Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Component
Uploaded by
api-26570979Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Component
Uploaded by
api-26570979Copyright:
Available Formats
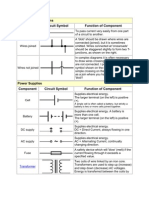
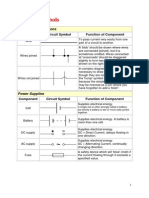
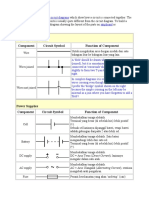
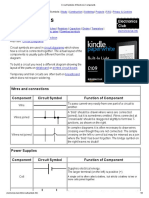
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This
Lamp (lighting) symbol is used for a lamp providing illumination, for
example a car headlamp or torch bulb.
A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This
Lamp (indicator) symbol is used for a lamp which is an indicator, for
example a warning light on a car dashboard.
Heater A transducer which converts electrical energy to heat.
A transducer which converts electrical energy to kinetic
Motor
energy (motion).
Bell A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Buzzer A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
A coil of wire which creates a magnetic field when current
Inductor passes through it. It may have an iron core inside the coil.
(Coil, Solenoid) It can be used as a transducer converting electrical
energy to mechanical energy by pulling on something.
Switches
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
Push Switch A push switch allows current to flow only when the button is
(push-to-make) pressed. This is the switch used to operate a doorbell.
This type of push switch is normally closed (on), it is open
Push-to-Break Switch
(off) only when the button is pressed.
SPST = Single Pole, Single Throw.
On-Off Switch
An on-off switch allows current to flow only when it is in the
(SPST)
closed (on) position.
SPDT = Single Pole, Double Throw.
2-way Switch A 2-way changeover switch directs the flow of current to one
(SPDT) of two routes according to its position. Some SPDT switches
have a central off position and are described as 'on-off-on'.
DPST = Double Pole, Single Throw.
Dual On-Off Switch A dual on-off switch which is often used to switch mains
(DPST) electricity because it can isolate both the live and neutral
connections.
DPDT = Double Pole, Double Throw.
Reversing Switch
This switch can be wired up as a reversing switch for a
(DPDT)
motor. Some DPDT switches have a central off position.
An electrically operated switch, for example a 9V battery
circuit connected to the coil can switch a 230V AC mains
Relay circuit.
NO = Normally Open, COM = Common, NC = Normally
Closed.
Resistors
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A resistor restricts the flow of current, for example to limit the current
passing through an LED. A resistor is used with a capacitor in a timing
Resistor
circuit.
Some publications still use the old resistor symbol:
This type of variable resistor with 2 contacts (a rheostat) is usually
Variable Resistor used to control current. Examples include: adjusting lamp brightness,
(Rheostat) adjusting motor speed, and adjusting the rate of flow of charge into a
capacitor in a timing circuit.
This type of variable resistor with 3 contacts (a potentiometer) is
Variable Resistor
usually used to control voltage. It can be used like this as a transducer
(Potentiometer)
converting position (angle of the control spindle) to an electrical signal.
This type of variable resistor (a preset) is operated with a small
screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is
Variable Resistor
made and then left without further adjustment. Presets are cheaper
(Preset)
than normal variable resistors so they are often used in projects to
reduce the cost.
Capacitors
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A capacitor stores electric charge. A capacitor is used with a
Capacitor resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to
block DC signals but pass AC signals.
A capacitor stores electric charge. This type must be
Capacitor, connected the correct way round. A capacitor is used with a
polarised resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to
block DC signals but pass AC signals.
Variable Capacitor A variable capacitor is used in a radio tuner.
This type of variable capacitor (a trimmer) is operated with a
small screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set
Trimmer Capacitor
when the circuit is made and then left without further
adjustment.
Diodes
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A device which only allows current to flow in one
Diode
direction.
LED
A transducer which converts electrical energy to light.
Light Emitting Diode
A special diode which is used to maintain a fixed
Zener Diode
voltage across its terminals.
Photodiode A light-sensitive diode.
Transistors
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A transistor amplifies current. It can be used with other components to make
Transistor NPN
an amplifier or switching circuit.
