Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cancer Chemo Table
Uploaded by
Christine NazarenoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cancer Chemo Table
Uploaded by
Christine NazarenoCopyright:
Available Formats
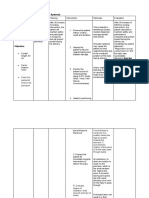
(1) CYTOTOXIC DRUGS
DRUG MOA
Bifunctional alkylation
CLINICAL USE
Nitrogen Mustard MOPP regimen for HODGKINS LYMPHOMA Phosphoramide Mustard Sarcomas Prior to Bone Marrow transplantation Chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoma Immunosuppressive therapy (SLE/ Rheumatoid therapy) Prior to Bone Marrow transplantation Gliomas; Brain tumors Multiple myeloma Bone marrow transplant ABVD regimen for HODGKINS LYMPHOMA Gliomas Radiation therapy
TOXICITY
Tissue necrosis
ANTIDOTE
ALKYLATING AGENTS
Mechlorethamine Cyclophosphamide Ifosfamide Melphalan Chlorambucil
Monofunctional alkylation
Hemorrhagic cystitis Hemorrhagic cystitis Mesna
Busulfan Nitrosoureas
Penetrates the CSF Carmustine / BCNU
Venoocclusive disease of the liver Phenobarbital
Dacarbazine Temozolomide
Generates active metabolite: MTIC (Monomethyl triazenoimidazole carboxamide) Dacarbazine analog
Flu-like syndrome of fever malaise, myalgias
Acetaminophen predication
ANTIMETABOLITES
(1) FOLIC ACID ANALOGS Methotrexate
Inhibits DHFR enzyme (DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE) S-phase specific Unable to polyglutamate methotrexate
Intrathecal prophylaxis in
lymphomas & leukemias Choriocarcinoma NON-HODGKINS LYMPHOMA Osteosarcoma Leukemia Urine alkalinization 1 line metastatic mesethelioma nd 2 line metastatic nonsmall cell lung cancer
st
Accumulation in 3 spaces (Ascites, Pleural effusion) Bone marrow suppression
rd
Leucovorin
Permetrexed
Multifolate antagonist Inhibits tumor enzymes
Vitamin B and Folic acid
(2) PYRIMIDINE ANALOGS
5-FU
Inhibits Thymidilate Synthase Inactivated by Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase enzyme in the liver Colorectal cancer Breast cancer Leucovorin
Capecitabine
(prodrug of 5-FU)
---Converted by Thymidine Phosphorylase to 5-FU Analog of 2-deoxycytidine Converted by Deoxycytidine kinase to an active for of 5 Induction of remission to ALL
Hand-foot syndrome
Cytarabine
Myelosuppression GI disturbances Conjunctivitis
Gemcitabine
monophosphate nucleotide --- Only drug effective for pancreatic cancer Mild therapy; no alopecia Myelosuppresion
(3) PURINE ANALOGS inhibits HGPRT enzymes Guanine analog Mercaptopurine Thioguanine Fludarabine Cladribine
Guanine analog
Induction of remission to ALL Induction of remission to AML Chronic lymphocytic leukemia Hairy cell leukemia
Myelosuppression Myelosuppression
Adenosine analog
CD4 T-cells depletion CD4-Tcells depletion
Adenosine analog
ANTIMITOTIC
(1) VINCA ALKALOIDS
Vincristine
NON-HODGKINS LYMPHOMA together with CHOP (Cyclo, Prednisone, Doxorubicin) HODKINS LYMPHOMA together with MOPP (Meclorethamine, Prednisone, Procarbazine) HODGKINS LYMPHOMA together with ABVD (Doxorubicin, dacarbazine, bleomycin) Adjuvant and metastatic NSCLCA Neurotoxicity, numbness, tingling, loss of DTR
M-phase specific; Binds to tubulin causing microtubule dissollution
Myelosuppression
Vinblastine
Vinorelbine
Myelosuppression
(2) TAXANE Paclitaxel
Promotes, rather than inhibits microtubule formation Prevents microtubule destabilization
Breast cancer Lung cancer Ovarian cancer Neutropenia Neuropathy More pronounced neutropenia than paclitaxel Metabolized in the liver by CYT p450 Metastatic Breast cancer Cromophore vehicle
Docetaxel (3) EPOTHILONES Ixabepilone
Similar to taxanesbut MORE POTENT!
