Professional Documents
Culture Documents
India's water resources shaped by climate, geography & geology
Uploaded by
Nandini MenonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
India's water resources shaped by climate, geography & geology
Uploaded by
Nandini MenonCopyright:
Available Formats
India is rich in water resources, being endowed with a network of great rivers & vast alluvial basins to hold
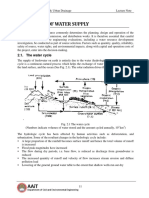
groundwater. Conditions, however, vary widely from region to region. Whereas there are some chronically drought affected areas, there are others which are frequently subject to damage by floods.On the whole, under the pressure of rapid population growth, the available resources of water are being developed & depleted at a fast rate & the situation seriously underlines the need for taking up integrated plans for water conservation & utilization for every agro-ecological area to meet the increasing demands of irrigation, water harvesting, human & livestock consumption,expanding industry, hydro-electric power generation, recreation,navigation & other uses. WATER RESOURCE CATEGORIES water resources are divisible into two distinct categories : the surface-water resources & the ground-water resources. Each of these categories is a part of the earth's water circulatory system,called the hydrologic cycle, & is ultimately derived from precipitation,which is rainfall plus snow. They are interdependent & frequently the loss of one is the gain of the other. The brief description of the run-off cycle,which is a part of the hydrologic cycle,will help us to understand the origin & the interdependence of these two categories of water resources. The precipitation that falls upon land & is the ultimate source for both the categories of water resources is dispersed in several ways. A sizeable portion is intercepted by the vegetal cover or temporarily detained in surface depressions.Most of it is later lost through evaporation. When the available interception or the depression storage are completely exhausted & when the rainfall intensity at the soil surface exceeds the infiltration capacity of the soils, the overland flow begins.Once the overland flow reaches a stream channel, it is called surface run-off, which together with other components of flow, forms the total run-off. Part of the water that infiltrates into the surface soil may continue to move laterally at shallow depth as interflow owing to the presence of relatively impervious lenses just below the soil surface & may eventually reach the stream channel when it is called the sub-surface runoff. A part of the sub-surface run-off may enter the stream promptly, whereas the remaining part may take a long time before joining the stream flow. A second part of the precipitation which infiltrates is lost through evapo-transpiration via plant roots & thermal gradients just below the soil surface. A third part may remain above the water table in the zone of unsaturated flow.A fourth remaining part percolates deeply into the ground-water.Part of this groundwater may eventually reach the stream channel & become the base flow of the stream. This portion is termed ground-water run-off or ground-water flow. Apart from infiltrated rain-water, the seepage from canals,ponds,tanks,lakes,irrigated fields,etc.is also dispersed & accounted for in the same manner. The total run-off in the stream channel includes the snow-melt, the surface run-off the sub-surface run-off, the ground-water run-off & the channel precipitation, i.e. the precipitation falling directly on the water surface of streams,lakes,etc. It constitutes what is known as the surface-water resources. The portion of the precipitation which, after infiltration,reaches the ground-water-table, together with the contribution made to ground water from a neighbouring basin, influent rivers,natural lakes,ponds,artificial storage reservoirs,canals,irrigation,& constitutes the ground-water resources.That quantity of water in the groundwater reservoir, which is not annually replenishable, is not taken into account, as it is a sort of dead storage which cannot be used on a continuing basis from year to year. The above phase of the run-off cycle pinpoints the inflow components for the surface-as well as for the ground-water resources. It has to be appreciated that there is always a balance between the inflow factors making up water resources of a region, whether surface or ground, & the outflow components.The surface water resource of a given basin in excess of the withdrawal use is accounted for on the outflow side by one or more of the following factors: (i)Stream outflow from the basin; (ii)loss through evaporation;and (iii)the influent recharge to the ground water. Similarly, the unutilised ground-water resource of a basin is accounted for by the following outflow factors: (i)Evapo-transpiration from the ground-water-table;
(ii)outflow to the neighbouring ground-water basin; (iii)the effluent discharge to the streams;and (iv)the addition to the ground-water storage. The interrelationship between the surface-water & the ground-water resources is evident from the above analysis.The surface-water resources contribute to the ground-water recharge in various ways: (i)by influent recharge from the streams; (ii)by seepage from natural lakes,ponds,etc; (iii)seepage from artificial storage reservoirs,canal systems,etc, & (iv)return flow from irrigation. These factors presently contribute to about 25 percent of the country's total ground-water resources. On the other hand, the bulk of the base-flow in the rivers, which represents the sustained fair-weather run-off is contributed by the ground-water resources. This contribution,presently, is roughly assessed at about 25 percent of the total surface-water resources of the country. FACTORS AFFECTING WATER RESOURCES The water resources of a region,conceived as a dynamic phase of the hydrologic cycle, are influenced by the following three major groups of factors: 1.CLIMATIC FACTORS