A transistor amplifies current. It can be used with other components to make
Transistor PNP
an amplifier or switching circuit.
Phototransistor A light-sensitive transistor.
Audio and Radio Devices
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
Microphone A transducer which converts sound to electrical energy.
Earphone A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Loudspeaker A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Piezo Transducer A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
An amplifier circuit with one input. Really it is a block diagram
Amplifier
symbol because it represents a circuit rather than just one
(general symbol)
component.
Aerial A device which is designed to receive or transmit radio signals.
(Antenna) It is also known as an antenna.
Meters and Oscilloscope
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A voltmeter is used to measure voltage.
Voltmeter The proper name for voltage is 'potential difference', but most
people prefer to say voltage!
Ammeter An ammeter is used to measure current.
A galvanometer is a very sensitive meter which is used to
Galvanometer
measure tiny currents, usually 1mA or less.
An ohmmeter is used to measure resistance. Most multimeters
Ohmmeter
have an ohmmeter setting.
An oscilloscope is used to display the shape of electrical signals
Oscilloscope
and it can be used to measure their voltage and time period.
Sensors (input devices)
Component Circuit Symbol Function of Component
A transducer which converts brightness (light) to resistance (an
LDR electrical property).
LDR = Light Dependent Resistor
A transducer which converts temperature (heat) to resistance
Thermistor
(an electrical property).
Logic Gates
Logic gates process signals which represent true (1, high, +Vs, on) or false (0, low, 0V, off).
For more information please see the Logic Gates page.
There are two sets of symbols: traditional and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission).
Gate Type Traditional Symbol IEC Symbol Function of Gate
A NOT gate can only have one input. The 'o' on the output
means 'not'. The output of a NOT gate is the inverse
NOT
(opposite) of its input, so the output is true when the input is
false. A NOT gate is also called an inverter.
An AND gate can have two or more inputs. The output of an
AND
AND gate is true when all its inputs are true.
A NAND gate can have two or more inputs. The 'o' on the
NAND output means 'not' showing that it is a Not AND gate. The
output of a NAND gate is true unless all its inputs are true.
An OR gate can have two or more inputs. The output of an
OR
OR gate is true when at least one of its inputs is true.
A NOR gate can have two or more inputs. The 'o' on the
output means 'not' showing that it is a Not OR gate. The
NOR
output of a NOR gate is true when none of its inputs are
true.
An EX-OR gate can only have two inputs. The output of an
EX-OR EX-OR gate is true when its inputs are different (one true,
one false).
An EX-NOR gate can only have two inputs. The 'o' on the
output means 'not' showing that it is a Not EX-OR gate. The
EX-NOR
output of an EX-NOR gate is true when its inputs are the
same (both true or both fal
In electronics the following units are used:
Symbol Quantity Symbol Unit
U Voltage V Volt
I Stroom A Ampere
R Resistance Ohm
C Capacity F Farad
L Induction H Henry
P Power W Watt
t Time s seconde
f Frequency Hz Hertz
Q Charge C Coulomb
Formulas
This is the relation between current, voltage, and resistance:
and and U=IR
This rule is known as Ohm's law.
Power can be calculated with this formula:
P = UI
And so:
P = I2R
Current is nothing more then the flow of charge so:
The number of units (Coulomb) that passes per second is the current in Amperes.
