Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan Format Recitation
Uploaded by
wayne2473Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan Format Recitation
Uploaded by
wayne2473Copyright:
Available Formats
Tillett 1
EDUC: 22241 - Teaching Methods W. Tillett 15/10/11 Lesson Plan Recitation Method Lesson Plan: Recitation Method Instructor: ______Wayne Tillett_______ Date: _12th Sept. 2011___ _ Grade Level & Subject: __ TD Level 1(2st form) Care and Use of Inst./Matl.__
Unit Topic: _Tech. Drg. Inst. /Matl. Lesson 1 in Unit 1:
Planning Module Goal: This Module is designed to introduce trainees to basic knowledge and skill of Technical Drawing. This module focuses on the different types of equipment and provides the trainee with background on preparing drawing paper. The module will serve as a tool to guide and prepare the trainees to convey ideas and information through drawing, which is a basic and natural form of communication. The exercise in the module are geared to help trainees to recognize that technical drawing is a universal language that can be used to record the objects and actions of everyday life in a manner that everyone can easily recognize and understand. Behavioral Objective: 1. Given the notes, trainees will be able to, identify seven basic drafting instruments/materials. (Cognitive: Comprehension) 2. Given handouts, trainees will be able to, state the use of seven basic drafting instruments/materials. (Cognitive: Knowledge) 3. Given handout, trainees will be able to, explain 10 out of 16 points for proper use and care of drafting instruments/material. (Cognitive: Comprehension) 4. Through oral questioning, trainees will share opinion on the importance of the care and proper use of drafting instruments/materials. (Affective: value)
Tillett 2
Essential Question(s): What are the seven basic tools used in the drafting room? 1. What are the seven (7) basic instrument/material used in the drafting room? 2. What is the use of the following drafting instruments? a. T-square b. Set square c. Protractor d. Compass e. Drawing paper f. Drawing pencil g. Drawing board 3. What are the ten (10) points to remember for the proper use and care of drafting instruments/materials? 4. Why is it important to adhere to the proper use of drafting instruments/materials? Assessment of BO/ EQ: Class participation Oral question on use and care of drafting instruments/materials. Note taking Worksheet completion
Preview Skill: Identify basic tools used in technical drawing List use of basic technical drawing tools Listing rules for producing accurate drawings Explain point for care of drafting instruments/materials. Share opinions on proper care of drafting instruments/materials.
Daily Planner: [Overview: list activities and estimated times] Teaching or Learning Activity 1. Begin Class Take Attendance Post EQs on white board. 2. Activating Strategy Have trainees list tools used for general drawing. 3. Development of lesson( Lecture, Oral questioning) Estimated Time (80 min) 3 min
8 min
32 min
Tillett 3
4. Introduction of new content(Lecture, Oral questioning) 5. Summary/Conclusion (Complete worksheet)
22 min 15 min
Lesson Format: DIRECT INSTRUCTION Activating Learning Strategies ______8____ minutes Activator & Description / Include instructional grouping of students: The instructor will open the lesson by having trainees list tools used for general drawing of shapes and figures. He will make a list on the white board of the trainees suggestions. From the list he will high light, and add if necessary, the basic ones which will be discuss in class.
Teaching New Content Describe Procedures for teaching new content: _____54_____ minutes A. New Content: Presentation, Use of 7 basic instruments/materials. Direct Instruction The instructor will pass out handout which shows diagrams of the seven (7) basic instruments/materials which will be discuss in class. Lecture with power point presentation will be used for each of the seven (7) instruments/materials, while trainees listen and high light notes. Power Point and Handout 1: Use of 7 basic drafting instruments THE T-SQUARE Horizontal lines are drawn with the T-SQUARE, Fig. 1 & 2. It also supports triangles when they are used to draw vertical and inclined lines. The T-square consists of two parts, the head and the blade or straight edge. The head is usually fixed solidly to the blade; however, a T-square with a protractor head and adjustable blade is also available. Clear plastic strips inserted in the blade edge of some T-squares makes it easier to locate reference points and lines. The blade must never be used as a guide for a knife or other cutting tool. If accurate line work is to be done, it is essential that the head of the T-square is held firmly against the working edge of the board.
Tillett 4
It is recommended that the blade be left flat on the board or suspended from the hole in its end. This will keep warping or bowing of the blade to a minimum.