A. Rainfall : its intensity,duration & distribution.
B. Snow
C. Evapo-transpiration
2.PHYSIOGRAPHIC FACTORS A. Basic characteristics.
1. Geometric factors : drainage area,shape,slope & stream density. 2. Physical factors : land use, surface infiltration conditions,soil types,etc. B. Channel characteristics : carrying capacity & storage capacity.
3.GEOLOGICAL FACTORS
A. Lithologic including composition, texture, sequenceof rock types & the thickness of rock
formations.
B. Structural, including chief faults & folds that interrupt the uniformity of occurence of rock types or
sequence of rock types also beds, joints, fissures, cracks,etc.
C. Hydrologic characteristics of the aquifers permeability, porosity, transmissivity, storability,etc
The physiographic features (including geological factors) not only influence the occurence & distribution of water resources within a region but these, particularly the orography, play a significant role in influencing rainfall & other climatic factors, such as temperature, humidity & wind. However, within a geographical location & physiographic framework, it is primarily the rainfall (its intensity, duration & distribution) & the climatic factors affecting evapo-transpiration that determine the totality of water resources in the region.
You might also like
- Concepts of HydrologyDocument8 pagesConcepts of HydrologyCamille SantosNo ratings yet
- Bsce 5a - Hydrology - Assignment #1Document5 pagesBsce 5a - Hydrology - Assignment #1김태태No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 4 PDFMesfin Mamo HaileNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument4 pagesWater Resourcessanjeeb_sonuNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Lecture 1Document31 pagesHydrology Lecture 1Noman Zafar100% (1)
- Water Resources Engineering GuideDocument7 pagesWater Resources Engineering GuideHeussen PrinceNo ratings yet
- Surface Water Runoff by Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre For Advanced Studies in Earth Science University of Mysore, IndiaDocument10 pagesSurface Water Runoff by Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre For Advanced Studies in Earth Science University of Mysore, IndiaDipankar NathNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGYDocument25 pagesHYDROLOGYSurekha Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- HYDROGEOLOGYDocument28 pagesHYDROGEOLOGYNifemi OwolabiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Water Resources Engineering: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Water Resources Engineering: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurVivekChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - (I) PDFDocument11 pagesUnit 1 - (I) PDFMOHD ASIF ANSARINo ratings yet
- Characteristics of WatershedsDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Watershedschandramohan ramamurthyNo ratings yet
- Report in HydrologyDocument6 pagesReport in Hydrologyrio jay bananNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument4 pagesHydrologic CycleDEXTURENo ratings yet
- 1 Ground Water HydrologyDocument11 pages1 Ground Water HydrologyVinay T VNo ratings yet
- First ChapterDocument12 pagesFirst Chapterbibek neupaneNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument57 pagesWater ResourcesA S M Hefzul Kabir100% (3)
- Introduction to Groundwater and the Water CycleDocument229 pagesIntroduction to Groundwater and the Water CycleEr Jogendra SorenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Water ResourcesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Water ResourcesAzree Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Depletion in IndiaDocument7 pagesGroundwater Depletion in Indiaanon_737829668No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2Rushed AlamaNo ratings yet
- Citation 1Document11 pagesCitation 1JedNo ratings yet
- WaterassinmentDocument21 pagesWaterassinmentPuzhal Selvi KNo ratings yet
- Water BalDocument7 pagesWater BaltikatikayuNo ratings yet
- Stream Water Surface Profile Modification For Wetland RestorationDocument25 pagesStream Water Surface Profile Modification For Wetland Restorationceice2013No ratings yet