You can use this formula to calculate the current through a capacitor:
You might also like
- Wire To Pass Current Very Easily From One Part of A Circuit To AnotherDocument8 pagesWire To Pass Current Very Easily From One Part of A Circuit To AnotherPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student VersionDocument25 pagesELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student Versionnaqirustambajwa90No ratings yet
- Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit SymbolsDocument4 pagesServicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit Symbols伊文伊文No ratings yet
- Applied Phy Lab ManualDocument109 pagesApplied Phy Lab Manualamirmehmood88No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics SymbolsDocument52 pagesElectrical and Electronics SymbolssorcererpcNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument17 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsMuhammad SajedNo ratings yet
- 100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument22 pages100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDavid Atkinson100% (1)
- Electronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsAlexander San Juan92% (112)
- Pertemuan Ke 2a - Pengenalan Komponen Dasar ElektronikaDocument16 pagesPertemuan Ke 2a - Pengenalan Komponen Dasar ElektronikaAffan NaufalNo ratings yet
- Electrical ComponentsDocument29 pagesElectrical ComponentshariprasadNo ratings yet
- Wires and ConnectionsDocument22 pagesWires and ConnectionsDanilo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Electric Shop Lab ManualDocument13 pagesElectric Shop Lab ManualHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- PESIT AE LAB – Supporting Notes Circuit SymbolsDocument40 pagesPESIT AE LAB – Supporting Notes Circuit SymbolsRohit Patil100% (2)
- ECE Workshop Exp No. 1Document6 pagesECE Workshop Exp No. 1Jai JohnNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice (Electric Shop)Document13 pagesWorkshop Practice (Electric Shop)muhammad omer100% (1)
- Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectrical & Electronic Circuit Symbolspc100xohmNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...Document12 pagesElectronic Component Function and Symbols ...Janneal Ann Endaya AlanoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols and Names ExplainedDocument21 pagesCircuit Symbols and Names ExplainedMehmet KARAHANLINo ratings yet
- Electrical Actuation SystemsDocument67 pagesElectrical Actuation SystemsMOHAMMED IRSHADNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Compone NT Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument7 pagesCircuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Compone NT Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentRalph MedinaNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)Document7 pagesLab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)awien28No ratings yet
- Essential Electronics Components GuideDocument48 pagesEssential Electronics Components GuidejojoNo ratings yet
- Circuits 1Document110 pagesCircuits 1Mark Ian Tanangonan Maravilloso100% (1)
- Simbologia Eletrica 1Document4 pagesSimbologia Eletrica 1SarjitoNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing Symbols for ElectronicsDocument6 pagesTechnical Drawing Symbols for ElectronicsLatif Santiago KhalidNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 2: Electrical SymbolsDocument22 pagesEngineering Utilities 2: Electrical SymbolsMona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- LegendDocument8 pagesLegendhassanpour5882No ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsCasandra ClarkNo ratings yet
- MODULE in Consumer ElectronicsDocument129 pagesMODULE in Consumer ElectronicsNyepni NelmiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument21 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsHassaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 pagesComponent Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentNelson CabingasNo ratings yet
- Simboli CircuitiDocument6 pagesSimboli CircuitiLuca MarzarioNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practices Laboratory: Lab ManualDocument51 pagesEngineering Practices Laboratory: Lab ManualKarthikeyan100% (1)
- Electronic Components Symbols FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectronic Components Symbols Functionsyamaha355No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsDocument16 pagesElectrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsSanjana Singh100% (1)
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentdasfagagNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practices Laboratory (12F1Z9) : Lab ManualDocument51 pagesEngineering Practices Laboratory (12F1Z9) : Lab ManualJoao Carlos DrumondNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and ConnectionsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols: Wires and ConnectionsAnonymous BwLfvuNo ratings yet