USING THE T-SQUARE TO DRAW HORIZONTAL LINES
USING T-SQUARE TO DRAW INCLINED PLANES
SET SQUARES (TRIANGLES) When supported on the T-square blade, the 30-60 deg. and 45 deg. TRIANGLES, Fig. 4, are used to draw vertical and inclined lines. They are made. of transparent plastic
Tillett 5
and are available in a number of different sizes. To prevent warping, the triangle should be left flat on the drawing board when not being used. Angles of 15 and 75 deg. can be drawn by combining the triangles. To draw vertical lines accurately, rest triangle solidly on the T-square blade while holding the T-square head firmly against the working edge of the drawing board fig.5. Setsquares are available in various heights, e.g., 6 inches, 8 inches, 10 inches, and 12 inches.
(a) 300 600 set square
(b) 450 set square Fig. 4
USING A SET SQUARE
Right-handed trainees
Left-handed trainees
Tillett 6
Fig. 5
PROTRACTORS A PROTRACTOR, Fig. 6, is used to measure and lay out angles on drawings. They are usually made of clear plastic and may be either circular or semicircular in shape. The degree graduations are scribed or engraved around the circumference of the protractor. When measuring or laying out an angle, place the center lines of the protractor at the point of the required angle as shown in Fig. 6. Read or mark the angle from the graduations on the circumference of the tool.
Fig. 6 COMPASS In drafting, circles and arcs are drawn with a COMPASS, Fig. 7. For best results the lead should be adjusted so that it is about 1/32 in. shorter than the needle. Both legs will be the same length when the needle penetrates the paper. Fit the compass with lead that Is one grade softer than the pencil used to make the drawing. The lead must be kept sharp. Several attachments are available for use with the compass. To set the compass to size, draw a line on a piece of clean scrap paper and measure off the required radius. Set the compass on this line. Avoid setting a compass on a scale. "Sticking" the compass needle into the scale will eventually destroy its accuracy. You will probably use a circle template instead of a compass.
Tillett 7
Fig. 7
DRAFTING PAPER (DRAFTING MEDIA) Drawings are made on many different materials - paper, tracing vellum, film, etc. A heavyweight opaque paper that is white, buff or pale green in color is used in many school drafting rooms. While this paper takes pencil lines well, it is difficult to erase because the pencil point makes a depression in the paper when a line is drawn. If this material is used, take special care to prevent mistakes. Industry make much use of vellum and film because reproductions or prints must, be made of all drawings. Drawing media is available in either sheet or roll form. Standard sheet sizes are identified by letter size: A - 8 1/2 x 11 or 9 x 12 (The one we will be using) B - 11 x 17 or 12 x 18 C - 17 x 22 or 18 x 24 D - 22 x 34 or 24 x 36 E - 34 x 44 or 36 x 48 PENCILS As most drawings are prepared with a pencil, it is important that the proper pencil be selected. The drawing media used will determine the type of pencil that should be used. The conventional graphite lead pencil is satisfactory with most papers and tracing vellums, while a pencil with plastic lead is necessary if the drawing is made on film. The draftsman can select from 18 grades of pencils that range in hardness from 9H (very hard) to 7B (very soft) fig.8b.
Tillett 8
Many draftsmen use a 4H or 5H pencil for layout work and an H or 2H pencil to darken the lines and to letter. In general, use a pencil that will produce a sharp, dense black line because this type of line reproduces best on prints. Avoid using a pencil that is too soft. It will wear rapidly, smear easily and soil your drawing. Also, the lines will be "fuzzy" and will not produce usable prints. A conical shaped pencil point Is preferred for most general purpose drafting. To sharpen the pencil, cut the wood away from the unlettered end. Use a knife or mechanical sharpener and point the lead on a pencil pointer. A semiautomatic pencil, Fig. 8a, is usually preferred to a wood pencil. With this type pencil it is not necessary to cut away the wood to expose the lead. The extended lead is shaped on a pencil pointer.
fig. 8a
For accurate layout work For general drawing and sketching Use almost exclusively for artwork
fig. 8b
Tillett 9
DRAWING BOARD The DRAWING BOARD, fig. 9, provides the smooth, flat surface needed for drafting. The tops of many drafting tables are designed for this purpose. Individual drawing boards are manufactured in a variety of sizes. The majority of them are made from selected, seasoned basswood.(reference will be made to drafting table in classroom) The right-handed draftsman will use the left edge of the board as the working edge; the left handed draftsman the right edge. The working edge should be checked periodically for straightness. Draftsmen often tape a piece of heavy paper or a special vinyl board cover to the working face of the drawing board to protect its surface. The vinyl surface is easily cleaned.