Metabolized in the liver by CYT p450
TOPOISOMERASE- INTERACTIVE AGENTS
(1) CAMPHOTERICIN Irinotecan
Major excretion pathway is GLUCORONIDATION by UGT1A1 s Patients with CRIGGLER NAJAR/ GILBERTS SYNDROME are more affected Delayed & Acute diarrhea
Metastatic ovarian cancer TOPOTECAN
Neutropenia
(2) EPIPODOPHYLLOTOXINS
Etoposide
Conditions lowering albumin levels will lead to increased free fraction, increasing toxicities Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia
TUMOR ANTIBIOTICS
(1) ANTHRACYCLINES Doxorubicin Daunorubicin Epirubicin Mitoxantrone Liposomal doxorubicin (2) BLEOMYCIN
Oxidative DNA damage Binds with Topoisomerase-II Generates free radicals Intercalates DNA Promotes apoptosis Lymphomas, Leukemia, Breast cancer, Sarcoma, SCLCA ALL and AML Breast Cancer Acute non-lymphocytic leukemia, hormone-resistant prostate cancer Ovarian cancer Lymphomas Less cardiotoxic Cardiotoxicity due to free radicals generated
Tumor antibiotic from streptococcus spp.
(3) MITOMYCIN
ANAL CANCER!
Less cardiotoxic, less neutropenia Pulmonary fibrosis Decline in CO2 diffusion capacity Cutaneous toxicity HUS
PLATINUM COMPOUNDS forms DNA ADDUCTS which are recognized by MMR, that will promote apoptosis
Cisplatin
ALL Germ cell tumor Lung cancer Head and neck cancer Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer Lung cancer GI cancer, Ovarian cancer Germ cell cancer Cervical cancer Pancreatic cancer Nephrotoxicity Most emetogenic Renal toxicity Ototoxicity Myelosuppression
Carboplatin Oxaliplatin
Less reactive than cisplatin, better tolerated Less neutropenia Less nephrotoxic, more neuropathic Hypersenistivity reactions Mimimal Bone marrow and GI toxicity Hyperglycemia, Hypoalbuminemia, protein C and S deficiency Adrenocortical carcinoma
L-asparaginase
Mitotane
(2) HORMONAL TREATMENT
DRUG
Adrenocorticosteroids
MOA Promote apoptosis
Aromatase Inhibitors
Prevent formation of estrogen from adrenal gland and adipose tissue by inhibiting AROMATASE
CLINICAL USE Immunosuppresion Glucose intolerance Osteoporosis Water retention GI ulcers Bone mineral density, bone pains, increased fracture rates Musculoskeletal problems!
TOXICITY
Anti-Estrogen
For post-menopausal ER/PR+ breast cancer patients in adjuvant, neoadjuvant, metastatic setting Blocks estrogen receptors itself
GnRH analogs
Stimulates FSH and LH production by the pituitary gland then will late cause negative feedback inhibition Binds to androgen receptors and causes complete androgen blockade
Breast cancer Prostate cancer
Thrombosis risk Endometrial CA Hot flashes, nausea, vomiting, menstrual irregularities Initial flare reaction
Anti-androgen
Prostate cancer
Decreased libido Hot flashes Gynecomastia Mastodynia Paradoxical stimulation of androgen receptors
BIOLOGICAL RESPONSE MODIFIERS
DRUG
Interleukin-2
CLINICAL USE Expands T-cell response that is cytolytic for tumor cells Melanoma Renal cell carcinoma AML Filgrastim/ Lenograstim Expands population of neutrophil precursors Prophylaxis for chemotherapy induced neutropenia
SIDE EFFECT Hypotension Peripheral edema Azotemia
ANTIDOTE
G-CSF
Fever Chills
TARGETED RESPONSE
DRUG CLINICAL USE Her2 receptor Vegf receptor Breast cancer Angiogenesis SIDE EFFECT CHF Hypersensitivity ANTIDOTE
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
Traztuzimab Bevacizumab Cetuximab Panitumomab Rituximab Imatinib (Gleevec) Gefitinib Erlotinib Sunitinib Sorafenib
Hypertension, bleeding, proteinuria Hypersensitivity reactions Skin rashes Hypersensitivity reactions Hypersensitivity reactions Hypersensitivity reactions
EGFR receptor
EGFR receptor CD20 receptor
Colorectal cancer Head and neck cancer Colorectal cancer B-cell lymphomas
TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS
Bcr-Abl TKO in CML CD 117 TKl in GIST EGFR TKl in NSCLCA EGFR TKl in NSCLCA Multikinase Renal and liver cancer Multikinase Renal and liver cancer
Rashes Asthenia Weakness
Lapatinib
EGFR and HER2 TKl Breast Head and neck cancer
PROTEOSOME INHIBITOR
Bortezomib
Degrades proteosomes that denatures IKb Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors Advanced renal cell cancer Advanced renal cell cancer
MTOR INHIBITOR
Everolimus Temsirolimus
Intrathecal Administration Can cross Blood Brain Barrier
Methotrexate Cytarabine Nitrosoureas Temoxolomide Teniposide Hydroxyurea
Cytotoxic agent (Antimetabolite) Cytotoxic agent (Antimetabolite) Cytotoxic agent (Alkylating agent) Cytotoxic agent (Alkylating agent) Topoisomerase interactive agent
