Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BSNL Report
Uploaded by
roger_dineshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BSNL Report
Uploaded by
roger_dineshCopyright:
Available Formats
PREFACE
Since time immemorial, a man has tried hard to bring the world as close to himse lf as possible. His thirst for information is hard to quench so he has continuou sly tried to develop new technologies, which have helped to reach the objective. The world we see today is a result of the continuous research in the field of co mmunication, which started with the invention of telephone by Grahm Bell to the current avtar as we see in the form INTERNET and mobile phones. All these techno logies have come to existence because man continued its endeavor towards the obj ective. This project report of mine, STUDY OF TRENDS TECHNOLOGIES IN COMMUNICATION AND N ETWORKING has been a small effort in reviewing the trends technologies prevailin g. For this purpose, no organization other than BAHRAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED cou ld have been a better choice.
Table of contents 1. Acknowledgement 2. Preface 3. Table of contents 4. Introduction 5. making a telephone call 6. About the exchange a. computer unit b. power plant c. central air conditioner d. main distribution frame 7. V-SAT network a. Design aspects b. Operational factors 8. Types of access V-SAT networks a. fixed assignment time division multiple access (F-TDMA) b. Random access c. Code division multiple access (CDMA) 9. The Internet a. Introduction b. Internet connectivity c.OSI model d. Communication b\w the layers e. File transfer the internet f. National internet backbone 10. Wireless in local loop a. Technical aspects b. Advantages 11. Global system for mobile communication (GSM)
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED (BSNL) An Introduction:Today, BSNL is the No. 1 telecommunication company and the largest public sector
undertaking of India and its responsibilities includes improvement of the alrea dy impeccable quality of telecom services, expansion of telecom services in all villages and instilling confidence among its customers. Apart from vast network expansions, especial emphasis has given for introducing latest technologies and new services like I-NET, INTERNET, ISDN (INTEGRATED SERV ICES DIGITAL NETWORK), IN (INTELLIGENT NETWORK), GSM and WLL (WIRELESS IN LOCAL LOOP) services etc. Now BSNL has also entered in mobile communication. BSNL has all the new services send technological advantages, which are available with any well, developed Telecom network anywhere else in the country. Full credit for all above achievement goes to the officers and staff of the BSNL . The administration is fully aware of the challenges lying ahead and quite comm itted to provide the latest and best telecom services by their continued support and active co-operation. BSNL Services:When it comes connecting the four corners of the country , and much beyond , one solitary name lies embedded at the pinnacle- BSNL. A company that has gone past the number games and the quest to attain the position of the leader. It is work ing round the clock to take India in to the future by providing excellent teleco m services for people of India. Driven by the very best of telecom technology from global leaders, it connects e ach inch of India to the infinite corners of the globe, to enable you to step in to tomorrow. The telecom services have been recognized the world over as an important tool fo r socio-economic development for a nation and hence telecom infrastructure is tr eated a crucial factor to realize the socio-economic objectives in India. Accord ingly the Department of Telecom has been formulating developmental policies for the accelerated growth of the telecommunication services in various cities. The department is also responsible for frequency management in the field of radio co nnection in close coordination with the international bodies. MAKING A TELEPHONE CALL A telephone call starts when the caller lifts the handsets of the base. Once the dial tone is heard, the caller uses a rotary or a push button dial mounted eith er on the handset or on the base to enter a sequence of digits, the telephone nu mber of called party. The switching equipment from the exchange removes the dial tone from the line after the first digit is received and after receiving the la st digit, determines the called party is in the same exchange or a different one s. If the called is in the same exchange, burst of ringing current is applied to the called partys line. Each telephone contains a ringer that responds to specif ic electric frequency. When the called party answers the telephone by pocking up the handset, steady start to flow in the called partys line and is detected by t he exchange. The exchange than stops applying ringing and sets up the connection between the caller and the called party. If the called party is in different ex change from the caller, the caller exchange set up the connection over the telep hone network to the called partys exchange. The called party then handles the pro cess of ringing, detecting an answer, and notifying the calling and billing mach inery when the call is completed. When conversation is over, one or both parties hang up by replacing their handset on the base, stopping the flow of current. T he exchange when initiates the process of taking down the connection, including notifying billing equipment of the duration of the call if appropriate.
