Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skin Summary Chart
Uploaded by
Marco HernandezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skin Summary Chart
Uploaded by
Marco HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
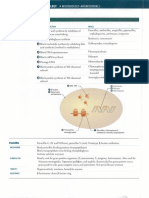
Name of Disease Folliculitis
BACTERIA Staphylococcal Keratosis pilaris Pseudofolliculitis barbae Sycosis barbae Propionibacterium acnes S. aureus
KEY NOTES ~can be superficial or deep
Acne Vulgaris Furuncles, Carbuncles
~open and closed comedomes ~progression of folliculitis ~may lead to cellulitis ~MRSA, resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics
Cellulitis
Group A Strep ~secondary to trauma (surgery or lesions) S. aureus in adults ~systemic response, vascular and lymphatic systems Hemophilus influenzae B in ~may see streaking children (rare) Infectious: B-hemolytic strep, ~subcutaneous adipose tissue (panniculitis) leprosy, TB Non-infectious: drug rxn, autoimmune conditions ~acute inflammation ~widening of septa = exquisite pain ~flatten and brusie, but NO SCARRING!!! ~subacute or chronic = septal fibrosis
Erythema Nodosum
Impetigo
S. aureus
~contagious, pururlent SUPERFICIAL skin infection ~in children at daycares ~pustule formation, rupture, wet erosions, honey-colored crusts
Name of Disease Dermatophyte Infections
FUNGI Tinea corporis Tinea cruris Tinea pedis Tinea Unguium Tinea manus ~Ringworm
KEY NOTES
~spares the scrotum, but affects the buttocks and thighs ~secondary bac. infections very prominent ~test with 10% KOH ~distal subungual = crumbling nail, most common ~proximal subungual = intact surface, separation, HIV px ~affects mucous mem, internal organs, skin ~opportunistic, pregnancy, antibiotics, diabetes, etc. ~mucous mems = necrosis and sloughing off
Onychomycosis
90% dermatophytes 6% yeasts 4% non-dermatophytic fungi yeast-like fungus
Candidiasis
**involves scrotum, beefy ~apposing skin surfaces = maceration of pustules, satellite pustules red with satellite lesions** ~mouth angles = maceration, fissures, 2 infections Oral candidiasis = Oral Thrush
Name of Disease Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
VIRUSES HSV-1; HSV-2 ~acute, recurrent vesicular eruptions
KEY NOTES
~4-10 day incubation period ~dormant in dorsal nerve root ganglion, CN 5 also seen in Epstein-Barr virus ~intial lesion = most contagious ~pregnancy, child blindness via ophthalmic branch, corneal scar ~only affects the epithelium = NO SCARS!!! ~skin-skin contact ~reactivation is localized Human Papilloma Virus(HPV) Genital Warts = HPV6,11,16 ~epithelial basal cells Genital Cancer = HPV16,18 ~children, young adults ~direct contact (2-6 mths) Varicella Zoster (VZV) ~chicken pox and shingles ~mucous mem, skin, neurons ~latent infection in sensory ganglia (dorsal root), similar mechanism as HSV ~respiratory droplets, bloodstream, systemic response ~Chicken pox = URT, 2 wks, torso to periphery, dew drops on rose petal ~Shingles = localized dermatomal distribution, infection of keratinocytes, itching, burning pain on nerve, skin has sim. dewdrop on rose petal
Name of Disease Pemphigus vulgaris
BULLOUS DISEASES autoimmune blistering dx large, painful, fragile
Bullous Pemphigoid
autoimmune blistering dx itchy, tense, large
KEY NOTES ~usu. Middle aged or older ppl ~CHRONIC blistering ***positive for Nikosky's sign*** ~IgG to intercellular adhesion molecules, acantholysis of DESMOSOMES ~fragile SUPRABASAL blisters, rupturing is very PAINFUL, erosions and crusting, 2 infections, loss of fluid, malnutrition, usu. Fatal ~common in elderly ~less aggressive and not life threatening ~on medial thighs and trunk ***NO ACANTHOLYSIS*** ~IgG directed to the basement membrane proteins (BPAG1, 2) ~destroys connection b/t dermis and epidermis (hemidesmosomes), tense SUBEPIDERMAL blister ~pruritis (itchiness)
Name of Disease Eczematous Dermatitis
