Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CPR Class Questionnaire
Uploaded by
Parikshit PekhaleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CPR Class Questionnaire
Uploaded by
Parikshit PekhaleCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Which among these is not a cause for a patient with no pulse and sinus tachycardia?
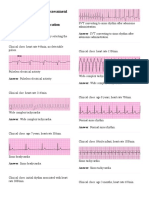
Hypoxia Tamponade Hypoglycemia Hypovolemia 2. A 4yr old male child was found collapsed, and you then arrived on the scene. As you examined the child, you realised that he was unresponsive, with no pulse and no breathing. if you were all alone on the scene you would Give 2 rescue breaths. Call for help, first, and then get the AED. Start chest compressions and complete 5 cycles of CPR. Wait for the another rescuer to come by. 3. A 68 yr old male came to the Accident and Emergency department with complaints of chest discomfort and palpitations. BP-120/80mm Hg, P-210/min, SpO2-96%. And the monitor showed. What will your first step be? Vagal manoeuvre. Adenosine (6mg) Amiodarone (150mg) Cardioversion 50Joules 4. A patient was brought unresponsive to the A&E, CPR was started for 25mins with 2 doses of epinephrine but the rhythm persistently showed an asystole. What will your next step be? IV Vasopressin 40 U. Continue chest compressions IIV Amiodarone 300mg. Discontinue CPR and consult expert. 5. A 60 yr female patient collapsed, CPR was going on. Of the 1st cycle, 1 min was over when the AED, you will, Finish 2 mins of CPR. Give 2 rescue breaths. Attach the AED immediately 6. Which is not a component of high quality CPR Compression state at least 100 pm Depth of more than 5 cm Compression ventilation ratio 15:2 No excessive hyperventilation 7. Patient came to hospital with chest discomfort. On examination, P = 50 pm, BP= 90/60 mm Hg, RR= 26pm, SPO2= 94% and monitor showing the following rhythm. What is the next step of action? Atropine 0.6mg IV
Transcutaneous pacemaker Epinephrine 1mg IV Cadioversion 8. What is compression ventilation ratio for child CPR to rescue 10:2 15:2 15:1 30:2 9. Which is not a complication of induced hypothermia Sepsis Coagulopathy Arrhythmia Stroke 10. ETCO2 reading shows 8mm during CPR. What is the next step? Continue chest compression Continue chest compression with adequate depth Check for advanced airway proper, placement Recheck ETCO2 machine 11. Shockable rhythms are all except VF Publess VT Torsaidus Asystole 12. Patient came unresponsive. CPR started and after 2 cycles of CPR and 2 shock, rhythm shows sinus rhythm. What will be the next step of action? Continue chest compression Check for pulse Give IV epinephrine 1mg Stop CPR 13. Compression ventilation ratio in adult CPR is 30:2 15:2 20:2 10:1 14. Following are used in advanced airways except LMA Combi tube Kings laryngeal tube Bagmark ventilation 15. Following can be used in CPR except
Epinephrine Vasopressin Amiodawne Atropine 16. Monitoring CPR can be done in following ways except Capnography Diastolic Bp Systolic BP ScVO2 17. Ideal depth of compression in adult CPR is 2/3rd of AP diameter More than or equal to 2inches 1-2 inches 1/3rd of AP diameter 18. Most important feature in CPR Rescue breaths Epinephrine Defibrillation Chest compression 19. The correct technique for CPR of a 7year old girl Compression depth of minimum 1 and 1/2inches Chest compressions with only one hand Lone rescuer rate of 15:2 Compression of chest wall of at least 1/3rd the depth 20. Special conditions needing specific actions for AED placement are all except Victims having hairy chest wall Victims with implanted pacemakers Victims in small puddle Victim with medicated transdermal patch 21. The rate of rescue breathing in an adult is One every 3-5 seconds without advanced airway One every 6-8 seconds with advanced airway One every 3-5 seconds with advanced airway One every 10-12 seconds without advanced airway 22. Components of effective rescue breath, all except Give over 1second Produce visible chest rise Provide tidal volume 600ml Provide tidal volume litre 23. Following sudden collapse of adult victim on road, your immediate response will be
Start chest compression Give rescue breath Active ENS Pulse check 24. Following is component of ACLS AED Manual defibrillation Drugs Physiologic monitor 25. Components of successful resuscitation, all except Pulse BP S Spontaneous wave form ECG organized rhythm 26. Ideal rate of chest compression 60-80 80-100 100-120 <140
You might also like
- Cardiac Arrest Drugs & ProceduresDocument8 pagesCardiac Arrest Drugs & ProceduresAstri Adel BudiarsoNo ratings yet
- AHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardsDocument8 pagesAHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardssallyNo ratings yet
- Cals ReviewbjvjvjDocument14 pagesCals ReviewbjvjvjCarl Jay M Ocariza100% (1)
- BLS FinalDocument47 pagesBLS Finalshouvik chowdhury100% (1)
- ACLS and PALS Certification Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesACLS and PALS Certification Practice Questionsdyah rahayu hutamiNo ratings yet
- 20 Questions in CPRDocument5 pages20 Questions in CPRأبوأحمد الحكيم100% (1)
- Regarding CPR in Adult Cardiac Arrest For Advanced Life Support ProvidersDocument2 pagesRegarding CPR in Adult Cardiac Arrest For Advanced Life Support ProvidersHasini Samarasinghe0% (1)
- Questionnaire: Instructions To The ParticipantsDocument8 pagesQuestionnaire: Instructions To The ParticipantsssNo ratings yet
- TestDocument11 pagesTestzenagit123456100% (1)
- ACLS QuizletDocument7 pagesACLS Quizletek.9006001No ratings yet
- 15 Item ACLS Drill With RationaleDocument12 pages15 Item ACLS Drill With RationaleLj Ferolino100% (1)
- What Is The Rate For Performing Chest Compressions For A Victim of Any Age A-30 Compressions Per Minute B - 50 Compressions Per Minute C - 80 Compressions Per MinuteDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Rate For Performing Chest Compressions For A Victim of Any Age A-30 Compressions Per Minute B - 50 Compressions Per Minute C - 80 Compressions Per MinuteHassan Shehri100% (2)
- BLS Training - Question PaperDocument3 pagesBLS Training - Question PaperNav J Kar100% (1)
- Aha Bls 2018 Test Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesAha Bls 2018 Test Questions and AnswersPellegas Junnie0% (1)
- BLS ALGORITHM As of February 2023Document2 pagesBLS ALGORITHM As of February 2023Mark Jason Rodriguez, RNNo ratings yet
- BLS MCQDocument8 pagesBLS MCQAmit BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Advanced Trauma Life Support RevisedDocument7 pagesAdvanced Trauma Life Support RevisedpaveethrahNo ratings yet
- AHA ELearning ACLS Precourse Self-Assessment and Precourse WorkDocument1 pageAHA ELearning ACLS Precourse Self-Assessment and Precourse Work9kjsntkrzcNo ratings yet
- PRN2155A ASHI G2015 BLS Exam VersionA Revised 100516Document5 pagesPRN2155A ASHI G2015 BLS Exam VersionA Revised 100516Clark Angelo Juan100% (1)
- 15 Item ACLS Drill Answers and RationaleDocument6 pages15 Item ACLS Drill Answers and RationaleAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- Adult Basic Life Support Algorithm For Healthcare ProvidersDocument1 pageAdult Basic Life Support Algorithm For Healthcare ProvidersKavya ShreeNo ratings yet
- APLS Scenario OSCE PDFDocument5 pagesAPLS Scenario OSCE PDFNikita JacobsNo ratings yet
- Introd To ECG Code Blue Champs March 2019Document52 pagesIntrod To ECG Code Blue Champs March 2019james rukenya100% (1)
- CPR 2Document3 pagesCPR 2Baebee Lou100% (1)
- Soalan MCQ Acls Fit Set BDocument3 pagesSoalan MCQ Acls Fit Set BAnonymous 89ilBIGhrmNo ratings yet
- Bls Question 1Document7 pagesBls Question 1balderas135384No ratings yet
- Amls Pretest BlsDocument13 pagesAmls Pretest BlsrkopecmdNo ratings yet
- ACLS PRETEST ANSWER KEY RHYTHM IDENTIFICATIONDocument3 pagesACLS PRETEST ANSWER KEY RHYTHM IDENTIFICATIONaditNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithmms_lezahNo ratings yet
- ACLS Practice TestDocument5 pagesACLS Practice Testprettynpink0867% (3)
- 15 item ACLS Drill ReviewDocument4 pages15 item ACLS Drill ReviewVal SolidumNo ratings yet
- Hospital and Critical CareDocument16 pagesHospital and Critical CareMarivy GalonNo ratings yet
- The Crash CartDocument39 pagesThe Crash Cartpramod kumawat100% (1)
- AclsDocument85 pagesAclsJulia CostaNo ratings yet
- ITLC Questions 2019Document9 pagesITLC Questions 2019Neil ThomasNo ratings yet
- PALS Precourse Self 2023Document9 pagesPALS Precourse Self 2023Airene SibleNo ratings yet
- Pepp Als PretestDocument4 pagesPepp Als PretestDave BoppNo ratings yet
- Mastering Electocardiograms - Honda-2Document3 pagesMastering Electocardiograms - Honda-2Christian MacielNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Otitis 2022Document20 pagesNecrotizing Otitis 2022asmashNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment FinalDocument5 pagesFormative Assessment FinalJonathan YeohNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document12 pagesPaediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)zacklim_2000100% (1)
- Testsv - Final 26971 32528Document63 pagesTestsv - Final 26971 32528Iris BakerNo ratings yet