Fig 9 Guided Practice The instructor and trainees will discuss the use of each drafting instruments/materials mentioned. Formative Assessment The instructor questions to recap the main points.(EQ) Q1. What are the seven (7) basic instruments/materials used in drafting? Q2. What is the use of the following drafting instruments/materials? T-square Set square (triangles) Protractor Compass Drafting paper (Drafting media) Pencil Drafting board. Direct Instruction Instructor transition to next content topic:
Tillett 10
Now that we are familiar with the basic drafting instruments. It is very important also to know how to care for and use them properly. In knowing to do this you will produce neat and accurate work. B. New Content: Care and proper use of instruments/materials Activator The instructor will give some examples showing some results when instruments/materials are not properly taken care of. He will also show incorrect use of the drafting instruments/materials. Reference will be made to the pencil in particular and the screws located on the head of the T-square fig 10 to 13.
The pencil as it comes from the draftsmans sharpener. The lead is exposed and un-pointed.
Fig.10 A long, tapering point produces clean, sharp lines.
Fig.11
Tillett 11
Handout will be given at this point Avoid dull, stubby points. Poor line-work results
Fig.12
POSITION OF PENCIL WHEN IN USE
Fig. 13 Handout will be given Direct Instruction The instructor will explain the point on aid to accuracy on handout. Power Point and Handout 2: Care of Instruments, Aids to accuracy i. Keep your instruments clean. ii. Do not abuse your instruments. iii. Be certain that the screws that ensure the T- square blade to the head are securely tightened. iv. Set Square should not be placed against the lower edge
Tillett 12
of the T- Square. v. Avoid drawing vertical lines with the T- Square placed against the bottom or top edge of the drawing board. vi. Always use the setsquare in conjunction with the TSquare, unless the line to be drawn is inclined at an angle not contained in the set- square. vii. Measure accurately. viii. Use light, inconspicuous dot to record your measurement on the drawing paper. ix. When possible, make your measurements along exiting lines. x. Views of objects that are drawn to the actual size of the object are said to be drawn full size. Scale full size can also be stated as scale 12 = 1 0 " xi. Keep the pencil sharp. xii. A properly sharpened pencil does not require heavy pressure to produce clean, sharp lines. xiii. To ensure control of the pencil, hold it to the sharpened end. xiv. Rotate the pencil slowly, away from you, as you draw a line. xv. Sharpen the pencil at the end that does not indicate the grade of the pencil. xvi. Do not push the pencil. Draw it in the direction it is leaning. Formative Assessment/Instructor & Trainee Summary Wrap (EQ): Q3. What are 10 points to remember in order to produce neat accurate drafting work? Q4. Why is it important to adhere to the proper use of drafting instruments/materials? Lesson Closure _____15______ minutes Trainee Summary: Trainee will use hand out on new content learn to complete short answer questions of worksheet provided by instructor to turn in. (see attached) Teacher Summary: The teacher will wrap up with random questions and instruct students to complete the worksheet. The assignment will also be given.
Tillett 13
Homework Assigned
1. Trainee is required to bring for next class all of the basic equipment/ material discussed. 2. Finish worksheet at the end of the unit in the textbook. Technical Drawing Level 1 (Unit 1, Page M1-19) Textbook: Technical Drawing Level 1 (Trainees Manual, Module 1, Unit 1, pages M1-3 to M1-18). Plane and Solid Geometry 1st Edition ( chapter 1, pages 4 to 8) Compass Ruler Set Square Clean Class room. Pencil Eraser handouts Markers Coloured Typing Sheets Projector (infocus) Supplemental material: http://www.ubatc.edu/course-d/intro-draft/tools_lessons.htm http://www.technologystudent.com/designpro/drawdex.htm Strengths Instructor: The handout provided by instructor was appropriate for lesson. It offers lots of visuals and the information was clear and to the point. Trainees: The trainee exhibited attentiveness to presentation. The trainees participated well in questioning sessions. Follow-up Activities: Worksheet was completed by trainees and approximately 80% of the class got 10 question correct form worksheet. Due to financial constraints trainees purchase instruments of inferior quality. Areas For Improvement: The furniture used is not appropriate for 54 min of lecturing. The seats are too tall making it uncomfortable sitting down for long periods. This is best done in a traditional classroom setting, with arm chairs.
