Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TP Filled
Uploaded by
Lianmuel De GuzmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TP Filled
Uploaded by
Lianmuel De GuzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
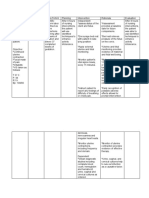
De Guzman, Lianmuel R. UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES, MANILA COLLEGE OF NURSING Sotejo Hall, P. Gil St.
, Ermita, Manila HEALTH TEACHING PLAN Objectives In a teaching learning session, the client will be able to learn: A. Knowledge 1. The definition of smoking Learning Content Learning Strategy venue/date/ti me Rochelle de guzman 30 years old 1110 rizal avenue, fugoso street, sta. cruz manila. August 23,2011 9am-11am Resources - Computer - Internet - References /Books - Printer - Ink - Bond Paper - Pentel pen - Colored Papers - Glue - Scissors Evaluation
The Health Sciences Centre
A. Knowledge
1. Client would be able to define smoking. Client would be able to verbalize factors why people smoke
2. Factors why people smoke a. Stress
1. Smoking is an act of inhaling burning tobacco fumes such as cigarette, cigar or pipe. (Websters Dictionary, 2003) 2. a. Smoking is perceived by many to have a calming effect and may also be seen as an enjoyable activity over which people can retain control no matter how difficult other parts of their life may be. (retrieved from www.ceitc.org.au) b. Many children start smoking because their friends have tried it and
1. LectureDiscussion 2. LectureDiscussion
2.
b. Peers
c. Environment
d. Nicotine addiction
3. Diseases related to 3. smoking a. Cancer a. Smoking is a major risk factor for at least 20 types of cancers such as lung cancer (140% risk in women, 130%risk in men), laryngeal (748% risk), oropharyngeal (455% risk) and esophageal cancer (401% risk) (Aonuevo, et.al, 2003)
they want to be part of the group. (retrieved from www.helpwithsmoking.com ) c. Many children may have started as they have grown up in an environment where their parents, grandparents and older siblings smoke and so they smoke in order to look and act like them.(retrieved from www.helpwithsmoking.com ) d. Thats because tobacco products/cigarette contains nicotine, which is addicting. The smoking habit results from the need to maintain a nicotine level in the blood. (Aonuevo, et.al, 2003)
3.
3. LectureDiscussion
Client would be able to enumerate diseases related to smoking
b. Cardiovascular diseases and stroke
c. Smoking ang lung disease
d. Impotence and infertility
b. Smoking is a major risk for heart diseases in stroke. Smoking in combination with other established risk factors, greatly increase the risk for ischemic heart disease. Smoking also cause three times more CAD deaths from lung cancer. Among older men and women, cigarette smoking remains a significant risk factor for intermittent claudicating and stroke. (Aonuevo, et.al, 2003) c. Smoking is the single established major risk factor for COPD. The risk of a smoker for developing COPD is almost 10 times more than that of a non-smoker. (Aonuevo, et.al, 2003) d. The poisons in cigarette smoking can damage a mans sperm cell and may be less able to make a woman pregnant. Smoking may make it harder for women to get pregnant. The smoke causes problems with the fallopian tubes where the egg cell passes from the ovaries to the uterus. Women who smoke also increases their chance of getting cancer of the uterine cervix and may go
4. Benefits of smoking cessation a. Overall mortality
4.
through menopause earlier. (Aonuevo, et.al, 2003) a. The number of premature deaths prevented by stopping smoking is similar across midline and older ages because of the higher burden of smoking-related diseases in older smokers it is reasonable to consider whether their quality of life or quality-of-life-adjusted survival can really be improved. (Palmer, 2000) b. The relative risk of cardiovascular mortality among older smokers compared with nonsmokers is in the order of 1.6, i.e, there is an excess mortality of 60% attributed to smoking. (Palmer, 2000) c. a 50% risk reduction has been shown 10-15 years after smoking at age 60-64 years. Stopping smoking may reduce the incidence of second primary tumors in those achieving long term remission. (Palmer, 2000)
4. LectureDiscussion
4.
Client would be able to state benefits of smoking cessation.
b. Decreased risk for cardiovascular diseases
c. Decreased risk for lung cancer and other pulmonary diseases
B. Skills Client would be able to devise a plan. START
B. a. S set a quit date b. T tell friends, family and neighbor about quitting c. A anticipate quitting benefits d. R remove tobacco products at home e. T talk to a doctor for therapies (retrieved from www. Mayoclinic.com) C. Affective benefits of cessation extend to people of all ages. Qutting enhances life expectancy and quality, even in people older than 60 years. It is never too late to quit. (Andrews, 1998 in CarpenitoMoyet, 2008)
