Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacterial pathogens overview
Uploaded by
Wesley CooperOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacterial pathogens overview
Uploaded by
Wesley CooperCopyright:
Available Formats
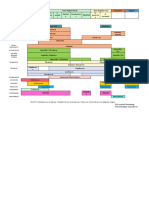
Name
Struct/Physio
Catalase (+), Coagulase (+) Grape cluster, Facultative anaerobe, Teichoic acid Prot A (evade immune) Fibronectin (adhere) Normal flora: nasopharangeal skin
Toxin/Virulence Factors
Cytosolic exotoxin: Hemolysins Superantigens: Enterotoxin TSS toxin Exfoliatin
Clinical
Skin infections: (Furuncle, carbuncles Impetigo) Osteomyelitis Acute endocarditis Septicemia Necrotizing pneumonia Gastroenteritis Toxic Shock Syndrome Scalded Skin Syndrome MRSA vs CA-MRSA Infection of prosthetic heart valves, catheters Acute pharyngitis Scarlet Fever Impetigo GAS disease Acute Rheumatic Fever Streptococcal toxic shock Acute bacterial pneumonia Otitis media Meningitis (adults common) Diphtheria: Upper resp infect Increase mucus blocks airway Myocarditis, congest heart failure, nerve/muscle paralysis Cutaneous Diphtheria Pulmonary anthrax: hemorrhagic pneumonia, inflamm lymph nodes Cutaneous anthrax Listeriosis: Septicemia, meningitis Skin lesions Fetal abortion Gonorrhea: Male urethritis, pus discharge Female vaginal pus discharge, gonococcal salpingitis, pelvic inflammatory disease Ophthalmia neonatorum Septic arthritis
Treatment
Nafcillin Oxacillin Vancomycin Linezolid Daptomycin
Staphylococcus aureus
Staph. epidermidis
Streptococcus. pyogenes
Strep. pneumoniae Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Catalase (+), Coagulase (-) Normal skin flora, clusters Slime layer (VF) Catalase (-) Non-motile Facultative anerobes Hyaluronic acid capsule Fimbriae (M Prot) Prot F (adhesion) Nasopharngeal/skin carriage Capsule (antiphago) Rod, small, slender Non motile Facultative anaerobes Blunt rods Endospore forming Non motile Aerobic Capsule (antiphagocytic) Catalase (+) Intracelluar pathogen (phagocytes) Slender, short rods Tumbling motility Utilize host actin to move Oxidase (+) Kidney shape diplococci Pilli (most imp VF) Aerobic
Pyrogenic exotoxins Streptolysin O,S Streptokinase C5a peptidase Streptodornase Hyaluronidase Autolysin/Pneumolysin enzymes Diphtheria exotoxin Stops prot synth ADP-ribosylation, EF2 factor Edema factor: up cAMP levels Lethal toxin: necrosis Protective antigen: entry toxins Listeriolysin O: escape phagosome
Nafcillin Oxacillin Vancomycin Penicillin G Clarithromycin Azithromycin
Penicillin G Vancomycin Horse serum antitoxin Erythromycin Penicillin Vaccine (toxoid) Cutaneous: Penicillin (not recommended) Doxycycline, Erthythromycin Pulmonary: Ciprofloxacin + rifampin + vanco Ampicillin TMP/SMZ
Bacillus anthracis
Listeria monocytogenes
Neisseria gonorrheae
LOS: IgM antibodies attack this OMP I +III : porin proteins OMP II: mediate attachment IgA protease (most imp VF)
Gonorrhea: ceftriaxone, doxycycline, spectinomycin Ophthalmia: tetracycline in newborns eyes
Name Neisseria meningitidis
Struct/Physio
Oxidase (+) Kidney shaped diplococci Capsule antiphago (VF) Pilli Catalase (+), Oxidase (-) Short rod Fimbriae/pilli Motile/non Capsule Facultative anaerobe Glu+, Lac+
Toxin/Virulence Factors
LOS endotoxin IgA protease OMPs Antigenic factors: O antigenLPS, H antigen-flagella, K antigen-capsule ETEC: enterotoxins, ST-cGMP, LT-cAMP EHEC: Verotoxin (VT)hemorrhage EPEC: Shiga-like toxin, destroy microvilli
Clinical
Meningitis (most freq cause)
Treatment
Penicillin G Cefotaxime Ceftriaxone Diarrhea: Rehydration/electrolyte replenish Antibio shorten course Meningitis: Cephalosporin + gentamicin UTI: TMP/SMZ, ciprofloxacin
