Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diabetic patient wound care
Uploaded by
Michael Anthony Cardenas MacaballugOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diabetic patient wound care
Uploaded by
Michael Anthony Cardenas MacaballugCopyright:
Available Formats
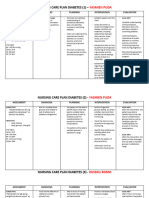
Assessment Subjective: Sige lang ko ug pangihi ug pirmi uhaw bisag sige ko inom ug tubig bugnaw as verbalized by the patient
Objective: Elevated temperature of 38 o C/ axilla Increased urine output Profuse sweating noted Excessive thirst noted Body malaise noted Dry skin, mucous membrane, and sunken eyeballs noted
Nursing Diagnosis Fluid volume deficit r/t intracellular dehydration 2o DM type II
Scientific Basis Glucose appears in the urine (glycosuria) because the kidney excretes the excess glucose to make the blood glucose level normal. Glucose excreted in the urine acts as osmotic diuretic and causes excretion of increased amount of water, resulting in fluid volume deficit or polyuria.
Planning Short term: After 3 of NI, patient shall have verbalized understanding of causative factors and purpose of individual therapeutic interventions and medications. Long term: After 2 days of NI, the patient shall have maintained fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individual good skin turgor, moist mucous membrane and stable vital signs.
Nursing Intervention Establish rapport
Rationale
To have a friendly relationship with patient and to be able to verbalize each others concern. To obtain baseline data Dry skin and mucous membranes are signs of dehydration To replace the
Evaluation Short term: After 3o of NI, patient has verbalized understanding of causative factors and purpose of individual therapeutic interventions and medications.
Take and record vital signs Assess skin turgor and mucous membrane for signs of dehydration
Encourage the fluid loss and patient to increase prevent oral fluid intake dehydration Administer IVF as ordered Administer antipyretic as ordered
To replace electrolytes and fluid loss To decrease body temperature and will have less occurrence of dehydration
Long term: After 2 days of NI, the patient has maintained fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individual good skin turgor, moist mucous membrane and stable vital signs.
Nursing Diagnosis Subjective: Imbalanced Nutrition: less Kusog ko mukaon than body pero murag gutom requirement r/t lang gihapon ko insulin pirmi as deficiency verbalized by the patient Objective: Poor muscle tone noted Generalized body weakness noted Increased thirst noted Increased in appetite noted Increased in urination noted
Assessment
Scientific Basis
Due to decrease or lack of insulin in the body, the glucose level continuously rises because glucose cant be utilized without the presence of insulin. Glucose is the source of energy, while insulin is the vehicle to transport glucose to the body tissues. Because of decrease insulin level in the blood stream, the cells starved, leading to alteration of metabolism. The body needs glucose for metabolism; there will be a breakdown of energy reserved from adipose tissue, muscles and liver (glucagons). This will result to weight loss. But the energy breaks down, the glucose level continuously increase because there is less amount of insulin. The body tissues need to be fed, this will lead to polyphagia and polydipsia because the tissue are not being fed and need glucose for metabolism.
Planning Short Term: After 3 of NI, patient shall have verbalized understanding of causative factors when known and necessary interventions and identified diabetic client. Long Term: After 1-4 months of NI, the patient shall have demonstrated weight gain toward goal.
Nursing Intervention Establish rapport
Rationale
To have a friendly relationship with patient and to be able to verbalize each others concern.
Evaluation Short Term:
Have patient understand personal nutritional needs
After 3 of NI, patient has verbalized understanding of causative factors when known and To increase necessary interventions and patients information about identified diabetic client. nutritional needs
for diabetics.
Long Term: After 1-4 months of NI, the patient has demonstrated weight gain toward goal.
Discuss eating habits and encourage diabetic diet as prescribed by the Doctor
To achieve health needs of the patient with the proper food diet for his disease.
Document actual weight of the patient
Patient may be un aware of their actual weight or weight loss due to estimating weight. To reveal changes that
Note total daily intake including patterns and time of eating.
should be made in clients dietary intake.
Consult dietician/physician for further assessment and recommendation regarding food preferences and nutri-tional support
For greater understanding and further assessment of specific foods.