INFLAMMATORY CONDITIONS antigen stimulation
KEY NOTES ~affects DERMIS and EPIDERMIS; NO IMMUNOLOGIC TARGETING ~Ag, inflammatory infiltrate, keratinocytes separated, dermal edema, vesicle formation, hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, lichenification, excoriation
Allergic & Contact Dermatitis
~hypersensitivity rxns (Type 4, cell mediated) ~any pruritic rxn, common in teenagers and young adults ~requires previous exposure, T-cell sensitization ~Ag, presented to nave CD4-T-cells, activationAg re-exposure, memory T-cells ~hypersensitivity rxn ~skin is dry, hyperkeratotic, easily lichenified
Atopic Dermatitis
linked to cataracts related to allergic rhinitis (IgE, eosinophils, His, mast ~begins in early childhood or adolescence cells)Otitis Externa
similar to RINGWORM (itchy, flaky lesion) so you must look ***not breastfed, hygiene hypo, diet, digestion, His release, emotional tension at borders and use 10% KOH Psoriasis ~due to hyperplasia, at any age ~family hx = autoimmune process, HLA tendency ~multifactorial, T-cell mediated, increased cGMP:cAMP ratio, INCREASED KERATINOCYTE REPLICATION, thinned stratum granulosum, Auspitz sign (pinpoint bleeding d/t exposed capillaries) ~triggers = phys. Trauma, drugs, infections, stress, diet, increased cGMP/cAMP ratio COMPARE TO ONYCHOMYCOSIS, need to NAILS = hyperkeratosis, shedding nail plate, punched out lesions, PITTING and crumbling of take scraping and dissolve in nail platehyperplasia of skin below the nail, debris, lifts the nail, irregular nail separationOIL 10% KOH, look for presence of SPOTTING psoriatic lesions, psoriasis also linked to hx of chronic joint pain Drug Eruptions Urticaria IN THE DERMIS!! ~mimic any skin condition, hypersensitivity or non-immunologic process, most commonly d/t antimicrobials and antipyretics, convulsants and diuretics ~to burn, acute or chronic, common His-mediated rxn to a trigger (stress, pressure, temp, chem. antigens) ~Antigen sensitization IgE, mast cell degranulation, His release, dermal vasc. hyperpermeability, dermal edema and pruritis ~mediator is HISTAMINE!!! ~may be an automimmune condition involving mast cells ~H1 receptors=on sensory nerve endings, pick up His, induce pruritis, so give H1 blockers for skin and resp. tract conds. ~H2 receptors=in gut lining, promote acid secretion, give to px with chronic ulcers ~last less than 24 hrs, wheals,
Name of Disease
BENIGN & PREMALIGNANT HYPERPLASTIC LESIONS
KEY NOTES benign, from melanocytes, very common, aggregate at the dermoepidermal junction, grow into the dermi, elevation above the epidermis, maturation, cord-like growth, very well differentiated!! Junction (flat, macular), Compound (from macuar to papular), Dermal
Melanocytic Nevi
Common Moles Atypical and Dysplastic Nevi Actinic Keratosis associated with malignant melanoma
~aquired, familial association, compound nevi woth abnormal growth and cells, lentigionous hyperplasia ~premalignant condition, ass'd w/chronic sun exposure, fair skinned ppl ~excess sun, basal cell hyperplasia atypia and dyskeratosis , fibroblast damage abnormal , synthesis, thickened dermis parakeratosis thickened stratum corneum , *** Need to remove before they progress into SCC***
Name of Disease Squamous Cell Carcinoma
MALIGNANT LESIONS
KEY NOTES ~affects epithelial keratinocytes, ass'd with chronic skin damage, second most common skin cancer ~small and removable,low invasive potential ~not very aggressive ~local growth via expansion into the dermis, lateral spreading under the skin along the bone, muscle, spread along the nerves or vessels, spread thru the lymphatics and then blood (lungs, liver, skin, brain, bone) ~most common skin cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma
SCALING, ULCERATION, EROSION, CRUST