Escherichia coli
Salmonella typhi
Catalase (+), Oxidase (-) Rods, flagella Facultative anaerobe Glu+, LacExclusively human Intracellular pathogen (phagocytes) See S. typhi Curved, spiral, S-shaped rod Single. polar flagellum Darting motion Microaerophilic Does not ferment CHO Capsular/flagellar antigen Catalase (+), Oxidase (-) Rod Non-motile Glu+, LacFacultative anaerobe Intracellular pathogen (large intest mucosa)
LPS Endotoxin
ETEC: enterotoxins increase ion/water loss, watery diarrhea EPEC: destruct microvilli, watery diarrhea (shiga-like) EHEC: hemorrhagic colitis (VT) Hemolytic Uremic Syndromeacute renal failure EIEC: dysentery-like, bloody diarrhea EAEC: watery diarrhea children, HIV patients Extraintestinal: UTI Neonatal meningitis Septicemia, endotoxic shock Typhoid Fever: infect macrophage lymphatic intest tiss Life threatening systemic illness Fever, ab pain, maculopapular rash on trunk Bacteremia: fever, headache, malaise, bloody diarrhea Enterocolitis: nausea, vomiting, ab cramp, diarrhea Food poisoning Systemic: fever, headache, myalgia Intestinal: acute enteritis, pseudoappendicitis, diarrhea, ulceration jejunum, ileum, colon Leading Cause Food-Borne Disease Shigellosis (bacillary dysentery) Bloody diarrhea, mucus, pain ab cramp, severe dehyro
Ceftriaxone Ciprofloxacin Vaccine (attenuated)
Salmonella enteriditis
LPS Endotoxin LPS, enterotoxin, cytotoxin
Fluid/electrolye replenish Antibioitics shorten disease Diarrhea: Fluids/electrolytes Antiobiotics: if severe, ciprofloxacin
Campylobacter jejuni
Shigella
Exotoxin: Shiga toxin, has endo/cytotoxic props, AB Toxin B: attachement, entry A: cleavage 28S rRNA 60S ribosome, inhibit prot synth
Fluid/electrolyte replacement Ciprofloxacin, azithromycin
Name
Struct/Physio
Oxidase (+)Short, curved, rod Single. polar flagellum Rapidly motile Facultative anaerobe Req/stimulated NaCl
Toxin/Virulence Factor
Cholera Toxin (enterotoxin) AB Toxin B: bind GM1 ganglioside receptor intest cell A2: penetrate cell membrane A1: ADP-ribosyl transferase Ribosylate G prot, act adenylate cylcase, increase cAMP, increase ion, water loss to lumen Urease: secrete NH3, lower acidity, damage tissue Cytotoxins HispB (heat shock prot) Adhesins Mucinase Phospholipase Superoxide dismutase Hib capsular antigen (Polyribose Phosphate) IgA protease (colonization)
Clinical
Cholera: Massive fluid/electrolyte loss
Treatment
Fluid/electrolyte replacement Doxycline to shorten duration
Vibrio cholerae
Heliobacter pylori
Urease (+) Curved, spiral rod Multiple. polar flagella Corkscrew motion Microaerophilic Live in mucous layer gastric cell Bacillus, pleopmorphic Capsulated/non Obligate pathogen (req host hemin/NADH+) Norm flora resp tract, conjuct, genital tract Coccobacillus Encapsulated Aerobic Human reservoir (respir droplets)
Haemophilis influenzae
Acute gastritis -> chronic gastritis Activate inflammatory cells Decreased mucous production Correlated to infection: Duodenal/gastric ulcers Risk factor: Gastric carcinoma, gastric B-cell lymphoma Flu Meningitis (common children) Otitis media, sinusitis, bronchopneumoniae Invades bloodstream Pertussis (Whooping cough): common young children Catarrhal phase: rhinorrhea, conjuct infect, malaise, fever Paroxysmal phase: severe cough, copious mucus, cyanosis, vomiting Leukocyte count> 50,000cells/L Localized: Eye: keratitis, endophthalmitis Ear: external otitis Skin: burn/wound sepsis, rashes UTI Resp tract: cystic fibrosis, congest heart failure GI: mild diarrhea to entercolitis CNS: meningitis, brain abcess Systemic: Bacteremia Endocarditis
Antibio and H+ pump inhibit Amoxicillin, clarithromycin, omeprazole