You might also like
- Name Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsDocument12 pagesName Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsM PatelNo ratings yet
- Anti Cancer DrugsDocument15 pagesAnti Cancer DrugsdatlaNo ratings yet
- Cancer DrugsDocument5 pagesCancer DrugsLinh HoangNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuideDocument6 pagesAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocument23 pagesFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Section on Antibiotics, Antivirals and AntifungalsDocument5 pagesPharmacology Section on Antibiotics, Antivirals and AntifungalsPathalee ThalpavilaNo ratings yet
- Cancer ChemotherapyDocument19 pagesCancer ChemotherapySamatha Mohan100% (1)
- Antitumor DrugsDocument93 pagesAntitumor DrugsNurul Mursyidah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Health, Stress, and CopingDocument43 pagesHealth, Stress, and CopingKar Gayee100% (1)
- Pharmacology 2 Long Exam Oncology-NkDocument7 pagesPharmacology 2 Long Exam Oncology-NkT'amo HanashNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument19 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationAnna MilliziaNo ratings yet
- MedicineDocument3 pagesMedicineIntanNurjannahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs Chart NursingDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Drugs Chart NursingSraddha PatelNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument16 pagesAntiemeticswalt65No ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs KathDocument29 pagesEmergency Drugs Kathmajin655No ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- 03 Adaptive Immune SystemDocument14 pages03 Adaptive Immune SystemEnea NastriNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument4 pagesChemotherapeutic DrugsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of - Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument4 pagesPharmacotherapy of - Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBaarid HamidiNo ratings yet
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- Lesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument28 pagesLesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugstheintrovNo ratings yet
- Cancer Treatment TypesDocument43 pagesCancer Treatment TypesM Sai Pradhyumna100% (2)
- Pharma CollectionDocument40 pagesPharma CollectionMuhd Nico DariyantoNo ratings yet
- Immune Disorders ExplainedDocument5 pagesImmune Disorders ExplainedThalia Fortune100% (1)
- Mnemonics For NursesDocument29 pagesMnemonics For Nursesashdmb217100% (2)
- Lecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsDocument3 pagesLecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- SyphilisDocument24 pagesSyphilisEvaG2012No ratings yet
- Drug Card Solu-MEDROLDocument2 pagesDrug Card Solu-MEDROLBenNo ratings yet
- USMLE NotesDocument165 pagesUSMLE NotesHerliani HalimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 026 CoagulationDocument7 pagesChapter 026 Coagulationthubtendrolma100% (3)
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsSheral Aida100% (2)
- Medical Terms in Lay Language2Document7 pagesMedical Terms in Lay Language2Mavra zNo ratings yet
- Prefix, Suffix of DrugsDocument6 pagesPrefix, Suffix of DrugsBriel Jake CabusasNo ratings yet
- Platin Platin - Platin: (Anthracycline Antibiotics - Adriamycin)Document2 pagesPlatin Platin - Platin: (Anthracycline Antibiotics - Adriamycin)Maryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocument28 pagesAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- MS2 USMLE Pharm ReviewDocument25 pagesMS2 USMLE Pharm ReviewAnna ArtyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicDocument13 pagesPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- Pharma GI CardsDocument16 pagesPharma GI CardsDoctorsHangout.comNo ratings yet
- Immuno Micro VirologyDocument15 pagesImmuno Micro VirologyReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Types of CancerDocument7 pagesTypes of CancerRegina SABSNo ratings yet
- Shock PresentationDocument20 pagesShock Presentationrosalyn sugayNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesExamination of The Central Nervous Systemkenners100% (13)
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument4 pagesClassification of AntibioticsNico AvellanaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesTreatment of Diabetes MellitusIrfan IdealistNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Management ATIDocument15 pagesDiabetes Management ATIJessica ChirinoNo ratings yet