- Groundwater Is: Image of The Entire Flow of The Near Going Into A Leading To The GroundwaterDocument11 pagesGroundwater Is: Image of The Entire Flow of The Near Going Into A Leading To The Groundwatersurya786kantNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF SURFAC-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesTYPES OF SURFAC-WPS OfficeDerrick OpurumNo ratings yet
- Surface Water Runoff: Technical ReportDocument11 pagesSurface Water Runoff: Technical Reportأبو أسامة حمديNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument87 pagesWater ResourcesJoe NjoreNo ratings yet
- River Basin Characteristics and ImpactsDocument6 pagesRiver Basin Characteristics and ImpactsMudasir Qaisrani BalochNo ratings yet
- Surface Water Runoff: October 2017Document11 pagesSurface Water Runoff: October 2017Dipankar NathNo ratings yet
- Rainfall-Runoff RelationDocument58 pagesRainfall-Runoff RelationEam100% (2)
- Unit-1 HWREDocument51 pagesUnit-1 HWREsaikiranreddyg555No ratings yet
- Catchment Basins and Watershed ComponentsDocument23 pagesCatchment Basins and Watershed ComponentsEricAkivagaNo ratings yet
- Water Management: (Type The Document Subtitle)Document10 pagesWater Management: (Type The Document Subtitle)Mansuri FaizanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Irrigation Engineering 10CV55: UNIT-1Document20 pagesHydrology and Irrigation Engineering 10CV55: UNIT-1yusuf anwerNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Fluvial GeomorphologyDocument14 pagesHydrology and Fluvial GeomorphologyTeernce RugoyiNo ratings yet
- Cec 208 Lecture Notes 2Document18 pagesCec 208 Lecture Notes 2Zaid HabibuNo ratings yet
- The Water TableDocument68 pagesThe Water TableProsper ShokoNo ratings yet
- GE Elective 1 Module Explores Human Impact on Water ResourcesDocument22 pagesGE Elective 1 Module Explores Human Impact on Water ResourcesJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering Module 1 Water ResourcesDocument656 pagesIrrigation Engineering Module 1 Water ResourcesGYAN PRAKASH 18BTAG136No ratings yet
- Flood Mangement ReportDocument25 pagesFlood Mangement ReportDheerajMadisettyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Groundwater and Surface Water ResourcesDocument48 pagesAssessment of Groundwater and Surface Water ResourcesDavid CollierNo ratings yet
- Stream Characteristics TitleDocument6 pagesStream Characteristics TitleKelly LimNo ratings yet
- Groundwater: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesGroundwater: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDragomir Gabriela MarianaNo ratings yet
- Groundwater and Hydraulics Course MaterialsDocument13 pagesGroundwater and Hydraulics Course Materialsyogesh73% (22)
- Reviewer Coastal Engineering Module 8 10Document15 pagesReviewer Coastal Engineering Module 8 10pabello2020317No ratings yet
- Ground Water Hydrology: Aquifers & RechargeDocument14 pagesGround Water Hydrology: Aquifers & RechargeLily May AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Sources & Urban Drainage LectureDocument27 pagesWater Supply Sources & Urban Drainage LectureSreelakshmi CJNo ratings yet
- Surface Water and Groundwater Sources For Drinking WaterDocument19 pagesSurface Water and Groundwater Sources For Drinking WaterJuliet Leslie BaquilodNo ratings yet
- Modelling in HydrogeologyDocument260 pagesModelling in Hydrogeologythirumangai6100% (5)
- The Water BalanceDocument8 pagesThe Water Balancemisbah ahmadNo ratings yet
- Faculty of EngineeringDocument41 pagesFaculty of EngineeringAhmed Abdi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Overview of Ground Water in India: Key Issues and ChallengesDocument12 pagesOverview of Ground Water in India: Key Issues and Challengesanon_633677476No ratings yet
- Sources of Fresh Water EditDocument6 pagesSources of Fresh Water EditRajatKumarNo ratings yet
- WFWR Web26-50Document25 pagesWFWR Web26-50lalitv_27No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2 NotesDocument57 pagesChapter 1-2 Notesroshan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Techniques for Discharge Studies - Part 1From EverandPhysical and Chemical Techniques for Discharge Studies - Part 1No ratings yet