ABOUT THE EXCHANGE
All telephone subscribers are served by automatic exchanges, which perform the f unctions the human operator. The number being dialed is stored and then passed t o the exchanges central computer, which in turns operates the switching to comple te the call or routes it a higher level switch for further processing. Todays aut omatic exchanges uses a pair of computers, one running the program that provides services and the second monitoring the operation of the first, ready to take ov er in a few seconds in the event of equipment failure. Various exchanges present in BSNL are: E-10B OCB283 EWSD All exchange has some purposes and some basic structural units, which are: 1. 2. 3. 4. subscribers connection unit switching network (CX) control unit OMC
For smooth working of an exchange following unit are very important:1. Computer Unit: - it deals with additional services of the exchange to the cus tomers with the help of computers. 2. Power Plant:- to feed proper power supply to exchange 3. AC Plant: - to maintain the continuous temperature + or 2 degree Celsius to t he digital switch (exchange). 4. MDF: - to connect switch (exchange) with the external environment (subscriber ) i.e. it is the interface between subscribers and exchange.
Computer unit As the name specified it is the main part of the exchange that deals with the al l services provided by the exchange to the customers with the help of computer. It also provides the updated data to all other part of the exchange. The customers are using the services of the exchange by using the internet also gets connected to the main server present this room via an internet room. It mainly consists of the servers that are providing the different services. The main servers of this room are:IVRS is used for the change number services provided by the exchange. CERS are provided by the exchange to avoid the problems that the users are facin g the repairing of telephone. In this system when the user enters its complained it gets directly entered to the server and user is allotted with an id number.
LOCAL DIRECTORY ENQUIRY is another services provided by the exchange, by using t his; subscribers calls the particular number and gets the directory enquiry. The server present in the main computer room provides this service. INTERNET DIRECTORY ENQUIRY is the latest service by the exchange. In this type o f service makes it enquiry using the internet, which gets connected to the main server at the internet room in the exchange and further to the main server in th e computer room.
POWERPLANT As we know that, the power is the main source or any organization. It is the cas e of E-10B exchange. That is the first requirement of any organization is the in put. The main source of this exchange is AC supply. However, as soon as the power sup ply is gone off, then what is source? No one think on this that the telephone is always plays its role in the human life. Even if the power supply gone off. Thu s there must be adjustment source of power. The main parts of the power room are: Batteries: - these are the instant sources of the power as soon as power is gone off. UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply):- the UPS must give supply to the computer. As we know there is some equipment which can withstand any type of power supply, bu t there are also some instruments which cannot withstand with this type of power supply, even a microsecond delay will cause the loss of data. Charging- Discharging Unit: - the batteries we are using in the power room need timely charging. As soon as the AC power supply is on, we make use of the chargi ng unit present in the power room. The slowly charging of the batteries is known as the trickle charging. But sometimes we need the BOOSTER charging. In this ty pe of charging awe take of the batteries from the load and charge separately, un til it gets fully charged. The main work of the discharging unit is to control the discharging of the batte ries. Inverter and Converter Unit: - the main use of this system is to change AC mains to DC and vice versa as required by the parts of exchange. Engine Room:-we know that the batteries are the instant source of supply but we cannot use it for much larger time, thus for this, we have an engine to generate the power supply. They are of 885 KVA. Thus, this room controls the supply of t he engine.
CENTRAL AIR CONDITIONER For the function of electrical equipment, cooling system is basic requirement. T he basic advantages of cooling systems are followingIt provides the thermal stability so that the temperature does not reach the tol erance limit of electronic equipment It saves equipment from dust so to avoid malfunction of equipments. It protects equipment from excess humidity which can caused rusting of equipment
. The basic unit of measurement used in the industry is known as ton of refrigerati on (TR) which is equivalent to the heat extracted in 24 hours for converting thou sands kg of liquid to ice at zero degree. The compressor is the heart of the AC system and the costliest. It increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas coming from the evaporator coil s by compressing it. Compressor comes in various types. The most widely used is simple reciprocal typ e a cylinder and piston arrangement. For capacity more than 120 TR, centrifugal compressors are used. The condenser liquefies the refrigerant gas by a heat exch ange process. The capillary tube or the expansion valve pressurizes liquid refri gerant and meters it flows to the evaporator. The refrigerant then passes trough the evaporator coils, which extract heat out of the ambience.