- House WiringDocument8 pagesHouse WiringUncle DrewNo ratings yet
- Simple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsDocument15 pagesSimple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsCiprian MihailaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic Symbolsprecious umingaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols Electronics ClubDocument6 pagesCircuit Symbols Electronics Clubayodeledamilola124No ratings yet
- Project Report Chapter 3Document7 pagesProject Report Chapter 3ibrar82No ratings yet
- PEI Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument44 pagesPEI Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inBoban MathewsNo ratings yet
- Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 pagesWires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentHanim HusaifNo ratings yet
- Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 pagesWires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentHanim HusaifNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light ControlDocument7 pagesAutomatic Street Light ControlFilza FatimaNo ratings yet
- MSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-LdrDocument16 pagesMSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-Ldrjigyasa BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Electronic SymbolsDocument15 pagesElectronic SymbolsJuliannie LinggayoNo ratings yet
- Emergency LightDocument12 pagesEmergency LightEysha qureshiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Identification FunctionsDocument16 pagesElectronic Components Identification FunctionsDarrel Mark MoralesNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrical/ Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesTable of Electrical/ Electronic Symbolscarmelle de lunaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsEBENo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols ExplainedDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols ExplainedAhmed Khaled100% (1)
- Basic Electronics by Cel - Phon PDFDocument12 pagesBasic Electronics by Cel - Phon PDFDaniel Etsey50% (2)
- Industrial AutomationDocument18 pagesIndustrial Automationvineet ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument24 pagesEngineering Thermodynamicsapi-26570979100% (2)
- Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering An Intramuscular Injectionapi-26570979100% (4)
- In Dus Try Integra Tion inDocument26 pagesIn Dus Try Integra Tion inapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Repeated and Reliable MeasurementDocument5 pagesRepeated and Reliable Measurementapi-26570979No ratings yet
- AARONDocument6 pagesAARONapi-26570979No ratings yet
- ^^Document2 pages^^api-26570979No ratings yet
- AaaaaadissssssDocument2 pagesAaaaaadissssssapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Administering A Subcutaneous InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering A Subcutaneous Injectionapi-26570979100% (5)
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENTDocument17 pagesACKNOWLEDGEMENTapi-2657097980% (5)
- Student No: 04-207-058 Assignment No: Name: Jenny Lee M. Antolin Yr & Sec: BSECE 4 - C Instructor: ENGR. ENRICO MANALO Date: TitleDocument2 pagesStudent No: 04-207-058 Assignment No: Name: Jenny Lee M. Antolin Yr & Sec: BSECE 4 - C Instructor: ENGR. ENRICO MANALO Date: Titleapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Data and Results Table 1. Summary of Job Orders (January-April 2007) Customer Description Date Received Date Delivered Duration (Working Days)Document10 pagesData and Results Table 1. Summary of Job Orders (January-April 2007) Customer Description Date Received Date Delivered Duration (Working Days)api-26570979No ratings yet
- Repeated and Reliable MeasurementDocument5 pagesRepeated and Reliable Measurementapi-26570979No ratings yet
- R&R For Private Recruitment and Placement Agency For Local EmploymentDocument14 pagesR&R For Private Recruitment and Placement Agency For Local EmploymentjoNo ratings yet
- Student No: 04-207-058 Assignment No: Name: Jenny Lee M. Antolin Yr & Sec: BSECE 4 - C Instructor: ENGR. ENRICO MANALO Date: TitleDocument3 pagesStudent No: 04-207-058 Assignment No: Name: Jenny Lee M. Antolin Yr & Sec: BSECE 4 - C Instructor: ENGR. ENRICO MANALO Date: Titleapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Saske ResumeDocument2 pagesSaske Resumeapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Scientific PaperDocument3 pagesScientific Paperapi-26570979100% (1)
- SANSDocument2 pagesSANSapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Travel and Tours ServicesDocument15 pagesTravel and Tours ServicesJeremy LugawNo ratings yet
