazy Horse Bonanza Farms Barbed Wire Steelhead Exodusters Texas Longhorn Comstock Lode Hydraulic Mining Dawes General Allotment Act Buffalo Soldiers Chinese Exclusion Act Treaty of Medicine Lodge
Battle of Little Big Horn Crazy Horse
Treaty of Medicine Lodge Battle of Little Big Horn
Crazy Horse
Unit II: The Second Industrial Revolution Essential Question: How did the second Industrial Revolution reorder and change American society?
Key Terms What global economic theories encouraged Industrialization in the United States? In what ways did the actions and businesses of the 19th century Industrialists benefit U.S. society? How did their actions/business help or harm the quality of life? What is the legacy of the Industrialists? What important technological and scientific advances led to the Industrial Revolution? How did business leaders, entrepreneurs and inventors contribute to the Industrial Revolution? Key Terms: Patent Transcontinental Railroad Telegraph Bessemer Process Steel Economics Capitalism Free Enterprise Social Darwinism Communism Socialism Utilitarianism Laissez-faire Corporation Trust Monopoly Vertical Integration Horizontal Integration Urbanization Anarchists Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Homestead Strike Homestead Riots Robber Baron Captain of Industry Philanthropy Gospel of Wealth Carnegie Rockefeller J.P. Morgan Vanderbilt Karl Marx Adam Smith Jeremy Bentham John Stuart Mill
Unit III: Urbanization & Immigration in a Changing World (our assessment for this unit was the neighborhood city tour) Essential Question: What factors pushed/pulled immigrants to move to the United States in the late 1800s and early 20th Century? Key Question: How did immigration change during the late 1800s? What challenges did immigrants face in the United States? Where culd immigrants find assistance What was the nativist response to waves of immigration? What was urban life like? How did social reformers uses settlement houses and churches to improve the lives of the poor? Terms: New v. Old Immigrants Benevolent societies Settlement houses Emma Lazarus Ellis Island Citizenship/immigration requirements Economic/Social/Political reasons for immigrating NY Neighborhoods/Ethnicities Anti-Irish sentiment nativism Unit IV: Politics & the Gilded Age Unit Essential Question: How did rapid industrialization, urbanization, and change in demographics change politics in the United States? Lesson Key Questions: How did political machines emerge in the United States? Were political bosses corrupt? What was the role of new immigrants in the political process? How did corruption and illegal activities develop in many urban political machines? What effect did Thomas Nasts cartoons have on corruption at Tammany Hall? What triggered the need for political reform? How did this desire change the Republican party? How was reforming the civil service system a way of restoring government during the Gilded Age? How did subsequent Presidents in the 19th century reform policies?
What factors lead to economic hardships for farmers? What was the platform and purpose of the Populist party? Why and how did the party attract millions of supporters? How did silver affect the economy and the 1896 presidential election ?
Terms: Political machines Political bosses Graft Kickbacks William Marcy Tweed Thomas Nast Tammany Stalwarts Pendelton Civil Service Act Credit Mobilier Mugwumps Unit V: Progressivism Essential Question: How did a Progressive agenda shape economic, social and political reforms in the United States? Main Idea: The Progressives challenged many aspects of 19th century society and economics, notably laissez-faire theories, heartless industrialization, and political corruption. Progressives took steps to protect the environment and secured the right to vote for women. Key Questions: What were the motivations of Progressive social reformers? How were their attitudes toward the other reflected in their programs and policies? What are the motivations behind progressive reformers actions and what ideas influenced their thinking? What does it mean to be scientific? In what ways did scientific thinking influence policies and ideas of the progressive era? Cooperatives Graduated income tax Gold standard Interstate Commerce Act Bland Allison Act Sherman Silver Purpose Act Populist Party James B. Weaver William Jennings Bryant National Grange Sourcing Contextualization Corroboration Presidents: Garfield Arthur Cleveland Harrison McKinley
What happens to a society when science & education defines human beings as superior or inferior? How do these ideas affect public policy and human lives? During the Progressive Age, how was science used and misused to develop policy? How did African Americans contribute to the Progressive Era? Who was a stronger advocate for African Americans: Washington or Dubois? In what ways did Progressive Politicians change American Society? Which President was the most progressive? To what extent did Theodore Roosevelt provide a square deal for the American people? What attitudes about women and their relationships with men had to be overcome before women could take their rightful place in American society? What were the arguments for and against suffrage? What divisions in the Republican Party lead to the formation of the Progressive Party? How did reformers seek to limit the power of big business and to make government more democratic in the early 1900s? Why were the 16th, 17th, and 19th Amendments adopted?