MAIN DISTRIBUTION FRAME The primary function of MDF is: The fault of telephone number is removed in the MDF; it is called as Fault Remov e Section. For removing the fault of telephone number, we use the testing These testing are T.T.Y. testing, Group testing, etc. For any type of testing firstly we need the vertical no. or the live tester, pri nter and computer test N.E. number of that particular telephone number. The telephone numbers are also disconnected in the MDF because of some specific reason.
ORGANISATION OF THE MDF PARTS OF THE MDF Horizontal side Vertical side HORIZONTAL SIDE: It is again subdivided in to two parts Exchange side Line side Description of the horizontal side:RACK: - On the rack, the tags are situated. One rack is having eight tags. The c ourting is done from up (0) to down (7). TAG: - Each rack consists of eight tags. 1 tag = 4 core 1 core = 4 bunch 1 bunch = 2 line N.E.:- The word NE stands for the NUMBER OF EQUIPMENT.
It is a 128 pair cable. The EWSD and MDF connected by NE. WEDGE:-If we want to disconnect any two numbers then we insert a wedge between s ubscriber side and exchange side. Here wedge works as insulator made of plastic.
VERTICAL SIDE: The vertical aside connected to the underground cable. This cable is having 100 pairs. These pair is distributed when we allot the telephone number to the subscriber. Vertical side is again subdivided in two parts: One part is connected with the horizontal side and another with the subscriber l ine by using 100 pair underground cable. This is how the present day telephone system works. Different exchanges have dif ferent architectures of switching call routing and other features. Now let us see how BSNL has kept up with the changing world and provided the sub scribers with the latest facilities technologies, which include the V-SAT networ k, Internet, the WLL (wireless in local loop) and the GSM mobile.
V-SAT NETWORK What is V-SAT? It can be defined as a class of very small aperture Intelligent Satellite Earth Station suitable for easy on-premise installation, usually operating in conjugat ion with a large size HUB earth station. Capable of supporting a wide range of t wo ways integrated Telecom Services. It has the following components: Micro Earth Station Mini Earth Station Personal Earth Station Roof Top Terminal Customer Premises Terminal
ADVANTAGES OF V-SAT Can be located in the user premises on roof top or backyard and hence eliminate last mile problem. Superior quality satellite based data services. Quick implementation time. Reliable communication. Broadcast feature on satellite communication. Communication to different areas. Flexibility for network and changes. Service in distance insensitive. Low cost. REASON FOR V-SAT EVOLUTION
The main reason for V-SAT evolution is due to advances in following areas: Packet transmission and switching. Efficient multiple access protocol. Powerful microprocessor. KU and RF electronics. Antennae miniaturization Spread spectrum techniques. Protocol standardization and implementation. LSI based FEC codec has and modems. Higher power satellites. CLASSIFICATION OF V-SATs V-SAT can be classified as following: 1. Modulation type 2. Application used for. 3. Transmission rate. 4. Cost. CATEGORIES OF V-SATs 1. Broadcast/ point to multipoint Types of services a. Broadcast video b. Program quality audio. c. Packetised data. In this mode of operation V-SATs transmit/receive data through a centralized HUB . This type of network is called star network. 2. Point to point Types of services a. Voice b. Data c. Image In this mode of operation, V-SATs transmit/receive data without the help of hub station. This type of network is called a mesh network. 3. Two way interactive Types of services a. Voice b. Data c. Image In this configuration, V-SATs can communicate both on star as well as mesh topol ogy.
DESIGN FACTORS FOR V-SAT SYSTEMS The capabilities of V-SAT system depend upon the following factors. I. Satellite characteristics II. Geographical and environmental factors. III. Transmission link properties. IV. Earth station characteristics. V. Information encoding and modulation. VI. Total system operation.