- San LuisDocument7 pagesSan Luisapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Venue and Sponsorship LetterDocument2 pagesVenue and Sponsorship Letterapi-26570979100% (1)
- Roxy PostcolonialismDocument2 pagesRoxy Postcolonialismapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Salon Price ListDocument2 pagesSalon Price Listapi-26570979No ratings yet
- RollyDocument2 pagesRollyapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Miranda, Marvin John R. Salta, Aldous Management Information System October 13, 2007Document5 pagesMiranda, Marvin John R. Salta, Aldous Management Information System October 13, 2007api-26570979No ratings yet
- RoseDocument2 pagesRoseapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Resume TinDocument4 pagesResume Tinapi-26570979No ratings yet
- RPGDocument1 pageRPGapi-26570979No ratings yet
- RomchellDocument3 pagesRomchellapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Hair NailsDocument4 pagesHair Nailsapi-26570979No ratings yet
- # 9 Arambulo Street BF Resort Village: Rex Magdangal Olila de OcampoDocument1 page# 9 Arambulo Street BF Resort Village: Rex Magdangal Olila de Ocampoapi-26570979No ratings yet
- ITU ISUP Release Cause CodesDocument5 pagesITU ISUP Release Cause Codesdelgado08No ratings yet
- 2014-6-2 PCED South Hill Coalition Proposed Elements MatrixDocument2 pages2014-6-2 PCED South Hill Coalition Proposed Elements MatrixSpokane City CouncilNo ratings yet
- Hard Disk DriveDocument4 pagesHard Disk DriveAbhishek AbhiNo ratings yet
- DR System ConciseDocument37 pagesDR System ConciseJiten KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Modernize Customer Service with a Cloud-Based Contact CenterDocument11 pagesModernize Customer Service with a Cloud-Based Contact CenterMishNo ratings yet
- LUCY SwitchgearDocument8 pagesLUCY SwitchgearHillary McgowanNo ratings yet
- EGIG - 10th - Report - Final - 09-03-2018 - v1Document50 pagesEGIG - 10th - Report - Final - 09-03-2018 - v1Paulo Marcos Cabral JuniorNo ratings yet
- Concrete: Concrete Is A Composite Material Composed of Fine and CoarseDocument36 pagesConcrete: Concrete Is A Composite Material Composed of Fine and CoarseclubmailusNo ratings yet
- Que Dice Ese Gesto Descargar GratisDocument2 pagesQue Dice Ese Gesto Descargar GratisjavierNo ratings yet
- Catalog Advantys AS-I IP20-IP67 - 803510 - DIA3ED2040909EN - 200408Document30 pagesCatalog Advantys AS-I IP20-IP67 - 803510 - DIA3ED2040909EN - 200408Jean MarzanNo ratings yet
- ESD Protection in CMOS: Characterization and Failure AnalysisDocument113 pagesESD Protection in CMOS: Characterization and Failure AnalysisElisavNirolfNo ratings yet
- Essential Roof Truss Design TermsDocument45 pagesEssential Roof Truss Design TermsAnkit SuriNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Thickness and Heat Transfer CalculationsDocument9 pagesBoundary Layer Thickness and Heat Transfer Calculationsannie100% (1)
- Analysis, Specification and Estimate On Road WorksDocument71 pagesAnalysis, Specification and Estimate On Road WorksAnonymous BACdUNvPZ280% (5)
- InverterDocument8 pagesInverterrajinipre-1No ratings yet
- NPTEL Science and Technology of PolymersDocument2 pagesNPTEL Science and Technology of PolymersAzhagiri PonNo ratings yet
- Lec 958975Document19 pagesLec 958975Rajasekar PichaimuthuNo ratings yet
- SteelKote EP ZN HS: High-Build Zinc-Rich Epoxy PrimerDocument3 pagesSteelKote EP ZN HS: High-Build Zinc-Rich Epoxy Primerprasanth cp100% (1)
- Nature of Acidity and Lime Requirement in Acid Soils of ManipurDocument8 pagesNature of Acidity and Lime Requirement in Acid Soils of ManipurIJASRETNo ratings yet
- Determining The Redundancy FactorDocument6 pagesDetermining The Redundancy FactorEdris Salehi GolsefidiNo ratings yet
- ESAB Welding HandbookDocument31 pagesESAB Welding Handbookhooky1100% (4)
- Lotus 1-2-3 For WindowsDocument75 pagesLotus 1-2-3 For Windowskennedy_saleh100% (1)
- List of Linkages2016Document74 pagesList of Linkages2016engrwho0% (1)
- Hanson G209 (SW Valves)Document12 pagesHanson G209 (SW Valves)AKSHEYMEHTANo ratings yet
- Murray Loop Test To Locate Ground Fault PDFDocument2 pagesMurray Loop Test To Locate Ground Fault PDFmohdNo ratings yet
- LDX2101 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesLDX2101 Spec SheetGaurav NarulaNo ratings yet
- ZXONE Quick Installation Guide - V1.0Document56 pagesZXONE Quick Installation Guide - V1.0kmad100% (2)
- Power and Simplicity: Pace ScientificDocument16 pagesPower and Simplicity: Pace ScientificAnonymous mNQq7ojNo ratings yet
- NDI Manual 2013 - v10Document13 pagesNDI Manual 2013 - v10Yudha Bhakti NugrahaNo ratings yet
- PML Rev-I Preferred Manufacturer List for PT Pertamina EPDocument12 pagesPML Rev-I Preferred Manufacturer List for PT Pertamina EPAndreas Schlager100% (1)