B. LectureDiscussion
B. Skills Client would be able to plan a strategy for smoking cessation.
C. Affective Have client verbalize her own reasons for quitting.
C. LectureDiscussion
C. Affective Client would be able to verbalize the benefits of smoking cessation for her.
References: Carpenito-Moyet, L.S. (2008), Nursing Diagnosis Application to Clinical Experience, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Palmer, Katharine J. (2000), Smoking Cessation, Hongkong: Adis International Limited. Aonuevo, C. A., et. Al, (2003), A training manual for health workers on promoting healthy lifestyles, Philippines: Manila www.mayoclinic.com/health/quit_cmoking www.leitc.org.au/why_people_smoke www.helpwithsmoking.com/why_people_smoke.php Websters Dictionary 2003
You might also like
- TVT Report and Error BurndownDocument5 pagesTVT Report and Error BurndownLianmuel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Duration of The StudyDocument1 pageDuration of The StudyLianmuel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Activity intolerance and powerlessnessDocument3 pagesActivity intolerance and powerlessnessLianmuel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Activity intolerance and powerlessnessDocument3 pagesActivity intolerance and powerlessnessLianmuel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Purity™ D: Supply Specification (Physical & Chemical Data)Document3 pagesPurity™ D: Supply Specification (Physical & Chemical Data)Thuy PhanNo ratings yet
- Impacting Employee Performance Through CoachingDocument5 pagesImpacting Employee Performance Through CoachingNANDANA BALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- London Sperm Bank FAQsDocument4 pagesLondon Sperm Bank FAQsdickenschuiNo ratings yet
- Infertility Caused by Jinn PDFDocument15 pagesInfertility Caused by Jinn PDFKarthik0% (1)
- Dabur India FMCG Leader With Ayurvedic RootsDocument5 pagesDabur India FMCG Leader With Ayurvedic RootsKaashvi HiranandaniNo ratings yet
- Ginkgo Biloba: One of the Oldest Trees on EarthDocument12 pagesGinkgo Biloba: One of the Oldest Trees on EarthlucaspadialNo ratings yet
- FinalstatementofintentDocument1 pageFinalstatementofintentapi-546274167No ratings yet
- Psychology Research Proposal Paper ExampleDocument7 pagesPsychology Research Proposal Paper Exampleqqcxbtbnd100% (1)
- Pay and Conditions Circular MD 4 2023 Final - 0Document31 pagesPay and Conditions Circular MD 4 2023 Final - 0asi basseyNo ratings yet
- NCP On Preterm LaborDocument2 pagesNCP On Preterm Laborinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- MSDS STOPRUST - NewDocument2 pagesMSDS STOPRUST - NewAnurag JainNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition MCQ CarboDocument6 pagesFood and Nutrition MCQ CarboShivangi Singh0% (2)
- Kamagradubai - Ae-Kamagra Dubai - Online Herbal Supplement Store in Dubai UAEDocument60 pagesKamagradubai - Ae-Kamagra Dubai - Online Herbal Supplement Store in Dubai UAEkamagradubai0No ratings yet
- 2021 09 02 Motorsport Uk Yearbook 2021Document472 pages2021 09 02 Motorsport Uk Yearbook 2021Marcello AssunçãoNo ratings yet
- Ai and Inequality British English StudentDocument7 pagesAi and Inequality British English StudentRosine PergamentNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 4Document20 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 4Firas Muhammad100% (3)
- Ed Psych NotesDocument3 pagesEd Psych NotesJorge GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Stress Management OutlineDocument7 pagesStress Management OutlineJericko Allen Resus100% (1)
- Letter Writing 12Document36 pagesLetter Writing 12renugupta141979No ratings yet
- A Clinical Pathway For Complete Immediate Denture TherapyDocument18 pagesA Clinical Pathway For Complete Immediate Denture TherapyPragya PandeyNo ratings yet
- MRCP 2 Practice Questions Book.3Document166 pagesMRCP 2 Practice Questions Book.3iban100% (1)
- Football Training GuideDocument30 pagesFootball Training GuideRichard Joseph Chang'aNo ratings yet
- HGU Fees FreshDocument9 pagesHGU Fees FreshAbhishek JainNo ratings yet
- Gender Differences in Exercise Habits and Quality of Life Reports - Assessing The Moderating Effects of Reasons For ExerciseDocument15 pagesGender Differences in Exercise Habits and Quality of Life Reports - Assessing The Moderating Effects of Reasons For ExerciseArischo MardiansyahNo ratings yet
- 15 Most Valuable Lessons of BuddhaDocument2 pages15 Most Valuable Lessons of BuddhaRoberto JiménezNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal DisordersDocument71 pagesCommon Neonatal DisordersRANJIT GOGOI100% (2)
- Drugs For VetDocument32 pagesDrugs For Vetrajkumar8719920% (1)
- 9783319706870Document383 pages9783319706870Alexandru Gheorghe100% (1)
- DopamineDocument4 pagesDopamineHassan KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Metacognitive Therapy Hjemdal 2013Document13 pagesMetacognitive Therapy Hjemdal 2013rnuevo2No ratings yet