When evaluating V-SAT system each of the above attributes should be given attent ion. However, few of more important attributes are Operational aspects Frequency bands Satellite access methods OPERATIONAL ASPECTS Considering a V-SAT system from its operational aspects, there are five broad fu nctions that determines how the system works. These are: Bandwidth allocation Multiplexing Network management Protocol handling Transmission
TYPE OF ACCESS FOR V-SAT DATA NETWORK There are three types access available for V-SAT data networks. They are: 1. Fixed assignment time division multiple access (F-TDMA) 2. Random access a. Pure aloha b. Slotted aloha c. Reservation i. Implicit ii. Explicit 3. code division multiple access (CDMA)
FIXED ASSIGNMENT TIME DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS (F-TDMA) In a fixed assignment TDMA, each frame is divided in to slots of fixed time dura tions among stations of network. The assignment of stations to slots is permanen t similar to TDMA system carrying digitalized voice except FTDMA does not have s ynchronization. Packets are sent asynchronously, with no frame sync signals. FEATURES No inter modulation problems. Transport utilization is better. Burst from different stations must arrive at satellite exactly in allocated slot s. Throughput is 70% to 80% Delay medium is too high. Complexity-medium.
RANDOM ACCESS
With TDMA schemes, signals are transmitted by earth stations in a burst mode. If no scheduling is provided b/w the transmitting station, this type of access is called time random multiple access. This simplest method for the stations to tra nsmit burst without regard for other station. Random access id of two types: Pure aloha Slotted aloha PURE ALOHA Pure aloha, also called unslotted aloha is the simplest form of random access sc hema. In this form of access stations transmit packets\bursts randomly. Packet from different stations may collide, thereby destroying information conte nt. Station transmits the packet until they are received correctly. The aloha channel throughout can be analyzed in terms of traffic offered through the following relationship: S=Ge-2g Maximum throughput is 13% to 18%. Delay- low Complexity- very low
SLOTTED ALOHA The maximum throughput of an unslotted aloha channel is limited to 18% due to co llision. To reduce probability of each collision time slots are introduced so that the tr ansmission could only at the start of the slots. The above network discipline reduces the rate of collision by half and hence inc reases the maximum throughput efficiency of the channel. In S-Aloha, each station has 2 queues. a. New packet queue b. Retransmit packet queue. Only if the retransmit packet queue is empty, a new packet queue is sent. The analysis of slotted aloha channel shows that S = Ge2g Maximum channel throughput is 36%. Delay- low. Complexity- low- medium. Reservation The low bandwidth utilization of pure aloha and the slotted aloha has led to man y proposals for increasing utilization by means of slot reservation schemes. The object of slot reservation schemes is to receive a particular time slot for a given station. This ensures that no collision takes place. This scheme has a higher throughput than either S- Aloha or F-TDMA depending on traffic. This increase in channel utilization efficiency is obtained at some overhead eit her in terms of allocation of bandwidth for reservation purposes and\or increase d complexity of the control mechanism in transmitting stations.
All reservation methods use some form of framing approach and the reservation sc heme can be either implicit or explicit. The implicit reservation method involves reservation by use. This is done whenev er a station successfully transmit in a slot; all the stations internally assign that slot in sub-segment frames for exclusive use by the successful station. Th is is called R-Aloha. In this there is no way to prevent a station capturing mos t or all of the slots in a frame for an indefinite time. The explicit reservation is a distinct and unique assignment of slots to a user by the network scheduler.
CODE DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS (CDMA) With CDMA transmission from earth station are spread over the time frequency pla ne by a code transformation. These techniques are referred to as Spread Spectrum Systems. In addition to their multiple access capabilities, they are useful in combating jamming, and are for this reason principally used in military systems.
Features All stations operate on the same transponder frequency using a large bandwidth t han needed for the data rate. Network needs no time for frequency coordination. Provide anti jam capabilities or protection against interference. Provide for a graceful degradation of network performance as the number of simul taneous users increases. Low spectral density compared to conventional emissions. It yields same capacity as FDMA. Limitations of CDMA Require large transponder ratio. Due to imperfect code orthogonalities, expected simultaneous users may be limite d. Requires a highly central earth station called HUB using star configuration. VSAT technology using SSMA is presently available only for low bit rate applicat ion. VSAT NETWORK IN DOT Department of telecommunication entered the VSAT era in 1991 by commissioning it s first satellite based low bit rate network known as REMOTE AREA BUSINESS MESSA GE NETWORK (RABMN). This has been engineered for users located in remote areas for stable and reliab le data communication. This service envisages installation of very small aperture terminals (VSAT) to w ork with satellite based pocket switched network. It has 3 main components:-
A large master earth station (hub) A satellite transponder located in geo stationary orbit A small micro earth station located at users premises
SERVICES OFFERED BY RABM NETWORK:Data communication up to 1200 bps Fax services. Access to Public Telex Network Access to international data network through VSNL gateway.
