Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AF Lab Tests
Uploaded by
hifzurrehmanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AF Lab Tests
Uploaded by
hifzurrehmanCopyright:
Available Formats
AF Lab Tests
http://www.aiims.edu/aiims/departments/physiology/AFL-Website/tests....
Tests @ AF Lab
Heart Rate Variability / Blood Pressure Variability HRV is done by using software package Nevrokard as well as the software developed by us using the concept of virtual instrumentaiton on LABView platform which are intended for analysis of heart rate variability (HRV) and Blood Pressure Variability (BPV) as well as assessement of Baroreflex Sensitivity (BRS) giving a non-invasive estimate of the function of sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic nervous systems in various patients. Power spectral EKG / BP data is obtained by using Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT). The analog to digital conversion of the data is done using A/D converter with the sampling frequency of 500 Hz. Artifacts and ectopic beats can be edited by using computer as well as manually. In a clear epoch of 5 minutes, the R wave of QRS complex is detected by using amplitude criteria and RR intervals is calculated.
Both the frequency and the time domain analysis of the data is done. In the frequency domain analysis, entire spectrum of frequencies is divided into three major frequency bands; the area under curve for each band is calculated and expressed in arbitrary units.(VLF - 0.01 to 0.04 Hz; LF - 0.04 to 0.15 Hz; HF - 0.15 to 0.5 Hz) By frequency domain analysis the following parameters are obtained: VLF, LF, HF, TP (Total Power), LF/HF Ratio and normalized LF and HF (LF/[total power-VLF] x 100). From the same data, time domain measures of HRV are also obtained. Following parameters are calculated: 1. Mean, Standard deviation (SD), Coefficient of Variance 2. Mean (MSD) and Standard deviation (SDSD) of successive RR interval differences 3. Mean of successive RR interval differences (MSSD) 4. Square root of MSSD (RMSSD)
Page Up
Traditional cardiovascular autonomic reflex tests Parasympathetic reactivity tests Deep breathing test: Patients are asked to take deep and slow breaths at the rate of 6 breaths per minute. Difference of the mean maximum and mean minimum hearts rates, delta HR and E:I ratio i.e. ratio of mean of longest R-R interval during expiration to mean of shortest R-R interval during inspiration of six respiratory cycles re taken. Valsalva manoeuvre: Patients are asked to forcibly blow out (making effort from chest) through a tube connected to a mercury manometer (Valasalva manoeuvre instrument), maintaining 40 mm Hg rise for 15 seconds. Valsalva ratio, i.e., the ratio of longest RR interval (in phase IV) to the ratio of shortest RR interval (phase II)is taken. Bradycardia ratio (minimum heart rate in phase IV / resting heart rate) and tachycardia ratio (maximum heart rate in phase II / resting heart rate) are also calculated. Lying to standing test: Patients are made to rest in supine position for 15 minutes. After rest, blood pressure is measured as resting blood pressure. The patients are instructed to stand up from lying down position in 3 seconds. The 30:15 ratio after standing is calculated (ratio of maximum R-R interval around 30th beat to ratio of minimum R-R interval around 15th beat). Sympathetic reactivity tests Isometric exercise test: Patient are asked to grip the handgrip dynamometer maximally with his dominant hand. Maximum value of these readings will be considered as maximum voluntary contraction (MVC). Patients are asked to hold the grip at 30% of MVC up to the maximum of four minutes. Rise of blood pressure at 1st, 2nd and 4th minute is measured in contra lateral arm before the release of handgrip. Cold Pressor test: Prior to the test the baseline BP is recorded. the subjects are asked to immerse the hands upto the wrist in 10 degrees centigrade cold water for 1 minute. BP is measured after first minute and 2.5 minutes hand immersion. The EKG is also continuously recorded.
Page Up
Sympathetic Skin Response The Sympathetic Skin Response (SSR) is a polysynaptic reflex generated in the deep layers of the skin by activation of sweat glands via sudomotor sympathetic efferent fibres. The SSR represents an unspecific arousal response to several endogenous (e.g., cough, inspiratory gasp) and exogenous (e.g., auditory, electrical or magnetic) stimuli. In clinical studies, the method most widely used to evoke SSRs is electrical stimulation. When using this technique large-myelinated somatosensory fibres convey the afferent pathway of the SSR. Although the central processing of the response is not fully understood, it seems to be influenced by input from various central nervous system structures such as the posterior hypothalamus and upper brain stem reticular formation. SSR should be recorded in a quiet, brightly-lit room with the ambient temperature maintained at 26 The subjects should be instructed to avoid abrupt limb movements, blinking, deep C. breathing and coughing. A headphone provided acoustic isolation. Care must be taken to ensure that the subject remaineds awake and relaxed during the procedure. SSR is recorded using pairs of surface non-polarisable Ag/AgCl disk electrodes, applied to the palm (active electrode) and dorsum (reference electrode) of the hands. Signals are amplified, filtered (0.5-3000Hz) and stored by means of biopotential analysers.