Cephalosporins TMP/SMZ Ampicillin w/ clavulanate Vaccine (conjugated Hib PRP) Erythromycin TMP/SMZ Vaccine: Killed cells Pertussis toxoid
Bordetella pertussis
Oxidase (+) Encapsulated rods Polar flagella, motile Obligate aerobe Opportunistic pathogen
Pseudemonas aeruginosa
Pertussis Toxin: A/B Type, sensitization to histamine, up insulin prod -> hypoglycemia Dermonecrotoxin: ischemic necrosis Tracheal cytotoxin: inhibit cilia Adenylate cyclase toxin: decrease phagocytosis Flimamentous hemagglutin Agglutinogens: atachement Pili Glycocalyx (anti phago) LPS (sepsis syndrome) Exoenzyme S/T, Exotoxin A: ADP-ribosylate EF2 Elastase, alkaline phosphates, Phospholipase C
Combo therapy: Aminoglycoside + fluroquinolone
Name
Struct/Physio
Toxin/Virulence Factor
Exotoxin (12 varieties): Alpha toxin (phospholipase C) Hemolytic, necrotic, cytotoxic Enterotoxins: heat labile, disrupt ions, fluid loss Hydrolytic enzymes: Hyaluronidase, protease, DNase Botulinum toxins A,B,E: neurotoxic, prevent ACh release at NMJ, flaccid paralysis 2 toxic polypeptides: Toxin A-enterotoxin, fluid loss, inflamm, cytopathic Toxin B-cytotoxin, inhibit prot synth Tetanus Toxin (tetanospasmin): plasmid encoded, AB toxin B: bind neuronal cells A: blocks nt release at inhibitory synapse, cleave vesicle prot Intracellular Pathogen Cannot survive outside host OMP promote adherence Hylauronidase
Clinical
Myonecrosis (gas gangrene) Alpha, exotoxins, hydro enzymes Ferment tissue CHO, gas Shock, renal failure, hemolysis Acute food poisoning Enteritis necroticans Clostridial endometritis Botulinum (food poisoning): unfocused vision, trouble swallowing, muscle paralysis, death by asphyxiation Floppy baby syndrome Clostridial anti-biotic associated diarrhea (AAD), colitis
Treatment
O2 exposure, hyperbaric chamber Penicillin, broad spectrum antibiotics
Clostridia perfringens
Horse serum antitoxin
C. botulinum
Blunt ended rods Endospore forming Motile Obligate anaerobe Opportunistic pathogen
C. difficile
Fluid/electrolyte replacement Metronidozole, vancomycin Do Not Use Beta-lactams!!! Vaccine (toxoid) Tetanus immune globulin Penicillin Penicillin Erythromycin, tetracycline
C. tetani
Tetanus: progressive spastic paralysis of muscle Death from paralysis of chest muscles, asphyxiation Syphilis (STD): Stage 1: hard genital chancre sore at site infection, spread through lymph system Asymptomatic Period Stage 2: red body rash, pale, moist papules anogenital, axiallary, oral region, hepatitis, meningitis, nephritis Latent period up to 30-40yrs Stage 3: degen nervous syst, CV lesions, skin gumma Congenital syphilis: thru placenta, death fetus, abormalities Stage 1: red circular lesion, rash, spread via lymph/blood to skin, CNS, musculoskeletal, heart Stage 2: arthritis, arthralgia, cardiac/neurologic complications Stage 3: chronic arthritis, degen CNS
Treponema pallidum
(Spirochetes) Long, slender corkscrew Flexible, highy motile Central protoplasmic cylinder Outer sheath glycosaminoglycans Endoflagella, axially orienteted Zootic disease, spread by tick bite to humans Invasive enzymes
Cephalosporins Amoxicillin Doxycycline
Borrelia burgdorferi
(Spirochetes)
Name Leptospira interrogans
(Spirochetes)
Struct/Physio
See Treponema pallidum
Toxin/Virulence Factor
Invasive enzymes
Clinical
Leptospirosis: Fever, 1-2wks then bacteremia Disappear Reappear, invade liver, kidney, CNS Jaundice, hemorrage, necrosis, aseptic meningitis Nongonoccocal urethritis (NGU) STD, males: urethral infect females: cervicitis, urethritis, mucoid discharge, like gonorrhea Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV): serotype L1-L3, invasive STD, chronic inflamm genital area Trachoma: chronic keratoconjuctivis, lead to blindness, lesions cloud cornea Primary Tuberculosis: Invade and reproduce in alveolar macrophage, attract T cells wh/ release cytokines, inflam, damage Tubercle forms as mass of cells around bacteria Lesion can arrest, or rupture and spread to other organs