TERMS Muckraker Settlement Houses Australian Ballot Personal Registration Laws Disenfranchisem ent Suffrage NAACP Socialism Square Deal Bull Moose Campaign Tariff Reform Progressive Income Tax Direct Primary
Initiative Referendum Seventeenth Amendment Wisconsin Idea Upton Sinclair Arbitration Elkins Act Hepburn Act Meat Inspection Act Pure Food and Drug Act National Park Service William Howard Taft Sixteenth Amendment
Woodrow Wilson Eugene Debs New Freedom Federal Reserve Act Clayton Anti Trust Commission Prohibition Federal Trade Commission National American Women Suffrage Association Alice Paul Nineteenth Amendment
Theodore Roosevelt Eugenics Samuel Morton
Jane Adams Jacob Riis Upton Sinclair Ida. B. Wells
Ida Tarbell Margaret Sanger
Unit VI: Imperialism (America becomes a world power. . . ) Unit Essential Question: What were the economic, social and political motivations for acquiring land and territories beyond the natural boundaries of the United States? Key Questions: Why was there such a huge debate about the decision of the United States to acquire territories outside its natural boundaries? How did Social Darwinism influence American Foreign Policy at the turn of the century? What were the arguments for and against American Imperialism? To what extent did the United States become an imperial power? Should one country have the right to dictate the actions of another country? How much influence and control did the Philippines have over its own territory? What benefits did America and European power gain from trading with Asia? Terms Imperialism White Mans Burden Rudyard Kipling The Berlin Conference Manifest destiny Subsidy Spheres of Influence Henry Cabot Lodge Kalakaua Liliuokalani John Hay World War I The Dole Company Open Door Policy The Boxer Rebellion Matthew Perry Jose Marti William Randolph Hearst USS Maine Teller Amendment George Dewey Emilio Aguinaldo Rough Riders Philippine Government Act Jones Act of 1916 Protectorate Dollar Diplomacy Platt Amendment Foraker Act Roosevelt Corollary (to the Monroe Doctorine) Mexican Revolution Pancho Villa
Essential Question: What was the role of the United States in World War I? Key Questions: What were the major causes of unrest in Europe? What role did (MAIN)Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, play in the build up of war? Why did the war come to a stalemate? How did trench warfare affect the fighting? What challenges did the U.S. face while trying to stay neutral? What events led to the US entry into the war and for declaration of war against Germany in 1917? What role did organized labor, volunteer organizations, and women play in contributing to the war effort? What motivated African Americans to migrate to the northern United States during this time? What domestic conflict caused Russia to surrender? How did the government create support for and limit opposition to the war? Did Woodrow Wilson provide effective leadership during World War I? What did Wilson's Fourteen Points hope to accomplish? Why was the Treaty of Versailles considered to be particularly punitive and vindictive? Terms/People/Events Acronym: Militarism Alliances Franz-Ferdinand The Balkans Austro-Hungarian Empire Ottoman Empire Armenia(ns), Genocide of. . . Young Turks Central Powers Allied Powers Statemate Trench warfare Eastern Front Western Front Imperialism Nationalism Battle of Somme Zimmerman Note Schlieffen Plan Lusitania Sussex Pledge National Defense Act Selective Service Act Food Administration War Industries Board Great Migration Battle of Gallipoli Committee on Public Information Espionage Acts Sedition Act Bolsheviks Russian Revolution: Trotsky, Lenin Battle of Argonne Forest Treaty of BrestLitovsk Fourteen Points Big Four Treaty of Versailles David Lloyd George
George Clemenceau Kaiser Wilhelm
Abdication League of Nations Reparations
Unit Essential Question: How did the 1920s represent a period of both prosperity and social division? Part I: Post War Troubles Key Questions What were the economic outcomes of demobilization? What were the causes of the strikes of 1919? What was the public reaction to the strikes? What caused the Red Scare? Why did the trial of Sacco and Vanzetti arouse public interest? How did Harding and the Republican Party encourage economic growth? What scandals plagued the Harding administration? Why did the movement to pass the Equal Rights Amendment fail? What accounted for the reemergence of the KKK? In what ways did African Americans combat discrimination and violence? What prompted Americans to demand restrictions on immigration? Why did Mexican American immigration increase during the 1920s What actions did American Indians take to protect their land?