~very slow growing, very rarely metastasize, locally invasive and destructive ONLY EPIDERMAL OR FOLLICULAR EPITHELIUM ~some cases are not even in sun exposed areas, eg ears and inner campus of the eyes ***NOT MUCOSAL*** ~UV, immunosupp ppl, defective DNA repair RED FLAG = WAXY, ~from basal keratinocytes PEARLY RAISED BORDER MAY HAVE CENTRAL ~UVB radiation!!!! ULCERATION MAY OR MAY NOT BE ~requires local stroma to support growth!!! PIGMENTED QUITE FIRM ~unpredictable growth, thus it is extremely aggressive locally ~multifocal growth = radial and lateral growth into the epidermis ~nodular growth = migration into the dermis
Malignant Melanoma
SUN, very aggressive, fatal via secondary metastasis Melanocytic Nevi: develop over decades, cells are Risk Factors = familiar and personal tendencies, large congenital nevus or immunosuppression differentiated, slower rate of mitosis <1/3 develop from nevi, need to ask evolution!!! Malignant Melanomas: develop over weeks, sample is ~radial growth, vertical growth, metastasis not differentiated, increased # of mitotic events
You might also like
- ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY WebpathDocument35 pagesENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY Webpathapi-3766657No ratings yet
- Female Genital TractDocument5 pagesFemale Genital Tractsarguss14100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFChethranNo ratings yet
- 2011-07-PATHO-Basic Pathology of SkinDocument17 pages2011-07-PATHO-Basic Pathology of SkindtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Document18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Ars MoriendiNo ratings yet
- Patho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Document12 pagesPatho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Grant GarcesNo ratings yet
- Robbins Ch. 26 Bones Joints and Soft-Tissue Tumors Review QuestionsDocument7 pagesRobbins Ch. 26 Bones Joints and Soft-Tissue Tumors Review QuestionsPA2014100% (1)
- Herpes, Pox, Rhabdo, Arena VIRUSDocument7 pagesHerpes, Pox, Rhabdo, Arena VIRUSErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- 7sgdfgf PDFDocument438 pages7sgdfgf PDFPratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- Pathology Test I Diseases GuideDocument6 pagesPathology Test I Diseases GuideBahaa Ibrahim HelmiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pathology: Disease Cause/Risk Factors SymptomsDocument12 pagesPediatric Pathology: Disease Cause/Risk Factors SymptomsherethemindNo ratings yet
- Parvo BacteriaDocument2 pagesParvo BacteriaErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Lung: Djumadi AchmadDocument26 pagesPathology of The Lung: Djumadi AchmadVivi DeviyanaNo ratings yet
- Antivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSDocument3 pagesAntivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Ear Deformities and MalformationsDocument5 pagesCauses, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Ear Deformities and MalformationsLuka Desabelle- JustoNo ratings yet
- Spongiotic Dermatitis: Aka EczemaDocument8 pagesSpongiotic Dermatitis: Aka EczemafadoNo ratings yet
- Pathology Description/Buzz Words DiseaseDocument5 pagesPathology Description/Buzz Words Diseasebea manzanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology Reviewer by Dr. VilaDocument5 pagesPhysiology Reviewer by Dr. VilarustonNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Repair OverviewDocument10 pagesInflammation and Repair OverviewMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Pathology - Chapter 4Document9 pagesPathology - Chapter 4Cory GrayNo ratings yet
- Git PathologyDocument113 pagesGit PathologyanggitaNo ratings yet
- Lung Head and NeckDocument26 pagesLung Head and Neckzeroun24100% (2)
- Liver Function Tests Diagnostic GuideDocument2 pagesLiver Function Tests Diagnostic GuideostarburstoNo ratings yet
