Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hepab
Uploaded by
Paolo CarubioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hepab
Uploaded by
Paolo CarubioCopyright:
Available Formats
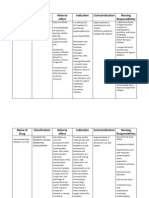
Causativ e Agent
Incuba tion Period
15 - 45 Days
Mode of Transmission
- Ingestion of food/water that is contaminated by stool containing HEP A virus - You come in contact with the stool or blood of a person who currently has the disease - A person with hepatitis A does not wash his or her hands properly after going to the bathroom and touches other objects or food - You participate in sexual practices that involve oralanal contact - BT - Direct contact with blood in health care settings - Sexual contact with an infected person -Tattoo or acupuncture with unclean needles or instruments - Shared needles during drug use - Shared personal items (such as toothbrushes, razors, and nail clippers) with an infected person
Individual at Risk
-International travel, especially to Asia or South or Central America - Living in a nursing home or rehabilitation center - Working in a health care, food, or sewage industry
S/Sx
Test Done
Preventio n and Control
Proper food handling
Hepatitis A
Hepatits A Virus (HAV)
- Dark Urine - Fatigue - Itching - Loss of Appetite - Low- grade fever - N/V - Clay colored Stool - Jaundice
HAV-AbIgM HAV-AbIgG HAV-Ab total
Hepatitis Hepatitis Virus B B
(HCV)
2 to 6 Months
- Being born, or having parents who were born in regions with high infection rates (including Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean) - Being infected with HIV - Being on hemodialysis - Having multiple sex partners - Men having sex with men
- You may have no symptoms - You may feel sick for a period of days or weeks - You may become very ill (called fulminant hepatitis) symptoms may appear after 6 months - Appetite loss - Fatigue - Fever, lowgrade - Muscle and joint aches -Nausea and vomiting
- Antibody to HBsAg (AntiHBs) - Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (Anti-HBc) -Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) - Hepatitis E surface antigen (HBeAg) -- a positive result means you have a hepatitis B infection and are more likely to spread the infection to others
- All children should receive their first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, and complete the series of three shots by age 6 months. Children younger than age 19 who have not been vaccinated should receive "catch-up" doses. -Avoid sexual
- Yellow skin and dark urine due to jaundice
through sexual contact or sharing needle
Hepatitis Hepatitis C Virus C
(HCV)
2 to 26 weeks
- BT of infected blood - Sexual Intercourse - Use of infected needles
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis - Have regular contact with blood at work (for instance, as a health care worker) - Have unprotected sexual contact with a person who has hepatitis C (this is much less
- Abdominal pain (right upper abdomen) - Abdominal swelling (due to fluid called ascites) - Bleeding from the esophagus or stomach (due to dilated veins in the esophagus or stomach called varices
- EIA assay to detect hepatitis C antibody - Hepatitis C RNA assays to measure virus levels (viral load) - Hepatitis C genotype. Six genotypes exist. Most Americans have genotype 1 infection, which is the
contact with a person who has acute or chronic hepatitis B. - Use a condom and practice safe sex. - Avoid sharing personal items, such as razors or toothbrushe s. - Do not share drug needles or other drug equipment (such as straws for snorting drugs). - Clean blood spills with a solution containing 1 part household bleach to 10 parts water. - Avoid contact with blood or blood products whenever possible. Health care workers should follow precautions when handling blood and bodily fluids. - Do not inject illicit
common, but the risk is higher for those who have many sex partners, already have a sexually transmitted disease, or are infected with HIV - Inject street drugs or share a needle with someone who has hepatitis C - Received a blood transfusion before July 1992 - Received a tattoo or acupuncture with contaminated instruments (the risk is very low with licensed, commercial tattoo facilities) - Received blood, blood products, or solid organs from a donor who has hepatitis C - Share personal items such as toothbrushes and razors with someone who has hepatitis C (less common) - Were born
-Dark Urine -Fatigue -Fever -Itching -Jaundice -Anorexia - N/V - Clay colored stools
hardest to treat. - Albumin level - Liver function tests Prothrombin time - Liver biopsy
drugs, and especially do not share needles with anyone. Be careful when getting tattoos and body piercings. - Sexual transmissio n is very low among stable, monogamo us couples. A partner should be screened for hepatitis C. If the partner is negative, the current recommend ations are to make no changes in sexual practices. - People who have sex outside of a monogamo us relationship should practice safer sex behaviors to avoid hepatitis C as well as sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV and hepatitis B.