Terms: Demobilization Red Scare Equal Rights Amendment Teapot Dome Scandal Marcus Garvey Immigration Act of 1924 William Joseph Simmons Andrew Mellon Part II: The Jazz Age Key Questions: How did the economic boom affect American society? In what ways did companies such as Ford Motors change and grow business? How did prohibition impact crime? What were the characteristics of the new youth culture? Bursum Bill A Mitchell Palmer Palmer Raids Nicola Sacco Bartolomeo Vanzetti
What did the Scopes Trial and subsequent religious movements reveal about American society? How did Jazz and Blues become popular nationwide? How did artists and writers of the Harlem Renaissance use their work to express pride in cultural heritage? How did writers of the Lost Generation portray American life?
Terms: Model T Assembly line Volstead Act Flappers Charles Lindberg Clarence Darrow Harlem Renaissance
Bessie Smith Lost Generation Diego Riveria Duke Ellington Paul Robeson Louis Armstrong F. Scott Fitzgerald Al Capone
Eliot Ness Untouchables 21st Amendment Cecil B DeMille
Unit Essential Question: How did President Roosevelts New Deal Programs provide relief from the Great Depression? Key Questions: How did the New Deal provide relief for the unemployed? How did the New Deal promote industrial and agricultural recovery? In what ways did the FDR administration address the concerns of the African American and American Indian communities? What criticisms were aimed at the New Deal? How did the need for a second New Deal enable FDR to win a second term? Why did the Supreme Court try to block FDRs social programs? In what ways did the Second New Deal benefit labor and agriculture? What were the effects of the Roosevelt Recession Where was the Dust Bowl and what were its effects? How did New Deal programs use photography, writing, and art to promote their goals? New Deal Terms: Huey Long Social Security Act Dust Bowl Sit down strike Grapes of Wrath Georgia OKeefe John Steinbeck Federal Project Number One
Dorothea Lange Alphabet Soup Agencies Wagner Connery Act Work Progress Administration Share-Our-Wealth Tennessee Valley Authority Civilian Conservation Corp Securities and Exchange Commission Marian Anderson John Maynard Keynes Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Bank Holiday National Industrial Recovery Act Agricultural Adjustment Administration
Unit Essential Questions: Why did the United States enter World War II? What were the political, social, and economic situations in Europe and Asia that convinced the United States to shift from being an isolationist power to being an allied force in World War II? Unit Goals/Objectives: Understand the U.S. response to Japanese expansion and imperialism in Asia during the 1930s Understand the expansionist policies of Axis Powers in Europe and Africa and how the U.S. tried to cope with them through the Neutrality Acts. Analyze the United States appeasement policies toward Italian and German aggressions. Distinguish the reasons for Americas general isolationist stance in the 1930s Discuss the reasons for American failure to anticipate the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the wartime policy of unconditional surrender
Discuss the reasons behind President Trumans decision to use the atomic bomb against Japan Trace the course of Allied Victory in Europewhat were air, naval and ground contributions? Describe the course of events in the Pacific war from Pearl Harbor to the Japanese surrender
Unit Outline: I. The Road to War: Aggression and Response a. The rise of Aggressor States b. U.S. Neutrality c. The Mounting Crisis d. The Outbreak of War in Europe e. Americas response to war in Europe f. Pearl Harbor II. Fighting the War in Europe a. Campaigns in North Africa in Italy b. Operation Overlord (Normandythe ground invasion of Europe). The Pacific Theatre a. Offense in the Pacific b. U.S. Strategy c. A New President-the A bomb, and Japans surrender
III.