Materials/Resources/ Technology/Safety
Evaluation
Tillett 14
Worksheet Drafting instruments/materials
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE -UNIT 1 1. The drawing board provides the _________________________________________ 2. A piece of heavy drawing paper or a special vinyl board cover is sometimes attached to the working surface of the board to: a) Provide a drawing surface. b) Protect its surface. c) Provides a surface to work out problems. d) All of the above. e) None of the above. 3. The T-square is used to ________________________________________________ 4. Vertical and inclined lines are drawn with ___________________________________ 5. The compass is used in drafting to draw ___________________________________ 6. Why is it important to slowly rotate the pencil away from you when you draw a line? ____________________________________________________________________ 7. Angles can be measured and laid out on drawings by using a ___________________ 8. The ___________________________ or pencil is recommended for layout work. 9. An ___________________________ or _________________________ pencil is used to darken the lines and for lettering. 10. Why is it important to keep instrument clean? ___________________________________________________________________ 11. List the five standard sheet sizes used in drafting: a. ___________________________ b. ___________________________ c. ___________________________ d. ___________________________ e. ___________________________ 12 List 10 points to remember in order to produce neat accurate drafting work.
You might also like
- Entrep Week 1Document6 pagesEntrep Week 1Gerald SulaboNo ratings yet
- Format of LP in English 2021Document4 pagesFormat of LP in English 2021Gail MejiaNo ratings yet
- Cot 1 Pastillas Wrapper LPDocument2 pagesCot 1 Pastillas Wrapper LPFarrahmae FrescoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Templateapi-347584593100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Samar State UniversityDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - Samar State UniversityLes LieNo ratings yet
- CHESS 1 - PE8GS-IIIc-1Document10 pagesCHESS 1 - PE8GS-IIIc-1Judy Ann MorilloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 7atz Kusain100% (1)
- Assessing Sky Lantern CraftsmanshipDocument1 pageAssessing Sky Lantern CraftsmanshipBeaMaeAntoniNo ratings yet
- Do No 42. Guidelines On Daily Lesson Preparation 2016Document32 pagesDo No 42. Guidelines On Daily Lesson Preparation 2016Ludovina Calcaña100% (1)
- Action Research PaperDocument37 pagesAction Research PaperKATE SHELOU TABIANNo ratings yet
- Assessment Rubric For Venn Diagram PointsDocument1 pageAssessment Rubric For Venn Diagram PointsJenielynFerreraArriolaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH 8Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH 8crimel cortezNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument1 pageNarrative ReportaceNo ratings yet
- DLP Fourth Quarter in MathematicsDocument53 pagesDLP Fourth Quarter in MathematicsAna Marrie PaviaNo ratings yet
- Dance Etiquette - CotDocument76 pagesDance Etiquette - CotAraNo ratings yet
- DLL Lesson 1Document7 pagesDLL Lesson 1Norico YvonneNo ratings yet
- Health Education Catch Up Friday PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Education Catch Up Friday PlanRejoice G. CasipleNo ratings yet
- Compostela, Davao de Oro: Project TitleDocument2 pagesCompostela, Davao de Oro: Project TitleAnabelle LagulosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan TemplateRami BouzoraaNo ratings yet
- School Nutrition ReportDocument2 pagesSchool Nutrition ReportGeraldo N. QuillaoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LogJobel Sibal CapunfuerzaNo ratings yet
- Expressing Insights RubricDocument1 pageExpressing Insights RubricRaven Quiin100% (1)