Page Up
Electroencephalography Data for EEG analysis is aquired by using BIOPAC MP 150 data acquisition system. The software automatically filters the data to display alpha, beta, delta, and theta wave components. The system records and displays the raw EEG together with the alpha wave and alpha-RMS activity. FFT analysis of the raw EEG can also be done. The effect of relaxation and mediatation on EEG can be seen. We are also seeing the EEG profile in intractable epiliepsy patients and we are interested to find out the neural correlates of EEG and HRV.
1 of 2
10-02-2012 PM 11:25
AF Lab Tests
http://www.aiims.edu/aiims/departments/physiology/AFL-Website/tests....
Electrogastrography (EGG) The patient is instructed to fast for 2 hours. Skin overlying the gastric area is prepared by cleaning it with sandy skin prep gel to reduce the impedance between electrodes and skin. Bipolar recording using 1 cm diameter Ag-AgCl EEG cup electrodes are used. Active electrodes are placed on the abdominal surface overlying pyloric antrum and greater curvature of stomach and reference electrode at least 5 cm away towards right of the electrode overlying pyloric antrum. Placement of different electrodes is as follows: 1st electrode 1-3 cm to the right of mid point of the line joining xiphysternum and umbilicus, 2nd electrode 8 cm to the left of 1st electrode and 3 cm above it. Third electrode at least 5 cm away to the right of 1st electrode and used as reference electrode. These signals are filtered off using high and low cut off frequencies, which should be set at 0.1 Hz and 0.05 Hz and time constant at 6 seconds. Preferably, recording frequency range should be adjusted in the range of 1-18 cpm. Baseline recording (after 2 hours of fasting) and after ingestion of 200 ml of water is done, EGG is recorded for 10 minutes each and stored in magnetic cassettes. Offline data analysis can also be done.
Page Up
Phono Cardiography Phonocardiography (PCG) test is performed to measure he QT/QS2 Ratio. Phonocardiography test should be done in the supine position. The microphone is placed over the precordium in left fourth of fifth inter costal space midpoint between mid-clavicular line and left sternal border. Microphone is connected to the Phonocardiograph unit. Sensitivity is adjusted so as to get the optimal response and the filter is adjusted accordingly. The filters are named arbitrary as f1, f2 etc. Prior to recording on the chart paper the heart sounds can be heard by a binaural stethoscope connected to the PCG unit to get the optimal response. Vascular Function Test Impedance Plethysmography (Rheography) is based on the measurement of changes in the electrical resistance (impedance) caused by blood volume changes. For this purpose a very low amount of high frequency alternating current is passed through the selected measuring segment. The measurement is possible because in comparison with other tissues like skin, muscle or bone, blood has a much lower resistance therefore the blood volume variation correspond with the measurable changes of the electrical resistance (impedance). The measuring device Rheoscreen compact allows you to use the four-electrode method. The current electrodes are the outer of the four electrodes necessary for impedance plethysmography. These electrodes are used to apply a very low measuring current not noticeable to the patient, which is passed through the measurement segment. The selected measuring segment defines the examination results and standard values that can be expected. A comparison of the strain gauge and impedance measurements is only possible only if the same segment is analyzed. Blood Flow Variability Blood flow variability can be obtained by using Medical Analyser software developed by Bhabha Atomic Research Centre(BARC), Mumbai, INDIA. The blood volume reaching the extremity with every cardiac ejection is commonly known as peripheral blood flow. There are several methods for the measurement of peripheral blood flow such as angiography, electromagnetic flowmetry, vascular ultrasound and plethysmography Blood flow variability by impedance plethysmography is obtained by taking the readings from both the limbs. The four electrodes are placed on the limb. The outer two electrodes are the current electrodes and the inner two are the voltage electrodes. The peaks are selected using the software from the data and then the FFT analysis of the data is done.