Treatment
Penicillin G Tetracycline
Chlamydia trachomatis
Round to ovid Two layer lipid bilayer envelope No peptidoglycan, muramic acid Resemble Gram (-) envelope Cysteine Rich Proteins Rigid prot layer connected to membranes (shell) Does Not Gram Stain
Obligate intracellular Parasite Depends on host ATP/NADH+ LPS Adhesins on cell envelope Elementary Body; resistant, spore-like, infects epithelial/macrophage, taken in by phagocytosis Reticulate Body: metabolically active, reproduces, reform EB and released from host cell Mycolic acid wall, resists harsh environment, and chem. attack Facultative Intracellular Pathogen Reproduce in alveolar macrophage Phospholipids inhibit fusion w/ lysosome
Tetracyclines, erythromycin, sulfonamides Safe sexual practices
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Slender, non-motile rods Cell wall 60% lipids, beta-OH fatty acuds, esp mycolic acid, make cell extreme hydrophobic Will Acid Fast Stain
Vaccine, Bacille Calmette-Gurin (BGC), attenuated M. bovis Multidrug therapy: Isonazid, rifampin
Gram (+) Gram (-) Do not traditionally Gram Stain Exotoxins: released by Gram (+/-) AB type toxin: B subunit adheres to cell; A subunit enters and causes damage Endotoxins: only Gram (-) LPS: in all Gram (-), always an endotoxin
You might also like
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- SJDWHDJSDJSDDocument358 pagesSJDWHDJSDJSDwide mind hackerNo ratings yet
- PHARMA SupertableDocument2 pagesPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioNo ratings yet
- Updated Antibiotic Chart - 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesUpdated Antibiotic Chart - 2016 PDFmugenzi eric100% (1)
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocument3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120No ratings yet
- MS2 USMLE Pharm ReviewDocument25 pagesMS2 USMLE Pharm ReviewAnna ArtyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (1)
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocument26 pagesA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- Drug of ChoiceDocument2 pagesDrug of ChoiceRia Tiglao Fortugaliza100% (1)
- Lang 10 EditionDocument235 pagesLang 10 Editionraju niraulaNo ratings yet
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Top 200 Brand Name DrugsDocument1 pageTop 200 Brand Name DrugsLen HuaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsManzoor AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anti Infective Drug ChartDocument1 pageAnti Infective Drug ChartJessica100% (1)
- Disease ChartDocument12 pagesDisease ChartMegNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics - Pathogen ChartDocument3 pagesAntibiotics - Pathogen ChartYanling LiNo ratings yet
- Clin Pharm Lile Antibacterial Classes and ExamplesDocument4 pagesClin Pharm Lile Antibacterial Classes and ExamplesNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Antidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteDocument1 pageAntidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteshangguanlongkuiNo ratings yet
- Drugs of ChoiceDocument3 pagesDrugs of ChoiceReeti R. Bhat100% (1)
- Drugs of Choice for CNS, Blood, GIT, Endo & Chemo /TITLEDocument9 pagesDrugs of Choice for CNS, Blood, GIT, Endo & Chemo /TITLESHAKEEL1991No ratings yet
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsPGI Custodio, Ed KristianNo ratings yet