V: Shaping the Peace a. the United Nations b. Justice & Tribunals (Nuremberg, etc).
Terms: Isolationism Kellogg Briand Pact Washington Conference Kristallnacht Axis Powers Allied Powers Appeasement Non-aggression pact Munich conference Lend-Lease Act Blitzkrieg Maignot Line Atlantic Charter Pearl Harbor Baatan Death March Battle of Coral Sea Guadalcanal Stalingrad Committee of War Information Japanese Internment Operation Overlord D-Day The Battle of the Bulge Yalta Island-hopping Okinawa Kamikaze Manhattan Project Enola Gay United Nations Nuremberg Trials People: Hitler Stalin Churchill Mussolini
Franco MacArthur Selective Service & Training Act Rommel
Henry Morganthau, Jr. Eisenhower Patton Truman
Hirohito
Please use recent cold war and civil rights materials to round out your study guide!
You might also like
- Usii 4-28Document1 pageUsii 4-28mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 3-4Document1 pageUsii 3-4mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Machiavelli ReadingDocument4 pagesMachiavelli ReadingmrsorleckNo ratings yet
- WWII Unit GuideDocument3 pagesWWII Unit GuidemrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 2-14Document1 pageUsi 2-14mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 4-4Document1 pageUsi 4-4mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 4-11Document1 pageUsii 4-11mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 4-28Document1 pageUsi 4-28mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 4-11Document1 pageUsii 4-11mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 3-14Document1 pageUsii 3-14mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 4-4Document1 pageUsi 4-4mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- World War I Unit Guide Essential QuestionDocument1 pageWorld War I Unit Guide Essential QuestionmrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 4-11Document1 pageUsi 4-11mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 4-4Document1 pageUsii 4-4mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 3-14Document1 pageUsi 3-14mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 3-1Document1 pageUsi 3-1mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 1-31Document1 pageUsii 1-31msrubackNo ratings yet
- Usii 2-14Document1 pageUsii 2-14mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 2-7Document1 pageUsii 2-7mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 2-7Document1 pageUsi 2-7mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Trail of Tears Brochure AssignmentDocument1 pageTrail of Tears Brochure AssignmentmrsorleckNo ratings yet
- HRP 2010-2011Document16 pagesHRP 2010-2011mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Industrialization WebquestDocument4 pagesIndustrialization WebquestmrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 1-31Document1 pageUsi 1-31mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- USII Midterm ReviewDocument8 pagesUSII Midterm ReviewmrsorleckNo ratings yet
- USI Review GuideDocument8 pagesUSI Review GuidemrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usi 1-10Document1 pageUsi 1-10mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Imperialism Unit GuideDocument2 pagesImperialism Unit GuidemrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Usii 1-10Document1 pageUsii 1-10mrsorleckNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- RA 8173 Act Granting All Citizens Arm Equal Opportunity To Be Accredited by ComelecDocument2 pagesRA 8173 Act Granting All Citizens Arm Equal Opportunity To Be Accredited by ComelecAdrianne BenignoNo ratings yet