- Acls ExamDocument42 pagesAcls ExamScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- ACLS Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesACLS Skills ChecklistKary ParraNo ratings yet
- ACLS and MegacodeDocument33 pagesACLS and MegacodeMark Joseph100% (1)
- BLS & AclsDocument29 pagesBLS & AclswcgokulNo ratings yet
- BLS Q ADocument13 pagesBLS Q AAhmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillation (AED) Training GuideFrom EverandCardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillation (AED) Training GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing the NeonateFrom EverandNursing the NeonateMaggie MeeksNo ratings yet
- ACLS Exam Version ADocument11 pagesACLS Exam Version AAhmed - Sawalha96% (26)
- AclsDocument13 pagesAclsMohamed Kelany100% (1)
- Cardio Pulmonary ResuscitationDocument8 pagesCardio Pulmonary ResuscitationRuchika Kaushal71% (7)
- ACLS Practice Test 1Document6 pagesACLS Practice Test 1tarrynwortmann5319100% (3)
- Dvanced Ardiovascular Ife Upport: A C L SDocument10 pagesDvanced Ardiovascular Ife Upport: A C L SErica Jane100% (1)
- ACLS Exam Version BDocument16 pagesACLS Exam Version BAhmed - Sawalha97% (61)
- Cardiac Function TestDocument8 pagesCardiac Function Testramanrajesh83100% (2)
- Daftar Pustaka KSMDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustaka KSMFajar YuniftiadiNo ratings yet
- 1.assignment On CPRDocument7 pages1.assignment On CPRsantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- ACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterDocument1 pageACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- The ECG in Hypothermia - Osborn WavesDocument2 pagesThe ECG in Hypothermia - Osborn WavesVid MirosevicNo ratings yet
- Second ExamDocument8 pagesSecond ExamMohnmad Zaitoon100% (1)
- Clinical Practice Guidelines - 2017 PDFDocument820 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines - 2017 PDFvijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Ep TrainingDocument35 pagesEp TrainingVatsal SinghNo ratings yet
- Pub1566 WebDocument124 pagesPub1566 WebRadoi Sandina RodicaNo ratings yet
- Ventricular ArrhythmiaDocument37 pagesVentricular Arrhythmiaelhassia elhassiaNo ratings yet
- Dharam Prakash SaranDocument89 pagesDharam Prakash SarankeerthanaaNo ratings yet
- Medical NotesDocument4 pagesMedical NotesRain CastillaNo ratings yet
- J Jacc 2020 11 018Document173 pagesJ Jacc 2020 11 018Ashvanee sharmaNo ratings yet
- Example 001Document13 pagesExample 001Priya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 16 PBL CVSDocument11 pagesKelompok 16 PBL CVSTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument43 pagesIschemic Heart DiseasevolcanflameNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Advserse Effects (Specify) Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Advserse Effects (Specify) Nursing InterventionsKaterina Petrova100% (1)
- Heart SoundsDocument18 pagesHeart SoundsAbcd100% (1)
- ECG Self Study BookDocument390 pagesECG Self Study BookChandramohan SettyNo ratings yet
- Naccarelli 2012 Electrocardiography of Arrhythmias A Comprehensive ReviewDocument1 pageNaccarelli 2012 Electrocardiography of Arrhythmias A Comprehensive Reviewraul gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest: Introduction & Disease OverviewDocument18 pagesSudden Cardiac Arrest: Introduction & Disease OverviewVivekanandGuptaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument45 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseBrandedlovers OnlineshopNo ratings yet
- EKG Cheat Sheet - Henry Del RosarioDocument1 pageEKG Cheat Sheet - Henry Del RosarioanwarNo ratings yet
- Ipd - KardiologiDocument116 pagesIpd - KardiologiWynda MuljonoNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia ATP4 GUIDLINESDocument9 pagesDyslipidemia ATP4 GUIDLINESSandy GunawanNo ratings yet
- 10.1038@s41572 019 0090 3Document20 pages10.1038@s41572 019 0090 3sari100% (1)
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument55 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseMimi Morallos-EspirituNo ratings yet
- Ecocardiografia NeonatalDocument10 pagesEcocardiografia NeonatalRonald MHNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mustafa Alshehabat's Guide to Heart Failure Definitions, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentsDocument20 pagesDr. Mustafa Alshehabat's Guide to Heart Failure Definitions, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentshuzaifahjusohNo ratings yet
- Introducing MSCT Imaging of Coronary ArteryDocument39 pagesIntroducing MSCT Imaging of Coronary ArteryConsita VictoriaNo ratings yet