- A Field Guide to Clean Drinking Water: How to Find, Assess, Treat, and Store ItFrom EverandA Field Guide to Clean Drinking Water: How to Find, Assess, Treat, and Store ItNo ratings yet
- River Engineering Ch2Document38 pagesRiver Engineering Ch2EBA AJEMANo ratings yet
- Dredgers and Archaeology - Shipfinds From The SlufterDocument206 pagesDredgers and Archaeology - Shipfinds From The SlufterMaritime Archaeology Programme University of Southern Denmark100% (3)
- UPSC IFS Geology Syllabus: Paper - IDocument3 pagesUPSC IFS Geology Syllabus: Paper - IDivyanshi SinghNo ratings yet
- T191Document2 pagesT191Budi ArbaNo ratings yet
- Advocacy FinalDocument1 pageAdvocacy FinalHena Milka Santillan CabrielNo ratings yet
- Here are the answers:Location: AMovement: MRegion: FPlace: P Human/Environment Interaction: HDocument55 pagesHere are the answers:Location: AMovement: MRegion: FPlace: P Human/Environment Interaction: HGail Aid100% (1)
- Tsunamis PPT PresentationDocument39 pagesTsunamis PPT PresentationArovet Irineo0% (1)
- ESS Topic 2.4 - BiomesDocument6 pagesESS Topic 2.4 - BiomesnisaNo ratings yet
- Agree (1) Agree (2), Neither Agree/Disagree (3), Disagree (4) and Strongly DisagreeDocument3 pagesAgree (1) Agree (2), Neither Agree/Disagree (3), Disagree (4) and Strongly DisagreeMhark ChavezNo ratings yet
- Module IVDocument55 pagesModule IVShairvi Ajmera100% (1)
- Carbon Cycle: How Carbon Is Exchanged Between Atmosphere, Biosphere, Geosphere, Hydrosphere and LithosphereDocument5 pagesCarbon Cycle: How Carbon Is Exchanged Between Atmosphere, Biosphere, Geosphere, Hydrosphere and LithospheregulaikawahNo ratings yet
- Class Project Forest FiresDocument6 pagesClass Project Forest Firesapi-300921816No ratings yet
- Year Count and Total Losses from Natural Disasters 1900-2020Document1,514 pagesYear Count and Total Losses from Natural Disasters 1900-2020Karun BamanuNo ratings yet
- I. Intro+Plate TectonicDocument56 pagesI. Intro+Plate TectonicWindariNo ratings yet
- UU CD TestsDocument24 pagesUU CD TestsDenver James RabaraNo ratings yet
- Regional Studies in Marine Science: R.L. Boufeniza, M.M. Alsahli, N.I. Bachari, F. Houma BachariDocument10 pagesRegional Studies in Marine Science: R.L. Boufeniza, M.M. Alsahli, N.I. Bachari, F. Houma BachariHugo Pecho ChipaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument146 pagesPDFClash of HackersNo ratings yet
- EECQ - 4242 - Revision QuestionsDocument10 pagesEECQ - 4242 - Revision QuestionsEICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- Paleocurrent Analysis 6 PDFDocument134 pagesPaleocurrent Analysis 6 PDFPaul LixfeNo ratings yet
- NH Geography Physical-and-Human-Environments 2022Document12 pagesNH Geography Physical-and-Human-Environments 2022AaronNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration TestDocument4 pagesStandard Penetration TestIrita Kayna Gobile100% (1)
- Geological Structures: Horizontal StrataDocument15 pagesGeological Structures: Horizontal StrataLuis Alberto Colan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Speech OutlineDocument2 pagesSpeech OutlineFiona Tieh100% (1)
- Foundation Engineering: Engr. Gabriel GamanaDocument27 pagesFoundation Engineering: Engr. Gabriel GamanaJelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Finals Week1exercises TeowDocument3 pagesFinals Week1exercises TeowNovem NacarioNo ratings yet
- Agriculture 13 00225 v2Document19 pagesAgriculture 13 00225 v2Prateek IngoleNo ratings yet
- Barangay Disaster Risk Reduction Management Committee (BDRRMC) StructureDocument13 pagesBarangay Disaster Risk Reduction Management Committee (BDRRMC) StructureWesmea WouburnNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics LabDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Labapi-209948896No ratings yet
- A Rainfall Infiltration Model For Unsaturated Soil SlopeDocument8 pagesA Rainfall Infiltration Model For Unsaturated Soil SlopeAnonymous FZeDzDBKvNo ratings yet
- Geography Mid-Term Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagesGeography Mid-Term Exam Study Guideswolfe2911No ratings yet