- Leg Res - and Justice For AllDocument4 pagesLeg Res - and Justice For AllbubuchokoyNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Agreement Maam MonaDocument2 pagesMemorandum of Agreement Maam MonaYamden OliverNo ratings yet
- Dizon V CTA DigestDocument2 pagesDizon V CTA DigestNicholas FoxNo ratings yet
- Amanquiton v. PeopleDocument4 pagesAmanquiton v. PeopleKeel Achernar DinoyNo ratings yet
- Municipal Council of Iloilo v. EvangelistaDocument2 pagesMunicipal Council of Iloilo v. EvangelistaWinterBunBunNo ratings yet
- Burma Will Remain Rich, Poor and Controversial': Published: 9 April 2010Document11 pagesBurma Will Remain Rich, Poor and Controversial': Published: 9 April 2010rheito6745No ratings yet
- Oracle Database 11g: Administration Workshop IDocument2 pagesOracle Database 11g: Administration Workshop IFilipe Santos100% (1)
- POLITICAL AND INTERNATIONAL LAW REVIEW: THE APPOINTING POWER OF THE PRESIDENTDocument16 pagesPOLITICAL AND INTERNATIONAL LAW REVIEW: THE APPOINTING POWER OF THE PRESIDENTJumel John H. ValeroNo ratings yet
- MARK Yao Ka Sin Trading Vs CaDocument1 pageMARK Yao Ka Sin Trading Vs CaAllenNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Systems: A) Global Tax SystemDocument10 pagesIncome Tax Systems: A) Global Tax Systemmyka.No ratings yet
- Crime and Punishment Around The World Volume 1 Africa and The Middle East PDFDocument468 pagesCrime and Punishment Around The World Volume 1 Africa and The Middle East PDFAnnethedinosaurNo ratings yet
- Cyber PdpaDocument30 pagesCyber PdpaSyafiq AffandyNo ratings yet
- Comfort Women Seek Official Apology from JapanDocument4 pagesComfort Women Seek Official Apology from JapanCistron ExonNo ratings yet
- People Vs Degamo April 30 2003Document2 pagesPeople Vs Degamo April 30 2003Vance CeballosNo ratings yet
- Citizens' Perceptions On Uganda's Governance - An Opinion Poll ReportDocument40 pagesCitizens' Perceptions On Uganda's Governance - An Opinion Poll ReportAfrican Centre for Media ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- PEOPLE Vs DE GRANODocument2 pagesPEOPLE Vs DE GRANOLoiseNo ratings yet
- Sponsor Change: Three Upline Approval FormDocument1 pageSponsor Change: Three Upline Approval FormClaudiamar CristisorNo ratings yet
- Rural Banks ActDocument2 pagesRural Banks ActveehneeNo ratings yet
- Armco - Simplified One-Page Hauling Agreement Template 2019Document3 pagesArmco - Simplified One-Page Hauling Agreement Template 2019Sulpi Casil100% (1)
- SC rules carrier liable for damages in sinking caseDocument1 pageSC rules carrier liable for damages in sinking caseKimberly RamosNo ratings yet
- Apt Rule1974Document116 pagesApt Rule1974Akhtar AbbasNo ratings yet
- VI. Bill of Rights - O To TDocument70 pagesVI. Bill of Rights - O To TCourtney TirolNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Philippine ConstitutionDocument7 pagesReviewer in Philippine ConstitutionMarvin Cabantac50% (2)
- Guaranteed Tobacco Arrival Condition DisputeDocument12 pagesGuaranteed Tobacco Arrival Condition DisputeFaye Cience BoholNo ratings yet
- Clinton v. Jones: No Presidential Immunity for Unofficial ActsDocument3 pagesClinton v. Jones: No Presidential Immunity for Unofficial ActsTon RiveraNo ratings yet
- Gross Negligence ManslaughterDocument53 pagesGross Negligence Manslaughterapi-24869020180% (5)
- Land Ceiling Laws in IndiaDocument25 pagesLand Ceiling Laws in IndiaRishabh Dubey50% (2)
- Guarin v. Limpin A.C. No. 10576Document5 pagesGuarin v. Limpin A.C. No. 10576fg0% (1)
- Cuozzo Speed Technologies, LLC v. Lee, No. 15-446 (June 26, 2016)Document3 pagesCuozzo Speed Technologies, LLC v. Lee, No. 15-446 (June 26, 2016)Mitali PatelNo ratings yet