to a hepatitis C-infected mother (this occurs in about 1 out of 20 babies born to mothers with HCV, which is much less common than with hepatitis B)
Hepatitis Hepatitis D virus D
(HDV)
- Can be as short as 30 days or as long as 180 days
- Use of infected needles - Sexual intercourse
- Having a tattoo or body piercing done with dirty tools that were used on someone else, sharing drugs, needles, and having sex with an infected person without using a condom
- Diarrhea, muscle pain, nausea or vomiting, a low-grade fever, exhaustion, weakness, and a loss of appetite
- Liver enzyme tests or tests that look for antibodies the body has made against the hepatitis D virus
Hepatitis HEPATITI SE E
VIRUS (HEV)
15-60 days
Saliva, air, cough, fecal-oral route, surfaces, blood, needles, blood transfusions, sexual contact, mother to fetus
- Exposure to contaminated food or water - Consuming untreated water - Consuming food prepared by an infected person. - Consuming raw produce or raw shellfish (e.g., oysters) - Traveling to countries where hepatitis E is
- Flu-like symptoms -Fever -Fatigue -N/V -Anorexia - Abd Pain - Diarrhea - Jaundice
- Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
- Get the hepatitis B vaccine or avoiding high-risk behaviors such as shooting drugs or sharing toothbrushe s, razors, nail clippers, washcloths, or anything else that could have an infected person's blood on it Avoiding tap water when traveling internationa lly and practicing good hygiene and sanitation. Avoid unprotected sexual contact with a confirmed individual
common and where there is little clean water or proper sewage disposal. Exposure to the stool or blood of an infected person, who is a: - Household member or sexual partner (men who have sex with men are at higher risk). - Child or staff member of a daycare center (including centers for the disabled). - Resident or staff member of a health care center.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- DermatologyDocument121 pagesDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- Competency Appraisal 1 Reviewer-1Document53 pagesCompetency Appraisal 1 Reviewer-1Paolo Carubio100% (1)
- Nutrition Support Internship Case Study 1Document5 pagesNutrition Support Internship Case Study 1api-457873289No ratings yet
- Rosie Timmins Resp Case StudyDocument2 pagesRosie Timmins Resp Case StudyPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- 12 Best Practice Tools and Guidelines Health Maintenance ContinenceDocument25 pages12 Best Practice Tools and Guidelines Health Maintenance ContinencePaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Leo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyDocument2 pagesLeo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Leo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyDocument2 pagesLeo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CaseDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CasePaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Pathophy MIDocument3 pagesPathophy MIPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- MI QuestionsDocument4 pagesMI QuestionsPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- NCP UEDocument2 pagesNCP UEPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CaseDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CasePaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Hematology AlterationsDocument10 pagesHematology AlterationsPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- NCP UEDocument2 pagesNCP UEPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy KPDocument5 pagesDrugstudy KPPaolo CarubioNo ratings yet
- HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (Talatanungan Ukol Sa Kalusugan) :: Please Read Carefully (Basahin NG Mabuti)Document2 pagesHEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (Talatanungan Ukol Sa Kalusugan) :: Please Read Carefully (Basahin NG Mabuti)Karen Kaye PasamonteNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy: Hemorrhage, Hypertension, IncompatibilityDocument4 pagesComplications of Pregnancy: Hemorrhage, Hypertension, IncompatibilityKimberly HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Hypo Ventilation SyndromesDocument22 pagesHypo Ventilation SyndromesFer45No ratings yet
- 3 Manifestasi Klinik StrokeDocument35 pages3 Manifestasi Klinik StrokeDea100% (1)
- HepatosplenomegalyDocument49 pagesHepatosplenomegalyTarun SinghNo ratings yet
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Primary Care ReviewDocument6 pagesSmall Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Primary Care ReviewjilujNo ratings yet
- BBLRDocument37 pagesBBLRHernina OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Health DiseaseDocument36 pagesMaxillary Sinus Health Diseasesaba mahrNo ratings yet
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument33 pagesAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsVimala BohoNo ratings yet
- Soal Uas B.ingDocument6 pagesSoal Uas B.ingNopriani InuarNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument95 pagesRheumatoid Arthritisvaleee92No ratings yet
- CT Public v82 8 9Document2 pagesCT Public v82 8 9Dida HermaNo ratings yet
- Practical Approach To GIB Dr. Chris Huang 7.12.2013Document86 pagesPractical Approach To GIB Dr. Chris Huang 7.12.2013Juni Zuhairah Abd GhafarNo ratings yet
- FCORL(SA) Final Exam PapersDocument7 pagesFCORL(SA) Final Exam PapersJustine NyangaresiNo ratings yet
- New Indications of SP Dynamis - Treatment of Rare Cases PDFDocument1 pageNew Indications of SP Dynamis - Treatment of Rare Cases PDFFredric SvenssonNo ratings yet
- Student SYB: Chet Cunha MS IV January 22, 2009Document15 pagesStudent SYB: Chet Cunha MS IV January 22, 2009okarasemNo ratings yet
- Tru Ong Case Study in PD Cns SpectrumDocument9 pagesTru Ong Case Study in PD Cns Spectrumlakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Neema Rawat Microteaching (Spina Bifida)Document67 pagesNeema Rawat Microteaching (Spina Bifida)Dimple GoyalNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Police Regional Health Service Ncrpo Physical Examination Guide For Annual Physical Examination (APE)Document2 pagesPhilippine National Police Regional Health Service Ncrpo Physical Examination Guide For Annual Physical Examination (APE)james antonioNo ratings yet
- Neurosensory Disorders 22306Document14 pagesNeurosensory Disorders 22306bekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- Stroke NoteDocument2 pagesStroke NoteHanry WijayaNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations: Soundarya. A - N Roll No.: 112Document17 pagesHallucinations: Soundarya. A - N Roll No.: 112Jayashree goveraNo ratings yet
- Abdminal Compartment SyndromeDocument9 pagesAbdminal Compartment SyndromeRafael BagusNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Sleep Disturbances in Children With Epilepsy A Questionnaire BasedDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Sleep Disturbances in Children With Epilepsy A Questionnaire BasednoiNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Assessment TableDocument2 pagesVital Signs Assessment Tableapi-250869701No ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument2 pagesAPPENDICITISRichie Marie BajaNo ratings yet
- La Consolacion College Manila School of Nursing Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesLa Consolacion College Manila School of Nursing Course SyllabusJayson Magdael SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Blood in StoolDocument3 pagesBlood in StoolRae RayNo ratings yet