Tariff and billing:A RABMN customer availabling VSAT has to pay the following charges:Registration charge Rs. 5000 per terminal Cost of each VSAT Rs. 5.2 lakhs Cost of each installation Rs. 15,000 per terminal License fees Rs. 100 per terminal Maintenance charges Rs. 25,000 per terminal annually Satellite access charges Rs. 5000 per month per terminal Traffic charges Rs. 50 per kilo segment of data
Network users: Some of the probable users are Banking network Civil aviation Airlines\railways Public\private sector industries Meteorological department Police department
RABMN NETWORK Introduction Satellite communication plays a vital role in long distance communication. Satellite medium offers high bandwidth making it suitable for data communication and computer networking. Satellite communication is of distance and cost effective. Multi access nature of satellites. Provides two way communications. Dynamic assignment of channels between geographically dispersed users. Satellite network provides point to point and point to multipoint communication needs.
Frequency division multiple access (FDMA):Bandwidth is split in to narrow frequency bands with multiple users each allocat ed a frequency range within the larger bandwidth. Time division multiple access (TDMA):Each terminal is allotted a short time slot in which to transmit on a sequential basis. This time slot is usually a fraction of a second.
Code division multiple access (CDMA) Each terminal is allotted a unique encryption code. The transmitted signals are encoded and only the terminal intended to receive it, can decode it. This is als o known as Spread Spectrum Multiple Access.
Statistical time division multiplexing (STDM):In TDM, time slots are allotted to the multiplexed lines even if they have no da ta transmit. In STDM, a time slot is allotted to the multiplexed line only if th ere is data to be sent. The multiplexed circuit is used more efficiently.
VSAT (very small aperture terminal) It is also called Micro Earth Station or Personal Earth Station. Its main features are as follows:Independent of terrain can be installed in hilly regions, islands and remote pla ces. Flexible service carrying data, Telex. No last mile problems of cable pair\overhead lines. Interference immunity. Data security The main services offered by VSAT are as follows:Interactive data communication. Connection to public telex network. Connection to Packet Switched Data Network INET. Connection to international gateway packet switch.
The different technologies used in VSAT areSatellite based Spread spectrum Packet switching
Tariffs:-
Cost of VSAT : about Rs. 7,00,000 Installation cost : Rs. 15,000 Maintenance cost : Rs. 25,000 Satellite access charge : Rs. 5,000 per month Charges for using VSAT are as follows: : : National : Rs. 50 per kilo segment of data Rs. 10 per min in addition to vol. of telex International : Rs.200 per Kilo segment of data Rs. 240 per hour duration.
Dialing codes for VSAT are as follows: Within RABMN: o 12 digit code o 4041xxxxxxxx to other data networks: o I-NET o 4043xxxxxxxx o international networks o DNICxxxxxxxx To telex networks NATIONAL Q008/area code/telex number INTERNATIONAL 0009/country code/telex number TELEX TO RABMIN 09841xxxxx (last 5 digits of telex number) Specifications for master earth station: There are two types of master earth stations: Outbound Inbound
Outbound: Each VSAT and host computer is allotted an HCL port NPG polls HCL ports and generates a 153.6 Kbps demand based STDM data stream Data stream contains variable length packets of data addressed to various VSATs Outmux chips the data @1:16 resulting in 2.4576 MB stream. BPSK modulator produced 5 MHz of spectrum Upconvertor converts to 5GHz RF Mes transmits 153.6KBps STDM/BPSK/SS carriers NPG provides FEC encoding for outbound data
Inbound: Inbound signals originates from VSATs VSAT has a unique PN code Data spread by its PN code and transmitted to satellite in 6 GHz band MES resolves the signal in 4 GHz band, converts to 70 MHz IF and sends to Demod section Demod cards compare the pattern of the to other PN code for its associated VSAT. When the correct pattern is detected, the original signal is extracted from the IF signal and transmitted to INMUX NPG polls INMUX for I\C data packets and transmits the packets to HCL
VSAT specifications Antennae module Reflector : 1.2M X 1.8M Weight : 60 KGs Tracking : fixed Amb. Temp : -40 to +50 deg. Cel. Wind speed : operating 100 kmph
Controller module Size : 15 cm(h) x 43 cm(w) x 55 cm (d) Weight : 15 kgs Power supply : 220V\60Hz, 300 watts Oper. Temp. : -5 to 50 deg. Cel. Humidity : up to 95%
Controller module : INPUT\OUTPUT PROCESOR
Converts raw data to packets Customer protocol to network protocol NETWORK PROCESSOR TRANS SIDE: generates BFEC & FCS Retains packets in buffer until ACKs receives and transmits if required. RECIEVER SIDE: checks BFEC & FCS ACKs the packets and requests retransmission of missing packets SPACE PROCESSOR TRANS SIDE Encodes the packets with PN sequence to 2.45MBps stream BPSK modulation of IF RECIEVER SIDE Demodulates IF signal to 2.45MBps Dispreads to 153.6KBps stream Checks destination link address in the header Discards packets addressed to other links. Micro earth station transmits 1.2KBps\9.6KBps BPSK/CDMA carriers bursts in absolu tely random access mode in the same frequency.