- Anti Emetic DrugsDocument3 pagesAnti Emetic DrugsFaria Islam JuhiNo ratings yet
- Aminogycoside AntibioticsDocument31 pagesAminogycoside AntibioticsNurul Febrina100% (2)
- Onco PharmacologyDocument9 pagesOnco Pharmacologyarn0ld21No ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityDocument118 pagesPharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityRojina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument24 pagesCommunicable DiseasesJanus de LeonNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus Influenzae: Occasional SitesDocument7 pagesHaemophilus Influenzae: Occasional SitesJireh LeeNo ratings yet
- Disease ChartDocument12 pagesDisease ChartMegNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckkkkkkDocument7 pagesHead and NeckkkkkkJoey A. RumbaoaNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics & HypnosedativesDocument18 pagesAnxiolytics & Hypnosedativesrey martino100% (1)
- Adjuvant AnalgesicsDocument44 pagesAdjuvant AnalgesicsZulfan EfendiNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs: Pharmacology 2Document74 pagesAnticancer Drugs: Pharmacology 2Hannah Laput100% (1)
- Summary of Normal Laboratory ValuesDocument7 pagesSummary of Normal Laboratory ValuesIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Study Protocol (Study Plan)Document19 pagesStudy Protocol (Study Plan)Deana NamirembeNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Radio ReviewerDocument3 pagesRadio ReviewerChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Americlerkship - de La Salle 2012Document11 pagesAmericlerkship - de La Salle 2012Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Americlerkship - de La Salle 2012Document11 pagesAmericlerkship - de La Salle 2012Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- GRP 5 - Project PlanDocument13 pagesGRP 5 - Project PlanChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Chest and Lungs 1Document11 pagesChest and Lungs 1Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Eval 8Document16 pagesEval 8Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Inside The Adolescent BrainDocument1 pageInside The Adolescent BrainChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- GRP 5 - Project PlanDocument16 pagesGRP 5 - Project PlanChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Revised Session Plan Group 5 OB - Appendix and References For PrintingDocument9 pages2nd Revised Session Plan Group 5 OB - Appendix and References For PrintingChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Revised Session Plan Group 5 OB For PrintingDocument6 pages2nd Revised Session Plan Group 5 OB For PrintingChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Respiratory System 1Document10 pagesDiseases of The Respiratory System 1Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Research Protocol - Group 15Document27 pagesResearch Protocol - Group 15Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Mycology ReviewDocument9 pagesMycology ReviewChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11 - Microscopic Morphology of Fungal CultureDocument82 pagesExercise 11 - Microscopic Morphology of Fungal CultureChristine Nazareno100% (8)
- Pre Lab RespiDocument37 pagesPre Lab RespiChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- DERMA 3 TableDocument3 pagesDERMA 3 TableChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Sputum Cytology: Prelaboratory DiscussionDocument10 pagesSputum Cytology: Prelaboratory DiscussionChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Prax ReviewerDocument4 pagesMicrobiology Prax ReviewerChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- SDLS 2008 Prescription Writing - Oral LiquidsDocument7 pagesSDLS 2008 Prescription Writing - Oral LiquidsChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- FAB Classification of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)Document2 pagesFAB Classification of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Output 4Document1 pageOutput 4Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Mycology ReviewDocument9 pagesMycology ReviewChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- ANS1Document11 pagesANS1Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- DERMA 3 TableDocument3 pagesDERMA 3 TableChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Output 4Document3 pagesOutput 4Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- DERMA 3 TableDocument3 pagesDERMA 3 TableChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- SDLS 2008 Prescription Writing - Parenteral Liquids and OthersDocument11 pagesSDLS 2008 Prescription Writing - Parenteral Liquids and OthersChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Cancer Chemo TableDocument4 pagesCancer Chemo TableChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- RRL by ChristineDocument10 pagesRRL by ChristineChristine Nazareno100% (2)