- Pharma MnemonicsDocument10 pagesPharma MnemonicsMuhammad Ali Aziz100% (4)
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocument21 pagesRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Drug Nomenclature HintsDocument1 pageDrug Nomenclature HintsJordynNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- 07.02 Topnotch Pharmacology TableDocument64 pages07.02 Topnotch Pharmacology TableskzskzNo ratings yet
- Pharma ChartsDocument33 pagesPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Medications and assessmentsDocument225 pagesMedications and assessmentsJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Medical MneumonicsDocument139 pagesMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNo ratings yet
- Nina Bacteria Chart Medical School Step 1Document11 pagesNina Bacteria Chart Medical School Step 1M PatelNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Step 1 Weird Exceptions and DetailDocument10 pagesMicrobiology Step 1 Weird Exceptions and DetailLucykesh100% (2)
- MicrobesDocument12 pagesMicrobesDiMa MarshNo ratings yet
- Faculty Of Medicine Tanta University Bacterial & Fungal InfectionsDocument12 pagesFaculty Of Medicine Tanta University Bacterial & Fungal InfectionsSyamil AzharNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases SummaryDocument12 pagesCommunicable Diseases SummaryBonjack ReyesNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus viridans Bacteriology ChartDocument13 pagesStaphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus viridans Bacteriology Chartthzone1986No ratings yet
- StaphylococciDocument73 pagesStaphylococcishahbaz100% (5)
- Micro Final Buzz Word CheatsheetDocument10 pagesMicro Final Buzz Word CheatsheetThesmith FamNo ratings yet
- 03 AmoebiasisDocument42 pages03 AmoebiasisKing IvyNo ratings yet
- Morning Report Mrs AlbineDocument50 pagesMorning Report Mrs AlbineTito Haposan TobingNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus & StreptococcusDocument100 pagesStaphylococcus & StreptococcusFahim NadvyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract MicrobiologyDocument68 pagesRespiratory Tract Microbiologysultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument28 pagesStaphylococcusAliyah SajaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria ChartDocument1 pageGram Positive Bacteria ChartAngelina IafanoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000Document86 pagesMicrobiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000skmvicky1483No ratings yet
- Actinic KeratosisDocument19 pagesActinic Keratosisattydoc1234No ratings yet
- ClostridiumDocument44 pagesClostridiummajoragarwal1195No ratings yet
- Amoebic DysenteryDocument15 pagesAmoebic DysenteryloujilleNo ratings yet
- 1.diseases of PigDocument154 pages1.diseases of PigPu Mignon100% (3)
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Document26 pagesMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci (Streptococcus)Document26 pagesMicrobiology: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci (Streptococcus)Shuler0071No ratings yet
- ProtozoaDocument56 pagesProtozoaSalim JufriNo ratings yet
- Lung Parasitic InfectionsDocument71 pagesLung Parasitic InfectionswaheedaNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Cocci Gram Positive BacilliDocument103 pagesGram Negative Cocci Gram Positive BacilliMacky IbayNo ratings yet
- Pinworm infection (Enterobius vermicularisDocument7 pagesPinworm infection (Enterobius vermicularisxxal123xxNo ratings yet
- Medicine & Pediatric SMLE Notes: Key Points for ExamsDocument23 pagesMedicine & Pediatric SMLE Notes: Key Points for Examsanmar alkhudhri100% (1)