Page Up
Bicycle Ergometry Physical performance tests For the physical performance tests the ECG electrodes are applied on chest and secured with a belt. The electrodes are connected to the respective sockets in connection board and then the corresponding amplifier (channel) is switched on. The exercise test is performed by incrementing the load after every 2 minutes of the magnitude of 25 watts till end point. The end point of exercise is time bound and is kept at 6 minutes. After recording the baseline HR and the BP, the subjects exercise on the bicycle for 6 minutes. The average cycling speed should be 50 rpm (range 40 to 60 rpm). The starting load should 25 watts. The EKG is recorded throughout the exercise and recovery. Blood pressure is also recorded at the interval of 1 minute during exercise and as well as during recovery. Since the upper limbs are stationary and free, it is convenient to measure BP during exercise.
Page Up
2 of 2
10-02-2012 PM 11:25
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Check List For Overall Piping Plot PlanDocument3 pagesCheck List For Overall Piping Plot PlankamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Reso Course PlannerDocument2 pagesReso Course PlannerSnehasishGhosh100% (1)
- Serial Number AutoCAD 2014Document5 pagesSerial Number AutoCAD 2014Punith Ky67% (9)
- The Interpretive TheoryDocument15 pagesThe Interpretive TheorySomia Zergui100% (14)
- Deswik 1Document94 pagesDeswik 1Daniel Alcides Arias Rafael100% (2)
- Grade 6 MathDocument12 pagesGrade 6 Mathapi-264682510No ratings yet
- ContentServer PDFDocument16 pagesContentServer PDFdaniel leon marinNo ratings yet
- Simple Backup/Restore Utility With SQL-: Introduction To SQL-DMODocument8 pagesSimple Backup/Restore Utility With SQL-: Introduction To SQL-DMOZaeni Marjiyanto, A.mdNo ratings yet
- Triac BT137-600DDocument6 pagesTriac BT137-600DEverton AlvesNo ratings yet
- Cavalieri Principle (Kin Y. Li)Document4 pagesCavalieri Principle (Kin Y. Li)Hicham ElyassamiNo ratings yet
- Manual Fx2n 485 BDDocument8 pagesManual Fx2n 485 BDaxo_vfrNo ratings yet
- AS TRONIC, The ZF-AS TRONIC Software Can Be: 4.7.6 EOL Programming Documentation of The EOL ProgrammingDocument3 pagesAS TRONIC, The ZF-AS TRONIC Software Can Be: 4.7.6 EOL Programming Documentation of The EOL ProgrammingThylaneNo ratings yet
- PAI Industries, Inc. - Catalog Polea de MotorDocument2 pagesPAI Industries, Inc. - Catalog Polea de MotorAlexis ValleNo ratings yet
- Esolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroDocument31 pagesEsolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroAll About MusicNo ratings yet
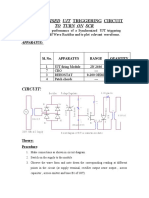
- Synchronised Ujt Triggering CircuitDocument2 pagesSynchronised Ujt Triggering Circuitsvinod s67% (3)
- Digital Electronics Basics - Flip-FlopsDocument6 pagesDigital Electronics Basics - Flip-FlopsPaolopiniNo ratings yet
- A Tour Through Mathematical Logic: Robert S. WolfDocument4 pagesA Tour Through Mathematical Logic: Robert S. WolfUrahara JefNo ratings yet
- HP Application Lifecycle Management Readme: What's New Installation InstructionsDocument36 pagesHP Application Lifecycle Management Readme: What's New Installation InstructionsBrandon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Narayana Iit Academy India: Paper - IDocument39 pagesNarayana Iit Academy India: Paper - Iaatt aattNo ratings yet
- Induction - George Ricarrson 2501987261Document11 pagesInduction - George Ricarrson 2501987261George RYNo ratings yet
- Pending Exception RDocument17 pagesPending Exception Rsyafri maryonoNo ratings yet
- Star and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesStar and Its PropertiesRemond BalabaNo ratings yet
- Mac MKD StyleguideDocument47 pagesMac MKD Styleguidetaurus_europeNo ratings yet
- KeyWords ISTQB FL v3.1Document1 pageKeyWords ISTQB FL v3.1testa4 zentestNo ratings yet
- Messenger No69Document72 pagesMessenger No69European Southern ObservatoryNo ratings yet
- PD05P XXX XXX B SeDocument2 pagesPD05P XXX XXX B SemaaoeNo ratings yet
- Skripsi #2 Tanpa HyperlinkDocument19 pagesSkripsi #2 Tanpa HyperlinkindahNo ratings yet
- Newtons CowsDocument9 pagesNewtons CowsLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- Pipesim Model Management Program: For Reservoir, Production, and Process ModelingDocument2 pagesPipesim Model Management Program: For Reservoir, Production, and Process ModelingMauricio AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- NFRC 200-2010Document45 pagesNFRC 200-2010reynolds534100% (1)