- PHCL 412-512 MidtermDocument144 pagesPHCL 412-512 Midtermamnguye1100% (1)
- Diary Card VorlageDocument3 pagesDiary Card Vorlagelaraschindlerhotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Harrell First Amended Complaint - (To FILE)Document38 pagesHarrell First Amended Complaint - (To FILE)John Del SignoreNo ratings yet
- 24-h Continuous Infusion of Platelets For Patients With Platelet Transfusion RefractorinessDocument4 pages24-h Continuous Infusion of Platelets For Patients With Platelet Transfusion RefractorinessKarineNo ratings yet
- 2015 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Infective EndocarditisDocument54 pages2015 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Infective EndocarditisFernando Muñoz SolteroNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Vital for Reducing Road Traffic Injury BurdenDocument7 pagesHuman Resources Vital for Reducing Road Traffic Injury BurdenIrma SetiawatiNo ratings yet
- Ginecologic ExaminationDocument24 pagesGinecologic ExaminationPeter HoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Processing On Physicochemical Properties and Efficacy of B-Glucan From Oat and BarleyDocument5 pagesEffects of Processing On Physicochemical Properties and Efficacy of B-Glucan From Oat and BarleyCQ SHONo ratings yet
- Juguilon, Rissa M. Bsn4b EssayDocument3 pagesJuguilon, Rissa M. Bsn4b EssayRissa Juguilon100% (1)
- Frederick W. Taylor's Scientific Management TheoryDocument3 pagesFrederick W. Taylor's Scientific Management TheoryMickey MoraNo ratings yet
- Citizen's Charter MDRRMODocument2 pagesCitizen's Charter MDRRMOLucille Teves100% (1)
- Shoulder Dystocia: Risks and InterventionsDocument3 pagesShoulder Dystocia: Risks and InterventionsNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Floor Hockey Block PlanDocument4 pagesFloor Hockey Block Planapi-249766784No ratings yet
- Acne TreatmentDocument2 pagesAcne TreatmentBps Azizah CangkringanNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Co-Ordination: BY: Suman Shaikh DPT 3 Year Cop, JPMCDocument13 pagesNeuromuscular Co-Ordination: BY: Suman Shaikh DPT 3 Year Cop, JPMCAli Mahdi AliNo ratings yet
- Sample Endorsement Invitation Letter To CandidatesDocument3 pagesSample Endorsement Invitation Letter To CandidatesKarl King EsmeraldaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Presentation On HousekeepingDocument14 pagesWelcome To The Presentation On HousekeepingskfahimuddinNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Acetate MSDSDocument5 pagesAmmonium Acetate MSDSPraditya AgungNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 violators should face sanctionsDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 violators should face sanctionsAkmal BagyaNo ratings yet
- GenSoc Skit - ScriptDocument2 pagesGenSoc Skit - ScriptPrincess Rachelle CunananNo ratings yet
- Fistulectomy: - Prepared byDocument65 pagesFistulectomy: - Prepared byMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- ICC - GMP Initiating Coverage Report - Oct 5 2017Document69 pagesICC - GMP Initiating Coverage Report - Oct 5 2017Anonymous 1pXKbrnNo ratings yet
- Okamura 1999Document4 pagesOkamura 1999Araceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- TBIHSS Program StatementDocument20 pagesTBIHSS Program StatementJoemar CafrancaNo ratings yet
- PSAE review-AWMS PDFDocument37 pagesPSAE review-AWMS PDFCynthia B.GayumbaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map PeDocument2 pagesCurriculum Map PeChristian Domenden IINo ratings yet
- Alfred AdlerDocument20 pagesAlfred AdlerChristian Arby BantanNo ratings yet
- Nurs208 Qa Practice Reflection Worksheet 1Document1 pageNurs208 Qa Practice Reflection Worksheet 1api-34714578980% (5)
- Note 13 - Grievance & DisciplineDocument3 pagesNote 13 - Grievance & DisciplineVishesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Dräger Incubator 8000 IC - User ManualDocument60 pagesDräger Incubator 8000 IC - User ManualManuel FloresNo ratings yet