- Q1 - Week1-2 - DLL - ICF 8Document7 pagesQ1 - Week1-2 - DLL - ICF 8Sheine Nasayao MatosNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts of LuzonDocument2 pagesArts and Crafts of LuzonCris Ann Pausanos100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in 1music 7Document5 pagesLesson Plan in 1music 7Shamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 11Document4 pagesA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 11Alma LibangNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Clean, Green, Organized and Eco-FriendlyDocument5 pagesRubrics For Clean, Green, Organized and Eco-FriendlyRoderick Beltran Lutang100% (1)
- PROFED LATEST With Answer KeyDocument16 pagesPROFED LATEST With Answer KeyErika Arcega100% (1)
- Eloisa de Guzman Meas EvalDocument4 pagesEloisa de Guzman Meas EvalEloisa Deguzman50% (2)
- Final Demo DLPDocument8 pagesFinal Demo DLPJoshua CondeNo ratings yet
- Episode 14 My First Classroom DemonstratDocument7 pagesEpisode 14 My First Classroom DemonstratVincentAlejandroNo ratings yet
- DLP-Performance Task - 1Document2 pagesDLP-Performance Task - 1Benito OmalNo ratings yet
- Rpms Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesRpms Lesson PlanEric John VegafriaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Job Application LetterDocument1 pageTeaching Job Application LetterChristopher CelisNo ratings yet
- Arts and Design - Performing Arts Production - 1 PDFDocument3 pagesArts and Design - Performing Arts Production - 1 PDFEljhie AllabaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 7 8 Las Week 6 Final AnnieDocument17 pagesCookery 7 8 Las Week 6 Final AnnieNorman PolilinNo ratings yet
- Tle 6 He DemoDocument6 pagesTle 6 He DemoJoan F. MaligNo ratings yet
- MODULE IN TLE 7 & 8 (Specialization-Cookery) First Grading/Week 3 Day 1Document6 pagesMODULE IN TLE 7 & 8 (Specialization-Cookery) First Grading/Week 3 Day 1Shi E LaNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument3 pagesDLPJunafel Boiser GarciaNo ratings yet
- Farm Tools Identification QuizDocument2 pagesFarm Tools Identification QuizLordy Picar100% (1)
- Science Module - Sample PDFDocument58 pagesScience Module - Sample PDFBETHUEL P. ALQUIROZNo ratings yet
- Performance Task For The 2nd Quarter g8Document6 pagesPerformance Task For The 2nd Quarter g8marife gupaal100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Carry Out Measurements)Document3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Carry Out Measurements)Glenda JavierNo ratings yet
- Filmed Role Play Culminating RubricsDocument1 pageFilmed Role Play Culminating RubricsEHealth HEconomicsNo ratings yet
- Checking Condition QuizDocument3 pagesChecking Condition QuizDaniel SampagaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed-Lesson-Plan-CKLC-Philippine FestivalsDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed-Lesson-Plan-CKLC-Philippine FestivalsAngela Kate PaminianoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanNorsid SandiganNo ratings yet
- Bethel Academy-Senior High School Department: Division of CaviteDocument3 pagesBethel Academy-Senior High School Department: Division of CaviteVIRGILIO JR FABI100% (1)
- Jan Grade 9 - DLL Week 2 FinalDocument4 pagesJan Grade 9 - DLL Week 2 Finalnhoj lowell perlasNo ratings yet
- Endorsement - MLSBDocument1 pageEndorsement - MLSBMarlyn Santos Deus SindanumNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log (DLL)Document2 pagesDaily Lesson Log (DLL)Jadess FusioNo ratings yet
- How To Cook Pork AdoboDocument3 pagesHow To Cook Pork AdoboJennyRoseVelascoNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 8Document2 pagesMapeh 8Jeje MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Plate/Present Meat Dishes Technology and Livelihood Education-10 CookeryDocument9 pagesPlate/Present Meat Dishes Technology and Livelihood Education-10 CookeryAj GemperoNo ratings yet
- Jmafte Improved Mechanics MostDocument16 pagesJmafte Improved Mechanics MostVeridica El EdgieNo ratings yet
- TOS Aquaculture Second GradingDocument27 pagesTOS Aquaculture Second GradingVaness Flor Cabug PuyatNo ratings yet
- Reflection Food ChainDocument3 pagesReflection Food ChainmariamNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 MapehDocument14 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 Mapeh3-D Reman Jhon Rey FloraNo ratings yet
- 4 PillarsDocument2 pages4 PillarsArlene BuzzNo ratings yet