INTERNET Introduction: The Internet is not a program, not software, not hardware or a big system. It is a group of various co-operating computers worldwide interconnected by computer based on TCP\IP communication protocols. People use it to get information over a standard communication link. The hundreds or thousands or millions of computer network are connected to each other for exchanging the information which is base d on the unique identity and set of procedures. Internet is a series of intercon nected networks providing global link to information. GIAS: BSNL launched the Gateway Internet Access Service (GAIS) through dial up/l eased/ISDN network. Users can access GAIS from 99 cities in India by this means.
INTERNET CONNECTIVITY INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
The basic function of Internet can be summarized as underInterconnecting of computers to form a network. Interconnecting of computers to form a network of networks. To establish a communication link between two computers within as network. To provide alternate communication link among the networks, even if one network is not working. These are based on TCP/IP communications protocol.
Transfer of a file through Internet:Suppose a file is to be transmitted on Internet from one computer to other ones Break the file in to small packets Attached destination and source address in o packets Multiplexed and transmit these packets At destination de-multiplex the packets Remove address bits from the packets and assemble the data in to the original fi le Make source bits as destination address and send the acknowledgement in to the s ource Therefore, it is clear that network hardware sends the packets to specified dest ination and network software reassembles of communications, the computer network performs the following functionsAddressing and routing Fragmentation and error correction Data error checking Connectivity control Multiplexing and de-multiplexing Data flow control End users interface etc. The data handling A single module cannot handle the entire process. One that adopted as a standard is an open system interconnection (OSI) model. OSI NETWORKING MODEL: The open systems interconnection model defines all the met hods and protocols needed to connect one computer to any other over a network. The OSI model separates the methods and protocols needed for a network connectio n in to seven different layers. Each higher layer relies on services provided by a lower level layer. The OSI model is sometimes called the seven layer model. It was developed by the I nternational Standards Organization (ISO) in 1983 and is documented as standard 7498. Layers are: Application layer Presentation layer Session layer Transport layer
Network layer Data link layer Physical layer
You might also like
- Ccnp1 - Mod 6 Ospf LabsDocument79 pagesCcnp1 - Mod 6 Ospf LabsRamdon999100% (1)
- Subnetting ChartDocument1 pageSubnetting ChartmathiasuoNo ratings yet
- Depreciation: Construction Engineering 221 Economic AnalysisDocument6 pagesDepreciation: Construction Engineering 221 Economic AnalysisHansley Templeton CookNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledroger_dineshNo ratings yet
- The FFT - An Algorithm The Whole Family Can UseDocument24 pagesThe FFT - An Algorithm The Whole Family Can Useroger_dineshNo ratings yet
- Fixed Line Technology: Fixed Line (Or Land Phone or Main Line or Land-Line) Refers To ADocument17 pagesFixed Line Technology: Fixed Line (Or Land Phone or Main Line or Land-Line) Refers To Aroger_dineshNo ratings yet
- Interview SkillsDocument5 pagesInterview Skillsroger_dineshNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of ComputerDocument5 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Computerroger_dineshNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Matrix Algebra by A.S.HadiDocument4 pagesMatrix Algebra by A.S.HadiHevantBhojaram0% (1)
- Carta Psicrometrica PDFDocument2 pagesCarta Psicrometrica PDFJuliethNo ratings yet