- Table of Genetic Disorders: Download A Copy of This Study GuideDocument11 pagesTable of Genetic Disorders: Download A Copy of This Study Guideerica perezNo ratings yet
- Urological History TakingDocument6 pagesUrological History TakingayuniNo ratings yet
- Heart BNHADocument13 pagesHeart BNHAX OloGyNo ratings yet
- Anti FungalsDocument5 pagesAnti FungalskakuNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 DiseasesDocument1 pageExam 1 DiseasesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Pathology - Lab: Pathology of The HeartDocument8 pagesPathology - Lab: Pathology of The HeartRazel PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument17 pagesChapter 10 - Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Lung - PathologyDocument34 pagesLung - Pathologyjmosser100% (3)
- Robbins Ch. 18 Liver and Biliary Tract Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesRobbins Ch. 18 Liver and Biliary Tract Review QuestionsPA2014No ratings yet
- Kidney NewDocument4 pagesKidney NewParth BhayanaNo ratings yet
- Lymphomas and Leukemias ChartDocument2 pagesLymphomas and Leukemias ChartPA2014No ratings yet
- Patho Robbins Sumary Pereira MDDocument22 pagesPatho Robbins Sumary Pereira MDNicole SarcosNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Ricketsiae BacteriaDocument2 pagesRicketsiae BacteriaErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of EthanolDocument5 pagesPharmacology of EthanolJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- CardiacArrhythmiasPathophysiology PDFDocument1 pageCardiacArrhythmiasPathophysiology PDFNeelam Raj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Male Genital SystemDocument75 pagesMale Genital Systemyaumilagus100% (1)
- Cell InjuryDocument23 pagesCell InjuryFiori MedNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Key WordsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Key Wordsmoilo86020% (1)
- Protein Synth Inhibs Target Bact RibosomeDocument61 pagesProtein Synth Inhibs Target Bact RibosomegirNo ratings yet
- Henoch-Schonlein Purpura, Atopic Dermatitis, Seborrheic Dermatitis & Oral Isotretinoin TherapyDocument5 pagesHenoch-Schonlein Purpura, Atopic Dermatitis, Seborrheic Dermatitis & Oral Isotretinoin TherapyJoan ChoiNo ratings yet
- Skin - PathophysiologyDocument29 pagesSkin - Pathophysiologyjmosser100% (2)
- GASTROINSTINAL TRACT Robbins 8th EditionDocument4 pagesGASTROINSTINAL TRACT Robbins 8th EditionLim EricNo ratings yet
- The Craming MDDocument132 pagesThe Craming MDRosalie Catalan EslabraNo ratings yet
- Most Common Medical Conditions and DiseasesDocument3 pagesMost Common Medical Conditions and Diseasesazul2233No ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inDocument13 pagesGenetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inQworld100% (1)
- Patho Common Stuff - RobbinsDocument7 pagesPatho Common Stuff - RobbinsMaf BNo ratings yet
- 20 Pathoma Skin DisordersDocument10 pages20 Pathoma Skin Disordersn alawiNo ratings yet
- TOPNOTCH Patho Supplement Handout For Sept 2018 UPDATED May 2018Document25 pagesTOPNOTCH Patho Supplement Handout For Sept 2018 UPDATED May 2018Waiwit KritayakiranaNo ratings yet
- 3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraDocument6 pages3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraCassey Koi FarmNo ratings yet
- RashDocument3 pagesRashNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Malassezia Furfur An-An Ap-Ap Naturally Found On The SkinDocument48 pagesMalassezia Furfur An-An Ap-Ap Naturally Found On The SkinNikki ValerioNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- LCD Kuliah Dermatitis Wa2008Document32 pagesLCD Kuliah Dermatitis Wa2008Made Wardhana100% (2)
- SOFIA SALSABILA Rangkuman On ProgressDocument10 pagesSOFIA SALSABILA Rangkuman On ProgressSofia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Skin Infections (Team Swabeh)Document13 pagesPathology Skin Infections (Team Swabeh)Barron KlaNo ratings yet
- MICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesDocument9 pagesMICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesRicoNo ratings yet
- Revised Organizational Structure of Railway BoardDocument4 pagesRevised Organizational Structure of Railway BoardThirunavukkarasu ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Rizal's First Return Home to the PhilippinesDocument52 pagesRizal's First Return Home to the PhilippinesMaria Mikaela MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Tong Hop Bai Tap Tieng Anh 8 Chuong Trinh Moi Co Dap AnDocument317 pagesTong Hop Bai Tap Tieng Anh 8 Chuong Trinh Moi Co Dap Anmrxuan tesol93No ratings yet
- Describing A CompanyDocument3 pagesDescribing A CompanyAfnanNo ratings yet
- Suntay V CojuancoDocument2 pagesSuntay V CojuancoJushiNo ratings yet
- Choi, J H - Augustinian Interiority-The Teleological Deification of The Soul Through Divine Grace PDFDocument253 pagesChoi, J H - Augustinian Interiority-The Teleological Deification of The Soul Through Divine Grace PDFed_colenNo ratings yet
- Yoga For The Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease (Hartley 2014)Document52 pagesYoga For The Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease (Hartley 2014)Marcelo NorisNo ratings yet
- Unit 20: Where Is Sapa: 2.look, Read and CompleteDocument4 pagesUnit 20: Where Is Sapa: 2.look, Read and CompleteNguyenThuyDungNo ratings yet
- Inmarsat M2M Terminal ComparisonDocument2 pagesInmarsat M2M Terminal Comparisonmaruka33No ratings yet
- FedSupport Codebook FY2020Document259 pagesFedSupport Codebook FY2020Aaron BlackmonNo ratings yet
- AR118 - MSDS 2023 (Chemlube) - 19.10.2023Document8 pagesAR118 - MSDS 2023 (Chemlube) - 19.10.2023sanichi135No ratings yet
- Hold-Up?" As He Simultaneously Grabbed The Firearm of Verzosa. WhenDocument2 pagesHold-Up?" As He Simultaneously Grabbed The Firearm of Verzosa. WhenVener MargalloNo ratings yet
- What are plot pointsDocument19 pagesWhat are plot pointsOpeeron OpeeNo ratings yet
- Summer 2019 English Reinforcement LessonsDocument31 pagesSummer 2019 English Reinforcement LessonsAizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- Ys 1.7 Convergence PramanaDocument1 pageYs 1.7 Convergence PramanaLuiza ValioNo ratings yet
- June 3rd 1947 Partition PlanDocument2 pagesJune 3rd 1947 Partition PlanZ_Jahangeer88% (16)
- PDFDocument72 pagesPDFGCMediaNo ratings yet
- OCFINALEXAM2019Document6 pagesOCFINALEXAM2019DA FT100% (1)
- Sar Oumad Zemestoun v01b Music Score سر اومد زمستون، نت موسیقیDocument1 pageSar Oumad Zemestoun v01b Music Score سر اومد زمستون، نت موسیقیPayman Akhlaghi (پیمان اخلاقی)100% (3)
- Importers in BOC List As of June 2, 2015Document254 pagesImporters in BOC List As of June 2, 2015PortCalls88% (8)
- Biological Control in Brazil An OverviewDocument10 pagesBiological Control in Brazil An OverviewGustavo Ferreira MoraisNo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges: College of NursingDocument2 pagesPines City Colleges: College of NursingmagisasamundoNo ratings yet
- Valmet - S Waste To Energy SolutionsDocument14 pagesValmet - S Waste To Energy SolutionsNardo LlanosNo ratings yet
- Polyester Staple Fibre Product ListDocument2 pagesPolyester Staple Fibre Product Listnunu7478No ratings yet
- User Manual: Imagenet Lite™ SoftwareDocument93 pagesUser Manual: Imagenet Lite™ SoftwareDe Mohamed KaraNo ratings yet
- MR GMAT Combinatorics+Probability 6EDocument176 pagesMR GMAT Combinatorics+Probability 6EKsifounon KsifounouNo ratings yet
- B1 Grammar and VocabularyDocument224 pagesB1 Grammar and VocabularyTranhylapNo ratings yet
- Explorations - An Introduction To Astronomy-HighlightsDocument10 pagesExplorations - An Introduction To Astronomy-HighlightsTricia Rose KnousNo ratings yet
- Philippines Disaster Response PlanDocument7 pagesPhilippines Disaster Response PlanJoselle RuizNo ratings yet