- Basic Technology Year 7 Note For Week OneDocument3 pagesBasic Technology Year 7 Note For Week OneAlvan MmaduwubaNo ratings yet
- Exhibitors-EXPO - Tamil Nadu (Coimbatore)Document14 pagesExhibitors-EXPO - Tamil Nadu (Coimbatore)Sujitha . KNo ratings yet
- Socolor Shade Chart: Getting Started With Socolor Coloring Grey With Socolor Additives Specialty CollectionDocument1 pageSocolor Shade Chart: Getting Started With Socolor Coloring Grey With Socolor Additives Specialty CollectionLeo CabelosNo ratings yet
- Artist and ArtisanDocument21 pagesArtist and Artisanlow keyNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document20 pagesModule 9Leonora CidNo ratings yet
- Bengal School & Rise of Modern Indian ArtDocument19 pagesBengal School & Rise of Modern Indian ArtSanskar MohapatraNo ratings yet
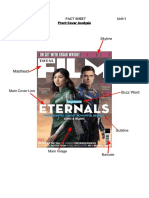
- Front Cover AnalysisDocument6 pagesFront Cover AnalysisCharlie ParkesNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawings: Ken Youssefi ME Dept., SJSUDocument16 pagesTechnical Drawings: Ken Youssefi ME Dept., SJSUsomu.cpNo ratings yet
- FA 30 List 1st ExamDocument3 pagesFA 30 List 1st Examxeno_saitoNo ratings yet
- BrunelleschiDocument13 pagesBrunelleschiEkta PatelNo ratings yet
- Landscape in The Mist ReviewDocument2 pagesLandscape in The Mist Reviewsk285431No ratings yet
- 02 Prepositions of Place FurnitureDocument17 pages02 Prepositions of Place FurnitureFrancesca CarranzaNo ratings yet
- TG - Art 3 - Q2Document29 pagesTG - Art 3 - Q2keziah matandogNo ratings yet
- The Handy Book of Artistic PrintingDocument232 pagesThe Handy Book of Artistic PrintingIvo Urrunaga CosmópolisNo ratings yet
- Demo Lesson Plan - Technical DraftingDocument4 pagesDemo Lesson Plan - Technical DraftingJude Metante100% (1)
- Art and Design Coursework PortfolioDocument7 pagesArt and Design Coursework Portfoliorhpvslnfg100% (2)
- Colour and Colour Idioms Conversation Topics Dialogs Warmers Coolers - 83084Document2 pagesColour and Colour Idioms Conversation Topics Dialogs Warmers Coolers - 83084fidanNo ratings yet
- Nombre: Grupo: Fecha: ActividadDocument4 pagesNombre: Grupo: Fecha: ActividadFrancisco Perez PerezNo ratings yet
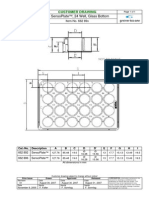
- Greiner Bio-OnE 24-Well Glass-Bottom Microplate - 662892Document1 pageGreiner Bio-OnE 24-Well Glass-Bottom Microplate - 662892mnrandNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Architecture Handout PDFDocument2 pages21st Century Architecture Handout PDFTon GomezNo ratings yet
- ImagineFX - June 2019 PDFDocument116 pagesImagineFX - June 2019 PDFJean Coelho Peres100% (1)
- On Tap Cuoi Ki AV4 - 5.2021Document6 pagesOn Tap Cuoi Ki AV4 - 5.2021Phạm PhátNo ratings yet
- Teresa Ivanore's Color Theory in Depth - 1 Step Further - Tints, Tones, Shades - Blank TemplateDocument3 pagesTeresa Ivanore's Color Theory in Depth - 1 Step Further - Tints, Tones, Shades - Blank TemplateViera ValachováNo ratings yet
- Office of Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) : Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP) Fy 2022Document4 pagesOffice of Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) : Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP) Fy 2022Jayson PalmaNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Erotic Act On The PerformatDocument21 pagesThe Ultimate Erotic Act On The PerformatGlennson BalacanaoNo ratings yet
- A B C D: Ground Floor PlanDocument1 pageA B C D: Ground Floor PlanCashmere AbutanNo ratings yet
- Rod A Demo Plan 4 Vernier ScaleDocument2 pagesRod A Demo Plan 4 Vernier ScaleAlfred BasiNo ratings yet
- Joseph Allen Stein's Philosophy of Architecture in NatureDocument10 pagesJoseph Allen Stein's Philosophy of Architecture in NatureHarsh BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Topic 8-Medium and Techniques of ArtistsDocument6 pagesTopic 8-Medium and Techniques of Artistsnorman mandoNo ratings yet
- Allen 1999 Infrastructural+UrbanismDocument10 pagesAllen 1999 Infrastructural+UrbanismMOGNo ratings yet
- Bacon - Analiza MaterijalaDocument548 pagesBacon - Analiza Materijalaslavica_restauroNo ratings yet