Assessment Subjective: Kapoy pirmi akong paminaw sa akong lawas as verbalized by the patient Objective: Generalized weakness noted Increased respiratory rate of 25cpm noted presence of nonhealing wound on right leg noted noted to get tired easily inability to perform ADL noted
Nursing Diagnosis Fatigue related to decreased muscular strength
Scientific Basis
Diabetes Mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by increased levels of glucose in the blood resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. In type 2 diabetes, people have decreased sensitivity to insulin and impaired beta cell functioning resulting in decreased insulin production. Glucose derived from food cannot be stored in the liver thereby remaining into the bloodstream. The beta cells of the islets of Langerhans release glucagon
Planning Short Term:After 2-3 of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to identify measures to conserve and increase body energy. Long Term:
Nursing Intervention
Assess response to activity
Rationale
Response to an activity can be evaluated to achieve desired level of tolerance. To determine the level of activity tolerance
Evaluation
Asses muscle strength of patient and functional level of activity. Discuss with patient the need for activity
After 3-5 days of nursing interventions, the patient will be free from Alternate activity signs of fatigue
Education may provide motivation to increase activity level even though patient may feel too weak initially Prevents excessive fatigue
with periods of rest/ uninterrupted sleep. Monitor pulse, respiration rate and blood pressure before and after activity Perform activity slowly with
Indicates physiological levels of tolerance
Tolerance
which stimulates the liver to release the stored glucose. After 8 12 hours, the liver forms glucose from the breakdown of non-carbohydrate substances, including amino acids resulting to muscle wasting which results to weakness.
frequent rest periods
develops by adjusting frequency, duration and intensity until desired activity level is achieved. Interventions should be directed at delaying the onset of fatigue and optimizing muscle efficiency. Symptoms of fatigue are alleviated with rest. Also, patient will be able to accomplish more with a decreased expenditure of energy.
Promote energy conservation techniques by discussing ways of conserving energy while bathing, transferring and other ADLs.
Provide adequate ventilation For proper oxygenation Instruct client to increase Vitamins A, C and D and For muscle strength and tissue
protein in her diet. Instruct also patient to increase iron in diet
repair
To prevent weakness and paleness
Assessment Subjective: Dugay mayo ang akong samad sa akong operason as patient verbalized Objective: Flushed appearance noted Wound drainage noted
Nursing Diagnosis
Scientific Basis
Planning
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
You might also like
- DM Care PlanDocument9 pagesDM Care PlanHarish Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa/Bulimia NervosaDocument15 pagesEating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa/Bulimia NervosaCay Sevilla100% (7)
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 4 Quarter 4 - Week 1-8: Grade 12Document64 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education 4 Quarter 4 - Week 1-8: Grade 12AA100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitusinagasi83% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDanica Salinas100% (1)
- Heat Stress PreventionDocument9 pagesHeat Stress PreventionGrace PassiniNo ratings yet
- NCP For DMDocument14 pagesNCP For DMLynzzky Virtudes AbranNo ratings yet
- DehydrationDocument8 pagesDehydrationNader SmadiNo ratings yet
- Practice Listening & Grammar TestDocument10 pagesPractice Listening & Grammar TestLê TùngNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanjamieboyRN91% (32)
- Discharge Plan DMDocument4 pagesDischarge Plan DMnoviemberNo ratings yet
- NCPs For Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesNCPs For Diabetes MellitusEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- NCP DMDocument4 pagesNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- Sambong UploadDocument6 pagesSambong UploadRaymond Christopher LimNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- NCP For Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesNCP For Diabetes MellitusNanes Tan75% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Kenneth Anthony Tiu Regida100% (8)
- Medical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Document4 pagesMedical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Hadeer Mahmoud Abuslima100% (1)
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument5 pagesNCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirementsrusnani100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Managing Nutrition for a Diabetic Patient with PneumoniaDocument5 pagesManaging Nutrition for a Diabetic Patient with PneumoniaCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- NCP On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument4 pagesNCP On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIJai - Ho78% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitus Fluid Volume DeficitDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitus Fluid Volume DeficitAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDiana Laura Lei100% (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument3 pagesLiver Cirrhosis NCPSharmaine MadlaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Patients with Uterine Fibroids and Acute Abdominal PainDocument10 pagesNursing Care for Patients with Uterine Fibroids and Acute Abdominal PainPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- NCP DiabetesDocument4 pagesNCP Diabeteskyshb67% (3)
- Nursing Care in Patient With Diabetes MellitusDocument24 pagesNursing Care in Patient With Diabetes Mellitusmira utami ningsih83% (6)
- IVF Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsDocument3 pagesIVF Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- CessnaAIM Pilot Safety and Warning Supplements (D5139-13) PDFDocument98 pagesCessnaAIM Pilot Safety and Warning Supplements (D5139-13) PDFsteveNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionFrances Mercado0% (1)
- Assessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixDocument16 pagesAssessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixNalzaro Emyril89% (19)
- Nursing care plan for hypertension, renal calculi, diabetesDocument3 pagesNursing care plan for hypertension, renal calculi, diabetesGimcy Dela Fuente100% (6)
- Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument6 pagesUnstable Blood Glucosetherese BNo ratings yet
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument24 pagesRisk For Unstable Blood GlucoseFerreze Ann100% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPRachel PerandoNo ratings yet
- COLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONDocument3 pagesCOLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- DiagnosisDocument2 pagesDiagnosisAngelica ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- Managing Fluid and Nutrition Deficits in Diabetes Type 1Document3 pagesManaging Fluid and Nutrition Deficits in Diabetes Type 1Kartika MilaningrumNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Fatigue Liver Cancer Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fatigue Liver Cancer Care PlanPC NNo ratings yet
- Nursing Analysis of HyperglycemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Analysis of HyperglycemiaDharylle Cariño100% (3)
- Lanjutan NCP DMDocument14 pagesLanjutan NCP DMVera Andri YaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Example:: What Additional Assessments Would The Nurse Want To Make To Plan Care For This Client?Document2 pagesClinical Example:: What Additional Assessments Would The Nurse Want To Make To Plan Care For This Client?Kim Kristine D. GuillenNo ratings yet
- GastroenteritisDocument8 pagesGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthAna Ramos LopezNo ratings yet
- NCP For DM1Document2 pagesNCP For DM1Pau Hipol MadriagaNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesLevofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusMarlon AnryNo ratings yet
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument10 pagesNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIChristine Karen Ang SuarezNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesAbdominal Paindelan7dust78% (18)
- Daily NCPDocument5 pagesDaily NCPKuennie SabalNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancerobbiematro100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- A Renal Failure (NCP)Document2 pagesA Renal Failure (NCP)Julie Aranda Hapin100% (1)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHypertension Nursing Care PlanSheila Mae Cabahug100% (1)
- NCP 2 Addison's DiseaseDocument4 pagesNCP 2 Addison's DiseaseRenee RoSeNo ratings yet
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Scientific ExplanationDocument9 pagesNursing Diagnosis Scientific ExplanationMarisol Dizon100% (1)
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- Chinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesChinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanLoveli Yuchongtian Kiok100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationJobie CasipongNo ratings yet
- HEALTH TEACHING PLAN NUTRITIONDocument3 pagesHEALTH TEACHING PLAN NUTRITIONAdriene Fay DominguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- Managing Diabetes and RisksDocument8 pagesManaging Diabetes and RisksChristopher LontocNo ratings yet
- Lethargic Weakness Decreased Performance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesLethargic Weakness Decreased Performance: Nursing Care PlanZhayree R.No ratings yet
- NCP CSDocument7 pagesNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- Reading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Document15 pagesReading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 (10F)Document16 pagesNCM 112 (10F)Justine April YbanezNo ratings yet
- Prevent Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument17 pagesPrevent Diarrhea in ChildrenZankhanaba RajputNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care Process GuideDocument44 pagesNutrition Care Process GuideKATH GONo ratings yet
- Human Water Needs: Nutrition Reviews July 2005Document11 pagesHuman Water Needs: Nutrition Reviews July 2005Yanti HarjonoNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Fluid ReplacementDocument8 pagesExercise and Fluid Replacementapi-528422127No ratings yet
- Hyperthermia, Hypothermia and DehydrationDocument33 pagesHyperthermia, Hypothermia and DehydrationManasseh EchivarreNo ratings yet
- Pe & HealthDocument4 pagesPe & HealthCharlene DanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Labor Pain and AnxietyDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plans for Labor Pain and AnxietyJP2001No ratings yet
- ALTERED BODY TEMPERATUREDocument10 pagesALTERED BODY TEMPERATUREMelvin VrNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy History and StandardsDocument31 pagesIV Therapy History and Standardsrommelrn100% (1)
- Sapna NCPDocument22 pagesSapna NCPgill priyaNo ratings yet
- Glucose-Loesung 5 08-07 03Document2 pagesGlucose-Loesung 5 08-07 03Andreea CaticiNo ratings yet
- NCP - Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesNCP - Diabetes MellitusYasmien MarieNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 3rd Edition Dewit Test BankDocument25 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 3rd Edition Dewit Test BankCodyDavisncfp100% (53)
- Acute Gastroenteritis 2020Document56 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis 2020CristinaGheorgheNo ratings yet
- Fish Poisoning (Print)Document65 pagesFish Poisoning (Print)Cristina SarinoNo ratings yet
- Fitness Exercises Mvpa ParticipationsDocument20 pagesFitness Exercises Mvpa ParticipationsJei Diao VillosoNo ratings yet
- Age Case PresentationDocument21 pagesAge Case PresentationDev AakashNo ratings yet
- Heat and Cold Stress Safety: Oshacademy Course 602 Study GuideDocument18 pagesHeat and Cold Stress Safety: Oshacademy Course 602 Study GuideIrfanadi PratomoNo ratings yet
- Art 28 - Goula2017 RB-MDocument44 pagesArt 28 - Goula2017 RB-MMaria MaldonadoNo ratings yet