- Capacity and Safety Analysis of Hard Shoulder Running HSR A Motorway Case Study 2016 Transportation Research Part A Policy and PracticeDocument22 pagesCapacity and Safety Analysis of Hard Shoulder Running HSR A Motorway Case Study 2016 Transportation Research Part A Policy and PracticeZen ZeeNo ratings yet
- Datasheet De14h (II) HC 1500v May2019 NTDocument2 pagesDatasheet De14h (II) HC 1500v May2019 NTkrishnakumar paamireddyNo ratings yet
- Procedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20Document6 pagesProcedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20ChocoNo ratings yet
- Approach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Document58 pagesApproach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- F588 PDFDocument8 pagesF588 PDFOscar Gutiérrez-JuncoNo ratings yet
- Abbey Pain Scale assessment toolDocument2 pagesAbbey Pain Scale assessment toolMuhammad RezgiaNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis Lab ReportDocument5 pagesGravimetric Analysis Lab Reportclaire_miller_16100% (1)
- Regular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionsDocument3 pagesRegular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionshumbyxNo ratings yet
- Reconsilation of Major Materials Steel SDA Lattice Ribs Rockbolts Admixture Etc.Document99 pagesReconsilation of Major Materials Steel SDA Lattice Ribs Rockbolts Admixture Etc.Rajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Narayana Sukta MeaningDocument4 pagesNarayana Sukta Meaningvinai.20No ratings yet
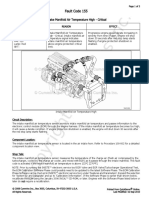
- Fault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - CriticalDocument3 pagesFault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - Criticalhamilton miranda100% (1)
- Pump Characteristics ExperimentDocument7 pagesPump Characteristics ExperimentJam JoNo ratings yet
- Orrick PostedbyrequestDocument4 pagesOrrick PostedbyrequestmungagungadinNo ratings yet
- MACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSDocument1 pageMACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSsensoham03No ratings yet
- PCS PADDLE SHIFTER INSTALL GUIDEDocument21 pagesPCS PADDLE SHIFTER INSTALL GUIDEAndreas T P ManurungNo ratings yet
- FHM Espana 2010 12 PDFDocument2 pagesFHM Espana 2010 12 PDFBrandenNo ratings yet
- 100kw TSP Agenitor-404b Biogas 60-hz 480v En-827879Document9 pages100kw TSP Agenitor-404b Biogas 60-hz 480v En-827879Julian BarreraNo ratings yet
- Gold Grade of Epithermal Gold Ore at Lamuntet, Brang Rea, West Sumbawa District, West Nusa Tenggara Province, IndonesiaDocument10 pagesGold Grade of Epithermal Gold Ore at Lamuntet, Brang Rea, West Sumbawa District, West Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesiasukri arjunaNo ratings yet
- Motor Cat 924HZDocument6 pagesMotor Cat 924HZAdemilson Rangelvieira100% (1)
- Rotary Gear Pump Manufacturers in India, Pulp Valve Manufacturers IndiaDocument3 pagesRotary Gear Pump Manufacturers in India, Pulp Valve Manufacturers IndiaKirit IndustriesNo ratings yet
- Akshay 71 Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesAkshay 71 Seminar ReportSanket Yadav25% (4)
- Features General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterDocument18 pagesFeatures General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterAntonioNobregaNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument9 pagesBiodiversityVienica Dauz Mico Balbin100% (1)
- History of Cancer ChemotherapyDocument9 pagesHistory of Cancer ChemotherapyJoydeep MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Astm A535 9 Percent NickelDocument5 pagesDokumen - Tips - Astm A535 9 Percent NickelJeovanne CabralNo ratings yet
- English Test 6Document87 pagesEnglish Test 6Ha PhanNo ratings yet
- CORRELATION AND LINEAR REGRESSIONDocument9 pagesCORRELATION AND LINEAR REGRESSIONSANKET GANDHINo ratings yet
- Vapour Bar Exchange IMFL PackageDocument4 pagesVapour Bar Exchange IMFL PackageNishank AgarwalNo ratings yet