- ID Bug chart-DKDocument92 pagesID Bug chart-DKNeil M D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasite TableDocument3 pagesMedical Parasite Tablesidman47100% (2)
- Microbiology, Infection and Antibiotic TherapyDocument86 pagesMicrobiology, Infection and Antibiotic TherapyRahul100% (1)
- Final Draft - Banana ChipsDocument34 pagesFinal Draft - Banana ChipsAubrey Delgado74% (35)
- On Prem Vs CloudDocument10 pagesOn Prem Vs CloudJeev AnandNo ratings yet
- Amma Mobile InsuranceDocument1 pageAmma Mobile InsuranceANANTH JNo ratings yet
- List of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Document2 pagesList of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Aejaz MujawarNo ratings yet
- Food Salt: By: Saad, Rehan, Asad, Hasan, Adil, Abdur Rehman, AzharDocument10 pagesFood Salt: By: Saad, Rehan, Asad, Hasan, Adil, Abdur Rehman, AzharsaadNo ratings yet
- Jobaid Investigating Causes PDFDocument16 pagesJobaid Investigating Causes PDFNina MarianaNo ratings yet
- Postnatal Care, Complaints & AbnormalitiesDocument38 pagesPostnatal Care, Complaints & AbnormalitiesBernice GyapongNo ratings yet
- Written Work Instruction (Sheet Piles Installation)Document14 pagesWritten Work Instruction (Sheet Piles Installation)cynthia100% (1)
- Proposed Rule: Airworthiness Directives: Bell Helicopter Textron CanadaDocument3 pagesProposed Rule: Airworthiness Directives: Bell Helicopter Textron CanadaJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Usos HummusDocument36 pagesUsos HummusAlisson FernandaNo ratings yet
- Crosbys Molasses and MoreDocument37 pagesCrosbys Molasses and MoreShaikh MeenatullahNo ratings yet
- Ten Laws of BoundariesDocument17 pagesTen Laws of Boundariesstjohn30067% (3)
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument8 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessSehar162No ratings yet
- NCL ReportDocument20 pagesNCL ReportSwati Tripathi33% (3)
- Research Paper - Perceptions of Grade 11 STEM Students Towards ContraceptivesDocument9 pagesResearch Paper - Perceptions of Grade 11 STEM Students Towards ContraceptivesKyle BinuyaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Personality ElementsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Personality Elementslilian_vera_1No ratings yet
- HVAC Report FINALDocument65 pagesHVAC Report FINALIanNo ratings yet
- Geoheritage of Labuan Island: Bulletin of The Geological Society of Malaysia December 2016Document14 pagesGeoheritage of Labuan Island: Bulletin of The Geological Society of Malaysia December 2016songkkNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy ProtocolDocument4 pagesOxygen Therapy ProtocolTeri Martin-Allen100% (1)
- Vocational training at BHELDocument36 pagesVocational training at BHELafNo ratings yet
- Viscometer Toki Sangyo - TV25 - 35Document12 pagesViscometer Toki Sangyo - TV25 - 35Eddy CurrentNo ratings yet
- Self Level Pu FlooringDocument2 pagesSelf Level Pu FlooringRyan EncomiendaNo ratings yet
- CKD EsrdDocument83 pagesCKD EsrdRita Lakhani100% (1)
- Communicating Across AgesDocument35 pagesCommunicating Across AgesConrad TarihoranNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2. Pair EssayDocument2 pagesExercise 2. Pair Essayrjay manalo75% (4)
- Typhoid FeverDocument9 pagesTyphoid FeverAli Al.JuffairiNo ratings yet
- AZIZ Ur RehmanDocument3 pagesAZIZ Ur Rehmantop writerNo ratings yet
- Red Velvet Cake RecipeDocument6 pagesRed Velvet Cake RecipeRuminto SubektiNo ratings yet
- Piling Procedure - IoclDocument8 pagesPiling Procedure - IocltpgggkNo ratings yet
- Kovach 1987Document10 pagesKovach 1987Quyen ta thi nhaNo ratings yet